
Towards an Enterprise Repository Framework
Dina Jacobs
1,3
, Paula Kotzé
2,3
and Alta van der Merwe
2,3
1
triVector, 12A Garsfontein Office Park
645 Jacqueline Drive, Garsfontein, 0081, South Africa
2
Meraka Institute, P O Box 395, Pretoria, 0001, South Africa
3
School of Computing, University of South Africa
P O Box 392, UNISA, 0003, South Africa
Abstract. The enterprise architect is dependent on the functionality of the en-
terprise repository to define and maintain the enterprise architecture. Two of
the specific functionalities are typical ‘warehouse’ related functionalities. The
one requirement is to integrate multiple business process reference models as
source models, similar to the reuse of data from different sources in a data
warehouse environment. The second requirement is the flexible visualization of
business process models that has a ‘slice-and-dice’ flavour as used in the data
warehouse domain. By means of analogical reasoning, our research investigates
using the theoretical foundation of the data warehouse domain to contribute to
the definition of an enterprise repository framework. Based on the similarities
found, an enterprise repository framework is derived.
1 Introduction
The enterprise repository is a key enabler for the enterprise architect to define and
maintain the enterprise architecture. Two of the critical success factors for the enter-
prise architect (with specific reference to the business architecture domain in this
paper) are the ability to integrate multiple business process reference models and to
enable flexible visualization of business processes. The objective is to accelerate the
definition of the business architecture and to enhance the completeness checking, the
validation, reuse and understanding of the business architecture, with the result being
a comprehensive business architecture definition.
The concept of a data warehouse is well established, where the data warehouse is
defined as an extension of a database to enable the analysis of data from various data-
bases and to create different views with consistent content to support decision-
making. The concept of an enterprise repository originates from the use in literature
of the concept of a warehouse populated with business process models (e.g. see [2,
9]). The purpose in our research is to explore whether it is possible to use the theo-
retical foundation of the data warehouse domain to contribute to the definition of an
enterprise repository framework (ERF). An enterprise repository framework provides
a basic conceptual structure, including a common vocabulary and a definition, to give
context to further discussions of the enterprise repository concept.
Jacobs D., Kotzé P. and van der Merwe A. (2009).
Towards an Enterprise Repository Framework.
In Proceedings of the Joint Workshop on Advanced Technologies and Techniques for Enterprise Information Systems, pages 77-89
DOI: 10.5220/0002193300770089
Copyright
c
SciTePress

To achieve this we used a process of analogical reasoning. Analogical reasoning,
is finding an analogy for a given thing or situation, where the analogy is in some way
like the given thing [16]. The similarities in the requirements that initiated the data
warehouse solution, and the use of the concept of multiple business process reference
models and flexible visualization as requirements for the enterprise repository, are the
point of departure for the analogical reasoning.
Section 2 of this paper introduces the theoretical foundation of this paper, discuss-
ing the enterprise architecture domain and the underlying concepts of the data ware-
house domain. This is followed by a short discussion in section 3 of our research
design and the rationale to use analogical reasoning to derive the ERF. In order to
confirm that it is indeed valid to use analogical reasoning, the argument of section 4
focuses on the similarities and differences between the data warehouse and enterprise
repository domains. The similarities provided us with a set of components of the data
warehouse domain that could be considered in deriving an ERF, whilst the differ-
ences highlighted the areas to be redesigned as part of the ERF. Section 5 proposes a
framework for an enterprise repository, derived from the data warehouse framework.
Section 6 provides some practical examples, whilst section 7 concludes.
2 Background
2.1 Enterprise Architecture Domain
Stevenson [15] relates a quote from Saarinen in Time Magazine of 2 July 1956 to the
concept of enterprise architecture. Saarinen states, ‘Always design a thing by consid-
ering it in its next larger context – a chair in a room, a room in a house, a house in an
environment, an environment in a city plan’. Similarly, as depicted in Fig. 1, a busi-
ness process is represented by a business process model, a business process model is
part of the business architecture, and the business architecture is a domain of the
enterprise architecture. The enterprise architecture domain, part of the information
management discipline, focuses on bridging the gap between business and informa-
tion management.
Enterprise architecture, according to Whitman, Ramachandran and Ketkar [17],
provides the mechanism by which the reality of the enterprise and its systems can be
aligned with management intentions. The business architecture, one of the enterprise
architecture domains, is representative of the enterprise, domain and systems levels
[11]. On enterprise level the business architecture addresses the business and man-
agement decisions, portfolio of businesses, mission, business strategies and visions.
On the domain level the business architecture includes the definition of the services
and products, as well as the business processes. On systems level the business re-
quirements for the systems and data management are included. The business architec-
ture on domain level includes business process models, reflecting how activities are
coordinated in the course of a business process [11].
Business process models are therefore positioned within the enterprise architec-
ture domain and are an important component of comprehensive business require-
ments. It is possible to close the gap between the enterprise architecture, business
78

process models and comprehensive business requirements by stating that, to some
extent, comprehensive business requirements, including business process models,
constitute part of bridging the gap between business and information management.
Set of
Business
Process
Models
Business Architecture
Enterprise Architecture Context
Information Architecture
Application Architecture
Technology Architecture
Business
Process
Set of
Business
Process
Models
Business Architecture
Enterprise Architecture Context
Information Architecture
Application Architecture
Technology Architecture
Business
Process
Fig. 1. Enterprise architecture context.
With business process models defined as part of the enterprise architecture do-
main, business process reference models can be defined as artefacts similar to busi-
ness process models. In this context, business process models that are predefined
business process models, and available for reuse, are referred to as business process
reference models [12].
To reuse these business process reference models, the warehouse concept is intro-
duced as part of the enterprise repository. The enterprise repository is a shared data-
base of information about engineered artefacts [1], specifically enterprise architecture
artefacts within the context of this discussion. Since the warehouse concept as part of
the enterprise repository is not well defined in literature, the intent is to propose an
enterprise repository framework (ERF) including warehouse concepts.
A framework is a basic conceptual structure used to solve or address complex
issues. The complex issue, in this instance, is to define an ERF to specifically address
the warehouse related functionality required from an enterprise repository. The
framework should at least cater for the integration of multiple business process
reference models and the enablement of flexible visualization of business processes.
The proposed ERF should include the basic components of an ERF and provides a
common vocabulary and definition for further discussion of the concept.
79
2.2 Database versus Data Warehouse versus Repository
The foundation for the data warehouse, as well as the repository, is the database. A
repository and a data warehouse are two specific variations of a database. Consider-
ing the enterprise repository as warehouse, the questions are whether it is a repository
extended with data warehouse functionality or a data warehouse extended with re-
pository management functionality. The dynamic interaction of these components is
provided in Fig. 2. The objective of Fig. 2 is to position the concepts database (A)
versus repository (B) versus data warehouse (C) and enterprise repository as ware-
house (D). The typical functionality and content addressed by each variant of a data-
base is indicated per component.
Functionality = Database
Content = Transactional data
Functionalit
y
= Database + repository managemen
t
Content = Enterprise architecture artefacts
Functionalit
y
= Database + “slice and dice”
Conten
t
= Transactional data from multipl
e
databases
Functionalit
y
= Repositor
y
+ “slice and dice
”
Content = Enterprise architecture artefacts
Database
Repository
Data
Warehouse
Enterprise
Repository
As
Warehouse
A
B C
D
Functionalit
y
= Data warehous
e
Conten
t
= Process related
Transactional dat
a
Process
Warehouse
Fig. 2. Database vs. repository vs. data warehouse vs. Enterprise repository (as warehouse).
Component A is the definition of the database concept. According to Date [4] a
database, in general, is both integrated and shared. Integrated means that the database
may be thought of as a unification of several otherwise distinct files, with any redun-
dancy among those files partially or wholly eliminated. Shared means that individual
pieces of data in the database may be shared among several different users as each of
those users may have access to the same piece of data (and may use it for different
purposes). Engles (as cited in [4]) defines a database as ‘a collection of stored opera-
tional data used by the application systems of some particular enterprise’. A database
is usually associated with operational or transactional data.
Component B focuses on the repository, a variation of a database. Additional
functionality is required in order to manage enterprise architecture artefacts that differ
from transactional data in a database. Adding this functionality to manage enterprise
architecture artefacts in a database, results in a variation of a database also known as a
repository. As mentioned in section 2.1 a repository is a shared database of informa-
80

tion about engineered artefacts [1] or enterprise architecture artefacts in contrast with
the transactional data that is usually stored in a database. A business process and
business process model are examples of enterprise architecture artefacts that are
stored in a repository. A repository includes specific repository management func-
tionality enabling the definition and management of these enterprise architecture
artefacts.
Component C positions the term data warehouse, which arose from the require-
ment to extend the database concept to enable the analysis of data from various data-
bases to create different views of the same data to support decision-making. A com-
monly used definition of a data warehouse comes from Inmon (as cited in [6]),
Srivastava and Chen [13], Zhou, Zhou, Tao and Hu [18] and Stefanov, List and
Schiefer [14]: ‘A data warehouse is a subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant, and
non-volatile collection of data to support decision-making’.
Component D introduces the concept of an enterprise repository as warehouse and
will be discussed in sections 3 and 4.
3 Research Design
The primary research method we used is analogical reasoning. Straker [16] states that
in analogical reasoning, an analogy for a given thing or situation is found, where the
analogy is in some way similar to the given thing. Other attributes of the analogical
situation are then taken to represent other attributes of the given thing as well.
In order to confirm that it is valid to use analogical reasoning it is necessary to fo-
cus on the similarities and differences between the data warehouse and enterprise
repository domains. Component D (Fig. 2) introduced the concept of an enterprise
repository as warehouse. The requirement is to extend the concept of a repository to
enable the analysis of business processes (examples of enterprise architecture arte-
facts) from various reference models, in order to create different views to enable a
better understanding and analysis of the business processes. The functionality re-
quired is similar to the initial data warehouse requirement to extend the database
concept to the data warehouse concept, namely to create different views from a set of
data. The intent is therefore to extend the repository concept to include the data ware-
house functionality. The definition of a data warehouse framework is to be used as
foundation for the proposed ERF (the concept of a framework and ERF were de-
scribed in section 2.1). The basic reasoning is that data from various sources are
loaded into a data warehouse and then the user has the ability to analyse and present
the information as required.
According to Gray and Watson [6], two key characteristics of a data warehouse
are that it is typically a dedicated database system that draws most of its data from
production systems, and users slice and dice the data in desired ways. In the article by
Bobrik, Reichert and Bauer [2] on the requirements for the visualization of system-
spanning business processes, there are statements that strongly relate to the data
warehouse characteristics as described by Gray and Watson [6], for example:
• ‘Since we want to integrate process models from different source systems’ – simi-
lar to the data warehouse sourcing data from various production systems, the en-
81

terprise repository (as warehouse) sources business process models from different
sources.
• ‘One-for-all visualization will not fulfil expectations and requirements. It should
permit us to aggregate or remove parts of a process schema or a process instance,
filter the elements according to their types and attributes, or combine several
processes in a single representation form’ – this is very similar to the slice-and-
dice concept of a data warehouse as described by Gray and Watson [6].
Considering these similarities between a data warehouse and an enterprise reposi-
tory, the enterprise repository (as warehouse) framework is based on the theory re-
lated to a data warehouse framework. Analogical reasoning is therefore an appropri-
ate research approach.
The research approach followed was to:
• Identify requirements from the enterprise architects to confirm the basic compo-
nents to be included in a proposed ERF.
• Select a generic definition of a data warehouse framework to be used as founda-
tion for the proposed ERF.
• Review a similar analogy between a data warehouse and a design warehouse,
highlighting potential differences and similarities to be expected in the compari-
son of the data warehouse framework and the proposed ERF.
• Propose an ERF based on the data warehouse framework.
4 Similarities and Differences between the Requirements of a Data
Warehouse and Enterprise Repository as Warehouse
In this section, we focus on the enterprise repository requirements, define the data
warehouse concept, derive a representative data warehouse framework and refer to a
similar analogy.
4.1 Enterprise Repository Requirements
Based on the work of Kirchmer, Brown and Heinzel [9] and Bobrik et al. [2] there
were at least five components to consider for the proposed ERF, namely:
• Source business process models from business process reference models.
• Build/populate a repository with business process reference models.
• Store business process models in a repository.
• Analyse business processes.
• Create alternative views of the business processes.
The approach followed was a logical process of using multiple business process
reference models as source data, to extract, load and transform the multiple reference
models into the repository, to manage the content of the repository, and then to pro-
vide flexible visualization of the business process models in the repository.
82
4.2 Data Warehouse Framework
In order to use the analogy of a data warehouse framework it was important to define
a data warehouse and select a data warehouse framework. The Inmon definition of a
data warehouse, as quoted in [6], was used: ‘A data warehouse is a subject oriented,
integrated, time-variant, and non-volatile collection of data to support decision mak-
ing’.
This definition of a data warehouse was adjusted to describe an enterprise reposi-
tory (as warehouse) with the specific enterprise architecture artefacts being business
process models. An enterprise repository (as warehouse) for business process model
artefacts is a business process-oriented, integrated, time-variant and non-volatile
collection of business process models to promote the use of business process refer-
ence models, and to support the flexible visualization of business process models to
minimise the causes of an inadequate business architecture.
Operational
databases
Extract load
transform
(ELT)
Data
warehouse
Online
analytic
processing
(OLAP)
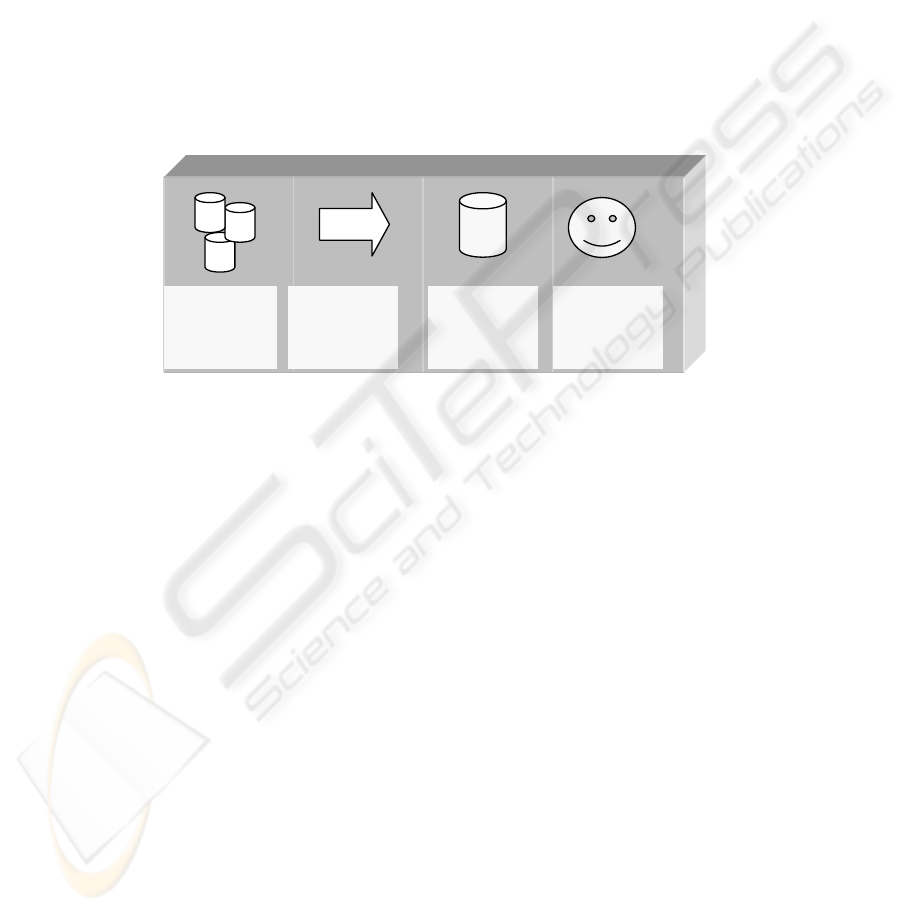
Fig. 3. Derived data warehouse framework.
A data warehouse framework (Fig. 3) was derived from the proposed data ware-
house frameworks by Gray and Watson [6], Dehne, Eavis and Rau-Chaplin [5] and
Chelluri and Kumar [3]. The component represented by all three of these sources was
the data warehouse component. Although not included in all three, the operational
databases, as included by Chelluri and Kumar, was selected as it is a prominent com-
ponent and part of the envisioned ERF to represent the business process reference
models as source for the business processes. The back-end extraction [6], cleaning
and integration [5] or operational data store [3] were combined and renamed to ex-
tract, load and transform. Lastly front-end use [6], OLAP (Online Analytic Process-
ing) and front-end tools [5], and query interface [3] were combined as online analytic
processing in the derived data warehouse framework.
4.4 Similar Analogy
Our focus was next on the question whether it is possible to learn from similar analo-
gies with a data warehouse framework. Laureri and Moke [10] discussed a design
warehouse, inspired by the model of a data warehouse. A key message is certainly not
to underestimate the complexity of the warehouse concept. They described rules that
83

characterise a design warehouse. The applicable rules from the ERF perspective were
rephrased to include:
• The business process model memory, independent from the source business proc-
ess model reference models.
• Multi-representation orientation, referred to as flexible visualization within the
enterprise repository context.
• Semantic complexity of business process models, as a reflection of reality and the
complexity of the navigation through the business process models is thus implied.
• Durability (independence of data from their process of creation) referring to the
possibility to represent the business processes even if the original business process
reference models are not available as source.
5 Proposed Framework for Enterprise Repository as Warehouse
Considering the required components for an ERF, the definition of a data warehouse,
the derived data warehouse framework, and the fact that a similar analogy to a data
warehouse was used to define a design warehouse, the conclusion is that there is
strong evidence that there are enough similarities to continue with the analogical
reasoning to define an ERF. Fig. 4 was the result of the translation of the data ware-
house framework components to the following proposed ERF components:
• Usage of multiple business process reference models as source models: Within the
data warehouse framework operational databases or other external sources are
used as input to the data warehouse. Within the enterprise repository context ex-
isting business process models are used as source data, specifically existing busi-
ness process reference models.
• A process to extract, load and transform multiple business process reference mod-
els into a repository: Within the context of the data warehouse framework the Ex-
tract, Load and Transform (ELT) is about populating the data warehouse with data
from the different operational databases. Within the context of the ERF ELT is
about populating the repository with multiple business process reference models
and other business process models.
• A description of repository functionality for managing enterprise architecture
artefacts: The repository is similar to the data warehouse but with the additional
capability to manage enterprise architecture artefacts.
• Flexible visualization of business process models: Instead of a comprehensive
online analytic processing (OLAP) functionality that is text- and number-based
the enterprise repository focuses on the flexible visualization of business process
models, including the additional challenges related to the manipulation of graph-
ics.
84
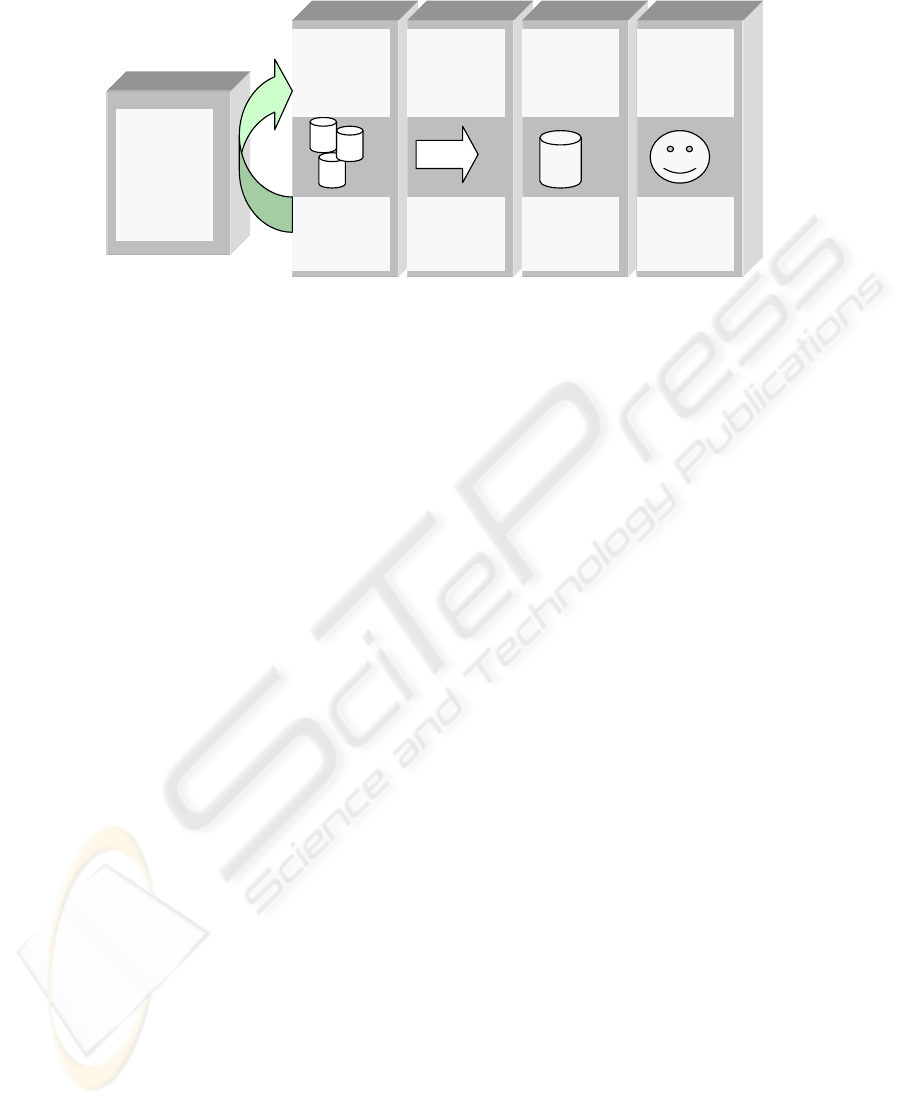
Operational
databases or
external
sources
Extract
load
transform
(ELT)
Data
warehouse
Online
analytic
processing
(OLAP)
Business
process
source
models
Extract
load
transform
Repository
Flexible
visualisation
From Data
Warehouse
to Enterprise
Repository
concept
Fig. 4. From data warehouse framework to enterprise repository framework.
6 Practical Examples
For illustrative purposes, we briefly provide two examples to illustrate the Extract-
Load-Transform (ELT) concept (section 6.1) and flexible visualization (section 6.2).
6.1 Practical Example Extract Load Transform (ELT)
For illustrative purposes of ELT, three sets of business process reference models were
successfully integrated in an enterprise repository [8]. The intent was to select two
sets of business process based reference models, as well as another set of application
based reference models. Integration of two sets of business process based reference
models was an indication that the business process reference model content may over-
lap. The method to integrate overlapping models differed from integrating comple-
mentary models. Integration with a set of application based reference models was an
indication of the complementary nature of non-overlapping reference models. By
creating a relationship, navigation to another set of models was possible. As proof of
concept, the following business process based reference models and an application
based reference model were selected:
• As business process based reference models, the Supply-chain Operations Refer-
ence-model (SCOR) and IndustryPrint 3.0 reference model were selected to illus-
trate dealing with overlapping content. The SCOR reference model is an industry-
specific reference model and IndustryPrint is a consulting reference model.
• As application based reference model, the SAP Solution Manager BPR reference
model was selected enabling complementary integration.
85

Process
Level 1
(SCOR)
SCOR
IndustryPrint
Process
Level 2
(SCOR)
Process
Level 3
(SCOR)
Process
(IP)
SubProcess
(IP)
Business
Activity (IP)
WorkStep
(IP)
Business
Scenario
(SAP)
Business
Process
(SAP)
Process
Step (SAP)
Transaction
(SAP)
SAP
consists of
enabled by
Fig. 5. Mapping of a meta-model.
The proposed ELT method consists of the following steps:
Metadata model creation:
• Analyse each business process reference model.
• Create a metadata model for each business process reference model.
Mapping of meta-model (Fig. 5):
• Mapping of a consolidated meta-model.
Extraction process:
• Identify the needed entities and relationships from the source business process reference
models.
Loading process:
• Create a temporary repository.
• Merge the selected entities and relationships to the temporary repository.
Transformation process:
• Merge the content of the temporary database into the business process warehouse re-
pository.
• Create relationships between the entities of the different business process reference
models.
The conclusion was that the proposed ELT method can be used to consolidate
multiple business process reference models into an enterprise repository. The map-
ping of the consolidated meta-model was the key to a successful ELT process. As
with the data warehouse ELT process the meta-model integration remains a complex
and human intensive task. A secondary outcome was the demonstration of the poten-
tial value of the use of multiple business process reference models as accelerator to
define the business processes, to enhance the completeness of business process mod-
els and to improve the understanding of the business process models.
6.2 Practical Example of Flexible Visualization
Examples of flexible visualization can be classified as follows:
Mapping
Mapping
1
86
• Enterprise architecture views per domain.
• Individual and merged viewpoints.
• Swim lane-based views.
• Notation-based views (BPMN vs UML).
• Scenarios (Refer to Fig. 6 and Fig. 7).
• Aggregation and reduction based views.
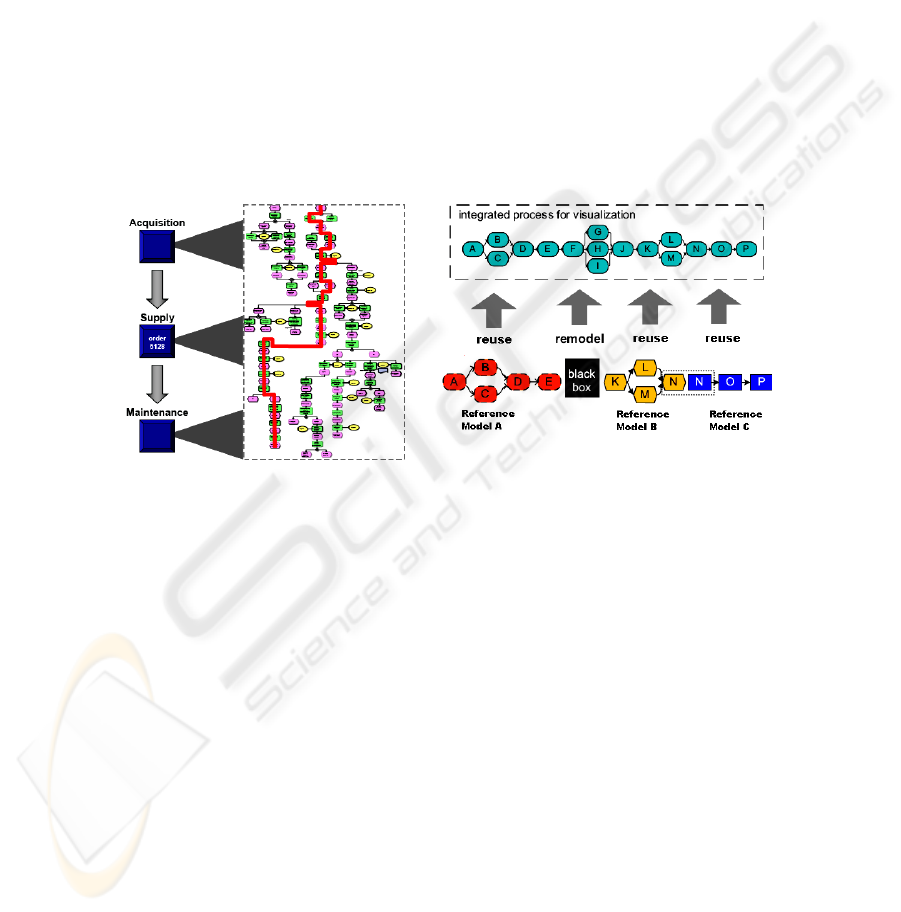
We briefly discuss scenarios as illustration of flexible visualization. A scenario is
a specific path through a set of business process models. Fig. 6 illustrates the re-
cording of a path from three different business process models (Fig. 6 is for illustra-
tive purposes and detail content is not readable IDS Scheer AG [7]). Conceptually,
the three business process models are combined in a single model. The selected ob-
jects are recorded and a new model is created to represent the scenario. The source
models are the acquisition, supply and maintenance models. The recorded objects
indicated by the red line will be used to generate a new model. The objects that are
not recorded will not be part of the new model.
Fig. 6. Scenario IDS Scheer AG [7]. Fig. 7. Mapping of scenario from reference
models.
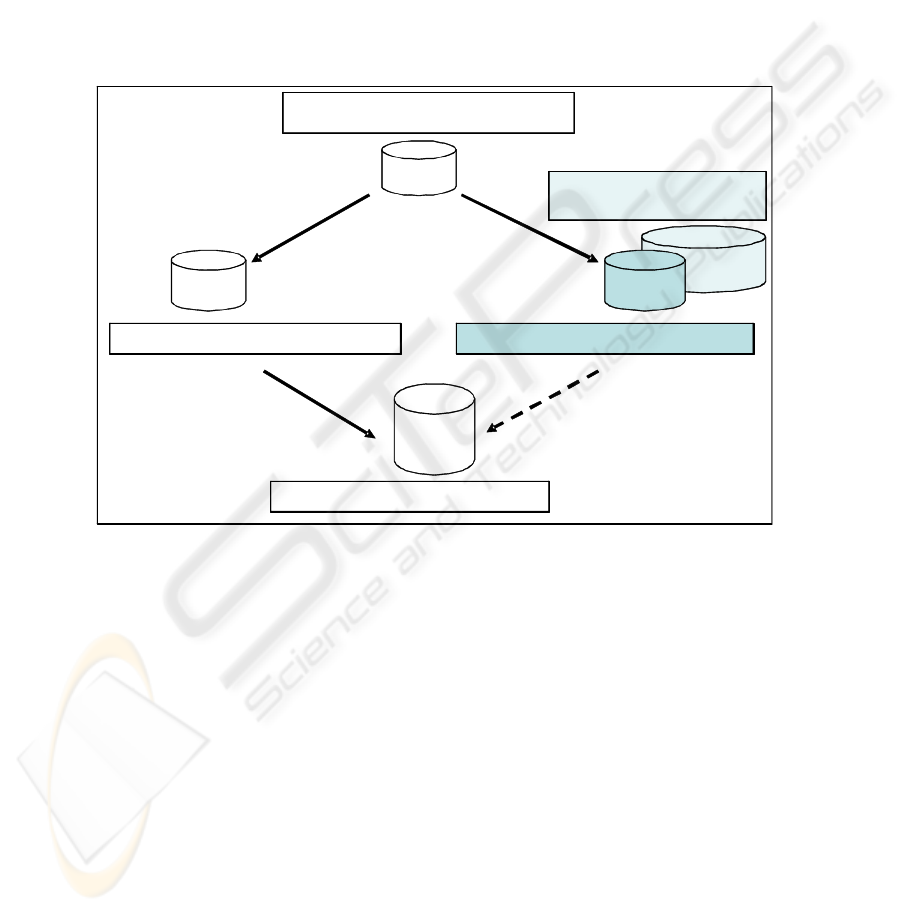
Fig. 7 is a variation of a diagram by Bobrik et al. [2] to illustrate the visualization
of system-spanning business processes in a complex enterprise environment. The
difference is that Bobrik et al.[2] is sourcing the information from different systems,
thus a bottom-up approach based on business activity monitoring, business process
diagnosis and log data. In Fig. 7 a top-down approach based on the reuse of multiple
business process reference models is illustrated. Such a top-down and bottom-up
approach should be seen as complementary and not as contradictory. The business
process reference models could provide context to the tasks executed by the systems
as well as the manual activities. The end user is interested in the integrated model for
visualization.
Three reference models are reused
• Reference model A with A, B, C, D and E as activities.
• Reference model B with K, L, M and N as activities.
• Reference model C with N, O and P as activities.
There are no existing reference models for activities F, G, H, I and J. These acti-
87

veties are modelled as a new process and added for future reuse to the enterprise
repository. The duplication of activity N was resolved as part of the review and inte-
gration. The end result is the process as required by the end-user by re-using existing
processes from the enterprise repository and extending the enterprise repository.
7 Conclusions
The argument of our research originated in the practical experience of defining a
comprehensive business architecture. The intent was to learn from a theoretical foun-
dation in defining an enterprise repository framework. The proposed enterprise re-
pository framework was based on such a theoretical foundation, namely a data ware-
house framework.
During our review of published research we couldn’t find a framework for the
concept of an enterprise repository as warehouse. We did, however, found references
to the concept of a business process model warehouse, the characteristics of a data
warehouse, and a similar analogy between a data warehouse and a design warehouse.
These sources were all considered together with the analogy to the data warehouse
framework as input in the development of the ERF we proposed. The proposed ERF
is a requirement specification of some of the functionality to be provided by the en-
terprise repository to assist the enterprise architect. However the proposed ERF also
provides context for the enterprise architect to position the value of the use of multi-
ple business process reference models and the importance to consider flexible visuali-
zation to add value for the end user of the enterprise repository content.
Acknowledgements
The following entities granted permission to refer to proprietary information and to
use specific technology as indicated. Without the support from these entities it would
not have been possible to prepare the case study for this research:
• Deloitte Consulting, for making part of IndustryPrint 3.0, a set of business process
reference models, available.
• IDS Scheer AG, for making the SAP Solution Manager BPR ST-ICO150 business
process reference models available and allowing the use of ARIS for SAP Net-
Weaver to create a number of business process models for illustrative purposes.
• Supply-chain Council, for authorising reference to the Supply-chain Operations
Reference-model (SCOR) as part of this research.
References
1. P.A. Bernstein, Repositories and object-oriented databases, ACM SIGMOD Record, 27(1),
88 - 96 (1998).
88

2. R. Bobrik, M. Reichert, and T. Bauer, Requirements for the visualisation of system-
spanning business processes, in: Proceedings of the 16th International Workshop on Data-
base and Expert Systems Applications (DEXA’05), edited by, (IEEE, 2005), pp. 948 - 954.
3. K. Chelluri and V. Kumar, Data classification and management in very large data ware-
houses, in: Proceedings of the Third International Workshop Advanced Issues of e-
Commerce and Web-based Information Systems (WECWIS’01), edited by, (IEEE, 2001),
pp. 52 - 57.
4. C.J. Date, An Introduction to Database Systems, Third ed (Addison-Wesley Publishing
Company, Reading, 1981).
5. F. Dehne, T. Eavis, and A. Rau-Chaplin, A cluster architecture for parallel data warehous-
ing, in: Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Cluster Computing and the
Grid (CCGRID ’01), edited by, (IEEE, 2001), pp. 161 - 168.
6. P. Gray and H.J. Watson, Present and future directions in data warehousing, The
DATABASE for Advances in Information Systems, 29(3), 83 - 90 (1998).
7. IDS Scheer AG, ARIS 6 Collaborative Suite ARIS Methods. Product Information. (IDS
Scheer AG, 2002).
8. D.E. Jacobs, Towards a Business Process Model Warehouse Framework, in School of
Computing. (University of South Africa, 2008), pp. 188.
9. M. Kirchmer and G.H. Brown, H., Using SCOR and other reference models for e-business
process networks, in: Business process excellence ARIS in practice, edited by A. Scheer, F.
Abolhassen, W. Jost, and M. Kirchmer, (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2002), pp. 45 - 64.
10. P. Laureri and G.M. Moke, ‘Design warehouse’: a ‘data warehouse’ for computer aided
design, in: Proceedings of the 3rd Basque International Workshop on Information Tech-
nology (BIWIT ’97), edited by, (IEEE Computer Society, 1997), pp. 197 - 205.
11. M. Pulkkinen, Systemic management of architectural decisions in enterprise architecture
planning. Four dimensions and three abstraction levels, in: Proceedings of the 39th Hawaii
International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS’06), edited by, (IEEE, 2006), pp. 179
- 187.
12. B. Ramesh and M. Jarke, Towards reference models for requirements traceability, IEEE
Transactions on Software Engineering, 27(1), 58 - 93 (2001).
13. J. Srivastava and P. Chen, Warehouse creation – a potential roadblock to data warehous-
ing. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering. IEEE, 11 (1), 118-126.,
(1999).
14. V. Stefanov, B. List, and J. Schiefer, Bridging the gap between data warehouses and busi-
ness Processes, in: Proceedings of the 2005 Ninth IEEE International EDOC Enterprise
Computing Conference (EDOC’05), edited by, (IEEE, 2005), pp. 3 - 14.
15. D.A. Stevenson, Positioning enterprise architecture, (cited 9 December 2006);
http://users.iafrica.com/o/om/omisditd/denniss/text/eapositn.html (1995).
16. D. Straker, Changing Minds: Analogical reasoning, (cited 24 November 2007);
http://changingminds.org/disciplines/argument/types_reasoning/analogical_reasoning.htm
(2002-2007).
17. L. Whitman, K. Ramachandran, and V. Ketkar, A taxonomy of a living model of the enter-
prise, in: Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Simulation, edited by, (IEEE Computer
Society, 2001), pp. 848 - 855.
18. S. Zhou, A. Zhou, X. Tao, and Y. Hu, Hierarchically distributed warehouse, in:
Proceed-
ings of the Fourth International Conference/Exhibition on High Performance Computing in
Asia-Pacific Region, edited by, 2, (IEEE, 2000), pp. 848-853.
89
