
THE RESEARCH ON THE INTERACTION EFFECTS OF RURAL
LOGISTICS AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
Xuegang Chen and Jianqin Zhou
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China
Keywords: Rural logistics, Economic development, Interaction effects.
Abstract: There are interaction effects between rural logistics and economic development. The effect rural logistics
has on the economic development presents as an S-shaped curve. So the interaction effects between rural
logistics and economic development vary at different stage. It’s necessary to analyse the interaction effects
to make the appropriate policies to promote the development of rural logistics. A model is constructed to
analyse the interaction effects. Then the contribution that rural logistics makes to economic development in
China is discussed. The interaction effects at present imply a result that the rural logistics elasticity
coefficient of economic development is less than 1. Finally, some policies to develop rural logistics are
proposed.
1 INTRODUCTION
As a large agricultural country, the important role of
rural logistics in the development of the national
economy is self-evident. The research on rural
logistics is also carried out extensively. Lu Jiang
pointed out that logistics about agricultural products
should be attached importance to, which provides
logistics security for building new socialist
countryside. The backward logistics equipment and
poor operation models are important factors which
lead to keep farmers’ income at low level even with
the increasing production. The application of new
logistics concepts and technologies is a very
important method to build new socialist countryside
(Lu jiang, 2006). With the summary of the
development characteristics of modern logistics in
developed countries, Wei Jigang put forward that
when concerned with the development of the
logistics in urban and rural, agriculture logistics and
rural logistics should be paid more attention to than
urban logistics (Wei Jigang, 2006).
Although rural logistics is so important, the
overall development of rural logistics is in low level
and low speed. There are some obstacles in rural
logistics, such as poor logistics infrastructure, high
transaction costs, backward logistics technologies
and low rate of the application of modern
information technologies. Relative to the
development level of overall economic, the
development of rural logistics is not satisfactory. So
many experts and scholars proposed
countermeasures and suggestions for the
development of rural logistics (Deng Shuhong and
Wei Feng, 2009). It is one of the most familiar
advices that the government should attach great
importance to the promotion of logistics
infrastructure in rural areas. The starting point of
these proposals implies that the development of rural
logistics should be supported by other economic
departments. However, there are some limits in these
studies. Because the rural logistics is a part of
national economy, there is a relationship between
them and the development scale of rural logistics
must match with the scale of the overall economy.
Therefore, empirical study is needed to educe the
relationship between the rural logistics and
economic development before the actual logistics
planning in rural areas. When the development of
rural logistics is in small scale stage and isn’t
conducive to economic development, it’s necessary
to increase investments to promote rural logistics.
When the scale of rural logistics is large enough,
policies should mainly be assigned to focus on how
to change the logistics development into an
important force for economic growth through the
optimization of rural logistics. In total, it is crucial to
find the appropriate scale of rural logistics and
policies should be put forward based on the principle
of mutual benefit for both of the development of
167
Chen X. and Zhou J..
THE RESEARCH ON THE INTERACTION EFFECTS OF RURAL LOGISTICS AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003487501670171
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2011), pages 167-171
ISBN: 978-989-8425-54-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

rural logistics and national economy.
Therefore, this paper analyzes the role of rural
logistics in the regional economics growth from the
quantitative point of view. Based on the result, the
matched scale of rural logistics and how to make
appropriate rural logistics policy are discussed,
which may do good to rural logistics planning.
2 MODEL OF THE EFFECTS OF
RURAL LOGISTICS ON
ECONOMIC GROWTH
There are many characteristics of rural logistics, so it
is necessary to adopt some of the sophisticated
theories and methods of modern logistics, especially
the quantitative research methods. Empirical
research methods have been maturely used in the
study of regional logistics. Wang Jun used the GDP
to represent the level of economic development,
while the level of development of the logistics
industry represented by the goods turnover (Wang
Jun, 2004). Then he revealed the relationship
between logistics industrial and economic
development by using the econometric approach.
Tan Qingmei et al used cargo turnover and volume
of passenger transportation as a unified index to
reflect the regional logistics capability, and analyzed
the relationship between logistics and economy in
Jiangsu Province by using regression approach (Tan
Qingmei and Wang Zilong, 2005). In quantitative
research about regional logistics and regional
economic growth, passenger and freight traffic
volume or passenger and freight traffic turnover are
always used to describe the development level of
logistics, and GDP is used to describe the economic
growth. To research the relationship between
regional economic and logistics, researchers mostly
use these econometric models: (1) regression model;
(2) the logic of economic growth trends (Logistic)
model; (3) co-integration analysis; (4) panel data
analysis (Song Shanmei and Xie Huiqiang, 2009). In
the paper, the interaction effects between the rural
logistics development and economic development
are analyzed with empirical research method, which
is maturely used to study regional logistics..
2.1 Data Resources
In this paper, the level of economic development is
represented by GDP (Wang Jun, 2004; Tan Qingmei,
2005), while the level of rural logistics is
represented by freight traffic volume of agricultural
products.
Wu Zhihui et al indicated that it’s
reasonable to use freight traffic volume to represent
the level of logistics development (Wu Zhihui and
Yu Qiaoyun, 2008). She pointed out that both of the
freight traffic volume and freight traffic turnover
speed have important influences on the development
of regional logistics. Then she analyzed the
influence that logistics had on the economic growth
of the three economic zones. The agricultural
products from farmers are eventually put into the
circulation through the logistics channels, so the
total freight volume of agricultural products is
calculated by the sum of the weight of farmers’
selling agricultural products, animal products and
aquatic products.
2.2 Gompertz Model
Gompertz model was designed to forecast the
population growth by the life insurance expert,
B.Gompertz in UK in 1820. Then the model was
used in market forecasting by the American scholar,
R.Prescott (Gu Jibao, 2010). And later it was widely
used for description and prediction in biological and
industrial growth. The function is as follow.
01
(/)
Y
bbX
e
+
=
(1)
Where, Y is the dependent variable and X is the
independent variable. b
0
and b
1
are unknown
constant. Its function curve is shown in Figure 1.
X
*
Y*
x
y
Figure 1: Function curve of Gompertz model.
As shown in Figure 1, the curve of Gompertz
model
is a typical S-shaped curve. Note that in the
left side of the turning point
**
(,)XY
, the curve is
concave bec
ause
'( ) 0, ''( ) 0yx y x>>
, while in the
right side of the turning point the curve is convex
as
'( ) 0, ''( ) 0yx y x><
. When
x
→∞, the curve is
close to a horizontal asymptote.
The contribution that rural logistics makes to
regional economic development can also be
described by the Gompertz model. The effect trend
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
168
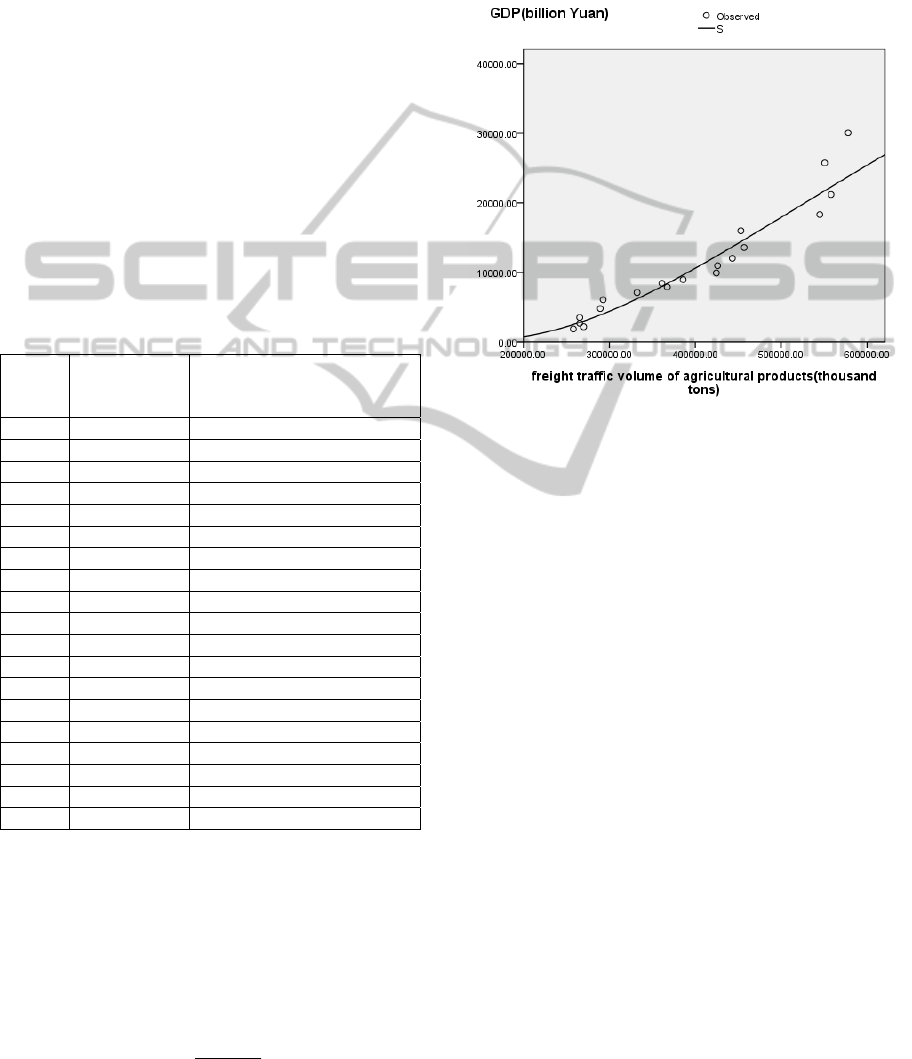
of freight traffic volume of agricultural products (x)
to GDP(y) is also presented as the S-shaped curve.
The development of rural logistics lags behind the
regional economic growth in the early stage, and its
contribution to economic growth is not obvious with
a flat trend. While the rural logistics is developed to
a certain degree, its contribution to the regional
economy may stand out with a rapid rise trend. After
the scale of rural logistics and the level of logistics
management are developed to a certain extent, the
contribution which the rural logistics makes to the
regional economy may accordingly reach the
maximum and then gradually become stable.
2.3 Empirical Research
Firstly, China's GDP during 1990-2008 and the total
freight traffic volume of agricultural products per
year are given in Table 1.
Table 1: China's GDP and freight traffic volume of
agricultural products.
Year GDP(billion
Yuan)
Freight traffic volume of
agricultural
products(thousands tons)
1990 1866.78 258003.57
1991 2178.15 270083.18
1992 2692.35 265372.87
1993 3533.59 265465.00
1994 4819.79 289315.60
1995 6079.37 282718.29
1996 7117.66 332219.04
1997 7897.30 367373.87
1998 8440.23 361125.16
1999 8967.71 385832.92
2000 9921.46 424534.22
2001 10965.52 425891.41
2002 12033.27 443147.41
2003 13582.28 456802.34
2004 15987.83 453026.16
2005 18321.74 544953.21
2006 21192.35 557975.40
2007 25730.56 550679.94
2008 30067.00 577907.39
Based on the model constructed before, now we
use the GDP (y) which indicated the level of
economic development as the dependent variable,
and freight traffic volume of agricultural products
(x) as the independent variables, indicating the level
of logistics development in rural areas. Here we
adopt the SPSS17.0 to fit the S-shaped curve and get
the S-shaped curve equation as follow:
1048593.36
(11.891 )
x
ye
−
=
(2)
Where the correlation coefficient
R2=0.941,P=0.000 achieve the significant level,
indicating that the positive effect China's rural
logistics have on economic development indeed
presents as the S-shaped curve. The fitting image is
shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Fitting curves of GDP and freight traffic volume
of agricultural products.
3 THE SCALE AND
DEVELOPMENT STRATEGIES
IN RURAL AREAS OF
LOGISTICS TO MATCH WITH
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
LEVEL
Having analyzed the positive effect that the rural
logistics have on China’s economic, it’s necessary to
adopt effective policies to promote the development
of rural logistics. In practice, because the level of
logistics development in rural areas can not always
match with the level of economic development, the
degree of the contribution that rural logistics makes
to economic development may not the same. That’s
why appropriate policies that made by government
should based on the regional economic environment,
i.e. the development level of rural logistics should
match with the development level of economic.
Before making the logistics policy, no matter the
infrastructure construction or investment scale and
intensity, it’s necessary to identify the interaction
effects between them.
THE RESEARCH ON THE INTERACTION EFFECTS OF RURAL LOGISTICS AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
169

3.1 The Interaction Effects between
Rural Logistics Development and
Economic Development
There are interaction effects between the level of
rural logistics development and economic
development, including pushing effect and pulling
effect. When studying the regional logistics, the
interaction effects are always described by regional
economic logistics flexibility (Tan Qingmei and
Wang Zilong, 2005). In this paper, the method is
adopted and improved to explore the interaction
effects between rural logistics and rural economic
development. In economics, elasticity is used to
describe the degree that an economic variable
changes under the other economic variables’
influence. Based on the definition of elasticity in
economics, the function that can be used to calculate
the rural logistics elasticity of economic
development is given as follow:
/
/
L
dy y dy x
E
dx x dx y
==i
(3)
Where x indicate the level of rural logistics
development, and y indicate the level of economic
development. When
L
E
>1, that for every 1%
increase of rural logistics industry will bring the
increase rate of economic growth more than 1%,
indicating the rural logistics performs pulling effect
on the overall economy. Similarly, the rural logistics
performs pushing effect on the overall economy
when
L
E <1. If 1
L
E = , that means the development
of rural logistics capabilities keep the same pace
with the development level of economic.
The rural logistics elasticity of economic
development can be calculated based on the function
given above:
1048593.36
L
dy x
E
dx y x
==i
(4)
Further obtained, when
L
E =1, indicating that the
development of rural logistics can keep up with the
development of our national economy when the
freight traffic volume of agricultural products is
equal to 1048593.36 thousand tons. And the
interaction effects of rural logistics and our national
economy is relative perfect at this stage. When
x<1048593.36 thousand tons, however, supports
from the national economy are urgent needed for the
development of rural logistics. That means the
development of rural logistics will mainly reckon on
the country increasing its investment strengthen in
the area. When x>1048593.36 thousand tons, the
development level of China's rural logistics over the
development level of overall economic with the
pulling effect on the economy. At this stage, the
modes of rural logistics development need to
transfer: from extensive to intensive and from
relying on state investment to strengthen the
logistics management.
3.2 Policy Recommendations for the
Development of Rural Logistics
A Until the end of 2008, China’s freight traffic
volume of agricultural products reached 577907.4
thousand tons, which is still far below the level of
1048593.36 thousand tons. As analyzed above, the
key point for developing rural logistics at this stage
is that our country should strengthen policy guidance
and strengthen investments. Specific policies
advices are proposed as follows:
(1) Strengthen the construction of logistics
infrastructure in rural areas. Logistics infrastructure
plays a decisive role at the early stage of the
development of rural logistics. At present, logistics
infrastructure in rural areas lags far behind the
development of regional economy. That is an
important factor which limits the development of
rural logistics. So the first priority is strengthening
the investments for the construction of rural logistics
infrastructure facilities.
(2) Improve the informationization level in rural
areas. Promoting the informationization process in
rural areas is an important part of the construction of
new countryside in China. Through the project,
information such as the agricultural market supply
and demand, trade, prices, can timely and accurately
delivery to farmers. That will reduce the
uncertainness and blindness in agricultural
production and selling. At the same time, through
the development of online trading platform like e-
commerce, transaction costs can be reduced while
the logistics efficiency and service level improved.
(3) Develop the rural logistics technologies and
strengthen the training of professionals. With the
development of modern logistics, many advanced
logistics technologies achieved rapid development
and improvement. But the circulation of agricultural
products in China is still facing problems such like a
low rate of primary processing and a high rate of
loss. As data shows, the circulation decay loss rate
of vegetables, meat, aquatic products even reached
20-30%, 12%, 15%, and annual loss of fruits and
vegetables only even reached more than 100 billion
Yuan. Therefore, we should vigorously develop
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
170

professionals that master the knowledge of logistics.
And more attention should be paid to the research
and practice of rural logistics technologies. These
measures may avoid the loss of agricultural products
in the logistics chain, which lead to keep farmers’
income at low level even with the increasing
production.
(4) Develop rural finance. The development of
rural finance affects the development of agricultural
and the rural logistics. Financial support is
especially needed at the initial stage of the
development of rural logistics. At present China's
rural financial services and products are relatively
simple, that makes it have little efforts to support the
development of rural area economy. So it’s
necessary to develop rural finance to ensure the
financial support in agricultural production and
logistics development.
4 CONCLUSIONS
A regression model is constructed to analyse the
interaction effects between rural logistics
development and economic development. Then
China is taken as an example of empirical research.
The research has some practical significance. On
one hand, through the regression model of rural
logistics and economic development, quantified
analysis of the relationship between them will be
available. The result will benefit the forecast of the
scale of rural logistics and economy. On the other
hand, because the interaction effects vary at different
stage, policy makers can find which state it is at
present through the interaction effects analysis
combined with the regional economic realities. That
is helpful for making appropriate policies for rural
logistics development and rural logistics plans.
Finally, according to the interaction effects in China
at present, policy recommendations that meet the
current needs for the development of rural logistics
are proposed.
REFERENCES
Lu Jiang, 2006. General Review of the Development of
China Logistics Industry in 2005 and the Perspective
of 2006. China Logistics & Purchasing 4, 18-21
Wei Jigang, 2006. Reference, Experience and
Characteristic of Logistics Development in Developed
Countries. China Business and Market 10, 15-18
Deng Shuhong, 2009. Wei Feng. Review of Rural
Logistics Research. Modern Agriculture 2, 62-64
Wang Jun, 2004. Empirical Analysis on the Effects of
Chinese Logistics Industry on Economic Growth.
SCI/TECH Information Development & Economy
14(1):69-70
Tan Qingmei, Wang Zilong, 2005. Elasticity of the
Regional Economic Logistics. Statistics and Decision
5, 56-57
Song Shanmei, Xie Huiqiang, 2009. Regional Logistics
Development and Regional Economic Growth in
China - A Case Study in Guizhou. China Economist
11, 267-268
Wu Zhihui, Yu Qiaoyin, 2008. Effect Analysis of
Regional MF Industry in Three Economic Zones for
Regional Economy Growth, Journal of Bejing
Jiaotong University(Social sciences Edition) 7(1), 43-
47
Gu Jibao, 2010. Forecasting on China's Civil Automobile-
owned Based on Gompertz Model, Technology
Economics 29(1),57-62
THE RESEARCH ON THE INTERACTION EFFECTS OF RURAL LOGISTICS AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
171
