
EFFICIENCY EVALUATION IN ACADEMIC UNITS APPLYING
DATA ENVELOPMENT ANALYSIS
Initial State of Project
Horacio Rojo, Silvia Adriana Ramos, Pedro Tolón Estarelles
Claus Stegmann, Leandro J. Raspa and Diego Castro
Grupo de Investigación Modelos de Gestión, Departamento de Gestión Industrial
Facultad de Ingeniería, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Avenida Las Heras 2214
Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires, Argentina
Keywords: DEA, Data Envelopment Analysis, Efficiency Analysis, Resource Administration, Multicriteria Decision.
Abstract: The aim of this paper is to present a procedure to look into the relative efficiency of university departments
in order to make a good allocation of resources. This procedure uses a model based on Data Envelopment
Analysis (DEA). DEA measures relative efficiency of a set of alternatives (decision making units – DMUs)
that consume multiple inputs and produce multiple outputs. Results of the model will help to plan
development of university departments in Facultad de Ingeniería of Universidad de Buenos Aires.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, Facultad de Ingeniería (Engineering
School) of University of Buenos Aires (FIUBA) has
established a policy in order to encourage research
activities mostly on new areas. As a result of this
policy, several professors with full dedication were
designated by open contest in some departments
such as Industrial Engeneering.
In the case of Industrial Management
Department (Departamento de Gestión Industrial),
incorporation of professors has led to the formation
of teacher-investigators groups that, even being still
small, are allowing to start an interesting series of
investigating activities. One of the mentioned cores
is the Management Models Group (Grupo de
Modelos de Gestión) which leads the working line
presented on this paper.
The aim of this Group is to provide tools for
decision making in order to analize, evaluate and
solve real problems in operations, processes and
management. The objective of this first project is the
asessment of FIUBA's teaching departments to
provide information for better allocation of
resources. This information will be based on
comparison of the teaching and research
performance.
Nowadays, resource allocation in FIUBA has
been implemented with intuitive, subjective
procedures, not properly focused within a problem
structure. Usually, not enough criteria were taken
into account.
Therefore, changing the indexes used in
productivity often leads to apparently inconsistent
results. That is, according to an index, performance
is well, but other index does not rate as well.
Sometimes, results among different indexes can be
complete opposites.
The idea of this paper consists in developing a
mathematical model in which different indexes
weights are the variables to calculate. In that way
objectivity can be achieved because it would be
possible to demonstrate that some of the evaluated
units would not be able to achieve the best results
even adopting the most favourable weights for them.
The starting point is the classical work of
Charnes, Cooper and Rhodes (Charnes et al, 1978)
in wich a new method for evaluating decision
making units named Data Envelopment Analysis is
proposed. Also the work of Banker, Charnes and
Cooper (Banker et al, 1984) broadens the field of the
first work.
In the present paper, we study factibility of
application of those approaches plus other posterior
works (Cooper et al, 2000), (Thanassoulis, 2001),
473
Rojo H., Adriana Ramos S., Tolón Estarelles P., Stegmann C., J. Raspa L. and Castro D..
EFFICIENCY EVALUATION IN ACADEMIC UNITS APPLYING DATA ENVELOPMENT ANALYSIS - Initial State of Project.
DOI: 10.5220/0003748904730475
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES-2012), pages 473-475
ISBN: 978-989-8425-97-3
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
(Ray, 2004) to academic departments of FIUBA,
taking those departments as operative units and
asessing, analyzing and evaluating their possible
inputs and outputs.
This project was accredited by University of
Buenos Aires with code 2002 0090 2006 29 in the
UBACyT 2010-2012 period.
2 METHOD
2.1 Hypothesis
In order to achieve that, validity of a quantitative
approach like DEA methodology will be
experimented. This methodology bases in this
essential hipothesis:
Input and output measures for each university
unit are known;
Efficiency for each unit is presented as a
weighted sum of the outputs defined divided
by the weighted sum of the inputs defined;
All efficiencies will be restricted to the (0, 1)
range;
Mathematical model proposed will ougth to
determine efficiency value for each unit by
maximizing its efficiency and determining
weights for inputs and outputs.
2.2 Information Used
The first plan is to use information that belongs to
last years of management in FIUBA. In subsequent
stages, when methodology would be validated,
extension to other internal academic units and
external units is planned.
One of the core aspects of the process will be the
selection of units to be evaluated. We have used
academic units as FIUBA Departments, Institutes,
Schools, trying to be relatively similar in dimension
and characteristics.
Once the units to be evaluated were identified
we defined inputs and output, according to available
information and apply some appropriate method for
selecting variables, restricting its quantity in order to
obtain a reasonable degree in discriminating
efficiencies and taking into account (Cooper et al,
2000, 2007) refering compliance of >= max((m .
s);3(m + s)) being m inputs and s outputs.
Other aspect that should be matter of analysis is
DEA's classical assumption that efficiencies of units
for every activity are equal. This assumption could
not be true in case of academic units, where
activities as teaching, research, extension may have
different efficiencies. This situation would force
rethinking the model to consider that fact.
2.3 Method
As mentioned early, a quantitative method based on
DEA approach is used. Within this central idea,
DEA method has a group of alternative models
available, from which the basic are CCR models,
owing their name to their authors: A. Charnes, W.
W. Cooper and E. Rhodes (Charnes et al, 1978),
who initially proposed them with a non linear
optimization structure.
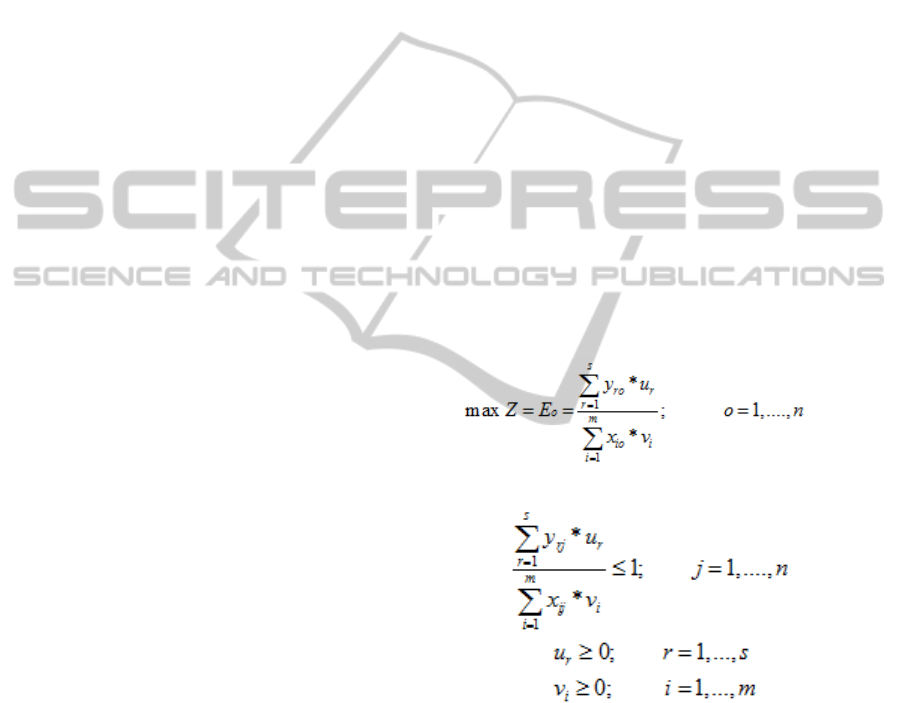
Non-linear CCR DEA model has an objective
function that maximizes efficiency E
o
, where j = o
means the generic S
j
system subscript. In this paper,
j is an academic or management unit for which
weights u
r
and v
i
are to be determined. This weights
u
r
and v
i
are applied in every S
j
efficiency expression
within ≤ 1 inequalities, trying to normalize its
values, therefore forming the model restrictions,
which are complemented with non-negativity
conditions for the weights u
r
and v
i
. The model
obtained has a non-linear structure.
(1)
Subject to:
(2)
The process is repeated for each of the n S
j
systems, leading to a series of n groups of weights u
r
and v
i
.
To determine efficiency of each functional unit,
it is needed to solve n models, one for each unit. The
basic model is a non-linear model, which can be
solved with non-linear optimizers. However, this
model can be taken to an equivalent linear form,
with the inherent advantages of linear models. This
is achieved fixing the objective
function
denominator as 1. In that way, the numerator itself
will measure efficiency, passing denominators of the
n restrictions to the second member and, then, the
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
474
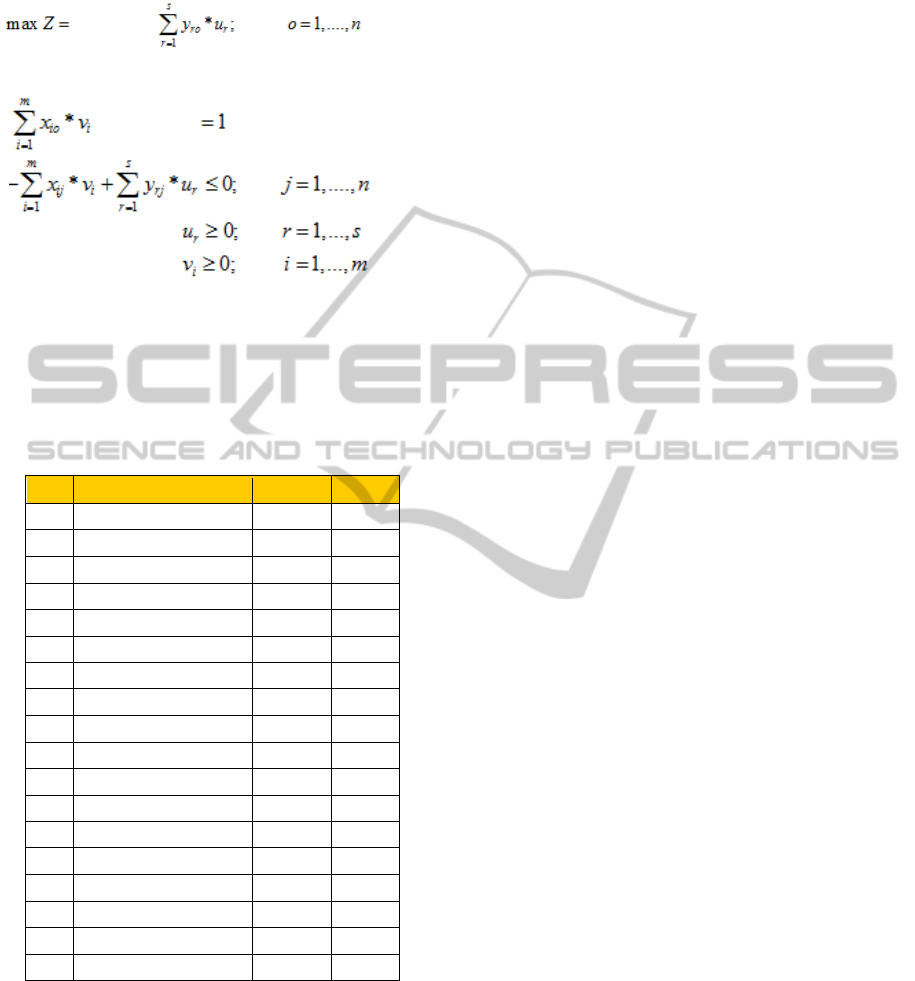
whole second member to the first
member. The
model obtained has a linear programming structure:
(3)
Subject to:
(4)
As in the non-linear model, the process repeats
in the same way for each of the n S
j
systems, thus
obtaining a series of n groups of weights u
r
and v
i
.
2.4 Preliminary Results
In Figure 1 is shown the preliminary results of our
project:
DMU Score Rank
1 Matemática 0,61 8
2 Física 0,55 10
3 Química 0,68 6
4 Estabilidad 0,61 7
5 Electrotecnia 0,44 15
6 Electrónica 0,43 16
7 Mecánica 0,55 9
8 Transporte 0,25 18
9 Hidráulica 0,46 13
10 Agrimensura 0,45 14
11 Economía 0,89 4
12 Industrias 0,87 5
13 Ingeniería Naval 0,38 17
14 Construcciones 0,52 11
15 Computación 1,00 1
16 Ing. Química 0,52 12
17 Ambiente y Trabajo 1,00 1
18 Idiomas 1,00 1
Figure 1: Preliminary Results
Further research might explore other DEA
models, like BCC (Banker et al, 1984), AR (Cooper
et al, 2000, 2007) and other models that may emerge
from investigation.
Another aspect to define will be the software to
use. This selection will depend on the dimension of
the Linear Programming formulated model. Some of
the specific decision analysis software are DEA
Solver, Frontier Analysis, Warwick DEA.
3 CONCLUSIONS
The approach proposed is not the only tool being
taken into account for decision making within
planning and management of FIUBA's academic
units, but is considered as a new contribution to be
integrated to the collection of other proceedings and
tools in use.
DEA methodology seems to be a suitable tool
for efficiency analysis in education.
As a not less important sub-product, the
investigation work already developed by the
Management Models Group during this first stage
and the work to develop during the project will
allow gain experience in research activities that will
not only benefit its members but also motivate other
teachers and students to initiate them in similar
activities, therefore responding to the policy
promoted by the authorities of FIUBA.
REFERENCES
Banker, R. D., Charnes, A. I., Cooper, W. W. 1984. Some
Models for estimating technical and scale
inefficiencies in Data Envelopment Analysis. In
Management Science, vol 30 (9). Pgs 1078 to 1092.
Charnes, A. I., Cooper, W. W., Rhodes, S. 1978.
Measuring the efficiency of Decision Making Units. In
European Journal of Operational Research, vol 2, Pgs
429 to 444.
Cooper, W. W., Seiford, L. M., Tone, K. 2000, 2007. Data
Envelopment Analysis: A comprehensive text with
models, applications, references and DEA-Solver
software. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell
Massachusetts.
Thanassoulis, E. 2001. Introduction to the theory and
application of Data Envelopment Analysis. Kluwer
Academic Publishers, Norwell Massachusetts.
Ray, S. C., 2004. Data Envelopment Analysis. Theory and
techniques for economics and Operations Research,
Cambridge University Press.
EFFICIENCY EVALUATION IN ACADEMIC UNITS APPLYING DATA ENVELOPMENT ANALYSIS - Initial State
of Project
475
