
Ontology-Based Solution for Building an Intelligent Searching
System on Traffic Law Documents
Vuong T. Pham
1,2,4 a
, Hien D. Nguyen
3,4 b,*
, Thinh Le
3,4
, Binh Nguyen
2,4 c
and Hung Q. Ngo
5d
1
Institute of Data Science and Artificial Intelligence, Sai Gon University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
2
Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Science, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
3
University of Information Technology, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
4
Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
5
Technological University Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Keywords: Knowledge Base, Searching System, Traffic Law, Law on Road Traffic, Legal Document.
Abstract: In this paper, an ontology-based approach is used to organize the knowledge base of legal documents in road
traffic law. This knowledge model is built by the improvement of ontology Rela-model. In addition, several
searching problems on traffic law are proposed and solved based on the legal knowledge base. The intelligent
search system on Vietnam road traffic law is constructed by applying the method. The searching system can
help users to find concepts and definitions in road traffic law. Moreover, it can also determine penalties and
fines for violations in the traffic. The experiment results show that the system is efficient for users' typical
searching and is emerging for usage in the real-world.
1
INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, transportation is a need for everyone.
Almost every adult has a vehicle - the traffic is
increasingly complicated, especially road traffic. In
Vietnam, there are more than three million traffic law
violations, with more than 14,500 traffic accidents in
2020 (National Traffic Safety Committee, 2020).
Some cases have resulted in injuries or deaths. The
reason for those cases is that people have low
awareness of the rules of traffic law.
Ontology is an effective approach to representing
knowledge (Jakus et al., 2013). This model has been
used to organize knowledge in education and
healthcare (Do et al., 2018). Moreover, several
studies adopt ontologies to represent the knowledge
of legal documents, while other studies use ontology
to organize legal knowledge (Valente and Breuker,
1992, Fawei et al., 2019). However, they did not
mention the traffic law for searching its content and
determining penalties for violations.
* Corresponding author
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3879-9677
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8527-0602
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5249-9702
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8246-8392
This paper proposes a method for building the
knowledge base for Vietnam road traffic law
(Vietnam National Assembly, 2008, Vietnam
Government 2019). This method is applied to
construct a search system in this law. The designed
system supports users in finding the content of the law
related to their queries, and it can determine penalties
for violations in road traffic via this law. In addition,
the system helps to raise people's awareness about
traffic law.
The primary value of the designed system is the
ability to search for penalties and fines for road traffic
offenses based on the keywords of the inputted query.
Therefore, the system's knowledge base is organized
as a relational ontology, which includes concepts,
entities, their relations, and the rules of Vietnam Law
on road traffic. In order to do that, the knowledge
domain about road traffic law is collected and
classified into knowledge components: concepts,
relations, and rules.
The following section presents related works for
constructing relational ontology, especially in the law
Pham, V., Nguyen, H., Le, T., Nguyen, B. and Ngo, H.
Ontology-Based Solution for Building an Intelligent Searching System on Traffic Law Documents.
DOI: 10.5220/0011635500003393
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2023) - Volume 1, pages 217-224
ISBN: 978-989-758-623-1; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
217

domain, and several search systems on legal
documents. Section 3 proposed an improved model of
Rela-model to represent the knowledge of the road
traffic code in Vietnam. Section 4 builds an
architecture and searching problems of an intelligent
querying system on Vietnam traffic code. The
designed system can support finding the content of
law related to the query and penalties for road traffic
offenses. The last section concludes the results of this
paper and gives some future works.
2
RELATED WORK
There are many studies to organize legal knowledge.
For example, Valente and Breuker (1992) stated three
approaches for the legal knowledge base: the logic
approach, the case-based approach, and the pragmatic
approach. Those approaches are used to build legal
ontologies and documents for data-retrieving systems
(Sator et al., 2011).
Ontology LIDO for Legal Informatics Document
is built based on the standard CEN Metalex (Sartor et
al., 2019). It represents legal actions that affect the
document, the legal temporal events, the structure of
the legal resource, and the semantic structure of
organization of legal documentss.
Ngo et al. (2021) proposed a method of data
augmentation based on legal domain knowledge for
the legal textual entailment. This method is used to
design a system for Vietnamese legal text processing.
Nguyen et al. (2022c) also proposed a training data
augmentation procedure and an unsupervised
embedding learning method to retrieve the legal
document. However, those proposed methods only
show the articles of a specified query and does not use
legal knowledge to explain its results clearly.
Pham et al. (2019) built an ontology-L for
representing the Law of Public Investment and
designed a consultant system for estimating the costs
of a project based on this law. In addition, an
intelligent chatbot was designed to tutor some
administrative procedures in printing licensing based
on the ontology Rela-Ops model (Nguyen et al.,
2020a). However, those methods are challenging to
apply in searching the content of a law document
related to the working domain.
There are some legal search systems in Vietnam,
such as the National Database of Legal Documents
(2022) of the Ministry of Justice and law library
(2022). However, these systems generally only allow
users to search for documents or entities with
keywords. However, they cannot help users find a
deeper search for legal documents in the real world.
For example, in traffic law, users need to search for
penalties and fines for a violation based on rules in
the legal document. Therefore, the current systems
are not suitable for supporting users in practice.
This study tends to build an intelligent search
system based on the ontology of the Vietnam road
traffic code. This ontology can be used to represent
the content of the law code and to deduce based on
the inference rules extracted from the code.
3
KNOWLEDGE BASE OF
VIETNAMESE TRAFFIC LAW
3.1 The Structure of the Vietnamese
Law on the Road Traffic
This section gives more details about the structure of
Vietnamese law on road traffic and the knowledge
model of the system. Through Vietnam National
Assembly (2015), the system of legal documents in
Vietnam has the following levels:
1. The highest validity is Constitution;
2. Codes/Laws and resolutions of National
Assembly;
3. Sub-law documents for instructing the detail of
the law established by National Assembly.
In general, a law document has a structure with
three parts: heading, content, and ending. The
heading shows the national name, the crest, number,
and sign of the document, enact place and date, type
and name of the document, and the basis of the
document. The content is a list of parts, chapters,
articles, clauses, and points. The ending is the signing
of the person that implements the document.
Inside the content, part is the highest level, then,
in order are chapters, sections, articles, clauses and
points. Through (Vietnam Ministry of Justice, 2011),
based on the type of document, there will be different
structures, for example some documents have
chapters, articles, clauses, and points but there is no
section. Each part, section, or chapter defines a
different factor. Below chapter are articles and
clauses which are used to define concepts, principles,
penalties, or regulations. If a clause needs more than
a sentence to define it, there will be several points in
addition to it.
Concepts in legal documents have two parts,
concept names and their definitions. For the offences,
each principle, penalty, or regulation which are
defined in articles and clauses of the legal document,
they always have the subject (the person or
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
218
organization that participate or engage in the event),
a fact (or action) and penalties if there is any.
In particular, the Vietnamese traffic law has the
same structure as stated. Two legal documents
currently implement and have most effect in the
social are: Law on road traffic (Vietnam National
Assembly, 2008) which prescribes interpretation of
concepts, road traffic rules, regulations for vehicles
and users on the road traffic; Decree of
Administrative of penalties for road traffic offences
and rail transport offences (Vietnam Government,
2019) (known as Decree 100) which states penalties
and fines for administrative violations of road traffic.
In addition, there is National Technical Regulation on
Traffic Signs and Signals (Vietnam Ministry of
Transport, 2019) to define and describe the road
traffic signs.
3.2 Knowledge Model for Road Traffic
Law
Ontology Rela-model is a useful ontology
representing the knowledge of relations. This model
includes three components about concepts, relations
between concepts (Nguyen et al., 2015). It is effective
to represent knowledge domains in education,
consultant the finance method based on the
investment law. Rela-model includes three
components which are used to represent concepts,
relations between concepts and inference rules of the
knowledge domain.
For representing the knowledge of a legal
document, Rela-model has been improved the
structure of its concept-component being suitable the
legal domain (Nguyen et al., 2022a). The knowledge
model for Vietnamese road traffic law is based on the
concepts or entities and their relations. Each relation
of them defines an action or event of road traffic.
Based on those relations and rules of law on road
traffic, the issues about retrieving the information of
offences and their penalties have been also proposed.
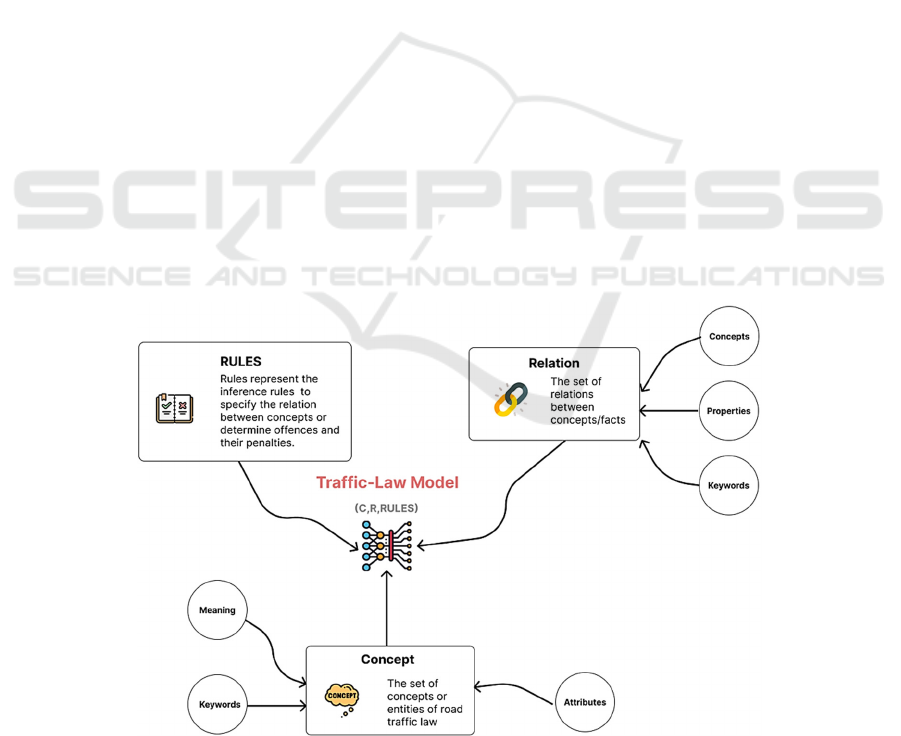
Definition 2.1: The knowledge model for
representing the legal domain of road traffic is
improved from ontology Rela-model, named Traffic-
Law model. This model consists of three components
as follows:
(C, R, Rules)
In which, C is the set of concepts or entities of road
traffic law, R is the set of relations between
concepts/facts, Rules represent the inference rules to
specify the relation between concepts or determine
offences and their penalties. The structure of Traffic-
Law model is summarized as Figure 1.
Set C is the set of concepts and entities in road
traffic law. There are three kinds of concepts in C:
users and vehicles of road traffic; traffic signs and
signals; road infrastructure. Based on those kinds,
each concept c ∈ C has the structure:
(Name, Meaning, Attrs, Keywords)
where, each element has the type and meaning for
specifying the corresponding concept as Table 1:
Figure 1: The Traffic-Law model.
Ontology-Based Solution for Building an Intelligent Searching System on Traffic Law Documents
219

Table 1: Structure of a concept.
Element T
y
pe Meanin
g
Name Tex
t
N
ame of the concepts
M
eanin
g
Tex
t
Meaning of the concepts.
Attrs Dict
List of attributes of the
concepts.
Keywords Set
Set of keywords
determined or related to
the concepts.
Example 1: The concepts “Electric motorcycle” in
(Vietnam Government, 2019) is described.
Element Content
Name Electric motorcycle
Meaning
“a two-wheel vehicle operated by
an electric engine with power not
exceeding 4 kW and maximum
speed not exceedin
g
50 km/h”
Attrs
A
ttrs = [kind, type, legal]
• kind: road traffic vehicle
• type: two-wheel vehicle
• legal: [Article 3, Clause 1, Point
d, Decree No. 100/2019/ND-CP]
Keywords
Motorcycle; electric; two-wheel
vehicle
Set R is the set of relations between concepts in
set C. These relations determine a specific fact or an
action of the road traffic code. Each relation r ∈ R has
the structure:
(Name, Conc, Meaning, Prop,Keywords)
where, each element has the type and meaning for
specifying the corresponding relation as Table 2:
Table 2: Structure of a relation.
Element T
y
pe Meanin
g
Name Tex
t
N
ame of the relation.
Conc List
List of parameters as
concepts of the relation.
M
eanin
g
Tex
t
Meaning of the relation.
Prop Set
Set of properties of the
relation. This study only
mentions two main
properties on a binary
relation: transitive and
s
y
mmetric.
K
eywords Se
t
Keywords of the relation.
Example 2: The relation “comply” of two concepts
“car” (or “car-like vehicles”) and “traffic light”,
denoted comply (car, traffic light), means “Operators
of car and car-like vehicles failed to comply with the
traffic lights”. Its keywords are “comply”, “over”.
Set Rules is a set of inference rules. Those rules
deduce relations between concepts or determine
offences based on road traffic law. Each rule r ∈
Rules has the form
u(r) → v(r)
where, u(r) is the hypothesis facts of rule r and v(r) is
the result of rule r.
The Rules-set is classified two kinds of rules:
Rules = Rule
infer
∪ Rule
offence
In which, Rule
infer
is the set of rules inferring the
relation between concepts, and Rule
offence
is the set of
rules determining offences and penalties.
3.3 Some Problems for Searching on
Traffic Law
Using the improved Rela-model, the knowledge base
for road traffic law has been organized. Based on this
knowledge base, the problems for searching on the
law document are studied. There are two issues for
searching on law, which are searching for the
concepts or definition of the law, especially the law
explanation, and determining offences and their
penalties and fines through the law document. To do
this, two searching problems need to be solved for
designing the intelligent searching system on the law
document:
Definition 2: The searching problems of an
intelligent searching system Traffic-Law model are:
• Problem 1: Extracting the keywords from the
inputted query to search the concepts and
relations in the legal knowledge base related
to the keywords.
• Problem 2: Retrieve the knowledge from the
knowledge base matching extracted concepts
and relations.
For solving Problem 1, the inputted query needs
to be classified. The input can be classified into two
kinds: query about meaning of a concept (“what is?”)
and query about the penalties & fines of an offence
(“how much”, “penalty”, “fines”). After that, from the
kind of the query, its main keywords are extracted. In
addition, some similar words for extracted keywords
are also achieved. The similar keywords can be
collected from legal document sources, experts (as
lawyers or legal lecturers), or from dictionaries. With
extracted keywords and determined similar words,
concepts related to those keywords are determined by
using rules in Rule
infer
. The process also finds
inference rules used to deduce concepts and their
relations.
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
220

Algorithm 3.1: Given a law document d which
is already represented using ontology based on
Traffic-Law model.
Input: The knowledge base K = (C, R, Rules)
as Traffic-Law model.
Query q.
Output: A set of keywords, relations, and rules
retrieved from query q and knowledge K
Algorithm.
Step 1: Classify the query using Vietnamese NLP
toolkit
Step 2: Extract keywords from the query q and
find similarly words based on the knowledge
base K.
W :=keywords(q)
Step 3: Classify the kind of query based keywords
in W.
Step 4: Expands W with similar keywords
collected from legal sources.
Step 5:
G :={} // Set of concepts
P :={} // Set of rules
For each keyword w ∈ W do
• Using Rule
infer
to search concepts and rules
related to w.
• From found concepts, determine required
keywords and add them to G.
• Add rules to P if not exists
Step 6: Return (G, P) are results of found
keywords and rules.
For solving Problem 2, after identifying the
concepts and relations, the article of legal documents
that states the offence is found by using rules in
Rule
offence
. Then, the information, penalties, and fines
of it are retrieved through the specified content of law
in the knowledge base. The process for solving this
problem is as follows:
Given the knowledge base K of road traffic law in
legal documents as Traffic-Law model. This
algorithm will determine the information, penalties,
or fines of an inputted query q.
Algorithm 3.2: Given a law document d which is
already represented using ontology based on Traffic-
Law model
Input: The knowledge base K = (C, R, Rules) as
Traffic-Law model, and a query q.
Output: Information, penalties, and fines of road
traffic offence for query q.
Algorithm.
Step 1: Retrieve set of keywords G from query q
based on Algorithm 3.1
Concept := {c ∈ C | c related to keyword in G}
Step 2:
Knowledge :={}
For each concept c ∈ Concept do:
• Using rules in Rule
offence
to find the offence
in the knowledge base K.
• Retrieve the information, penalties, and
fines of the determined offence from the
specified law document.
• Update the results into Knowledge.
Step 3: Return Knowledge.
4
THE SEARCHING SYSTEM OF
VIETNAMESE LAW ON ROAD
TRAFFIC
4.1 Requirements of a Searching
System on Legal Documents
The intelligent searching system on legal documents
needs to be supported the understanding of users
about the legal domain. In road traffic law, moreover,
the ability for solving of necessary issues of the
searching system, this system has some criteria of
intelligent software evaluation in searching (Nguyen
et al., 2020b, Giakoumakis and Xylomenos, 1996):
o Portability: This is the level of difficulty to
work with the same project with different machines.
o Installation: The requirements of software,
hardware for the simulator, and how straightforward
is the installation in a supported system.
o Usability: this criterion shows whether the
content is suitable and detailed with the current law
domain and whether it is updated and easily to use in
the practice.
o Understandability: this is one of the most
important characteristics of intelligent law searching
software quality. This system has to help users
understand the law content in legal documents. It can
influence users’ feelings about software and reliability
of software evolution in reuse or maintenance.
Besides, the process for building this system is
worked through the constructing of a knowledge-
based system (Nguyen et al., 2022b). At first, the
databse of traffic regulations will be collected, and
orgnaized by Traffic-Law model as the knowledge
base of this system. After that, the searching
mechanism is designed through problems on traffic
Ontology-Based Solution for Building an Intelligent Searching System on Traffic Law Documents
221

law searching and their alogrithms. Finally, the user
interface and testing of this system will be processed.
4.2 The Dataset of Traffic Regulations
The traffic regulation dataset is a combination of 2
documents:
1. Vietnam National Assembly, Law on Road
Traffic (known as 23/2008/QH12).
2. The Decree of Administrative of penalties
for road traffic offences and rail transport
offences (Vietnam Government, 2019),
abbreviated as Decree 100.
From both documents, there are 175 articles
collected. The general structure of these documents
is: Chapter – Section – Article – Clause – Point.
Traffic-Law model is used as an ontology to represent
this knowledge.
By default, questions about Vietnamese
transportation are classified into many intents. There
intents include but not limited to:
• Querying about concepts: These queries ask
definitions of concepts in the law. The system extracts
the apporiate article for the required concept.
• Querying about penalties: These queries ask
about the penalty or fines for a traffic violation, such
as running the red light, driving contrariwise, etc.
• Querying about procedures: The system give a
proceduce in traffic law, such as fine payment
procedure, the procedure for issuing driving licenses,
etc.
• Querying about signs: This function support
user to retrieve the information of an inputted sign.
This function related to image processing.
However, because the scope of this study, only the
kinds of querying about concepts and penalties are
focused in this paper. There are 160 practical
collected queries related to road traffic regulation.
These queries will be augmented and used for training
query intent classification in Problem 1.
4.3 The Architecture of the Searching
System on the Traffic Law
The architecture of the search system on traffic law is
presented in Figure 2. The system consists of the user
interface, the knowledge base, and the search engine.
The knowledge of the road traffic codes is
collected from (Vietnam Government, 2019, Vietnam
Table 3: Query Classification.
Class Meanin
g
Quantit
y
Concept
Require identifying the
meanin
g
of a concept.
54
Penalties
Require identifying the
fine of an offence.
83
Out of
scope
Queries that do not belong
to above kinds.
23
Total 160
National Assembly, 2008). These facts and entities of
those documents are organized as a knowledge base
by the improved ontology Rela-model and stored
inside a graph database. The similar words are
manually established via the collection of intellectual
experts and their experiences.
When a user inputs the query, the search engine
will execute the extract keywords tasks by Problem 1,
which are classifying the query, checking typo,
removing stop words, checking synonyms, and
checking equivalent keywords, to generate the query
values. From the extracted keywords, the similar
words will be determined through the knowledge base
Traffic-Law model. Those are used to search the
necessary knowledge by using inference rules of the
knowledge. In addition, their penalties and fines are
also retrieved by Problem 2. The result will be ranked
by the search engine before showing it in the user
interface.
4.4 Testing Results
Based on the knowledge base that has been organized
in Section 3 and the proposed architecture in Section
4.2, an intelligent searching system on Vietnam Road
traffic law is designed. This section presents some
testing results of the system through some kinds of
inputted queries.
Example 3: The inputted query q
1
= “What is
motorcycle?”
The system will extract keywords from the query
q
1
: “What is”, “motorcycle”. From that, it returns the
results as follows:
“Motorcycle means a motor vehicle that has two
or three wheels with a cylinder capacity of 50 cm
3
or
higher, maximum speed over 50 km/h, and net weight
not exceeding 400 kg.”
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
222

Figure 2: The architecture of an intelligent searching system on the Vietnam road traffic.
The word “what is” is used to classify the query
into the kind of declaring the meaning of a concept.
The keyword “motorcycle” helps to find the concept.
The result is retrieved from Article 3, Clause 3.31 of
National Technical Regulation on Traffic Signs and
Signals (Vietnam Ministry of Transport, 2019).
Example 4: The inputted query q
2
= “The fines of
operator of motorbike driver who does not wear
helmet”
The keywords of the query q
2
are “fines”, “not
wear”, helmet”, “operator of motorbike”. The word
“fines” is used to classify the query into stating
penalties and fines of offences. The word “operator
of motorbike” consists of “motorbike” that is similar
to the word “motorcycle”. The word “helmet” is in the
keywords of the concept “motorcycle helmet”.
Hence, the concepts of the query q
2
are “operator of
motorcycle” and “motorcycle helmet”. The relational
keyword is “not wear”. With the concepts and
relation, the rules were used to match them and find
the result.
The result is returned:
“Through article 6, Decree 100/2019/ND-CP:
Penalties imposed upon operators of mopeds and
motorcycles (including electric motorcycles) and the
like violating road traffic rules.
2. A fine ranging from VND 200,000 to
VND 300,000 shall be imposed upon a vehicle
operator who commits any of the following
violations:
i) The operator or the passenger on the vehicle
does not wear a motorcycle helmet or does not wear
it properly;”
The designed system can do some common
searching on road traffic law. It is effective in finding
usual penalties and fines from road traffic law. This
system was tested on a set of 137 queries about the
road traffic codes. The results are shown in Table 4:
Table 4: Results for testing of queries.
Kind Quantity Correct Rate
Queries about
concepts /
definitions
54 42 78%
Queries about
penalties and fines
83 61 73%
Total 137 103 75%
5
CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper proposed an ontology-based model for
representing legal knowledge in the Vietnam road
traffic codes. This model is improved based on
ontology Rela-model in the structure of concepts,
relations, and inference rules. Through the designed
knowledge base, several searching issues on the
Vietnam road traffic codes are proposed, such as
extracting keywords and inferring the matched result
for inputted query. Moreover, the architecture of an
intelligent search system on road traffic law has been
constructed. This system can do several common
search queries, such as finding concepts/definitions in
the law and determining penalties for violations in the
road traffic. At the moment, most knowledge is
Ontology-Based Solution for Building an Intelligent Searching System on Traffic Law Documents
223

collected by manual collection method. The next
work is the improvement of the collection method
within by using an automatic method.
In the future, the system can be involved other
legal aspects such as commercial law, civil law, etc.
Further, the system can be used to provide an e-
learning system for legal aspects. The abilities to use
AI to identify entities and concepts from an image or
use voice recognition to identify searching input are
also features considered to add more to the system.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by The VNUHCM-
University of Information Technology's Scientific
Research Support Fund.
REFERENCES
Do, N., Nguyen, H., Selamat, A. 2018. Knowledge-Based
model of Expert Systems using Rela-
model. International Journal of Software Engineering
and Knowledge Engineering 28(8), 1047 – 1090.
Fawei, B., Pan, J.Z, Kollingbaum, M., Wyner, A.Z. 2019.
A Semi-automated Ontology Construction for Legal
Question Answering. New Generation Computing
37(4), 453-478, 2019.
Giakoumakis, E.A., Xylomenos, G. 1996. Evaluation and
Selection criteria for software requirements
specification standards. Software Engineer Journal,
11(5), 307-319.
Jakus, G., et al. 2013. Concepts, Ontologies, and
Knowledge Representation. Springer Nature.
Law library. (2022). https://thuvienphapluat.vn/
National database of Legal documents. 2022.
http://vbpl.vn/botuphap/Pages/Home.aspx
National Traffic Safety Committee. 2020. Final report the
traffic accidents in 2020. Vietnam Government.
Ngo, H., Nguyen, T., Nguyen, D., Pham, M. 2021.
AimeLaw at ALQAC 2021: Enriching Neural Network
Models with Legal-Domain Knowledge. In KSE 2021,
13th International Conference on Knowledge and
Systems Engineering, Nov. 2021. IEEE.
Nguyen, H.D., et al. 2015. A Mathematical Approach for
Representation Knowledge about Relations and Its
Application. In KSE 2015, 7
th
IEEE International
Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering,
Oct. 2015. IEEE.
Nguyen, H., Tran, D., Pham, H., Pham, V. 2020a. Design
an intelligent system to automatically tutor the method
for solving problems. International Journal of
Integrated Engineering 12(7), 211 – 223.
Nguyen, H., Do, N., Tran, N., Pham, H., Pham, V. 2020b.
Some criteria of the Knowledge Representation method
for an Intelligent Problem Solver in STEM education.
Applied Computational Intelligence and Soft
Computing 2020, Article ID 9834218.
Nguyen, T., Nguyen, H.D., Pham, V.T., et al. 2022a. Legal-
Onto: An Ontology-based model for Representing the
Knowledge of a Legal Document. In ENASE 2022, 17
th
International Conference on Evaluation of Novel
Approaches to Software Engineering, April 2022.
Scitepress.
Nguyen, H. D., Do, N. V., Pham, V. T. 2022b. A
methodology for designing knowledge-based systems
and applications. In Applications of Computational
Intelligence in Multi-Disciplinary Research. Academic
Press, Elsevier.
Nguyen, D., et al. 2022c. An Unsupervised Learning
Method to improve Legal Document Retrieval task at
ALQAC 2022. In KSE 2022, 14th International
Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering,
Oct. 2022. IEEE.
Pham. H., Do, N., Nguyen, H. 2019. A Consulting System
for Estimating Costs of an Information Technology
Hardware Project based on Law of Public Investment.
In ICSSE 2019, 7
th
IEEE International Conference on
System Science and Engineering, July 2019. IEEE.
Valente, A., Breuker, J. 1992. A Model-Based Approach to
Legal Knowledge Engineering. In: Legal Knowledge
Based Systems: Information Technology & Law,
Grütters, et al. (eds), JURIX'92, Koninklijke Vermande,
Lelystad, NL, 1992.
Sartor, G., Casanovas, P., Biasiotti, M., Fernandéz-Barrera,
M. 2011. Approaches to Legal Ontologies. Springer
Dordrecht Heidelberg, London, New York.
Vietnam National Assembly. 2008. Law on Road Traffic.
Law No. 23/2008/QH12.
Vietnam National Assembly. 2015. Law on Promulgation
of Legislative Documents. No. 80/2015/QH13.
Vietnam Government. 2019. Decree on Administrative
penalties for road traffic and rail transport offences.
No. 100/2019/ND-CP.
Vietnam Ministry of Justice. 2011. Circular of the Minister
about the formats, and techniques for legal documents
of the Government, the Prime Minister, Ministers, and
joint legal documents. No. 25/2011/TT-BTP.
Vietnam Ministry of Transport. 2019. National Technical
Regulation on Traffic Signs and Signals. QCVN
41:2019/BGTVT, 2019.
ICAART 2023 - 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
224
