
Research on the Intelligence of Carbon Number in Data Center
Hongzhen Xie, Fang Zhou, Junlong Xu, Qi Chen
*
, Zhijun Mu and Zhisong Ge
Shanghai Institute of Measurement and Testing Technology, Shanghai, China
Keywords: Data Center, Carbon Verification, Intelligence, Monitoring Software, Accounting System.
Abstract: Introduced carbon verification in the data center and designed carbon monitoring software. Based on the R-
8555CDMA Modem wireless communication module, builds an intelligent accounting system for the energy
and carbon data of the data center, which realizes the intellectualization of the carbon emission verification
of the data center.
1 INTRODUCTION
A data center is composed of a computer site
(computer room), other infrastructure, information
system hardware and software, information resources
(data) and personnel, and corresponding rules and
regulations. It is mainly a construction site that
provides an operating environment for centralized
electronic information equipment. It can be one or
several buildings, or it can be a part of a building
(GB/T32910.1, GB 50174). As an infrastructure for
storing, processing, and utilizing computing power,
data centers can be divided into enterprise data
centers (EDCs), internet data centers (IDCs), and
other institutional data centers (Wang Jiye, 2022).
The construction of data centers is one of the
seven key construction tasks of the "new
infrastructure", and it is also the key to the digital
transformation of the economy. With the rapid
development of social economy, data centers are also
expanding rapidly. As the infrastructure of the digital
economy, data centers occupy a large area, are mostly
located in urban centers, have a large number of
devices, and consume a lot of energy. Their huge
energy demand inevitably leads to an increase in
carbon emissions. The data center industry belongs to
the consumer side of energy in energy activities. The
main sources of its energy activities include the
consumption of electrical energy in the power supply
sector and the use and consumption of diesel
generators. Among them, diesel generators are used
to ensure continuous power supply for the data center
center.Its energy consumption accounts for a very
low proportion of the energy consumption of the
entire data center. Therefore, under the premise of
thermal power generation, the carbon emissions of
the data center mainly come from the power
consumption of the power supply department.
2 ARBON VERIFICATION IN
DATA CENTER
Article 6 of the Measures for the Administration of
Carbon Emission Trading (Trial) stipulates that the
formulation of technical specifications for national
carbon emission trading and related activities, as well
as the supervision and management of local carbon
emission quota allocation, greenhouse gas emission
reporting and verification shall be "the Ministry of
Ecology and Environment, with assistance from
relevant departments of The State Council."
Greenhouse gas emission reporting and verification is
the process of comprehensively verifying and
verifying the emission facility information,
accounting boundaries, accounting methods,
emission factors, activity data, and other relevant
information of carbon dioxide generated by national
key emission (quota management) units.
The verification of the carbon emissions of data
centers and the production of reports must be carried
out in accordance with the requirements of the
accounting methods and reporting standards for
greenhouse gas emissions in the Measures for the
Administration of Carbon Emissions Trading (Trial);
And relevant standards and technical specifications.
The verification process mainly includes: initiating
verification, arranging verification, establishing
verification technical working group, document
review, establishing on-site verification group, on-
site verification, writing verification report,
362
Xie, H., Zhou, F., Xu, J., Chen, Q., Mu, Z. and Ge, Z.
Research on the Intelligence of Carbon Number in Data Center.
DOI: 10.5220/0012284000003807
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Seminar on Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Information Technology (ANIT 2023), pages 362-366
ISBN: 978-989-758-677-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

informing verification results, saving verification
report, and ending verification.
Carbon verification is the main way to achieve the
"dual carbon" goal, and scientific, accurate, and
efficient carbon emission measurement and
accounting methods are the foundation for achieving
"measurable, reportable, and verifiable" carbon
emission data. They are also key factors for
controlling total carbon emissions and optimizing
resource allocation. As the main assessment and
supervision object for government to achieve energy
savings and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the
carbon emission measurement and accounting of data
centers has also become a key influencing factor for
their rapid development.
Against the backdrop of new developments such
as carbon peaking and carbon neutrality, in order to
focus on solving the key tasks of optimizing resource
allocation and energy conservation and carbon
reduction in data centers, using energy measurement
as the basis and carbon verification as a means to
calculate carbon emissions in data centers has become
an effective way to strengthen energy conservation
and carbon reduction management in data centers and
continuously promote green, low-carbon, and
efficient operation. The measurement and accounting
of carbon emissions in data centers is based on the
emission factor method.
Article 27 of the "Energy Conservation Law of the
People's Republic of China" stipulates: "Energy-
consuming units should strengthen energy
measurement management, and equip and use energy
measuring instruments that have passed the legal
inspection in accordance with regulations. Energy-
consuming units should establish energy
consumption statistics and energy utilization. And
ensure that energy consumption statistics are true and
complete. Among them, as the basis of energy
measurement, the meter used for energy measurement
shall comply with the requirements of GB17167-
2006 "General Rules for the Equipment and
Management of Energy-using Unit Energy
Measuring Instruments". The general rules specify
the proportion of energy measuring instruments in
energy-using enterprises, the limit values of energy
consumption of primary secondary energy units and
tertiary main energy devices, and the accuracy of
energy metering meters (GB17167).
Table 1. Limit values of energy consumption value per unit
of main secondary energy consumption.
Energy
type
Electricity
Coal,
Coke
Crude oil,
Refined oil,
Petroleum
liquefied gas
Heavy
oil,
Residual
oil
Gas,
Natural
gas
Steam,
Hot
water
Water
Other
Unit
kW
t/a
t/a
t/a
m^3/a
GJ/a
t/a
GJ/a
Limit
value
10
100
40
80
10000
5000
5000
2926
Note 1: a in the table is the symbol of "year" in the legal unit
ofmeasurement.
Note 2: m^3 in the table refers to the standard state, same as table 2.
Note 3: 2926GJ is equivalent to 100t standard coal.Other energy sources
should be converted according to the equivalent calorific value, as shown
in Table 2.
Table 2. Limit values of energy consumption (or power) of
main energy-consuming equipment.
Energy
type
Electricity
Coal,
Coke
Crude oil,
Refined oil,
Petroleum
liquefied gas
Heavy
oil,
Residual
oil
Gas,
Natural
gas
Steam,
Hot
water
Water
Other
Unit
kW
t/h
t/h
t/h
m^3/h
MW
t/h
GJ/h
Limit
value
100
1
0.5
1
100
7
1
29.26
Note 1: For energy-consuming units (device, system, process, workshop, etc.) that
can be assessed separately for energy measurement, if the energy-consuming unit is
equipped with energy measuring instruments, the main energy-consuming equipment
in the energy-consuming unit may no longer be equipped separately.
Note 2: If the energy use body such as boiler room, pump room and other
centralized management of similar equipment, if it has been reasonably equipped with
metering meters, the main energy use equipment can no longer install energy metering
meters.
Table 3. Provisioning rate requirements of Energy
Measuring Instruments Unit: %.
Energy type
In and out
energy
consumption
unit
Access to
main and
secondary
energy-
consuming
units
Main energy-
consuming
equipment
Electricity
100
100
95
Solid
state
energy
Coal
100
100
90
Coke
100
100
90
Liquid
energy
Crude
100
100
90
Refined oil
100
100
95
Heavy oil
100
100
90
Residual oil
100
100
90
Gaseous
energy
Natural gas
100
100
90
Liquefied gas
100
100
90
Gas
100
90
80
Energy-
carrying
medium
Steam
100
80
70
Water
100
95
80
Surplus energy that can
be recycled
90
80
—
Note 1: Seasonal heating steam (hot water) entering and exiting energy-
consuming units can adopt other measurement and settlement methods that
do not directly measure the flow of energy-carrying working fluid.
Note 2: Seasonal heating steam (hot water) entering and exiting major and
secondary energy-consuming units may not be equipped with energy
measuring instruments
Note 3: Electricity and steam, water and other energy-carrying working
media used as auxiliary energy on the main energy-consuming equipment,
if the energy consumption is very small (less than the requirements in Table
2), energy measuring instruments may not be equipped.
Research on the Intelligence of Carbon Number in Data Center
363

A secondary energy consumption unit whose
energy consumption (i.e. energy produced or
transported) is not less than one or more of the energy
consumption limits in Table 1 shall be regarded as a
primary secondary energy consumption unit.
The energy consumption of a single device is
greater than or equal to one or more limit values of
energy consumption in Table 2 as the main energy-
consuming equipment.
The proportion of energy metering instruments
shall comply with the requirements of Table 3.
The activity data involved in the accounting is
obtained based on annual consumption statistics, and
the emission factor data mostly adopts regional
default values. However, when obtaining carbon
emission inventory activity data based on annual
consumption statistics, the workload of data
processing is large, which is prone to issues such as
missing information, manual statistical errors, and
ineffective verification of data authenticity.
In recent years, the widespread use of
technologies such as intelligent networking, artificial
intelligence and aggregated data has essentially
changed the management, control and development
mode of many basic operation architectures (Gang
Xiong, 2020). Based on information technology,
intelligent collection and accounting of data center
energy consumption data and carbon emission data
are realized. It can not only improve the accuracy and
security of data collected in the data center, but also
save resources and improve work efficiency.
3 ENERGY AND CARBON
NUMBER INTELLIGENT
ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
This paper uses the CS development model to design
and develop an energy carbon monitoring software,
and based on the R-8555CDMA Modem wireless
communication module, builds a data center energy
carbon number intelligent accounting system, thereby
realizing the intelligentization of data center carbon
emission accounting. Figure 1 shows the system
diagram of the data center energy carbon number
intelligent accounting system.
The energy and carbon intelligent accounting
system consists of a data center energy consumption
main control cabinet, AF-HK 100 data acquisition
instrument, front-end computer, laptop, R-8555
CDMA Modem wireless communication module, and
LIMS system. In Figure 1, the portable computer is
equipped with data center energy and carbon
monitoring software. After connecting to the LIMS
system through the network cable, the data interaction
with the LIMS system can be realized. During field
monitoring, the af-hk100 data acquisition instrument
is connected to the main control computer system of
the data center, and the real-time monitoring data is
collected into the front-end computer. RS232 serial
cable is used between the front-end computer and the
portable computer, and the R-8555CDMA Modem
wireless communication module is used to transmit
the carbon emission accounting data back to the
LIMS server continuously, so as to realize intelligent
monitoring.
Figure 1. Data center energy carbon number intelligent accounting system diagram.
ANIT 2023 - The International Seminar on Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Information Technology
364
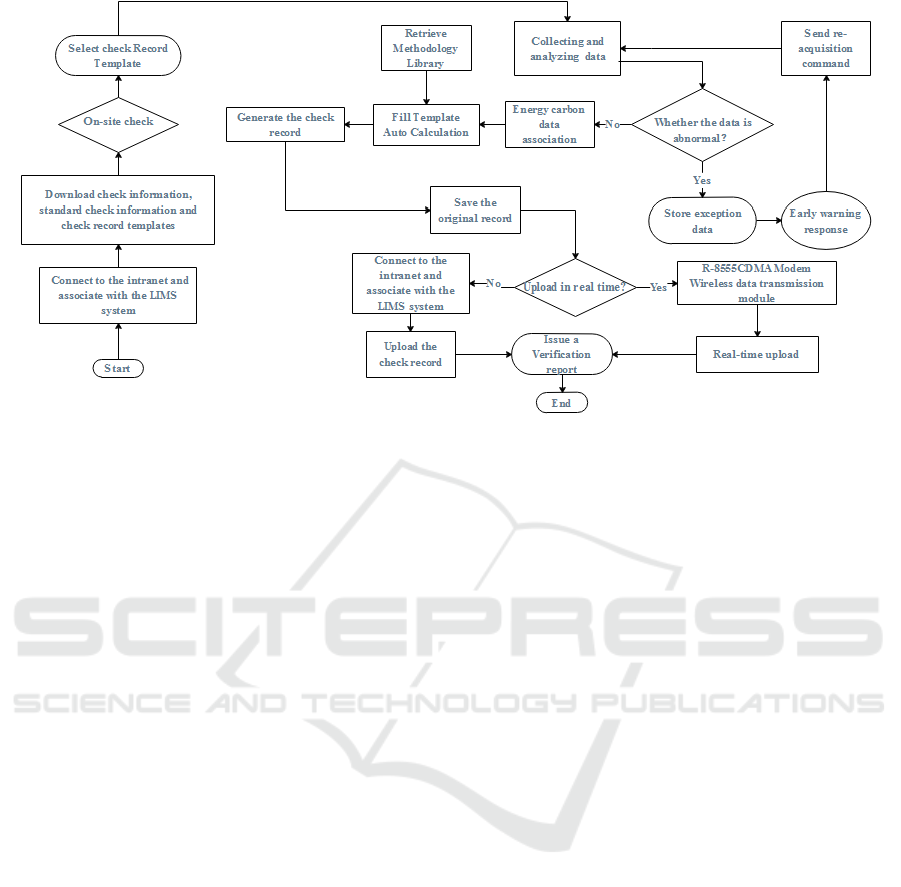
Figure 2. The process of intelligent calculation of energy carbon number.
3.1 Monitoring Software Design
The monitoring software is developed based on CS,
and Access is used as offline database, and unified
communication protocol is written to realize single
data transmission, so as to ensure the security of data
collection and transmission. According to the
protocol requirements, different types of data centers
use energy master computers to send monitoring data
to the energy Carbon monitoring monitoring software
in real time without obtaining data.
The collection and monitoring software integrates
LIMS connection module, data collection and
analysis unit, data anomaly disposal unit, carbon
emission method library call unit, energy carbon
association unit, carbon emission data automatic
calculation unit, data storage library, network security
guarantee unit, and has the functions of historical
information verification, template, standard
information, historical verification information
download and data sharing. The data monitoring and
analysis unit can collect energy metering data
transmitted by the data center in real time and parse it
into fields in a specific format. Exception handling
units are distinguished based on the collection and
parsing of data. If the collected and analyzed data
does not meet the corresponding field requirements,
data missing or blank, etc., the abnormal alarm
mechanism will be triggered, and are collection
command will be sent. The abnormal data will be
saved to facilitate later investigation of the cause of
the abnormality. The methodology library unit
establishes an industry carbon emission accounting
factor library based on the national, Ministry of
Health and Environment, and local levels, facilitating
the retrieval of emission factors corresponding to
activity data according to needs during enterprise
carbon emission accounting. The energy carbon
correlation unit matches the fuel type corresponding
to the carbon emission calculation based on the
collected energy subcategory data. The carbon
emission data automatic accounting unit can
automatically calculate the carbon emission data
based on the emission factor method. The storage unit
is used to store monitoring process related data and
separate and save abnormal data for the convenience
of analyzing the cause of data anomalies.
3.2 Intelligent Accounting Process for
Energy and Carbon Number
The monitoring software utilizes an intranet linked
LIMS system to obtain verification tasks and
download verification information, verification
standard information, verification record templates,
and other information. During on-site verification, a
laptop equipped with data center monitoring software
is connected to the front-end computer through an
RS232 serial port cable to collect monitoring data in
real-time and parse and fill in the verification record
template. The generated verification records are
saved locally and return the LIMS system in real-time
through the R-8555CDMA Modem wireless
communication device, achieving intelligent
collection and efficient certification of carbon
emission verification data in the data center. The
Research on the Intelligence of Carbon Number in Data Center
365

process of intelligent calculation of energy carbon
number is shown in Figure 2.
4 CONCLUSION
An energy Carbon monitoring software was designed
and developed, and based on the R-8555CDMA
Modem wireless communication module, an
intelligent accounting system for energy and carbon
data in the data center was built, thus realizing the
intellectualization of carbon emission accounting in
the data center. Not only can reduce the workload of
monitoring implementation process, avoid human
error, but also solve the data center monitoring data
storage is not convenient, query trouble, data
classification is easy to confuse the problems, on the
basis of effectively improving the carbon accounting
efficiency of data centers and data security, but also
for the intelligent application and promotion of data
center online monitoring provides a foundation.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by Shanghai
2022 "Science and Technology Innovation Action
Plan" project (22dz1208800) fund.
REFERENCES
GB/T32910.1-2017.Data center—Resource utilization—
Part 1: Terminology(S). Beijing: National
Standardization Management Committee. 2017.
GB 50174-2017. Code for Design of Data Centers(S).
Beijing: National Standardization Management
Committee. 2006.
Wang Jiye, Zhou Chunlei, Li Yang, et al. Review of Key
Technologies and Development Trends in Data Centers
(J). Power Information and Communication
Technology, 2022, 20 (8): 21.
GB17167-2006. General principle for equipping and
managing of the measuring instrument of energy in
organization of energy using(S). Beijing: National
Standardization Management Committee. 2006.
Gang, Xiong, Xisong, Dong, et al. Research Progress of
Parallel Control and Management (J). IEEE/CAA
Journal of Automatica SiFnica, 2020, 7(2):13.
ANIT 2023 - The International Seminar on Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Information Technology
366
