
UI/UX Evaluation on Entrepreneurial Mindfulness Mobile Application
Lukas Tanto Kurniawan
1,5
, Sasmoko
2,5
, Yasinta Indrianti
3,5
, Sonya Rapinta Manalu
1,5
and Jurike V. Moniaga
4,5
1
Mobile Application and Technology, School of Computer Science, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
2
Primary Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Humanities, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
3
Entrepreneurship Department, Agung Podomoro University, Jakarta, Indonesia
4
School of Computer Science, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
5
Research Interest Group in Educational Technology, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
jurike@binus.edu
Keywords:
UI/UX Evaluation, Entrepreneurship, Mobile Application.
Abstract:
Entrepreneurship is a very important process to increase economic growth because it encourages innovation
and creates new jobs. In entrepreneurship, mindfulness is required as it affects entrepreneurial practices and
psychological well-being for entrepreneurs. With mindfulness, entrepreneurs become more aware of the cur-
rent situation so that they can take advantage of the current situation to create better business solutions. The
entrepreneurial mindfulness application is developed in the form of a mobile application with the aim that
entrepreneurs can self diagnose anywhere and anytime so that they can easily find out the level of mindfulness
they have. To fulfill this purpose, the application needs to get feedback from users. Therefore, this study aims
to determine the UI/UX quality of the application through responses from users. UI/UX evaluation is con-
ducted using Neuroresearch methods with an emphasis on explanatory research in the form of user surveys.
The questions contained in the survey were made based on the Eight Golden Rules by Ben Shneiderman. The
number of espondents who took the survey was 31 and the results of the survey provided some insight into
the user experience when using the application. The results of this study show that the appearance and flow
of the application have been able to provide a fairly good experience to users. However, there were also some
suggestions and criticisms of the appearance and flow of the application. Therefore, some improvements were
made and some displays were added to the application to increase user satisfaction in using the Entrepreneurial
Mindfulness application.
1 INTRODUCTION
Entrepreneurship is the fundamental process of creat-
ing or starting a new venture to identify and develop
opportunities for growth and success. Entrepreneur-
ship plays an important role in the economy as it
drives innovation, creates jobs, and promotes eco-
nomic growth (Malecki, 2018). In recent years, tech-
nologies such as mobile computing, cloud computing,
social media, data analytics, etc. have become var-
ious aspects of innovation in entrepreneurship. En-
trepreneurship is also changing the nature of uncer-
tainty inherent in the process and outcome of en-
trepreneurship and how to deal with such uncertainty
(Nambisan, 2017).
Entrepreneurship is a strategic component in the
world of practitioners and academics on a national
and international scale to build a competitive advan-
tage. The concept of entrepreneurship is now not only
owned by entrepreneurs but has begun to be intro-
duced to students in schools. At the higher educa-
tion level, students are equipped with entrepreneurial
practices to prepare them to enter the world of work.
Competition in the industry 4.0 era characterized by
various technological advances and knowledge shifts
has demanded new, more complex competencies (In-
drianti et al., 2020), (Nowi
´
nski et al., 2019).
Entrepreneurial practice is synonymous with sit-
uations of uncertainty, high risk, uncertain roles and
increasingly fierce competition. Entrepreneurs who
are able to harmonize their thoughts and adjust them-
selves so that they are able to take concrete actions
based on the right intentions, strategies and consider-
ations are mindfulness entrepreneurs (Indrianti et al.,
218
Kurniawan, L., Sasmoko, ., Indrianti, Y., Manalu, S. and Moniaga, J.
UI/UX Evaluation on Entrepreneurial Mindfulness Mobile Application.
DOI: 10.5220/0012447100003848
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advanced Information Scientific Development (ICAISD 2023), pages 218-226
ISBN: 978-989-758-678-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

2020).
Mindfulness is a human’s awareness of events
happening in the present moment and will influence
how the human responds to those events. The ef-
fects that mindfulness plays in organizational and
business settings have been considered using a sam-
ple of employees and principals, while the topic has
been briefly explored in entrepreneurship and in fam-
ily businesses. Family businesses represent single or-
ganizations that need to manage some emotional logic
to survive in the long term. Mindfulness has emerged
as an important concept as it stimulates the ability
to focus on the present moment (Plana-Farran et al.,
2022).
Mindfulness has an important role for each in-
dividual in facing difficulties and making decisions.
Mindfulness of each individual needs to be developed
from an early age, the role of parents is needed in ed-
ucating their children because it will affect their mo-
tivation in entrepreneurship in the future. Mindful-
ness not only affects the health and life of individu-
als but also affects their work and career, including
the formation of adolescents’ human capital, sense of
job success, work adaptability, and even attitude to
change (Shan and Tian, 2022), (Liu et al., 2022).
The development of mindfulness in the practice of
entrepreneurship is the basis for developing a mobile
application. Mobile applications have an increasingly
significant role in this day and age. Since November
2016, there is more network traffic created by mobile
devices with a percentage of 48.19% than desktops
or laptops which have a percentage of 47% (Tashildar
et al., 2020). Google has also announced that every
day there are 500,000 new android users (Hoehle and
Venkatesh, 2015).
Therefore, it is necessary to develop a mobile ap-
plication to increase the use of entrepreneurial mind-
fulness.Through the developed application, people
can self-diagnose with the aim of measuring their
level of mindfulness so that people can improve their
mindfulness as needed in industry 4.0. The level of
mindfulness contained in this application is divided
into 7 levels. After taking the test, users can find out
the position of mindfulness they have along with an
explanation and some suggestions on how to improve
mindfulness so as to achieve a balance between en-
trepreneurial pressure and having fun. This applica-
tion uses a machine learning model to determine a
person’s entrepreneurial mindfulness level (Oktavius
et al., 2022).
The Entrepreneurial Mindfulness app was devel-
oped not only to fulfill the purpose of allowing en-
trepreneurs to see their level of mindfulness but also
to feel comfortable when using the app. A good
UI/UX in an application aims to ensure that the ap-
pearance and use of the application can be done eas-
ily and comfortably. With good UI/UX, app users
can easily find important information according to
their wants and needs and feel comfortable in using
the app. In addition, the application must have good
UI/UX because in this industry 4.0 era, people use
mobile devices anywhere and anytime so that the ease
of use of the application is important to fulfill the ob-
jectives of this research.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Mindfulness and Entrepreneurial
Mindfulness, defined as ”receptive attention and
awareness of present events and experiences”
(Gelderen et al., 2019). ”Mindfulness involves inten-
tionally bringing one’s attention to the internal and
external experiences occurring in the present moment
and is often taught through various meditation prac-
tices”. Meditation is a formal expression of mind-
fulness and is one of the most researched self-help
interventions to date. Mindfulness training has been
shown to have many benefits. It not only reduces
stress and improves well-being, but also increases
awareness, empathy, compassion, and the ability to
observe oneself, as well as providing cognitive and
behavioral flexibility (Kelly and Dorian, 2017).
The definition of mindfulness describes non-
judgment and openness. By cultivating non-
judgment, we generate acceptance. Non-judgmental
acceptance sets the stage for developing empathy, an
important component of relationships. Empathy is
one of the abilities to understand the feelings of others
over time. Mindfulness-based practices enable one to
realize this humanistic ideal, evident in all relation-
ships, including business (Kelly and Dorian, 2017).
With a high level of mindfulness, it will help an
entrepreneur to make the right decisions by taking
into account the various conditions and problems that
exist today (Gelderen et al., 2019), (Kelly and Dorian,
2017).
2.2 Mobile Application Development
The Entrepreneurial Mindfulness application was cre-
ated using Flutter framework as the frontend and
Flask framework as the backend. Flutter is used to
create the application display where users will inter-
act with the application. Flask is used to process data
which is then stored in a MySQL database and pro-
cess user answers when taking tests using Artificial
UI/UX Evaluation on Entrepreneurial Mindfulness Mobile Application
219

Intelligence to determine the results of the test.
Flutter is a cross-platform framework used to de-
velop applications that can run on Android, iOS, and
Google’s next-generation operating system, Fuschia.
Flutter itself was created by Google and published
in 2016. Flutter uses the Dart programming lan-
guage which is the successor to Javascript and incor-
porates many features in the Javascript ES7 standard,
Dart also uses the concept of Object Oriented Pro-
gramming (OOP) (Mamoun et al., 2020)(Kurnia and
Aditya, 2022)(Hassan, 2022)
In developing applications using Flutter, an archi-
tecture called Model View View-Model (MVVM) is
used to distribute roles and responsibilities strictly be-
tween objects. By using MVVM, all data logic prepa-
ration for the UI will be placed in the View-Model ob-
ject which will be displayed in the View. The Model
itself is used to organize the data that will be used in
the form of objects (Aljamea and Alkandari, 2018).
Provider in Flutter is a library that works by wrap-
ping multiple widgets and sending changing state in-
formation to the components or widgets inside. The
Provider will notify the observer (Consumer) when
data changes in the class that manages the state
(ChangeNotifier). Later, Consumer and ChangeNo-
tifier will communicate through ChangeNotifier-
Provider (Mantik et al., 2021). In the development
of this application, Provider will be used as a View-
Model in MVVM architecture
2.3 Flask REST APIs
Flask is a lightweight python-based application
framework designed for fast and easy application de-
velopment, with capabilities that can serve millions
of users or clients. Flask has 2 main components,
Werkzeug and Jinja2. Werkzeug is responsible for
providing routing, debugging, and Web Server Gate-
way Interface (WSGI). While Jinja2 is used as a tem-
plate engine. Flask has a fairly large and active com-
munity with hundreds of open-source extensions (Re-
lan, 2019).
Representational State Transfer (REST) is a soft-
ware architecture style for web services that provides
an Application Programming Interface (API) for data
exchange between multiple systems. Web services or
API is a web application that will interact with other
applications to exchange data. REST architecture al-
lows the requesting system or application to access
and manipulate data using a uniform and predefined
set of stateless operations (Relan, 2019).
2.4 Integration and Usability Testing
The integration testing method is the most frequent
and important type of testing in software testing,
where each unit or component is tested for connec-
tivity with all existing units (Janaki, 2021). The main
purpose of the test method is to place the units in the
desired environment and exercise their complete in-
teraction. This test method will evaluate how well the
interface has performed. In this test method, there are
3 criteria, namely All-modules, All-multiplerelations,
and All-call-sequences. All-modules will test each
unit at least once. All-multiple-relations will test all
relationships between units. All-call-sequences will
test the flow or running order of the application (De-
lamaro et al., 2001).
The usability testing method will be carried out
by giving some specific tasks to users who have never
used the application before. With this approach, infor-
mation will be obtained about the comfort and level of
ease in using this application carried out by users with
natural human thinking (Ahmad et al., 2014). Usabil-
ity itself can be defined as ”the extent to which a prod-
uct can be used by specific users to achieve specific
goals with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction
in a specific context of use” (Weichbroth, 2020).
2.5 User Interface and User Experience
User interface (UI) in information technology refers
to the symbol or command structure used in Human
Computer Interaction (HCI). User interface can be
defined as an interactive system display where users
can interact with the system through the display on
the smartphone screen. The user interface includes
menus and various features contained in the appli-
cation to control or do something according to the
wishes and needs of the user (Joo et al., 2014). Creat-
ing an effective UI is one area that is always empha-
sized because an effective UI provides the potential to
improve the overall performance of the system (Pun-
choojit and Hongwarittorrn, 2017). There are also
several studies related to the development of mobile
applications by paying attention to the user interface
during the process of making the application display
design (Khairul et al., 2020), (Gkatzidou et al., 2015).
User experience (UX) refers to the perceptions
and feelings of users resulting from the use of a sys-
tem, product, or service, including emotions, beliefs,
preferences, etc (Chen et al., 2020), (Sauer et al.,
2020). UX can also be considered as the quality of in-
teractive technology that focuses on people not prod-
ucts. In UX, we can see the emotions of the user
when using the application which will be an indica-
ICAISD 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Information Scientific Development
220

tor to see whether the user is satisfied and comfort-
able with the appearance of the application (Dirin and
Laine, 2018). Factors that influence UX are the driv-
ing factors that trigger user satisfaction and dissatis-
faction. In addition, user satisfaction depends on the
user’s existing needs, expectations, and experiences
(Chen et al., 2020).
Based on the importance of UI/UX in mobile ap-
plication development, it is necessary to evaluate the
appearance of the entrepreneurial mindfulness appli-
cation to determine user satisfaction when using the
application and get suggestions regarding the appear-
ance of the application. Evaluation of UI/UX in this
application uses the Eight Golden Rules of Interface
Design by Ben Shneiderman which consists of:
1. Strive for consistency.
2. Cater to universal usability.
3. Offer informative feedback.
4. Design dialogs to yield closure.
5. Prevent errors.
6. Permit easy reversal of actions.
7. Support internal locus of control.
8. Reduce short-term memory load (Paryudi and
Fenz, 16th).
Based on the Eight Golden Rules, a questionnaire
was created as a survey that was distributed to get re-
sponses from users. The questionnaire uses a Likert
scale where each number will be given a statement
then users can respond by choosing between strongly
disagree, disagree, undecided, agree, and strongly
agree. The statements given in the questionnaire in-
clude:
1. The icons used in the application already describe
the function of the feature
2. The localization feature (Indonesian and English)
makes it easier for users to understand the expla-
nations in the application.
3. The dark mode and light mode features provide
comfort to the eyes of users in using this applica-
tion.
4. The information provided by the application after
you perform an action is clear and informative so
that you know what steps you should take next.
5. The flow of the application when taking the test
is clear, starting from the beginning of the test in-
structions to the release of the test results.
6. Error messages in the application such as on the
registration / registration page are sufficient to ex-
plain the error so that you know what to fix.
7. Users can easily cancel the action performed by
pressing the back button.
8. You feel comfortable with the appearance and
flow of the application.
9. The structure of the application display makes it
easy for you to understand the flow of the appli-
cation.
10. The button placement is good and easy to reach
by the user’s hand.
Based on the explanation above, the main purpose
of UI/UX evaluation is to improve the application to
make it easier to use, efficient, and can make users
feel comfortable when using the application. UI/UX
has a very important role because the application is
expected to be in accordance with user expectations
in terms of appearance design and function of each
feature in the application (Punchoojit and Hongwarit-
torrn, 2017). Therefore, UI/UX evaluation of the en-
trepreneurial mindfulness application is needed to in-
crease user satisfaction with the application so that the
purpose of the application that will provide benefits to
entrepreneurs can be achieved.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The research method used is the Neuroresearch
method with the explanatory research stage through
a survey conducted to users of the Entrepreneurial
Mindfulness application (Sasmoko et al., 2018). This
research started with developing a survey by consid-
ering the Eight Golden Rules by Ben Shneiderman.
After the survey questions were developed, the survey
was distributed to Entrepreneurial Mindfulness users
to get their feedback after using the Entrepreneurial
Mindfulness app.
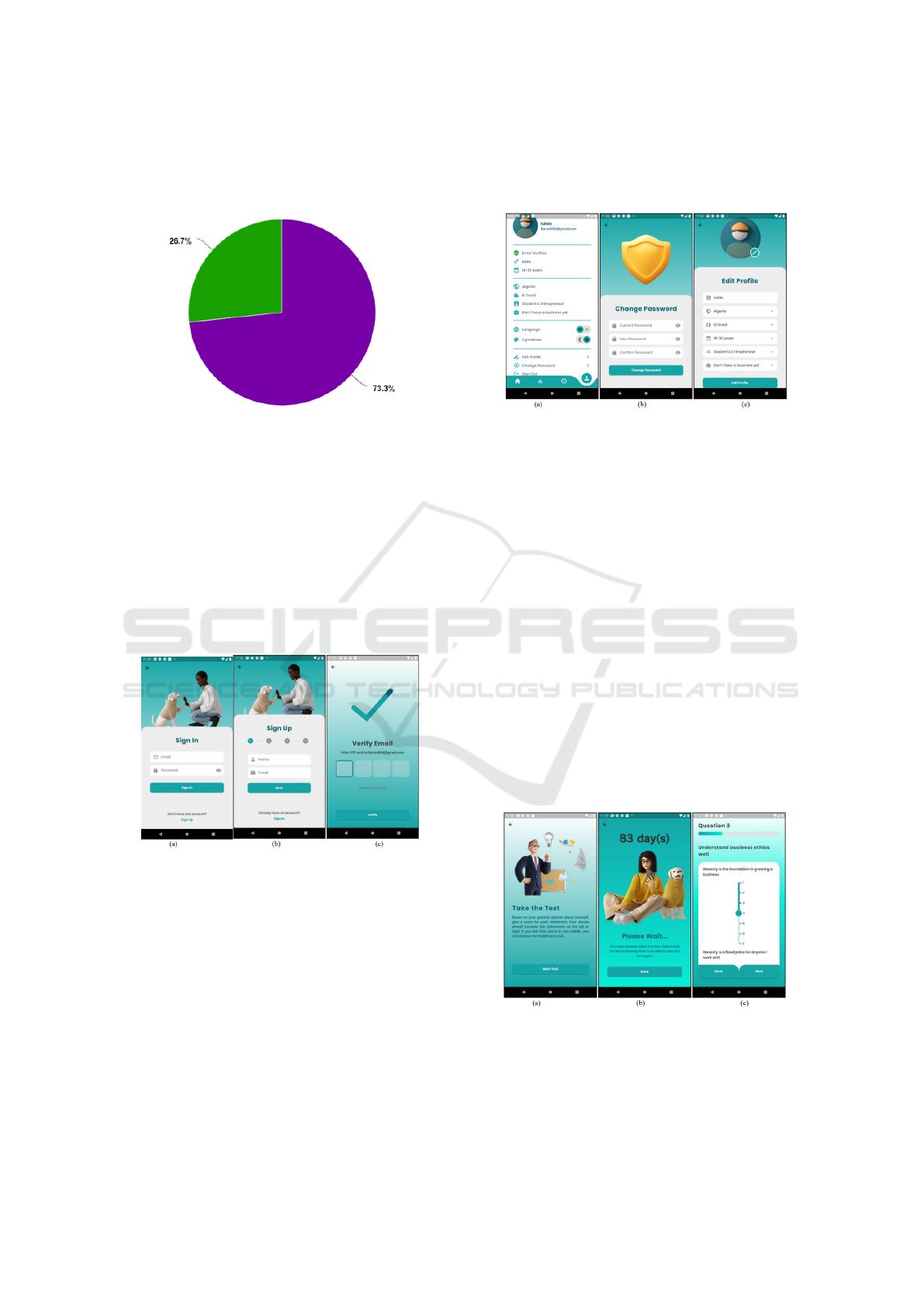
The survey involved 31 respondents with demo-
graphic data dominated by 73.3% male respondents
and 27.3% female respondents. The survey results ob-
tained were then analyzed and obtained some sugges-
tions and criticisms which then became the basis for
improving the quality of the appearance and flow of
the application to increase user satisfaction and com-
fort when using the application.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
In this research, the appearance of the features con-
tained in the Entrepreneurial Mindfulness application
is made by paying attention to the user interface and
user experience so as to increase user satisfaction in
UI/UX Evaluation on Entrepreneurial Mindfulness Mobile Application
221
using the application. Some of the main features on-
tained in the Entrepreneurial Mindfulness application
are as follows.
Figure 1: Percentage of respondents by gender.
1. Login and Register
Users need to log in first using an email and pass-
word to access several features such as taking
tests, viewing test history, and viewing test re-
sults. If the user does not have an account, the
user can register first by entering some personal
data such as name, email, date of birth, address,
and so on. After registering, the application will
send an OTP code to the user’s email and then the
user is asked to enter the OTP code into the appli-
cation as shown in Figure 1 (c) to verify the email
Figure 2: Login and Register.
2. Profile
In the profile page, users can view their personal
data such as name, email, address, and so on.
There are also several buttons that can be used for
specific functions, namely Logout, Change Pass-
word, and Edit Profile. The Logout button is used
to log out of the user account. The Change Pass-
word button is used to move to a page where users
can change their password by entering their cur-
rent password and new password. The Edit Pro-
file button is used to move to a page where users
can change some of their personal data such as
name, address, and so on. There is also a toggle
to change the language between Indonesian and
English, and a toggle to change the mode between
dark and light
Figure 3: Profile, Change Password, and Edit Profile.
3. Take the Test
This feature can be accessed through the ”Take
the Test” button on the home page which will be
directed to the test taking page. When the user ac-
cesses this feature, the user will be directed to a
page that contains a brief briefing on how to take
the test as shown in Figure 3 (a). After that, the
user can start the test and the application will val-
idate whether the user has taken the test before
or not. If the user has taken the test before, the
user must wait for 90 days before taking the test
again, the application will display how long the
user must wait before taking the test as shown in
Figure 3 (b). If the user has never taken a test or
has passed 90 days after the previous test, the user
will be directed to the test taking page as shown
in Figure 3 (c). In the test taking page, there
are 10 sections where each section the application
will display 2 statements and the user must choose
which statement better describes themselves
Figure 4: Take the Test.
4. Test Result and History
After the user has completed the test, the user
will be directed to the test results page where the
score obtained along with an explanation of the
ICAISD 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Information Scientific Development
222

score and a radar chart of the dimensions owned
by the user based on the user’s test answers are
displayed. The test result display can be seen in
Figure 4 (a) and (b). Each test taken by the user
will be stored in the database, the user can review
the results of the tests that have been taken on the
test history page as shown in Figure 4 (c). In the
test history, the user can select one of the histo-
ries which will then be redirected back to the test
results page to view the test results in detail.
Figure 5: Test Result and History.
5. Statistic Data
In this page, statistical data of all user members
will be displayed including radar charts of each
dimension and charts of demographic data.
Figure 6: Statistic Data.
From the appearance of the application that has
been developed, an evaluation of UI/UX is carried out
to find out whether users feel comfortable and satis-
fied when using the Entrepreneurial Mindfulness ap-
plication. The evaluation was also carried out with
the aim of improving the UI/UX of the application
based on suggestions and criticisms received from
users. The UI/UX evaluation of the Entrepreneurial
Mindfulness application was conducted by distribut-
ing a questionnaire containing 10 questions based on
the Eight Golden Rules by Ben Shneiderman.
From the results of the survey obtained from 31
respondents, data normality testing was carried out
for the distribution of UIUX EM variable data. The
normality test was carried out by estimating the pro-
portion through the Blom formula with the P-P Plot
approach. The P-P Plot approach was chosen because
the number of samples in this study was less than 200
users. The results can be seen in Figure 7.
Figure 7: Normality Test of PP Plot Proportion Estimation
Formula of Variable Blom UIUX EM.
Based on the normality test results, it can be ex-
plained that the normal P-P Plot calculation shows
that the UIUX EM sample data is normal. The data
distribution tends to point to the normal line, and the
data distribution does not have outliers. Meanwhile,
when viewed based on the Detrended Normal P-P Plot
seen in Figure 8, it can be interpreted that the distri-
bution of UIUX EM variable data does not describe
a sine or cosine curve. So it is concluded that all
UIUX EM variable data distributions have a normal
distribution.
Figure 8: Detrended Normal PP Plot Distribution Variable
UIUX EM.
In proving this, the researcher analyzed the data
from the survey results and determined 5 categories
UI/UX Evaluation on Entrepreneurial Mindfulness Mobile Application
223

of UIUX EM, namely strongly disagree, disagree, un-
decided, agree, and strongly agree. The results can be
seen in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Descriptive Inferential Variable UIUX EM Re-
sults.
Statistic Std. Error
VAR
UIUX
EM
Mean 47.1290 .56936
95% Confidence
Interval for Mean
Lower Bound 45.9662
Upper Bound 48.2918
5% Trimmed Mean 47.3978
Median 48.0000
Variance 10.049
Std. Deviation 3.17009
Minimum 38.00
Maximum 50.00
Range 12.00
Interquartile Range 5.00
Skewness -1.079 .421
— Kurtosis .711 .821
The data analysis in Table 1 was carried out with
confidence intervals at a significance level of 5%, and
the resulting lower and upper bounds were between
45.9662 and 48.2918. Based on these results, it can
be concluded that Entrepreneurial Mindfulness (EM)
app users tend to be significantly interested at α <
0.05.
Figure 9: Results of Classification and Regression Trees
(CART method) of each indicator againts the UIUX EM
Variable.
To find the indicators of the Eight Golden Rules
of UIUX EM that must be improved, an analysis with
Classification and Regression Trees (CART method)
was conducted. From Figure 9, it can be interpreted
that the most dominant in determining the EM ap-
plication is responded by users who tend to agree
with the attractiveness of the application display is
determined by the Support Internal Locus of Control
(CONTROL) indicator. If this indicator is developed,
the EM application user response will increase 6.658
times from the current user response condition. Im-
proving the Support Internal Locus of Control (CON-
TROL) indicator can only be realized through im-
proving the Cater to Universal Usability (UNIVER-
SAL) indicator. Improving this indicator can increase
user response to the Support Internal Locus of Con-
trol (CONTROL) indicator by 1.679 times from the
current condition. Based on the results of the analy-
sis above, there are 6 indicators in the EM application
that must be improved, namely: (1) Strive for Consis-
tency (CONSISTENCY), (2) Offer Informative Feed-
back (INFORMATIVE), (3) Design Dialogs to Yield
Closure (DESIGN), (4) Prevent Errors (PREVENT),
(5) Permit Easy Reversal of Actions (REVERSAL),
and (6) Reduce Short-Term Memory Load (SHORT-
CUT).
Figure 10: Results of Classification and Regression Trees
(CART Method) for each item from the Eight Golden Rules
indicator on the UIUX EM Variable.
To find items from the Eight Golden Rules
UIUX EM indicator that must be improved, an anal-
ysis with Classification and Regression Trees (CART
method) was conducted. The results can be seen in
Figure 10. From Figure 10, it can be interpreted that
the most dominant determines the EM Application re-
sponded by users who tend to agree with the attrac-
tiveness of the application display is determined by
the Ease Reversal of Actions (ACTION) item. If the
item is improved through 1 (one) program interven-
tion, the EM application user response will increase
5.910 times from the current user response condition.
Improving the Ease Reversal of Actions (ACTION)
item can be realized through improving the Clarity
of Application Design Structure (STRUCTURE) item
which is able to increase the response to the Ease
Reversal of Actions (ACTION) item by 2.269 times
from the current condition. Based on the results of
the above analysis, there are 8 items in the EM appli-
cation that must be improved, namely: (1) Suitabil-
ity of Icons in the Application (ICON), (2) Usability
of Localization Feature (LOCALIZATION), (3) Us-
ability of Dark and Light Mode Feature (MODE), (4)
Clarity of the Information Given in the Application
(INFORMATION), (4) Clarity of Application Flow
(FLOW), (5) Clarity of Error Message in the Appli-
cation (MESSAGE), (6) Ease of Reversal of Actions
(ACTION), (7) Convenience of Application Flow and
Design (CONVENIENCE), and (8) Accuracy of the
Button Placement (BUTTON).
Based on the analysis results of the UI/UX evalu-
ation survey of the Entrepreneurial Mindfulness ap-
plication, it can be concluded that users tend to
ICAISD 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Information Scientific Development
224

agree on the attractiveness of the appearance of the
Entrepreneurial Mindfulness application. However,
there are several indicators and items that need to
be improved and developed to increase user satis-
faction with the appearance and flow of the applica-
tion. Therefore, some improvements and develop-
ments were made to the appearance and flow of the
application which are described as follows:
1. Improve the flow of the application where after
the user finishes registration, the user immediately
logs into his account so that there is no need to
re-login. The flow of the application after being
improved can be seen in Figure 11.
Figure 11: Update of Registration Flow.
2. Add a short tutorial on how to answer the test by
using animation or pointing to the slider on the
test page to inform users that the slider on the test
page can be moved up and down.
Figure 12: Simple tutorial about how to answer the test.
3. Direct the user to login when the app is first
opened, but still provide a button to skip the di-
rective and go straight to the home page
Figure 13: Login page when user just opened the app for
the first time.
5 CONCLUSION
Entrepreneurial Mindfulness application is developed
by paying attention to the quality of the appearance
and function of each feature. With a good appearance
and function in the Entrepreneurial Mindfulness ap-
plication can help researchers in introducing the ap-
plication more widely so that the application can be
used in accordance with the purpose of the application
development itself. By always improving the quality
of the application’s appearance, users will be more
satisfied and comfortable in using the application and
this will provide more benefits for the development of
the Entrepreneurial Mindfulness application.
Based on the results of the UI/UX evaluation
conducted on the Entrepreneurial Mindfulness appli-
cation, several important aspects can be identified
for further application development. Entrepreneurial
Mindfulness application as a platform that helps en-
trepreneurs in assessing their level of mindfulness not
only pays attention to the right function, but also
a good appearance and easy-to-understand flow for
users so that users feel comfortable and satisfied when
using the application. From the survey results, it was
concluded that the appearance and flow of the appli-
cation were able to provide a fairly good experience to
users. However, there were also some suggestions and
UI/UX Evaluation on Entrepreneurial Mindfulness Mobile Application
225

criticisms from the respondents so that some develop-
ments and improvements were made to improve the
appearance and flow in the application. It is expected
that the Entrepreneurial Mindfulness application can
increase the number of users so that they want to be
proactive in using the pplication to increase their ca-
pacity and competence as entrepreneurs
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work is supported by Research and Technol-
ogy Transfer Office, Bina Nusantara University as
a part of Bina Nusantara University’s International
Research Grant entitled Entrepreneurial Mindfulness
Based on Artificial Intelligence with contract num-
ber: 017/VR.RTT/III/2021 and contract date: 22
Maret 2021. We also want to say thanks to Uni-
versitas Teknologi Malaysia and Universitas Agung
Podomoro for the contribution as partners in research
REFERENCES
Ahmad, N., Boota, M., and Masoom, A. (2014). Journal of
Software Engineering and Applications, 07:1045.
Aljamea, M. and Alkandari, M. (2018). IAENG Int. J. Com-
put Sci, 45.
Chen, T., Peng, L., Jing, B., Wu, C., Yang, J., and Cong, G.
(2020). Sustainability (Switzerland, 12.
Delamaro, M., Society, I., Maldonado, J., and Mathur, A.
(2001). IEEE Transactions On Software Engineering,
27:228.
Dirin, A. and Laine, T. (2018). Computers, 7.
Gelderen, M., Kibler, E., Kautonen, T., Munoz, P., and Win-
cent, J. (2019). Journal of Small Business Manage-
ment, 57:489.
Gkatzidou, V., Hone, K., Sutcliffe, L., Gibbs, J., Sadiq,
S., Szczepura, A., Sonnenberg, P., and Estcourt, C.
(2015). BMC Med Inform Decis Mak, 15.
Hassan, A. (2022). Al-Mukhtar Journal of Sciences, 37:251.
Hoehle, H. and Venkatesh, V. (2015). MIS Q, 39:435.
Indrianti, Y., Sasmoko, N. A., Rabiha, S., Setiadi, N., Han-
drimurtjahjo, A., and Waspodo, M. (2020). J Phys
Conf Ser, 1641.
Janaki, D. (2021). International Journal of Mechanical En-
gineering, 6:459.
Joo, Y., Lee, H., and Ham, Y. (2014). J Comput High Educ,
26:143.
Kelly, L. and Dorian, M. (2017). New England Journal of
Entrepreneurship, 20:26.
Khairul, A., Ahmad, A., Baharom, S., Rahaman, A., Ab-
dullah, M., Nasiruddin, M., and Aziz, A. (2020). Ide-
alogy Journal, 5:17.
Kurnia, Y. and Aditya, G. (2022). Bit-Tech, 4:109.
Liu, X., Wu, X., Wang, Q., and Zhou, Z. (2022). Front
Psychol, 13.
Malecki, E. (2018). Geogr Compass, 12.
Mamoun, R., Nasor, M., and Abulikailik, S. (2020). In
International Conf. on Computer, Control, Electrical,
and Electronics Engineering, ICCCEEE.
Mantik, J., Prayoga, R., Munawar, G., Jumiyani, R., and
Syalsabila, A. (2021). Jurnal Mantik, 5:1591.
Nambisan, S. (2017). Entrepreneurship: Theory and prac-
tice 41, 1029.
Nowi
´
nski, W. and Haddoud, M. Y. and Lan
ˇ
cari
ˇ
c, D. and
Egerov
´
a, D. and Czegl
´
edi, C.(2019). Studies in
Higher Education, 44:361.
Oktavius, A., Manalu, S., Indrianti, Y., and Moniaga, J.
(2022). In IEEE 7th International Conf. on Infor-
mation Technology and Digital Applications (ICITDA,
vol. 1.
Paryudi, I. and Fenz, S. (16th). In International Conf. on
Information Integration and Web-Based Applications
& Services - IiWAS, page 469.
Plana-Farran, M. and Blanch,
`
A. and Sol
´
e, S.(2022). Int. J.
Environ Res Public Health, 19.
Punchoojit, L. and Hongwarittorrn, N. (2017). Advances in
Human-Computer Interaction 2017.
Relan, K. (2019). Building REST APIs with Flask. Apress.
Sasmoko, Y., Karsidi, R., Wuisan, D., and Ruliana, P.
(2018). International Journal of Engineering and
Technology (UAE, 7:134.
Sauer, J., Sonderegger, A., and Schmutz, S. (2020). Er-
gonomics, 63:1207.
Shan, T. and Tian, X. (2022). Front Psychol, 13.
Tashildar, A., Shah, N., Gala, R., Giri, T., and Chavhan, P.
(2020). International Research Journal of Moderniza-
tion in Engineering Technology and Science, 2:1262.
Weichbroth, P. (2020). IEEE Access, 8, 55563.
ICAISD 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Information Scientific Development
226
