
EVOLUTION OF A MOBILE ROBOT’S NEUROCONTROLLER
ON THE GRASPING TASK
Is Genetic also Generic?
Philippe Lucidarme
Lisa, University of Angers, France
Keywords: Evolutionary algorithm, mobile robot, artificial neural networks controller, grasping task.
Abstract: This paper presents a survey on the generic evolution of mobile robot’ neurocontrollers with a particular
focus on the capacity to adapt these controllers in several environments. Several experiments on the
example of the grasping task (autonomous vacuum cleaner for example) are performed and the results show
that the produced neurocontroller is dedicated to the trained conditions and cannot be considered as generic.
The last part of the paper discusses of the necessary changes in the fitness function in order to produce
generic neurocontrollers.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the past years, biology has been an inspiration for
computer science researches. Genetics algorithms
and artificial neural networks are probably the best
illustration. Evolutionary algorithms are today used
to optimize, classify or control in a large number of
problems. The efficiency of the methods has been
experimentally and sometime theoretically proven
on given problems (Jansen, 2002), (Bäck, 1996) and
(Floreano, 1994). In the particular field of robotics,
especially in the case of real robots, proving the
efficiency of the methods is very hard due to the
complexity of the interactions between the
environment and the robot. In spite of this,
evolutionary algorithms are commonly used to
optimize the parameters of robot’s controllers.
The first experiment in the field of robotics has
been performed in 1994 by Dario Floreano and
Francesco Mondada (Floreano, 1994). Based on the
used of a genetic algorithm, the aim of this
experiment was to optimize the parameters of an
artificial neural controller in order to generate an
obstacle avoidance behavior. The experiment was
performed on a real Kephera robot (Mondada 1993)
and required 100 generations of 80 individuals. Each
generation lasts 39 minutes. The results were
remarkable, after 50 generations (32 hours) the robot
already performed a behavior close to the optimal.
Note that the Khepera robot is not a symmetrical
robot: front face has 6 proximity sensors versus 2 for
the rear face. During the evolution, the robot
naturally selected the front face as the best direction.
Few years later, the same team extended the
experiment on a bigger robot with a different
proximity sensors disposition (Floreano 1998). They
continued the evolution on a Koala robot (described
in section 4.4 of (Nolfi 2000)). In approximately
thirty generations the best individuals reported
fitness values similar to the experiment previously
described with the Khepera robot (Floreano, 1994).
The first experiment proved the possibility of
using evolutionary algorithm in order to learn basic
behaviors on real robots. The second experiment
proved that the previous results are platform
independent, and this result can even be extended:
from the neurocontroller point of view, inputs are
the proximity sensors, and outputs are motor’s
commands. It means that the geometry and the
kinematics of the robot are external to the controller.
Then, the results of this second experiment can be
extended to the environment, as the authors
explained in (Nolfi 2000): “From the point of view
of the neurocontroller, changing the sensory motor
characteristics of the robot is just another way of
modifying the environment”.
These results have been exploited on several
experiments like motion planning (Ahuactzin, 1992)
or humanoid walking (. Yamasaki 2002) with a
recurrent argument: the adaptive capacity of the
evolutionary algorithms. According to the previous
explanations, this capacity cannot be contested, but
what about the neurocontroller? In fact, the
306
Lucidarme P. (2008).
EVOLUTION OF A MOBILE ROBOT’S NEUROCONTROLLER ON THE GRASPING TASK - Is Genetic also Generic?.
In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics - ICSO, pages 306-313
DOI: 10.5220/0001491003060313
Copyright
c
SciTePress

neurocontroller is not generic; it has been optimized
for the environment where the experiment has been
performed. It means that if the robot needs to evolve
in a different environment the evolutionary process
needs to be restarted like for the Koala robot. In
practice, and especially on real robots, the
evolutionary algorithms need to be stopped to avoid
performing dump behaviors due to unfortunate
crossovers. The study presented in this paper
evaluates the faculty of a neurocontroller to be
adapted in several environments.
Second section of the paper describes the context
of the experiment, based on a grasping task (Arkin,
1992). Introduced by R.C. Arkin in the 90’s, this
task consists in exploring a given environment (for
example for mowing or painting the floor).
From section three, the following of the survey is
based on a methodology inspired from biology:
evolutionary algorithms are used to generate eight
neurocontrollers in eight different environments.
These neurocontrollers are stored as standard
behavior and are compared in the seven other
environments to evaluate there performances in
different contexts.
The fourth part of the paper introduces a new
experiment where the robot is trained in the eight
environments: the fitness function is the average
performance. Results are analyzed and compared
with the standards previously defined.
The last part of the paper introduces a new
fitness function based on the performance in the
worst environment. A general conclusion ends the
paper.
2 EVOLUTIONARY
ALGORITHMS ON THE
GRASPING TASK
2.1 Grasping Task
As explained in the introduction, the grasping task
has been introduced in a paper on multi-agents
systems in 1992 by R.C. Arkin. This task has been
choosen because the duration of the evaluation of
one individual can be bounded and also because the
fitness function is easy to evaluate in simulation
(explored area divided by total surface). Note that
another kind of tasks would have been used like
obstacles avoidance or target tracking.
Due to the duration of the experiments, all the
presented results are obtained by simulation. Note
also that our purpose in not to obtain an efficient
neurocontroller on real robots but to compare the
results in several contexts. Real experiments suffer
from noise on sensors, wheels slipping or battery
discharge that make the comparison sometime
difficult. In spite of this, the simulator computes the
model of the real robot Type 1 (described in the next
section) and the environments are scaled around this
robot. The simulator is designed with a library of
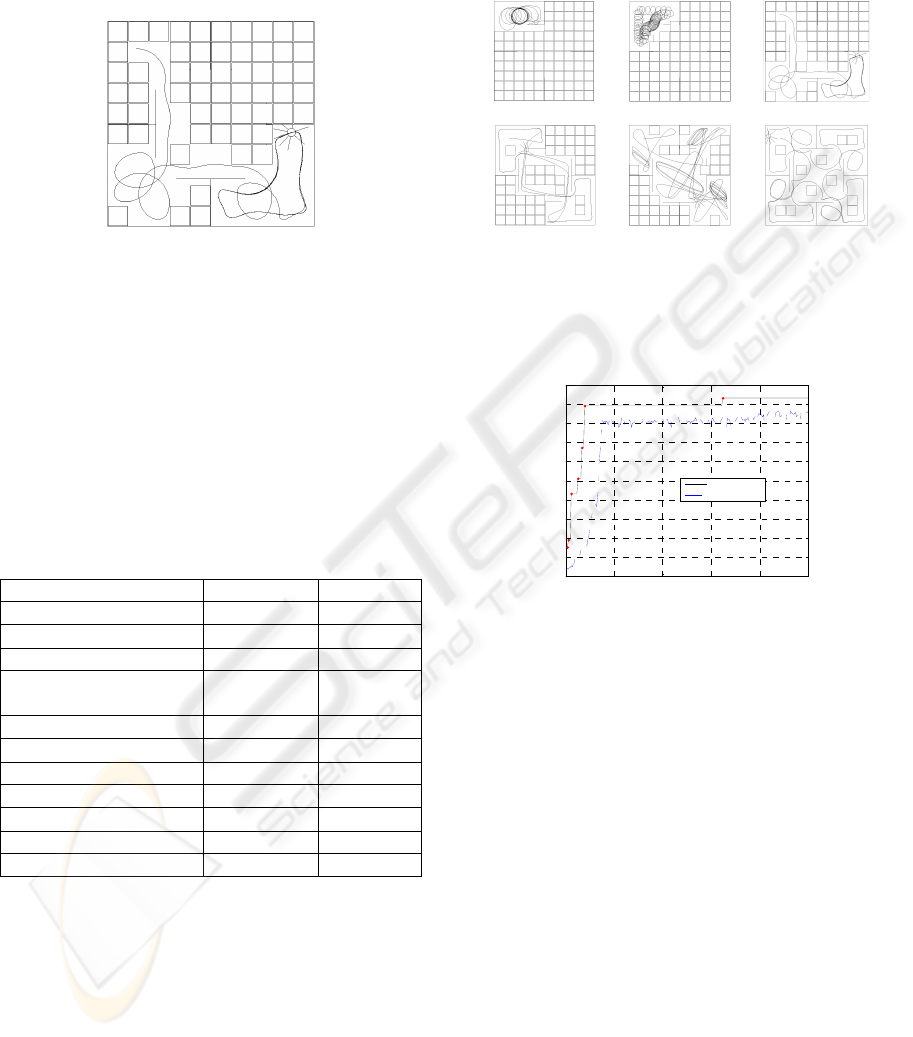
eight environments. Each environment has a squared
shape (length of the side: 3 meters). The disposal of
walls has been chosen so as to do three kinds of
environments: with large spaces (Figure 1.a,b,c and
f) , with narrow corridors (Figure 1.d and g.) and
mixed (Figure 1.e and h).
a. b. c.
d. e. f.
g. h.
Figure 1: The eight environments used to compare the
learned behaviors.
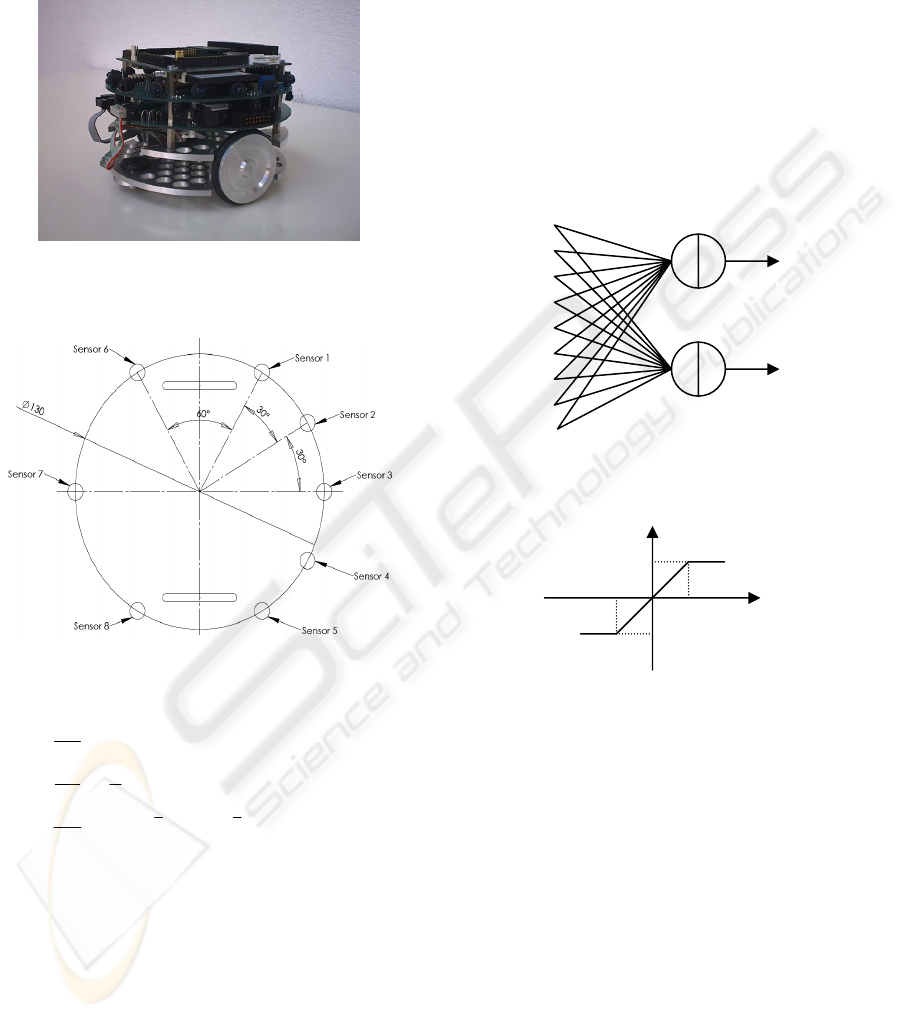
2.2 The Mobile Robot Type 1
The kinematics model of the robot and sensor’s
disposal are similar to the robot Type 1 described in
(Lucidarme, 2006). It has a 10 cm-height and 13 cm-
diameter cylindrical shape (figure 5). Two wheels
actuate it. Two small passive ball-in-socket units
ensure the stability in place of usual castor-wheels.
DC motors equipped with incremental encoders (352
pulses per wheel's revolution) control the wheels.
The encoders may be used for both speed control
and robot localization by odometry. The robot is
surrounded with 16 infrared emitters and 8 receivers
(shown on figure 2 and 3). The sensors use a carrier
frequency of 40 kHz for a good noise rejection. An
embedded PC (80486 DX with 66 MHz clock)
manages the robot.
Figure 3. shows the model used in the simulator,
especially the sensor’s positions. The kinematics
model used in the simulator is described by equation
1. This robot has been chosen because in the case
where real experiments would have been necessary,
EVOLUTION OF A MOBILE ROBOT’S NEUROCONTROLLER ON THE GRASPING TASK - Is Genetic also
Generic?
307
Type 1 has many of the characteristics required by
the evolutionary approach: fully embedded
computation power (x86 processor), up to two hours
of autonomy (Li-ion batteries) and large memory
capacity (compact-flash).
Figure 2: Picture of the mobile robot Type 1 equipped
with infrared proximity sensors and the embedded PC104
visible on the top.
Figure 3: Description of the model used in the simulator
and position of the sensors (Dimensions are in mm).
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡
Ω
Ω
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
−
ΨΨ
ΨΨ
=
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
Ψ
l
r
ll
r
dt
d
dt
dY
dt
dX
.
11
)sin()sin(
)cos()cos(
2
(1)
where :
• X and Y are the coordinate of the robot in the
environment frame,
• Ψ is the orientation in the same frame,
• Ω
l
and Ω
r
are the angular speed of the left and
right wheels,
• r is the wheel’s rayon,
• l is the distance between two wheels.
2.3 The Neurocontroller
As explain in (Floreano, 1994) and (Haussler, 1995)
genetic algorithms can be used to train and optimize
artificial neural networks (ANNs). Such solution has
been selected here for its interesting link with
biology and its anteriority in the field of robotics.
Previous works (Braitenberg, 1986) prove that
simple neurocontroller can be used to performed
obstacle avoidance. Assuming that the grasping task
is similar to an obstacle avoidance behavior from the
neurocontroller point of view, the same structure for
the neural network without hidden layer has been
chosen (Figure 4 shows the neural network).
Figure 4: Neurocontroller’s structure.
Figure 5: Transfer function for each perceptron.
In order to homogenize the simulation and the result
analysis, all the data are scaled in the interval [-1;1].
For example, in the case of the wheel’s angular
speed: +1 applied to the motors is equivalent to the
maximum speed (0.1 rad.s
-1
). For the same reason,
the synaptic weights are bounded in the same
interval and the output of the perceptron is also
bounded (Figure 5) to reproduce the mechanical
characteristics of the motors. Proximity sensor’s data
is applied on the input of the network that computes
the command on each motor. Note that a synaptic
link with a constant value applied to the input (equal
to one) has been added allowing the robot to move
when none of the sensors are providing a value, i.e.
when all the c
i
are equal to zero. As usual, the neural
network is just a friendly representation of a
mathematical expression (equation 2). In this
f(x)
x
1
1
-
1
-
1
Se
n
so
r 1
Sensor 2
Se
n
so
r 3
Se
n
so
r 4
Se
n
so
r 5
Se
n
so
r 6
Se
n
s
o
r
7
Se
n
so
r 8
l
e
ft m
o
t
or
right motor
W
i
f
f
Σ
Σ
1
ICINCO 2008 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
308

equation, all the parameters are known except the 18
synaptic weights, optimized by the evolutionary
algorithm.
).(
9
8
1
wcwf
i
iil
∑
=
+=Ω
).(
18
8
1
9
wcwf
i
iir
+=Ω
∑
=
+
(2)
where :
• Ω
l
and Ω
r
: command applied on the motors,
• w
i
, i∈[1;9] : synaptic weight for the left motor,
• w
i
, i∈[9;18] : synaptic weight for the right
motor,
• c
i
: distance detected by the sensor i.
2.4 The Evolutionary Algorithm
The algorithm is based on a classical genetic
approach described as follow.
2.4.1 Chromosome
As the structure of the neurocontroller has been
fixed, only the synaptic weights have to be
optimized. The chromosomes are only containing
these weights. An intuitive approach consists in
coding the weights in binary, providing a series of 0
and 1. The drawback of this approach results in the
most important influence of most significant bit
during crossovers and mutations. To avoid this
problem, an elementary component of the
chromosome is not a 0 or a 1, but the weight himself
as described in table 1.
Table 1: Structure of a chromosome.
w
1
W
2
… w
i
… w
17
w
18
2.4.2 Crossovers
Crossovers are performed with two individuals
selected from previous generation. The selection of
the individual is based on the roulette-wheel
reproduction as described in (Nolfi, 2000) that
allows the best individual to be statistically selected
more frequently. The probability for an individual n
to be selected is given by the equation 3.
Once the two parents are selected, one of them is
randomly selected (each with a probability of 0.5) to
provide the first gene, and this process is repeated 18
times (one for each weight). The crossover’s
strategy is multipoint as described in (Mitchell,
1997).
∑
=
=
N
i
n
n
fi
f
P
0
(3)
where :
• P
n
: probability of selection for the individual n,
• f
j
: fitness of the individual j
,
• N : number of individuals in the previous
generation
2.4.3 Mutation
According to the strategy chosen, the mutation
process is very important. Assume that the optimal
weights for a given gene aren’t present in none of
the 100 individuals: without mutation, it is strictly
impossible to find the optimal solution. Mutations
are indeed very important and the mutation rate must
be high enough to ensure a good exploration of the
space. The mutation process is performed after the
crossovers; 10% of the new individuals are
randomly selected. For each individual a gene is
randomly selected and replaced by a random value
in the range [-1,1]. For each draw, the probability is
uniform.
2.4.4 Fitness Function
As our goal is a grasping task, the fitness function
must be linked with the explored area. The
environment is sampled with a sampling rate of 30
cm for each axis. As the size of the environment is
3m x 3m the space is divided into 100 squares. At
the end of the evaluation of each individual, the
fitness function is computed with the equation 4.
Figure 6 shows a snapshoot of the simulator.
Total
lored
j
N
N
f
exp
=
(4)
where :
• f
j
: fitness of the individual j
,
• N
explored
: number of squares explored
• N
Total
: total number of squares
2.4.5 Parameters
In the first version of the simulator, a noise was
added on the motors. After analyzing the results we
discovered that this noise prevented from comparing
EVOLUTION OF A MOBILE ROBOT’S NEUROCONTROLLER ON THE GRASPING TASK - Is Genetic also
Generic?
309
the results. We decided to eliminate this noise in
order to make the simulator deterministic. For the
same reason, the initial position of the robot is
always located at the same place (at the top left, c.f.
Figure 6) to prevent from favoring individuals.
Figure 6: Snapshoot of the simulator showing the
trajectory of the robot and the explored area. The current
fitness of the robot is 0.43 (43 explored squares divided by
100 total squares).
Note that collisions between robot and walls are
considered. As the neurocontroller has been
designed without hidden layer, it is impossible for a
jammed robot to escape from a collision. To
decrease the computation time, when a robot is
jammed its evaluation is stopped and the fitness is
computed. Table 2 describes the parameters of the
simulator.
Table 2: Parameters of the simulations.
Description Name Value
Wheel’s rayon r 0.05 m
Distance between wheels l 0.1 m
Sensor’s range Sr 0.2 m
Maximum angular speed of
the wheels
Ω
max
0.1 rad.s
-1
Size of the environment - 3x3 m
Sampling rate (space) - 0.3m
Size of the population N
individual
100 ind.
Mutation rate - 10%
Sampling rate (time) Δ
t
0.01 s
Duration of an evaluation - 30 s
Number of generations - 250 gen.
3 STANDARD BEHAVIORS
3.1 Standard Experiments
For each environment a neurocontroller has been
trained. This controller is considered as the standard
behavior in the following. The evolution of the 250
generations lasts around two hours on a desktop
computer. Figure 7 shows the evolution of an
individual in the environment c. Figure 8 shows the
evolution of the fitness. For each environment, an
efficient strategy has been generated that confirms
the relevance of the used parameters.
a. b. c.
d. e. f.
Figure 7: Evolution of the robot’s behavior in the
environment c. (see Fig.1) at generations 2,3,6,13,17 and
162 with respective fitness: 0.15, 0.19, 0.43, 0.51, 0.66
and 0.93.
0 50 100 150 200 250
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Generations
Fitness
Fitness vs Generations
Best indivudal
Average Fit ness
Figure 8: The fitness of the individuals (Fitness of the best
individual (continuous line) for each generation and
average (dotted line) of the whole population).
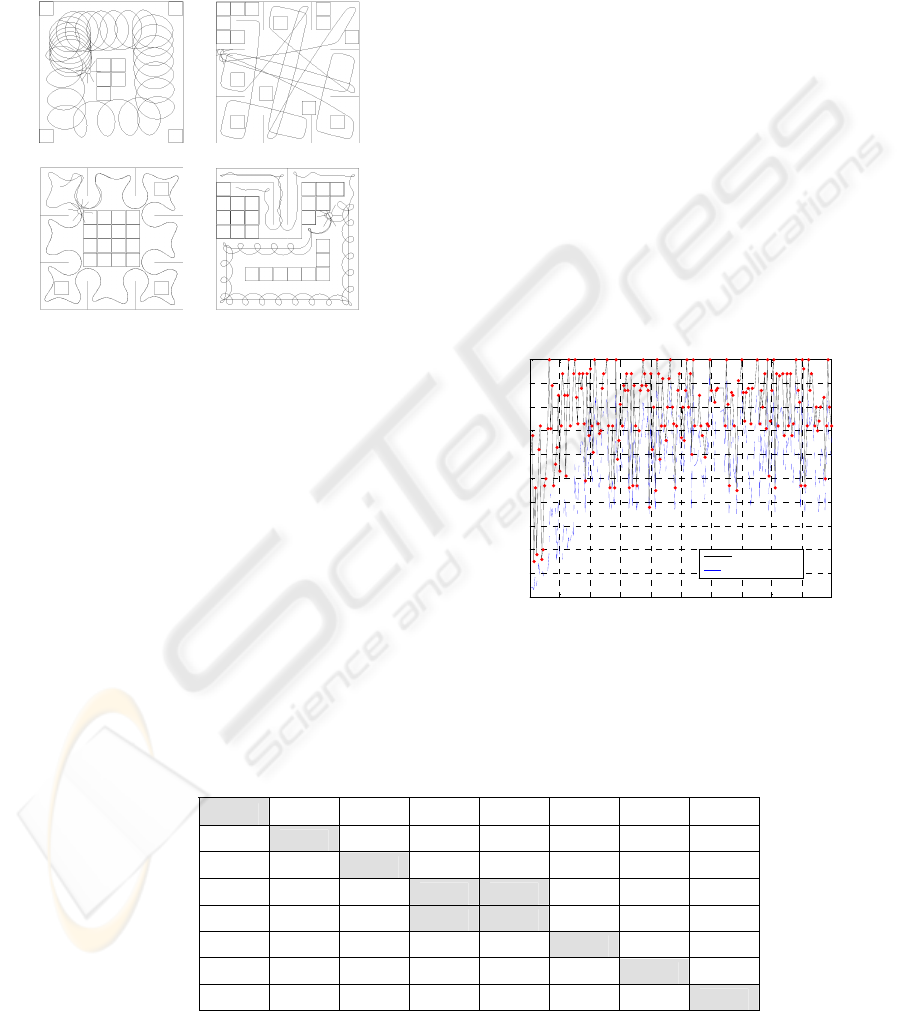
Analyzing the results shows that efficient behaviors
can be classified in three categories:
• performing epicycloidals trajectories
(Figure 9.a),
• moving straight and avoiding obstacles
(Figure 9.b)
• wall following (Figure 9.c)
Best strategies are usually a mixed of the previous
behaviors (Figure 9.d)
3.2 Swapping the Environments
In order to evaluate how generic are the produced
behaviors, each individual is placed in the seven
other environments. Note that the genetic process is
stopped. Table 3 summarizes the results. For
example bolded 38% presents the performance in the
environment a of the individual trained in the
ICINCO 2008 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
310
environment d. Grey cells show the best
performance for each environment. This agrees with
the diagonal that represent the performance of each
individual in “its” environment except for
environment d. and e. where individuals are equally
ranked, probably due to the fact that environments d.
and e. are quiet similar.
a. b.
c. d.
Figure 9: Examples of strategies used for exploring the
environment.
This preliminary result allows us two conclusions:
the neurocontroller produced by the genetic process
cannot be considered as generic. An nice illustration
is shown on table 3.: the performance in the
environment g. is very poor except for the
individuals trained in this kind of environment.
These results also confirm that genetic algorithm
may be considered as generic: the produced behavior
is nicely adapted to the trained environment, on table
3. the best fitness are always located on the diagonal.
The last part of the paper will discuss about the best
strategy for generating generic neurocontrollers.
4 GENERIC
NEUROCONTROLLERS
4.1 Random Selection of the
Environment
The first idea for building generic neurocontrollers
consists in mixing the environments during the
evolution. A new simulation has been performed,
but the environment is now randomly selected for
each generation. After 1500 generations, the
synaptic weights never converge to a stable value.
Figure 10 shows the evolution of the fitness during
the 200 first generations (no changes were observed
after). Compared to Figure 8 this evolution cannot
be considered as satisfying. Results have shown that
random selection of the environment makes the
global system non-deterministic and prevents the
genetic algorithm from finding the optimal solution.
To avoid this problem, each individual is now
trained in the eight environments.
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Generations
Fitness
Fitness vs Generations
Best indivudal
Average Fitness
Figure 10: Fitness versus generations.
Table 3: Performance of the best individual of the final generation in the seven other environments.
Explored environment
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h.
a.
96 % 70 % 6 % 9 % 12 % 10 % 1 % 1 %
b. 94 % 98 % 4 % 11 % 14 % 11 % 2 % 2 %
c. 14 % 13 % 93 % 92 % 33 % 20 % 15 % 15 %
d. 38 % 62 % 9 % 100 % 86 % 81 % 11 % 11 %
e. 7 % 7 % 7 % 100 % 86 % 5 % 4 % 4 %
f. 41 % 65 % 8 % 9 % 9 % 85 % 14 % 14 %
g. 38 % 62 % 17 % 23 % 84 % 77 % 77 % 72 %
Trained environment
h. 44 % 64 % 90 % 93 % 84 % 83 % 61 % 76 %
EVOLUTION OF A MOBILE ROBOT’S NEUROCONTROLLER ON THE GRASPING TASK - Is Genetic also
Generic?
311
4.2 Evolution in the Eight
Environments
For the reason explained in the previous section,
each individual is now successively trained in the
eight environments. The fitness is similar to the
previously described equation 4 (equivalent to the
average performance in the eight environments). The
experiment lasts about fifteen hours (eight times
longer than for one environment). The evolution of
the fitness is now asymptotic (similar to figure 8)
that proves the convergence of the genetic
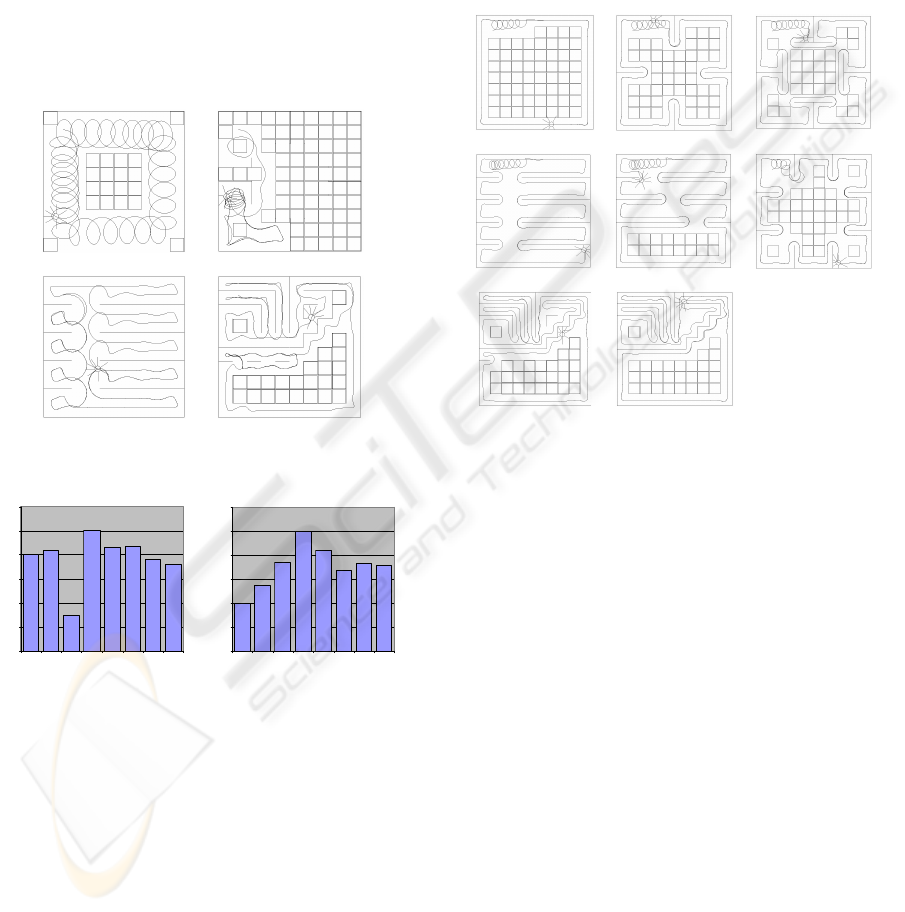
algorithm. Examples of trajectories are shown on
figure 11.
a. b.
c. d.
Figure 11: Example of trajectories in four environments.
80%
84%
29%
10 0 %
86%
87%
76 %
72%
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
120%
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h.
40%
55%
74 %
100%
84%
67%
73%
72 %
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
120%
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h.
a. b.
Figure 12: Performance of the best individual (last
generation) in the eight environments.
Figure 12.a. shows the fitness in each environment.
The global performance is satisfying (76.75%) to the
detriment of the environment c. (only 29%). Figure
11.b. shows the trajectory of the robot in this
environment; the robot is quickly jammed in a dead
end. However it’s hard to conclude about the
adaptability of the neurocontroller. Indeed, it is clear
that the performance in the environment c. has been
sacrificed in favour of global fitness. Considering
that generic means able to perform a high fitness in
any situations, this goal isn’t reach.
4.3 Increasing the Last
To avoid having a “sacrificed” environment, we
performed the previous experiment with a new
fitness function. The average isn’t longer
considered. Each individual is evaluated in the eight
environments and the new fitness is the performance
in the worst environment. For example, on figure
12.a, the performance used to compute crossovers is
the weakest: 29% (environment c.).
a. b. c.
d. e. f.
g. h.
Figure 13: Trajectory of the robot in each environment.
Figure 12.b shows the performance in each
environment of the best individual (last generation).
The worst performance is 40% in the environment a.
(slightly better than the previous 29%). The
trajectories of the robot are clearly based on a wall
following strategy visible on figure 13. As the
environment a. has no wall (except the outline walls)
the performance is poor. In spite of this, this result is
encouraging. The average performance is 70.62%,
not so far from the previous 76.75%. This means
that the global performance isn’t too much affected.
Even if these results are globally worst, it stays
encouraging. Probably that the chosen
neurocontroller (without hidden layer) does not
allow the robot to perform a high performance in the
eight environments at the same time. These results
tend to show that taking the performance of the
worst case may provide more generic controllers
than averaging the fitness
ICINCO 2008 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
312

5 CONCLUSIONS
We presented in this paper some experiments based
on the grasping task (for example an autonomous
vacuum robot). These experiments are based on the
genetic evolution of a neurocontroller without
hidden layer. In the first part we evolved in
simulation eight neurocontrollers (each in a given
environment). The neurocontroller were swapped
and the performances in the other environments
were evaluated. For some researchers, there is
sometime a mix-up between the genetic algorithm
and the generated behavior. We’ve shown that
genetics algorithms can be easily adapted with the
same parameters to several problems. We’ve also
shown that the generated neurocontroller is
dedicated to the trained environment. It means that
genetics algorithms are generic, contrary to
neurocontrollers that are dedicated. This result can
probably be extended to all the parameters of the
evaluation: noise, robot’s hardware, battery charge,
etc.
In the second part of the paper, several strategies
were experimented to produce generic
neurocontrollers. First, the evaluation of the
individual was done in the eight environments and
the average performance was used for the fitness
computation. This experiment provides good results
except in one environment where the fitness was
very poor. In the final experiment the performance
in the worst environment was used to compute the
fitness. The global performance is slightly smaller
than in the previous experiment, but the performance
is more distributed in the environments. Generating
generic controllers using genetic algorithms stay a
complex problem but we’ve shown that taking the
worst case for evaluating the individual may be a
first step in the automatic generation of generic
neurocontrollers.
REFERENCES
Jansen T. and Wegener I., 2002, On the analysis of
evolutionary algorithms: A proof that crossover really
can help. Algorithmica, Springer New York, Volume
34, Number 1 / July, 47-46.
Bäck T., 1996, Evolutionary algorithms in theory and
practice: evolution strategies, evolutionary
programming, genetic algorithms. Oxford University
Press.
Floreano D. and Mondada F., 1994, Automatic Creation
of an Autonomous Agent: Genetic Evolution of a
Neural Network Driven Robot. 3rd International
Conference on Simulation of Adaptive Behavior
(SAB'94).
Mondada F., Franzi E. and Ienne, P., 1993, Mobile Robot
Miniaturization: A Tool for Investigation in Control
Algorithms, 3rd International Symposium on
Experimental Robotics III, October 28-30, 501-513.
Floreano D. and Mondada F., 1998, Evolutionary
Neurocontrollers for Autonomous Mobile Robots.
Neural Networks, 11(7-8), 1461-1478.
Nolfi S. and Floreano D., 2000, Evolutionary Robotics:
The Biology, Intelligence, and Technology of Self-
organizing Machines. Bradford book, MIT Press,
Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Ahuactzin J.M., Talbi E-G, Bessiere P. and Mazer E.,1992
, Using genetic algorithms for robot motion planning.
European Conference on Artificial Intelligence
(ECAI92), Wien (Austria).Yamasaki F., Endo K.,
Kitano H. and Asada M., 2002, Acquisition of
humanoid walking motion using genetic algorithm -
Considering characteristics of servo modules.
Robotics and Automation, Proceedings. ICRA '02.
IEEE International Conference on Robotics and
Automation, 3123-3128.
Arkin R.C., 1992, Cooperation without Communication,
Multiagent Schema-Based Robot Navigation, Journal
of Robotic Systems, Vol. 9 (3), avril , 351-364.
Lucidarme P. and Simonin O.,2006 , Le robot mobile Type
1, Journée des démonstrateurs en automatique,
Angers, France.
Haussler A., Li Y., Ng K.C., Murray-Smith D.-J.
and Sharman, K.C., 1995, Neurocontrollers designed
by a genetic algorithm. First conference on genetic
algorithms in engineering systems: innovations and
applications, Sheffield, UK, Publ. No. 414.
Braitenberg V., 1986, Vehicules – experiments in synthetic
psychology, Bradford books.
Mitchell T.M., 1997, Machine learning. McGraw-Hill
Science.
EVOLUTION OF A MOBILE ROBOT’S NEUROCONTROLLER ON THE GRASPING TASK - Is Genetic also
Generic?
313
