
PRICE TO PROVIDE RFID SECURITY AND PRIVACY?
Tim Good and Mohammed Benaissa
Dept. of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of Sheffield, Mappin Street, Sheffield, S1 3JD, U.K.
Keywords: RFID, protocol, security, privacy.
Abstract: The applications for Radio frequency identification (RFID) systems are rapidly expanding and privacy
concerns have been highlighted. Existing protocols fit into the challenge-response model and either fail in
terms of privacy or have security vulnerabilities. A new symmetric key based protocol for RFID, named
“PRICE: to Prevent RFID Insecurity Cryptography Essential”, is presented. This provides tag and reader
authentication together with secure transfer of the tag’s identifier whilst still remaining within the challenge-
response model. A security analysis of the protocol is given together with discussion of areas of weakness.
The tag-borne security measures only require a single symmetric cipher encryption primitive.
1 INTRODUCTION
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems have
grown in popularity in recent years. The process is
non-contact and depending on RF band and antenna
operate at ranges from few centimetres to meters.
The technology already pervades and adds
benefit to our daily lives, however there are negative
aspects (Peslak 2005, Lockton and Rosenberg 2006,
Garfinkel et al 2005). The majority of tags form part
of the supply chain and are removed or disabled at a
point of sale. A second class, where in normal
operation, the tag remains active whilst in the
possession of an individual, pose far greater privacy
and security concerns. Examples include: identity
cards, car keys, car tyres, medicine packaging and
some higher value retail products.
Research in RFID technology is very active and
summarized in two recent review papers (Jules
2005, Lehtonen et al 2006). The challenge is to
develop secure RFID protocols which do not leak
sufficient information which in turn may be used to
derive personal information about its owner / bearer.
Previous attempts have focussed exclusively on
privacy at the expense of security, and vice-versa.
Even the best previous attempts at such protocols
have vulnerability to either Denial of Service (DoS)
attacks, radio-relay attack (Kfir and Wool 2005) or
allow user tracking via a constellation of non-unique
identifiers (Weis et al 2004).
This work attempts to set out the necessary aims
for an RFID authentication protocol with protection
of user/bearer privacy within the challenge-response
model. It builds on the work in (Weis et al 2004,
Engberg et al 2004, Chatmon et al 2004, Dimitriou
2005, Tsudik 2005, Kfir and Wool 2005, Dominikus
et al 2005) to address the vulnerabilities of each.
This protocol, PRICE (stands for: to Prevent RFID
Insecurity Cryptography Essential), is aimed at
providing a security level of 2
64
against known
attacks attempting to recover the (private) identifier.
Only a single cryptographic primitive is required in
the tag, for example, a low resource symmetric
cipher or keyed hash. Recent work shows a number
of the newly developed eSTREAM ciphers to be
suitable (Good and Benaissa 2008). The protocol
provides for a fast non-identifying authentication
based on multiple challenges to a tag together with a
relatively slower part for securely recovering the
tag-ID and a mechanism for session key exchange.
A discussion of the limitations of this (and any
widely deployed secret-key system) approach is
given together with the inevitable trade-off between
cost, utility and privacy.
2 PRICE PROTOCOL
The notation used is: each of the values used in the
protocol is assigned a letter (eg A
64
), the subscript
indicating the number of bits. Concatenation of two
or more values is represented as A|B. Extraction of
most significant and least significant words is
represented by MSW and LSW respectively.
209
Good T. and Benaissa M. (2008).
PRICE TO PROVIDE RFID SECURITY AND PRIVACY?.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Security and Cryptography, pages 209-213
DOI: 10.5220/0001925002090213
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2.1 The Challenge
In order to fit within the challenge-response model
the reader must initiate communication. The first
step for the tag is to authenticate the reader to
prevent replay attacks. Relay attacks cannot be
prevented by cryptographic means (see later
discussion). The reader broadcasts an authenticated
timestamp, T
42
, and the tags store the last time, L
42
,
they received an authenticated access (Engberg et al
2004). This requires a source of time which changes
more rapidly than the challenge-response cycle (say
every millisecond) but does not require precise
synchronization to an external time reference.
Passive tags are not powered outside the RF field
thus can only store the last authenticated time. In
order to support multiple parties the readers must
have some identifier, S
22
, which needs to be
communicated to the tag (i.e. which key to use).
Although T|S forms a once only value (nonce) it is
highly predictable thus to provide security against
pre-computation an additional cryptographically
secure random value, A
64
, will be required too. The
final part of the challenge is to include an
authentication code, X
64
, derived from A|T|S using a
shared secret system-key, K
128
. To support rekeying
and multiple data users the tag may require a small
list of K
128
indexed by some part of the ReaderID
(S
22
). A keyed encryption primitive, E
K
is used to
give X
64
= LSW E
K
(A
64
|T
42
|S
22
). The transmitted
challenge is 192 bits: A
64
|T
42
|S
22
|X
64
2.2 Unique Response
The tag is powered on receiving the RF and starts by
checking the time, T
42
>L
42
. Further, checks are
possible to give a tag a definite expiry date or even a
maximum lifetime between challenges. These
advantages alone merit the inclusion of time in the
protocol. Failing any of the time tests results in the
tag remaining silent, thus once expired a tag is
essentially soft-killed (Molnar et al 2005) even
though a fuse effect (Weis et al 2004) is not used.
Reader authentication is done by performing the
same cryptographic operation inside the tag to give a
local copy of the signature X′
64
= LSW
E
K
(A
64
|T
42
|S
22
). At the same time a fresh temporary
shared secret A′
64
= MSW E
K
(A
64
|T
42
|S
22
) is
generated.
On successful validation (X
64
equal to X′
64
), L
42
is updated and tags response prepared. The response
must be specific to the readers challenge and
unidentifiable to any eves-dropper. Further, in order
to protect privacy, it must be computationally
expensive for a permitted but “dishonest” data-user
to create a database containing a large number of
IDs enabling individual tracking and / or association
with personal data.
It is proposed that the tag stores its own random
number, B
64
, based on the cryptographically secure
operation used to create the response (does not
require dedicated RNG). This value is combined
A′
64
to yield a value A′
64
|B
64
which is then encrypted
using the tags identifier, ID
128
. The result of this
operation is used in part to form the response Y
64
=
MSW E
ID
(A′
64
|B
64
) and update the stored random
B′
64
= LSW E
ID
(A′
64
|B
64
) ). The tag now broadcasts
its 128-bit response B
64
|Y
64
.
2.3 Reader Authenticates Tag
If the reader was to immediately commence
verifying the response then it may be vulnerable to a
DoS attack, also it is continuously broadcasting
ciphertext/plaintext pairs which facilitate key
recovery attacks. To frustrate both, it is proposed
that the reader transmit a series of challenges both
with valid and invalid signatures (X
64
’s). By
monitoring the response/silence of a queried tag then
a set of N challenges gives a probability of 1-0.5
N
of
a valid tag. i.e. 20 challenges for ~1:10
6
chance of a
forged response. This proves that both the reader and
tag know K. For many applications simply proving a
tag is valid may be sufficient (in this protocol
without a list of valid IDs this is all that can be
learned from the protocol). This should be seen as a
significant advantage of this approach.
2.4 Recover TagID
The next step is for the reader to recover the ID this
is deliberately made a computationally expensive
process forcing the data user to keep ID’s in a
database only when absolutely necessary. The use of
A′
64
and B
64
to create the response prevents pre-
computation. An excessively large database will
degrade the operation of the system and/or require
large computational resource.
It is an essential part of the protocol that both
ID
128
and K
128
be generated randomly and uniformly
distributed within key-space. To maintain a security
of 2
64
these keys must be 128-bit as the collision
(birthday) attack may apply. The probability of two
tags with the same ID is negligible 1:2
64
).
The ID recovery process starts with the updated
random (A′
64
) which has NOT been broadcast and
the value B
64
from the tags response. The combined
value A′
64
|B
64
is encrypted, Y′
64
|B′
64
= E
IDi
(A′
64
|B
64
),
with each ID
i
stored in the data-user’s database until
a corresponding match, Y′
64
for the broadcast Y
64
is
SECRYPT 2008 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
210

found thus recovering the ID. It should be noted that
the tags response is unique to every challenge thus
an eves-dropper learns no useful information. For a
large database given only the response from the tag
the lookup time will be excessive, however, non-
unique information volunteered by the individual
concerned (eg name, post/zip-code or even a PIN
number) can reduce the search space considerably
(and adds a second independent factor of identity).
This approach is suitable for many applications
whilst providing good privacy protection.
2.5 Secure Session
The final phase, if required, is to use A′
64
|B′
64
as a
shared session key to secure any commands and
responses between tag and reader. If such a session
is used then the stored A
64
& B
64
will need their
generation process iterating to prevent disclosure of
the session key during the next challenge-response
cycle. To minimize tag resources the reader would
use the decryption primitive for both directions so
the tag only needs the encryption primitive. The
commands and status message packets need
protection from man-in-the-middle attacks and
measures to ensure data integrity. A simple sequence
number and CRC/checksum is sufficient.
2.6 Tag Design Resources
All of the above operations can be performed using a
single cryptographic encryption primitive (such as
Grain-128 for which the NAND gate-equivalent area
is 1857 (Good & Benaissa 2008)).
By far the largest consumer of area and power
for an RFID tag is the memory. For this scheme the
minimal amount is 256 bits write once / production
etched ROM (ID
128
K
128
) and 106 bits rewritable
non-volatile memory (B
64
L
42
) such an
implementation would not support key changes. The
total storage cost is 362 bits to support a 128-bit ID
thus 2.8L in the notation of Yang (Yang et al 2005).
A more typical figure is 618 bits rewritable
memory (B
64
L
42
4×K
128
) and a 128 bit production
etched ROM containing the tagID, totalling 746 bits,
5.8L in Yang’s notation. As a comparison the
numerous hash based ID replacement schemes
(Yang et al 2005, Peris-Lopez et al 2006) require
between 1.5L and 6L.
2.7 Scalability
This approach is scalable in that multiple readers
and data users / databases can be supported. The
refreshed-ID systems require a centralized database
so cannot offer this advantage. This proposal
requires knowledge of the ID in order to test for its
presence. This property greatly enhances privacy by
effectively placing a timeliness limit on the number
of IDs which can be checked.
The ID recovery process requires an encryption
operation per known ID in the database. Even a
modest modern PC is capable of performing
approximately 10 million encryptions per second for
most efficient cipher primitives. So a back-end
server can certainly support the ID recovery against
a database of approximately 10
6
tags.
It is proposed that readers contain some form of
trusted module which can include its own internal
time source and be synchronized periodically with a
reference source (eg internet NTP). Tag responses to
challenges can be stored for later batch processing
thus to determine actual ID thus offline (eg
handheld) readers can be supported.
2.8 Key Management
Key management may be supported by the reader
broadcasting challenges for more than one K
128
and
establishing the secure session with a tag not using
the most current K
128
and then sending the update
(using secret sharing based on the ID
128
and K
128
being updated). The secure session could also be
used for some applications to store and retrieve
information in a secure memory within the RFID.
The tag may also have additional access control
based on the presented S
22
/K
128
to provide for
multiple levels of security and write access control.
As part of a more secure key management
strategy the data-user should be considered untrusted
and prevented from generating, reading or viewing
any K
128
. Thus the hardware to generate challenges
should be contained within a secure module within
the reader. As a further anti-counterfeiting measure
it may be desirable that the ID be assigned at time of
manufacture (eg laser etched) to make it more
difficult to create tags with duplicate IDs.
3 SECURITY ANALYSIS
The following analysis examines the measures in the
protocol / system necessary to protect against a
series of attack games (Chatmon et al 2006) within
the security model. The time complexity or
approximate order of each attack is given.
Counterfeit: adversary tries to duplicate tag or
tag’s responses.
• Tag only transmits {B|Y} where Y=E
ID
(A′|B),
A′=E
K
(A|T|S) and B a random determined by the
PRICE TO PROVIDE RFID SECURITY AND PRIVACY?
211

tag, thus response is unique to the challenge so can
only be replicated by a collision O(2
64
).
• Simply respond with a random value and hope it
is correct O(2
64
), however protocol uses repeated
challenges thus diminishing the risk even further.
• Even if ID is known, authentication cannot be
achieved without knowledge of K. Also see
compromise (below).
Absence: adversary tries to authenticate herself to a
reader using a distant valid tag. The radio relay
attack: prevented via tight timing window between
challenge and response, reduces distance over which
attack can be carried out. This is a non cryptographic
threat for which the effective range can be found.
Anonymity: adversary tries to learn private
information (ID) from tag.
• Without K adversary cannot derive A′ (guess at
cost of 2
64
), even with A′, B and Y to find the static
ID must perform a key recovery attack O(>2
64
).
• Data-users can normally only check tags response
against a list of known IDs. Without the ID, has to
perform a brute force attack O(2
128
).
• If the adversary can copy or relay the challenge
from a valid reader then a tag may be stimulated. A
response will leak information on which S the tag
responds to. Depending on how specifically K is
used this may allow formation of a constellation
based ID. This protocol cannot fully prevented by
this attack as authentic signals can be recorded and
replayed later before a tag receives a fresh authentic
time from a legitimate reader. The readers signal can
however be made difficult to record (wide
bandwidth, variable frequency and multiple antennas
to localize the “good signal zone” and provide much
multipath corruption of signal at a safe measuring
distance). This is a non-cryptographic challenge, a
distance bound may be established.
Compromise: adversary tries to recover K from tag
or reader
• Recovery of K will compromise entire system.
Prevented by tamperproof packaging in reader
(trusted module) however both tag and readers-
trusted module must also be secure against side
channel attacks including differential electro-
magnetic analysis, DEMA (Agrawal et al 2003) and
fault injection (Piret and Quisquater 2003). This is
the Achilles heel of symmetric cipher security. It is
mitigated by the following factors: supporting
updates to K, transmitting valid and invalid X’s as
part of protocol (frustrates key recovery analysis
from known CT-PT pairs). Only keeping K in secure
modules in readers and ensuring good testing against
side channel attacks is the defence however the risk
is unquantifiable.
• Reverse engineering: the reader trusted module
can have an internal power source so can detect and
act upon tampering, however, the tag may be
attacked whilst not powered so with access to IC lab
facilities can be physically attacked. Precautions can
be taken to make physical attacks more difficult
however given sufficient time and resources would
be successful. The best protection is the frequent
changing of K to make attack uneconomic. This is
an unquantifiable risk.
• In order to satisfy anonymity K must be generic
however this increases the key’s intrinsic value thus
its probability as target for attack and impact on
compromise. This dilemma forms an intractable
compromise: intrinsic value of K and the impact of
its disclosure versus privacy loss due to constellation
tracking.
Availability: adversary disrupts future transactions
between tag and reader only using earlier interaction
with tag, reader or both.
• Attempt to write wildly inaccurate time (L) into
tag; prevented by authentication signature, X. O(2
64
)
• Deluging server with invalid tag responses for ID
recovery (prevented by multiple valid/invalid
challenges) O(2
64
)
• Hijacking secure session, protected by unique
random key (and detected by checksums/CRC
within command and status packets), brute force
O(2
128
)
• Strictly non-adversarial, however, two IDs giving
collision in Y, multiple challenges (with different
T|A) permit resolution of any ambiguity. O(2
32N
) for
N-challenges. Thus for two challenges O(2
64
).
Totalitarian: legitimate operator of reader attempts
to database information derived from all tags.
• Operator can only recover tags with IDs already
stored in database, alternative is a brute force on
tagID of O(2
128
)
• Lookup time (per challenge) is proportional to no
of entries in database O(Ntags) each requiring a
cipher operation. Tracking at a wider scale requires
O(Ntags×Nchallenges) cipher operations, O(N
2
)
cipher operations per unit time.
• The inclusion of B alone in protocol precludes
pre-computation of Y→ID irrespective of the
readers attempts at cheating, O(2
64
).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Formal assessment of the overall security of any
system can only be carried out on the specific
implementation. Table 1 categorizes the resistance to
specific attacks and relative cost of the tag.
SECRYPT 2008 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
212
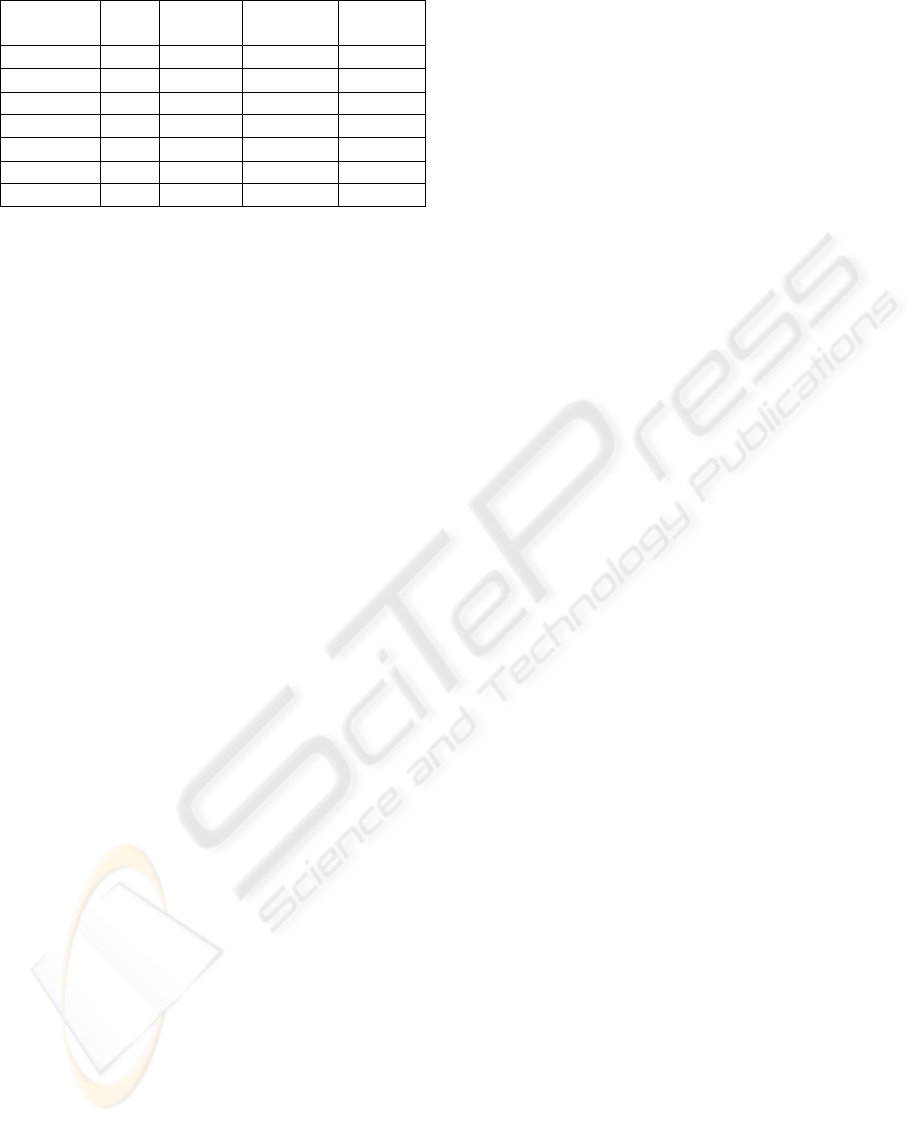
Table 1: Resistance to the various attack games.
Attacks Static
ID
Refreshed
ID
Asymmetric Symmetric
(PRICE)
counterfeit low high high high
absence low low low high
anonymity low med. low high
compromise n/a n/a medium* low*
availability high low high high
totalitarian low low low high
tag cost cheap moderate high moderate
* Reverse engineering and side channel remain very real threats.
Even the best refreshed-ID scheme, which by
definition must not possess a shared secret cannot
then authenticate the reader thus must be vulnerable
to DoS attack.
The PRICE protocol shows good resistance to a
number of attacks with a theoretical security of 64-
bits (2
64
) however is at unknown risk from
compromise of K through reverse engineering or
unanticipated side channel leakage of any particular
implementation. Proving side channel resistance and
assessing the difficulty in reverse engineering are
both still open problems.
The requirement in the protocol to perform
encryption operations to recover the tag’s ID
mitigates against the formation of large databases.
The wider scale ID tracking game is O(N
2
), a
computational complexity which provides improved
privacy.
With PRICE, the security measures needed in the
tag only requires a single encryption primitive
together with some non-volatile storage. As lower
resource strong ciphers primitives become available
then the price in terms of area will be further
reduced. An asymmetric scheme would limit the
impact of compromise however implementation of a
secure asymmetric crypto primitive on a RFID tag is
(currently) too costly in terms of area and response
time.
From a practical perspective, RFID is a
balancing act between conflicting requirements of
utility, privacy and cost. It is hoped that this paper
will provoke further research in the area of RFID
security and privacy.
REFERENCES
Agrawal, D., Archambeault, B. , Rao, J., and Rohatgi, P.,
The EM side-channel(s): Attacks and Assessment
Methodologies, CHES 2002, San Francisco, LNCS
2523, pp 29–45, Springer, 2003.
Chatmon, C., Le, T.v., and Burmester, M., Secure
anonymous RFID authentication protocols. Technical
Report TR-060112, Florida State University, Dept of
Computer Science, Tallahassee, Florida, USA, 2006.
Dimitriou, T., A Lightweight RFID Protocol to protect
against Traceability and Cloning attacks. In IEEE
SecureComm05, Sept 5-9, Athens, Greece, Sept 2005.
Dominikus, S., Oswald, E., and Feldhofer, M., Symmetric
authentication for RFID systems in practice. ECRYPT
Workshop on RFID and Lightweight Crypto, Graz,
Austria, July 14-15, 2005.
Engberg, S., Harning, M., and Damsgaard-Jensen, C.,
Zero-knowledge device authentication: Privacy &
security enhanced RFID preserving business value
and consumer convenience, Conf. on Privacy, Security
and Trust – PST, New Brunswick, Canada, Oct. 2004.
Garfinkel, S.L., Juels, A., and Pappu, R., RFID Privacy:
An Overview of Problems and Proposed Solutions. In
IEEE Security & Privacy May/June 2005.
Good, T., and Benaissa, M., Hardware performance of
eStream phase-III stream cipher candidates. At SASC
2008 conference, Lausanne, Feb 2008, available
www.ecrypt.eu.org/stvl/sasc2008
Juels, A., RFID Security and Privacy: A Research Survey.
In IEEE J. on Selected Areas in Communications, vol.
24 no. 2, pp 381–394, invited paper, Feb 2006.
Kfir, Z., and Wool, A., Picking virtual pockets using relay
attacks on contactless smartcard systems. available at
http://eprint.iacr.org/2005/052, 2005.
Lehtonen, M., Staake, T., Michahelles, F., and Fleisch, E.,
From Identification to Authentication – A Review of
RFID Product Authentication Techniques, RFIDsec06,
Graz Austria, July 2006.
Lockton, V., and Rosenberg, R. S., RFID: The next
serious threat to privacy. In Ethics and Information
Technology 7:221–231, Springer, 2006.
Molnar, D., Soppera, A., and Wagner, D., Privacy for
RFID through trusted computing. in Proc. Workshop
on Privacy in the Electron. Soc., 2005.
Peris-Lopez, P., Hernandez-Castro, J.C., Tapiador, J.M.
E., and Ribagorda, A., LMAP: A Real Lightweight
Mutual Authentication Protocol for Low-cost RFID
tags. RFIDsec06, Graz Austria, July 2006.
Peslak, A.R., An Ethical Exploration of Privacy and Radio
Frequency Identification. In Journal of Business
Ethics 59: 327–345, Springer, 2005.
Piret, G., and Quisquater, J-J., A Differential Fault Attack
Technique against SPN Structures, with Application to
the AES and Khazad. CHES 2003, Cologne, Germany,
LNCS 2779, pp 77–88, Springer, 2003.
Tsudik, G., YA-TRAP: Yet Another Trivial RFID
Authentication Protocol, IEEE Intl. conf. on Pervasive
Computing and Communications, Pisa, March 2006.
Weis, S.A., Sarma, S.E., Rivest, R.L., and Engels, D.W.,
Security and Privacy Aspects of Low-Cost Radio
Frequency Identification Systems. In Security in
Pervasive Computing 2003, LNCS, vol. 2802, pp 201–
212, Springer, 2004.
Yang, J., Park, J., Lee, H., Ren, K., and Kim, K., Mutual
Authentication Protocol for Low-cost RFID, ECRYPT
Workshop on RFID and Lightweight Crypto, Graz,
Austria, July 14-15, 2005.
PRICE TO PROVIDE RFID SECURITY AND PRIVACY?
213
