
CREATING A LOC BASED PORTABLE
HEALTH-CARE PLATFORM
Using a Universal Mobile NFC Host Environment
Babak Akhgar, Fazilatur Rahman, Lukasz Jopek, Jawed I. Siddiqi, Sally Atkinson
Alberto Savoldelli, Doris Prato, Secondo Montrucchio, Federico Guella
Sheffield Hallam University, Howard Street, S1 1WB, Sheffield, U.K.
Brian James, Mike Pinkerton
Rotherham NHS Foundation Trust, Rotherham, S60 2UD U.K.
András Vilmos
SafePay Systems Ltd. Budapest, Hungary
Keywords: Lab-On-Chip (LOC), Micro-Array, Mobile, NFC.
Abstract: This paper presents our recent plan to provide support for a portable diagnostic health care platform (namely
POCEMON) based on Lab-On-Chip (LOC) concept. The idea is based on our achievements on creating a
host environment that combines mobile phones/PDAs with the Near Field Communication (NFC) wireless
technology to further support mobile diagnostic health care applications. NFC enabled mobile phone based
host environment works as a reference platform regardless of the phone type and the nature of the services
required. In connection to this, we will describe further insights on how this cutting edge technology may be
leveraged in the health care sector providing efficient point-of-care monitoring and diagnosis.
1 COMBINING LOC AND NFC
FOR MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS
Use of miniaturized devices in molecular diagnostics
has gained wide spread popularity. The detection of
genomic and proteomic sequences has diagnostic
and large prognostic value. This impact can be easily
enhanced by using diagnostic lab-on-a-chip (LOC)
devices at the primary care level for the diagnosis of
the significant autoimmune disorders. Lab-on-Chip
(LOC) refers to a single chip miniature device that
performs biological procedures in analytical
chemistry enabling fast response and portable, low
cost analysis data suitable for real-time operating
conditions for a wide variety of health and life
science applications such as the diagnosis of genetic
disorders or the testing of food and water supplies
for contamination etc (Ghafar-Zadeh and Sawan,
2008; http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lab-on-a-chip).
Such devices integrate fluid-handling functions such
as sample preparation, analysis, separation, and
detection and combines electronics with biology to
open new application areas such as point-of-care
diagnosis, on-chip DNA analysis, and automated
drug discovery (Hwang et al., 2006).
POCEMON (Personal Health Systems for
Monitoring and Point-of-Care Diagnostics) is an
ICT-Large Scale Integrating project that will have
great impact on the methodologies available for both
autoimmune diseases and drug discovery and
consequently impact on the scope and throughput of
new pharmaceutical developments. POCEMON
aims to create a portable diagnostic platform
supplied with advanced software and hardware
technologies for the diagnosis of autoimmune
diseases, coupling fundamental bioinformatics
sciences with technological advances in the fields of
micromachining and micro-fabrication of silicon
chips will lead to a lab-on-a-chip (LOC) for large-
scale diagnosis of autoimmune disorders.
38
Akhgar B., Rahman F., Jopek L., I. Siddiqi J., Atkinson S., Savoldelli A., Prato D., Montrucchio S., Guella F., James B., Pinkerton M. and Vilmos A. (2009).
CREATING A LOC BASED PORTABLE HEALTH-CARE PLATFORM - Using a Universal Mobile NFC Host Environment
.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics, pages 38-42
DOI: 10.5220/0001542300380042
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Near Field Communication (NFC) technology
has gained interest among the business community
and has attracted researchers to overcome
interoperability, infrastructural issues as well as
creating new business cases. At present there is no
common secured communication infrastructure over
which interested parties from diverse domains and
actors can play their role with confidence in terms of
security and trust. To encounter these problems,
‘Store Logistics and Payment with NFC’ (StoLPaN)
is a European project that has defined open
commercial and technical frameworks for NFC-
enabled services on mobile devices and hence
creates a universal environment that will facilitate
the deployment of NFC-enabled mobile applications
across a wide range of vertical markets, regardless of
the mobile device type and the nature of the services
required. The host environment also promotes the
deployment of NFC-enabled mobile applications in
many diverse application domains.
In this paper, we outline the applicability of LOC
and mobile NFC in the diagnosis of health but
particularly focusing on the insights leveraged
through the proposed the universal NFC based host
environment to deploy LOC functionalities and
major innovations of the proposed plan.
2 PORTABLE HEALTH CARE
DIAGNOSTIC PLATFORM
2.1 Identification of the Problem:
Application of Mobile NFC
An NFC device with an internal power supply is
considered active. A device with no internal power
supply, such as a smart card, is considered passive
and. Inductive coupling causes a passive device to
absorb energy from an active device when it gets
close enough. Once powered up, the passive device
can communicate and exchange data with the other
device. The ability of NFC devices to work as both
passive and active enables them to function as either
contact-less cards or readers (Ortiz, 2006; Leong et
al., 2006). Near Field Communication or NFC
technology can be used in various health care
applications as a robust way of gathering, processing
and automating the process of e.g. reminding
patients when it is time to take their prescribed
drugs, based on the prescriptions provided by
pharmacy (http://www.nfcnews.com/articles/2008/
01/28/nfc-competiton-winners-announced).
Moreover, NFC-enabled devices can be used for off-
line monitoring of heart rates, glucose or blood
pressure (http://www.parksassociates.com/
digitalhealth/research/report3.htm). Other application
areas would be in making our environment
friendlier, which applies mainly to disabled persons.
NFC-enabled mobile platforms are rapidly
evolving, getting into our daily activities and are in
general interests of ordinary people. Common
mobile technology used with inexpensive easily
available tags, and soon possibly sensors as well,
makes the functionality widely available.
Networked medical devices will enable to
provide healthcare where constantly gathered and
analyzed information enables to protect patients
continuously with ad hoc decision support system.
Furthermore, NFC-enabled health monitoring and
diagnostic platform will create new opportunities for
the medical health care, but as well for the whole
medical device industry. In addition, some of
treatments will require no more regular doctor visits
and should be achievable by integration of different
NFC-enabled devices.
Besides, health measurements devices can
support self-care (Kaasinen, 2005), which could help
societies to deal with illnesses caused by unhealthy
living. For example, many of health problems might
be related to overweight and in number of cases
implementation of self-motivation system that
stimulates efforts or eating healthy food could
possibly solve, or at least marginalize the problem.
Monitoring and presentation of analyzed data with
goals matching could give feedback that will enable
people to consciously keep fit and healthy.
2.2 Towards a Solution: An NFC Host
Environment
In order to accurately address the interoperability
issues currently affecting the mobile NFC
technology, various usage cases are to be defined
within the StoLPaN framework and tested
throughout Europe. These use cases will contribute
to the identification of a common set of business
rules, which will define the roles and responsibilities
of every player in the NFC ecosystem. The results
will then be submitted for approval to the relevant
industry bodies for standardization of payments,
mobile, transit and ticketing as well LOC
applications.
Based on these findings, the consortium will
look into the specifications for technical
requirements and the security aspects of NFC-
enabled applications. They will also explore the
connection to existing contact-less platforms, easing
CREATING A LOC BASED PORTABLE HEALTH-CARE PLATFORM - Using a Universal Mobile NFC Host
Environment
39

the burden on individual providers. At the same time
the project team will demonstrate how the business
rules and technical requirements can be
implemented in existing contact-less infrastructures.
A NFC host application will be developed to support
a range of services, including payment, access
control, ticketing, loyalty, connectivity, and the
retail check-out process; which consumers will be
able to use with any NFC-enabled device.
The host environment developed under StoLPaN
project demonstrates a universal mobile J2ME host
application that will provide transparent uniform
operating environment in the mobile handsets for the
selected (and potentially other) NFC applications
neutralizing specifics of the handset design and
taking care of resource management.
The application will on the one hand, hide the
specifics of the various mobile handsets – different
manufacturers, different operational specifics,
different versions, etc – and will on the other hand
provide all the necessary resources and features –
communication access, security solutions, etc.- that
were identified during the technical analyses for the
individual NFC use cases. There will be one generic
version of J2ME host application to be run on any
selected mobile handset models.
Remote deactivation of unsorted multiple smart
tags without interfering with the user functionality,
but at the same time providing adequate security
protection for the smooth user operation as well
have been addresses by StoLPaN initiative.
Specification of a new J2ME host for NFC
business applications handles the basic technology
and also provides a general operating environment
for the various business instruments that may
individually be integrated into the application. The
output of this research will have to be presented for
future standardization, otherwise handset
independence is hard to realize. The same
application would provide the operating
environment for the NFC purse, establish the
necessary connection between the handset’s
resources and the chip. This solution most probably
will be based on the extension of the general NFC
Java API.
Establishment of secure bidirectional
transmission between wireless channels and NFC
chip where the mobile purse can be recharged over
the air it must be ensured that secure communication
can be established between the wireless channels
and the NFC chip. The same functionality and
technology is necessitated for the remote
management of the various NFC applications that
can be stored in the mobile host environment.
Similar is the requirement in case when the mobile
handset acts as payment terminal, where the secure
communication between the chip and the wireless
channels is required into the other direction.
Creating secure NFC chip-to-chip
communication for P2Pby a useful extension may be
the elaboration of the technology that ensures secure
chip-to-chip communication to facilitate direct
purse-to-purse payment. This work does not only
involve technical research, but has an operational
and security aspect as well, as the applied
technology must be supported with adequate
operation and fraud prevention.
2.3 Proposed Platform Combining
POCEMON and StoLPaN
This The POCEMON platform has been aimed to develop
a portable monitoring system for auto immune diseases
such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and multiple sclerosis
(MS) (http://www.rheumatoid.org.uk/index.php?page_id
=36; http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=10031
&page=17).
Health authorities aim to provide patients with
personalised diagnosis and treatments, driven by
state of the art diagnostic and communication
technologies. The system is based on Lab-on-Chip
(LOC) technologies that use microarray genotyping
and microelectronics to carry out diagnostic testing
at the primary healthcare level. The system provides
rapid diagnosis via mobile diagnostic devices and
wireless communications. Basically, it uses LOC
technology to allow rapid DNA analysis from small
quantities of blood/saliva. The chip functions by
increasing the quantity of sample via replication of
the patients' DNA, followed by hybridisation of the
patients' DNA with a microarray of characteristic
autoimmune disease gene templates. The microarray
scanning and recording of genotyping results are
controlled through the PDA via a multipurpose LOC
adapter.
Figure 1: POCEMON Operation.
HEALTHINF 2009 - International Conference on Health Informatics
40
The genotyping data generated by the LOC are
assessed using intelligent algorithms linked with the
laboratory information system to provide detailed
diagnosis and medical treatment advice. This
process functions through the LOC's integration with
mobile devices and communication with the
laboratory information system via wireless
communications.
Recent research efforts suggest the high-
potential of NFC technology for short-range
connectivity between health monitoring devices and
mobile terminals and data stores propose practices to
apply NFC to some health monitoring applications
and study the benefits that are attainable with NFC.
The value of these is significant, especially in long-
term diagnostic analysis and in chronic disease
management. From the usability point of view,
wireless communication links are preferable to
cables because they facilitate measurements and
management of diagnostic analysis at real-life
settings (Strommer et al., 2006).
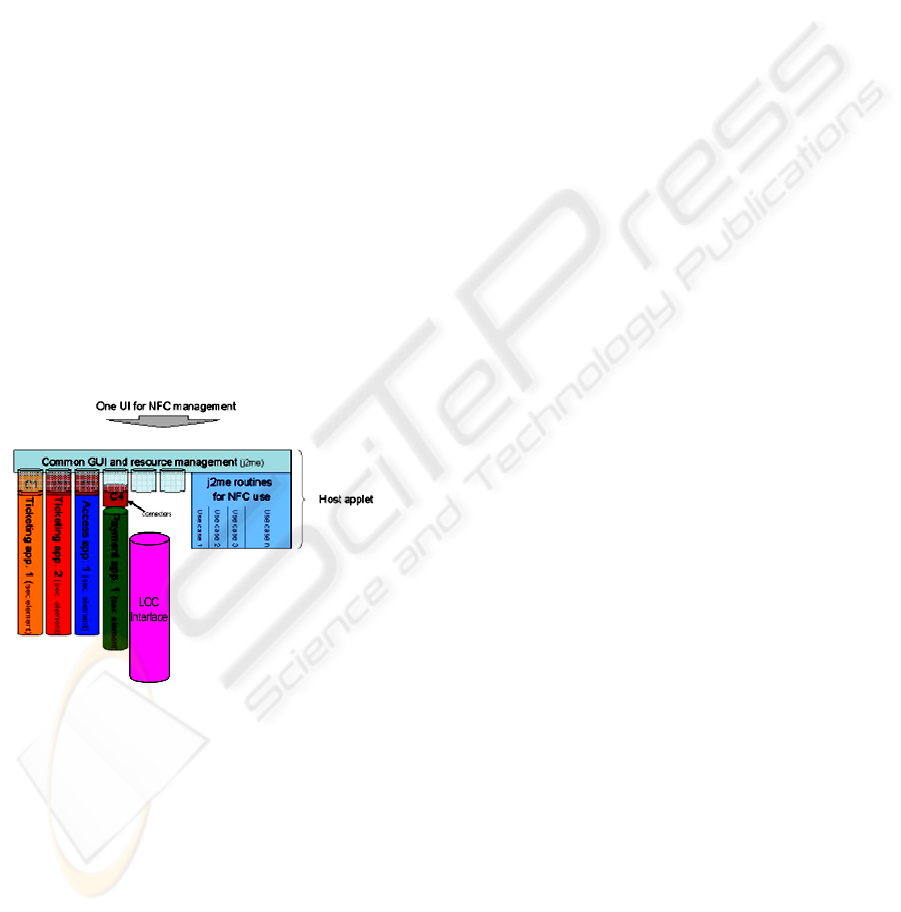
The StoLPaN host application (Benyo et al.,
2007) allows the collaboration among the diverse
applications, diverse service providers, diverse
network operators and the diverse of type of mobile
devices.
Figure 2: StoLPaN Host Environment.
The host is able to support multiple NFC
services, provide access to the phone's resources and
facilitates the loading, use, maintenance and deletion
of third party NFC enabled applications via common
API between the third party application and the
mobile device's, common API between the service
provider and the third party's application
provisioning Platform, simplifying validation of
adherence to their service level agreements. Besides
a common User Interface for applications loaded
into the Secure Element or the host's JAVA storage,
providing value added features to existing contact-
less services. It will simplify the learning curve
associated with any new application.
3 INNOVATIONS OF THE
PROPOSED APPROACH
Major POCEMON objectives directly arises by the
integration of multi-technology sets that underlie
new functionalities, services and applications
sufficient enough to provide portable and mobile
ICT systems which facilitate point-of-care diagnosis
at the primary care level. Also, new diagnostic
software will be developed for PDA/Mobile devices
making this technology more attractive to primary
care and allowing future mobile devices to be used
for health monitoring, even at home (connected any
time, anywhere and to many services). The
development of the diagnostic Lab-on-Chip device
will lead to innovative technological achievements
which will strength European microelectronics
industry offering smaller systems, cheaper, smarter
and friendlier.
The main part for the point-of-care diagnosis of
autoimmune diseases is based on the development of
the appropriate software capable to perform
automated micro-array analysis to measure the genes
expression. The software will be implemented for
desktop workstations and for PDAs.
Image processing is an important part of every
micro-array experiment. Reliability of this part
strongly influences the results of data analysis
performed on extracted gene expressions. The image
analysis functions will use the filenames and the red
and green channels of the spotted images. The main
image analysis software will be developed using
Contrast enhancement, Sub-array extraction,
Dilation and erosion, Extraction of individual spots,
and Information extraction.
Also, communication software will be developed
both for information exchange and data transmission
between the PDA/Mobile Device and LOC as well
PDA/Mobile Device and the desktop station
(Laboratry Information Server - LIS) which will be
accommodated in a laboratory of a large medical
centre. The communication will be mainly wireless
(except for large-distance primary care diagnostic
point-of-care places) using the well established
internet communications protocols and the data will
be transmitted securely in a private network.
All these procedures will be developed as
standalone software that will interact with the LOC
from the PDA/mobile device. The detailed version
CREATING A LOC BASED PORTABLE HEALTH-CARE PLATFORM - Using a Universal Mobile NFC Host
Environment
41

of the automatic micro-array image analysis
software and the diagnosis extraction mechanisms
will be hosted on the LIS. Also the desktop station
software will be capable to provide treatment
advices for autoimmune diseases and the knowledge
will be extracted by combining all the stored gene
data. In order to allow new diagnostic tests to be
performed and new decision rules to be applied the
PDA software and the cards will be able to change.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, the NFC host environment provides a
seamless interface for analyzing LOC data, without
requiring any detail handling of hardware/software
interface issue. As a result the thorough research
carried out under POCEMON will be facilitated
from StoLPaN environment that will provide the
delivery of mobile information services in the
professional primary care environment, and to
present solutions for providing decision support
information on small, portable or wearable
platforms. The main objective of providing mobile
devices packaged with relevant high-quality
software tools for health-practitioners in the near
future will accelerate the establishment of
interoperability standards and secure communication
of health diagnostic data between all involved
partners of the project, including patients.
REFERENCES
GSM Association aims for global mobile payments using
NFC Card Technology Today, Volume 19, Issue
2, February 2007, Pages 1, 3
Ondrus, Jan; Pigneur, Yves. An Assessment of NFC for
Future Mobile Payment Systems. International
Conference on the Management of Mobile Business,
2007. ICMB 2007. 9-11 July 2007 Page(s):43 - 43
Ortiz, S., Jr. Is near-field communication close to success?
Computer, Volume 39, Issue 3, March 2006
Page(s):18- 20
Leong, C.Y.; Ong, K.C.; Tan, K.K.; Gan, O.P. Near Field
Communication and Bluetooth Bridge System for
Mobile Commerce. IEEE International Conference on
Industrial Informatics, 2006. Aug. 2006 Page(s):50 -
55
Ebrahim Ghafar-Zadeh and Mohamad Sawan. A Core-
CBCM Sigma Delta Capacitive Sensor Array
Dedicated to Lab-on-Chip Applications. Sensors and
Actuators A: Physical, In Press, Accepted
Manuscript, Available online 2 March 2008
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lab-on-a-chip
http://www.assaabloyfuturelab.com/FutureLab/Templates/
Page2Cols.aspx?id=1907
Strommer, E.; Kaartinen, J.; Parkka, J.; Ylisaukko-oja, A.;
Korhonen, I.;Application of Near Field
Communication for Health Monitoring in Daily Life.
International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Society, 2006. EMBS '06. 28th
Annual . Aug. 2006 Page(s):3246 - 3249
Benyo, B.; Vilmos, A.; Kovacs, K.; Kutor, L. The Design
of NFC Based Applications. 11th International
Conference on Intelligent Engineering Systems, June
29 2007-July 1 2007 Page(s):277 - 280
William L. Hwang, Fei Su, Krishnendu Chakrabarty.
Automated design of pin-constrained digital
microfluidic arrays for lab-on-a-chip applications.
DAC '06: Proceedings of the 43rd annual conference
on Design automation. July 2006
http://www.nfcnews.com/articles/2008/01/28/nfc-
competiton-winners-announced
http://www.parksassociates.com/digitalhealth/research/rep
ort3.htm
Eija Kaasinen, Timo Tuomisto & Pasi Välkkynen,
(October 2005) Ambient Functionality – Use Cases
http://www.rheumatoid.org.uk/index.php?page_id=36
http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=10031&pag
e=17
HEALTHINF 2009 - International Conference on Health Informatics
42
