
SEMANTIC FRAMEWORK FOR INFORMATION
INTEGRATION
Using Service-oriented Analysis and Design
Prima Gustiené
Department of Information Systems, Karlstad University, 651 88 Karlstad, Sweden
Irina Peltomaa, Heli Helaakoski
VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, P.O. Box 3, 92101 Raahe, Finland
Keywords: Service-oriented analysis and design, Enterprise modelling, Information integration, Semantic technologies.
Abstract: Today’s dynamic markets demand from companies’ new ways of thinking, adaptation of new technologies
and more flexible production. These business drivers can be met effectively and efficiently only if people
and enterprise resources, such as information systems collaborate together. The gap between organizational
business aspects and information technology causes problems for companies to reach their goals.
Information systems have increasingly important role in realization of business processes demands which
leads to demand of close interaction and understanding between organizational and technical components. It
is critical for enterprise interoperability, where semantic integration of information and technology is the
prerequisite for successful collaboration. The paper presents a new semantic framework for better quality of
semantic interoperability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today’s rapid changes in markets force companies
to produce their products with better quality and
more flexibly, which results in necessity for
introduction of new technological solutions. The role
of information systems, as support for realization of
business process demands, becomes of great
importance. Traditionally there is a gap between two
communities; business administration professionals
and information technology experts. Business people
tend to consider technological issues as a
subordinate aspect in business process and
technology experts consider that business goals
issues do not deserve much attention (Weske, 2007).
As goals stated by business experts at the
organizational level should fit with the outputs from
implementation, it is necessary that all partners
involved have a common understanding of both
organizational and technical aspects. Growing
business enables growing of data. The business will
suffer service disruptions if there is no strategy how
to manage relevant information.
The fundamental problem with conventional
methods for information system development is that
they do not take into account some important
semantic interdependency types between static and
dynamic models, which are crucial for gluing
strategic, organizational and technical descriptions
into one computation independent and integrated
representation (Gustas and Gustiené, 2007). There is
a lack of integrated models and systematic methods
to support business process modelling across
organizational and technical system boundaries.
Semantic problems of communication between
business analysis and design experts lead to
ambiguous and incomplete system requirement
specifications as well as causes enterprise
interoperability problems (Sarjanoja et al., 2008).
In business modelling is an important to
determine how an information system contributes to
the objectives of the organization (Bennett, 2002).
Traditionally graphical representations of enterprise
architectures are constructed fragmentally and not
aligned with information system design. It causes
difficulties to maintain semantic integrity of multiple
enterprise architectural specifications (Gustas and
64
Gustiené P., Peltomaa I. and Helaakoski H. (2009).
SEMANTIC FRAMEWORK FOR INFORMATION INTEGRATION - Using Service-oriented Analysis and Design.
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Databases and Information Systems Integration, pages 64-69
DOI: 10.5220/0001950800640069
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Gustiené, 2008). The success of enterprise
interoperability much depends on how static (data)
and dynamic aspects of enterprises are integrated.
This integration enables preservation of the meaning
of information about the context (Sarjanoja et al.,
2008). The description of integrated service
architectures should be established before
implementation specific solutions are discussed.
The paper proposes an extended framework for
improving semantic quality of business processes
using service-oriented approach. It enables
integration of static and dynamic aspects of business
processes, facilitates information integration across
organizational boundaries and provides possibilities
to check consistency and completeness as well as to
track undesirable system qualities (Gustas and
Gustiené, 2004; Gustiené, 2003).
2 SEMANTIC ISSUES
Semantics i.e. study of meaning is the central part of
communication. We have to understand the meaning
of the message unambiguously in order to reach a
successful communication. Ambiguity is one of the
deficiencies of the natural and system modelling
languages, it causes misunderstanding. Ambiguity of
concepts in system modelling may occur because a
construct, formal expression or natural language
sentence has more than one meaning (Dori, 2002),
or because of incompleteness or inconsistency of
conceptual models.
Ontology captures consensual knowledge in a
generic way to be reused and shared across software
applications and by groups of people (Gomez-Perez
et al., 2005; Gruber, 1995). It defines a common
vocabulary for information sharing in a domain
(Noy and McGuinness, 2001; Uschold and
Gruninger, 1996). Creation of a business ontology
which is describing the semantics of the essential
concepts of company will offer better possibilities
for unified process management and system
interoperability. Through business ontologies it is
possible to view an integrated view of company’s
data (Pollock and Hodgson, 2004).
The most important issue in information system
development is how to manage its complexity.
According to Dietz (Dietz, 2006), complexity can
only be mastered under two conditions: to have a
comprehensive theory about the things whose
complexity one wants to master and the other
condition is that there are appropriate analysis
methods and models based on that theory. To
manage complexity it is necessary to have an
integrated method and a coherent, comprehensive,
consistent and concise conceptual model of the
enterprise. Semantic interoperability can be ensured
by providing contextual knowledge of domain
applications (Ram and Park, 2004). Interoperability
is comprised of both technical integration and
information integration (Peltomaa et al., 2008). The
main technical challenge is the lack of
interoperability of different systems and data sources
thus most of the current solutions are focused only
on technical integration, to link disparate software
systems to become part of a larger system.
Information integration is enabled by semantic
interoperability that emphasizes the importance of
information inside enterprises and focuses on
enabling content, data, and information to
interoperate with software systems outside their
origin (Pollock and Hodgson, 2004).Yet any
moderately complex integration work requires both
technical and information integration.
The semantic interoperability research has
categorized three broad research areas: mapping-
based, intermediary-based, and query-oriented
approaches (Park and Ram, 2004). Mapping-based
approach attempts to construct mappings between
semantically related information sources while the
intermediary-based approach may also rely on
mapping knowledge established between a common
ontology and local schemas. Query-oriented
approach is focused on interoperable languages
which can be used for formulating queries over
several databases.
Semantic architectures for information
integration are divided within the methodologies
into three groups which are one-to-one mapping,
single shared ontology and ontology clustering
(Alexiev et al., 2005). These methodologies use
differently global ontology together with local
ontology. Either local ontologies are used alone
(one-to-one paradigm), or a global ontology exists
either without (single-shared ontology) or with local
ontologies (mix of single-shared and one-to-one
mapping) (Alexiev et al., 2005; Bruijn and Feier,
2005).
3 SEMANTIC FRAMEWORK
Enterprises need more effective way to manage
information related to their business. The
management of information includes communication
between personnel and the integration of
information in separate information systems.
SEMANTIC FRAMEWORK FOR INFORMATION INTEGRATION - Using Service-oriented Analysis and Design
65
The ambition of service orientation is to provide
system designers with a constructive way of
integrating business as a set of linked services. It is a
way of designing an integrated business process as a
set of loosely coupled services. Service architectures
can be used for specifications of business processes
in terms of organizational and technical services
(Gustas and Gustiené 2007; Gustas and Gustiené,
2008).
Mappings
Pragmatic level
Semantic level SOAD
Service-oriented approach presented for analysis
and design process (SOAD) (Gustas and Gustiené
2007; Gustas and Gustiené, 2008; Gustiené and
Gustas, 2008) has semantic power to conceptualize
organizational and technical system components, by
distinguishing intersubjective and objective views,
that facilitates better semantic integrity control
between static and dynamic aspects. The advantage
of such modelling is that it integrates semantics of
different aspects in one type of diagram. Conceptual
representation of service architectures define
computation independent aspects that are not
influenced by any implementation solutions and are
more comprehensible for business people as well as
system designers.
Sebi-framework (Peltomaa et al., 2008) defines
framework for information integration using
semantic technologies. Interoperability between
separate information systems is achieved by
developing a shared information model for the
information. Different views of information are
available for other information systems or humans
through shared information model which can be
called integration ontology.
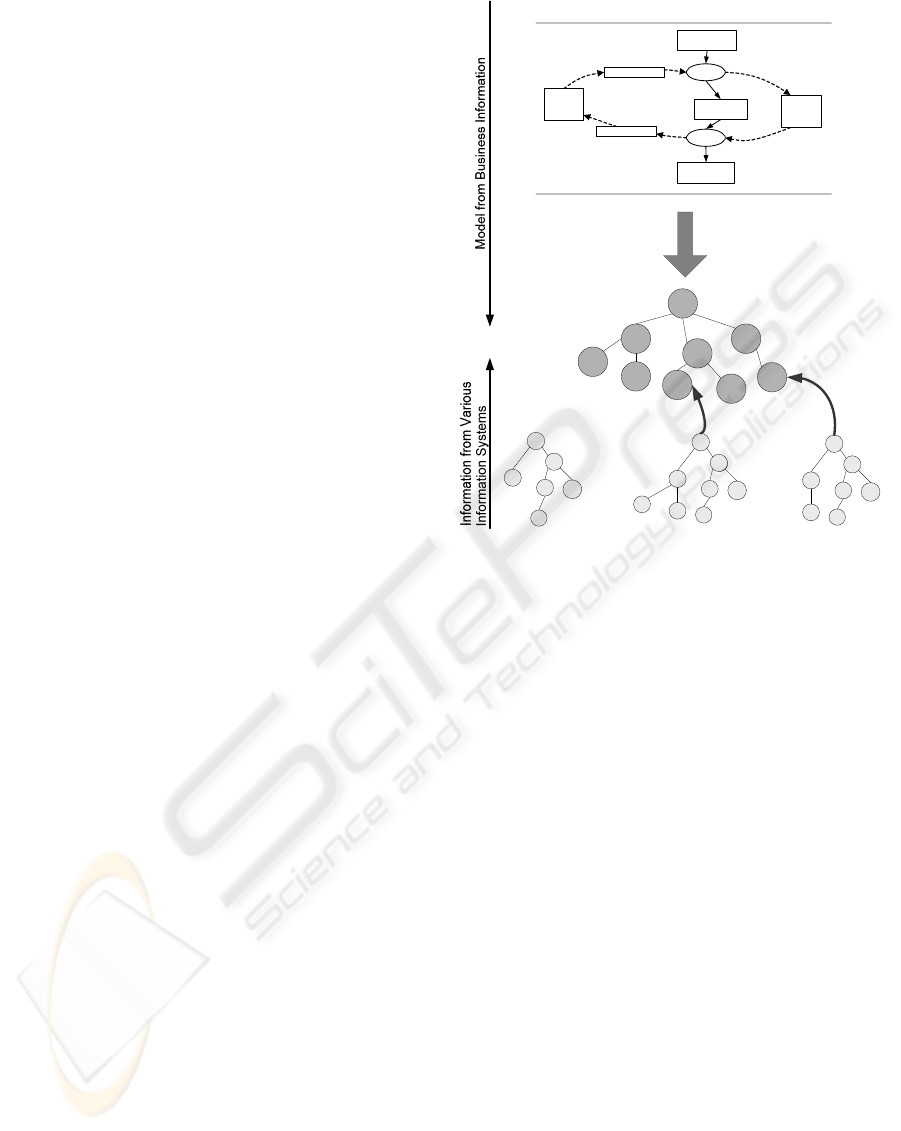
In figure 1 proposition of combining these two
approaches is presented. The most important part of
the Sebi-framework is the development of
integration ontology, which is developed in close
collaboration with business experts to determine
correct concepts and their relationships. As a method
for integration ontology development Sebi-process
(Sarjanoja et al, 2008) is used. Completing Sebi-
process with SOAD the process of business
modelling is included in the framework and more
accurate integration ontology can be developed.
Integration is implemented by connecting concept
models formed from information in separate
information systems to the developed integration
ontology using mappings.
Extension of Sebi-framework with SOAD
approach will contribute to a better quality of
semantic interoperability, because this approach has
more semantic power in comparison with other
methods, to identify and control undesirable
semantic characteristics such as inconsistency and
incompleteness that lowers the quality of data.
Various
concept models
Syntactic level
Integration
ontology
igure 1: An extension of Sebi-framework with SOAD to
Being computation neutral service-oriented
ana
4 ANALYSIS
The primary goal of Service-Oriented Architecture
l system
com
F
ensure a better quality of semantic interoperability.
lysis facilitates better involvement of
stakeholders without deep technical knowledge in
the area of information system. In the following
chapters the components of this approach are
introduced more closely.
(SOA) is to align the business design with the
information technology (IT) innovations in order to
make both organizational and technical system parts
more effective (Gustas and Gustiené, 2007).
Business and IT solutions can be expressed using
graphical representations of Enterprise Architecture
that provides possibilities to understand and
determine the continual needs for changes.
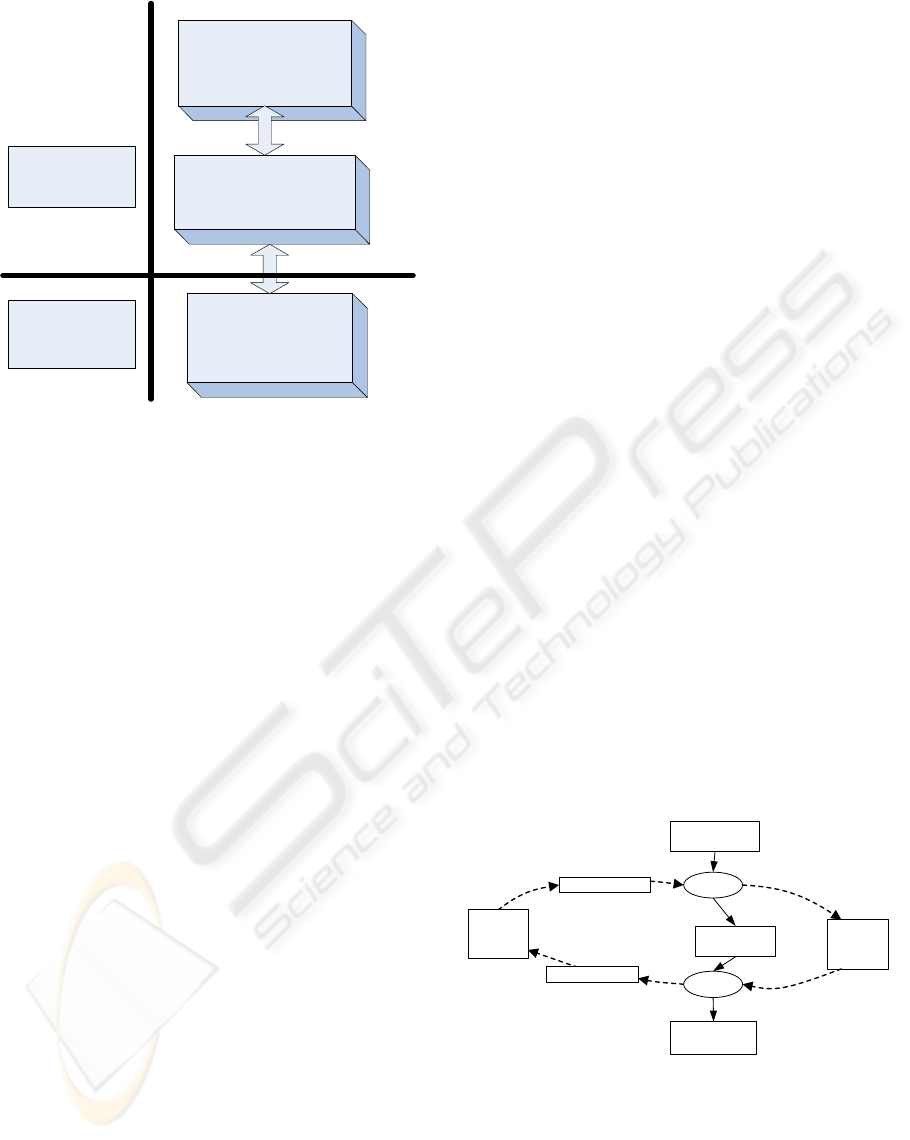
To understand how and why technica
ponents are useful and fit to the overall
organizational system, then at least three levels of
information system models are necessary to take into
consideration for maintenance of a systematic
change. Three levels are represented in Figure 2.
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
66
Pragmatic Level
Business-Oriented
Analysis
Semantic Level
Service-Oriented
Analysis
Syntactic Level
Technology-
Oriented Analysis
Computation
Independent
Modeling (CIM)
Computation
Dependent
Modeling (CDM)
Figure 2: Three levels of Enterprise.
Pragmatic level is the businesses-oriented
analysis level, which is the most abstract one. This
level provides motivation behind new business
solutions. Goals stated at this level will be specified
further at semantic level. These specifications drive
and guide the activities at the semantic level.
At semantic level service-oriented analysis is
done. This level has capacity to describe clearly
static and dynamic structures of business processes
across organizational and technical system
boundaries. At this level semantic dependencies are
used for conceptual modelling, which provide
possibility to identify and overcome such
undesirable system characteristics as inconsistency,
incompleteness, redundancy of data, ambiguity and
incoherence (Gustas and Gustiené, 2004; Gustiené,
2003).
At syntactic level technology-oriented analysis is
done. This level defines implementation-oriented
details, which explain the data processing need of a
specific application or software component.
All three levels are interrelated as they define the
same artefact. The framework of three levels
provides the natural view to understand the
modelling artefact as a whole. It provides with a way
for semantic traceability via all three levels and
enables interplay between business needs and
technical solutions.
One of the advantage of the concept of service is
that it can be applied equally well to the
organizational as well as software components
which can be viewed as service requester and
service provider. Enterprise system can be defined
as a set of interacting loosely connected
components, which are able to perform specific
services on request.
Conceptual representations of service
architecture are defined by using one or more
interaction loops between enterprise actors that can
be viewed as organizational or technical
components. Modelling method using service as an
interaction loop or a composition of loops provides
the holistic view of an enterprise as a system.
The core elements of the service-oriented
modelling are actors, communication flows, and
actions. Actors (service requesters or service
providers) are the active elements of an enterprise,
the ones who initiates the actions. The structure of a
service as an interaction loop could be defined by
five phases or steps necessary for modelling of
service structure. They are as following:
1. Identification of interaction flows
2. Identification of actions
3. Identification of transition dependencies
4. Identification of attribute dependencies
5. Semantic integration
Identification of interaction flows and actions
represent intersubjective perspective of the
communication action, which is represented by
interaction dependency link. Identification of
transitions and attribute dependencies define the
objective perspective. It defines the state changes
that objects overcome when actions take place
(Gustas and Gustiené, 2008). Modelling of data can
not be done separately from process. These steps are
important for integration of static and dynamic
aspects, which facilitate reasoning and define the
holistic understanding of enterprise architecture.
Pre-condition
Object Class
Service
Provider
Service request
Service
request
Service
Requester
Intermediate
Object Class
Service response
Service
response
Post-condition
Object Class
Figure 3: Example of .
Service-oriented constructs used for service-
orie
one interaction loop
nted modelling is based on three events:
creation, termination and reclassification events
(Gustiené and Gustas, 2008). Composition of three
types of basic constructs provides possibility to
conceptualize the lifecycle of objects in a service
SEMANTIC FRAMEWORK FOR INFORMATION INTEGRATION - Using Service-oriented Analysis and Design
67

interaction loop. Objects define the data from
business environment which is necessary to integrate
and which is critical for forming an integrated
ontology. The example is represented in Figure 3.
Intersubjective and objective perspectives are
imp
5 SEBI-FRAMEWORK
The Sebi-framework (Peltomaa et al., 2008) uses
tegration ontology is the most
im
ucceed in integration ontology
dev
method for
bus
-process is
sta
ontology is physically created with
ont
tes as a link between
diff
6 CONCLUSIONS
Enterprise interoperability becomes a prerequisite
for successful business accomplishment and requires
ortant to distinguish for conceptualization of
organizational as well as technical parts of the
system. Ability to integrate these aspects in one
modelling notation provides possibility to control
and integrate static and dynamic aspects of the
system. Enterprise ontology models should clearly
define the semantic details about the state of
attribute values when creation, termination or
reclassification action takes place.
semantic technologies to enable information sharing
among separate information systems. The developed
framework enables the combination of all three
different approaches if interoperability: mapping-
based, intermediary-based, and query-oriented. As
ontology architecture mixed paradigm with one
global and several local ontologies is used. By using
semantic technologies, an integrated view for
heterogeneous data sources can be provided through
integration ontology.
The definition of in
portant part of using Sebi-framework in the
semantic integration. The most significant results are
achieved, when the integration ontology is broad
enough. Including the whole enterprise in integration
ontology is not possible; the integration ontology
covers one or several domain areas. The integration
ontology can be expanded and further specified
when new information systems are included in the
integration. The integration ontology has to include
all the important concepts, but not be too detailed. It
should not be too simple in order to enable
integration and to provide semantic consistency. On
the other hand too detailed integration ontology
wastes time and resources without providing
additional benefit.
In order to s
elopment the communication gap between
business, domain and IT-experts has to be
eliminated. Pure technical framework is not enough
for achieving the mutual understanding, and
therefore a process for using Sebi-framework is
built. This Sebi-process consists of four sub-
processes: Case Envisioning, Business, Expertise
and IT Domains. In Case Envisioning the basis for
integration ontology development is created. The
foundation of Case Envisioning is on Solution
Envisioning with Capability Cases - approach
(Polikoff et al., 2005). Solution Envisioning
provides means for definition of common
vocabulary between different parties and to make
right technology selection from the constantly
growing mass of available IT solutions.
The process does not specify any
iness process modelling. In semantic framework
presented in figure 1, the Pragmatic level could be
seen as a part of the Case Envisioning process,
where business needs and possibilities are defined.
Semantic level relates closely to the development of
integration ontology and syntactic level is connected
to Business, Expertise and IT Domains where
implementation dependent work is done.
The technical implementation of Sebi
rted by defining the integration ontology. Data in
various information systems is stored in
heterogeneous sources and formats. Using ontology
engineering tools a concept model can be
automatically formed from data sources. This
requires that the data is stored in suitable forms
including common relational database structures,
ontology files, XML-documents and xls-files. If data
is not in suitable form manual data processing is
required.
Integration
ology building tool. Mappings are used to
connect automatically generated concept models and
manually build integration ontology. Mappings
between the concepts in integration ontology and the
concepts in source concept models are done
manually. The purpose of mappings is to connect
concepts which have the same semantics. When
direct correspondence between concepts is not found
the mappings are done using reasoning. The
reasoning may be based on similarity of concepts
and the meaning of concepts.
Integration ontology opera
erent information systems by offering access to
the source information. The information is requested
by executing queries into integration ontology by
using middleware tool. The requested information
can be delimited according to application’s or
person’s needs so the information obtained is just
the information needed.
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
68

by
mo
ation sharing among separate
inf
holistic representation of the enterprise
wh
REFERENCES
. Information Integration with
Ontologies: Experiences from an Industrial Showcase,
Berlin and Heidelberg
digm, Springer, Berlin.
of Knowledge Management, e-Commerce and the
Semantic Web, Springer, London, UK.
Gu the Enterprise
Systems. V,
Gu
Gu
Spain,.
1.
Pel J., 2008.
Pol
Pol n.
e, NJ.
Knowledge and Data
Sar
Enterprises, 12-14
Usc
We s Management.
Concepts, Languages, Architectures, Springer-Verlag
Berlin Heidelberg.
both technical and information integration. This
integration greatly depends how well the
communication among different stakeholders
involved in the information development process
succeeds. Lack of integrated methods and
implementation bias are examples of the problems.
This paper presents a semantic framework for
increasing the quality of enterprise interoperability
means of effective information integration. The
paper contributes with a semantic framework, where
Sebi-framework is extended with SOAD approach.
The advantage of SOAD is that by combining
intesubjective and objective aspects in one
delling notation it facilitates to better
understanding and reasoning about service
architecture across organizational and technical
system boundaries. It combines business data and
business process dimensions and integrates static
and dynamic aspects in one diagram type. Being
computation neutral, service-oriented approach used
for analysis and design is more comprehensible for
business experts.
The Sebi-framework uses semantic technologies
to enable inform
ormation systems. Interoperability between
separate information systems is achieved by
developing a shared information model of the
information.
The presented semantic framework will facilitate
to maintain a
ich is necessary for systematic analysis of service
architectures as well as to enterprise interoperability
where internal and external views are visualized
together.
Alexiev, V. et al., 2005
John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, UK.
Bennet, S., McRobb, S., Farmer, R., 2002. Object-
Oriented System Analysis and Design using UML.
McGrraw-Hill.
Bruijn, J.D., Feier, C., 2005. D4.6.1.1 Report on ontology
mediation for case studies V1. SEKT-project Report
2005-08-05.
Dietz, J.L.G., 2006. Enterprise Ontology Theory and
Methodology, Springer-Verlag
New York.
Dori, C., 2002. Object-Process Methodology: A Holistic
System Para
Gomez-Perez A, Corcho O, Fernandez-Lopez M., 2005.
Ontological Engineering with examples from the areas
Gruber, T.R., 1995. Towards principles for the design of
ontology used for knowledge sharing,. Int. J. Human–
Computer Studies, 43 (5/6), pp.907–928.
stas, R., Gustiené, P., 2004. Towards
Engineering Approach for Information System
Modelling across Organisational and Technical
Boundaries. In Enterprise Information
Kluwer Academic Publisher, Netherlands., pp. 235-252.
stas, R., Gustiené, P., 2007. Service-Oriented
Foundation and Analysis Patterns for Conceptual
Modellling of Information Systems. In 16th
International Conference on Information System
Development, August 29-31, Galway, Ireland.
stas, R., Gustiené, P., 2008. A New method for
Conceptual Modelling of Information Systems. In 17th
International Conference on Information System
Development, August 25-27, Paphos, Cyprus.
Gustiené, P., 2003. On Desirable Qualities of Information
System Specifications. In International Conference on
Concurrent Engineering: Research and Applications,
26-30 July, Madeira, Portugal.
Gustiené, P., Gustas, R. 2008. Introducing Service-
Orientation into System Analysis and Design. In 10th
International Conference on Enterprise Information
Systems, June 12-16, Barcelona,
Noy, N.F. and McGuinness, D.L., 2001. Ontology
Development 101: A Guide to Creating Your First
Ontology, Stanford Knowledge Systems Laboratory
Technical Report KSL-01-05, March 200
Park, J., Ram, S., 2004. Information Systems
Interoperability: What Lies Beneath?. ACM
Transactions on Information Systems, 22(4), pp. 595-632.
tomaa, I., Helaakoski, H., Tuikkanen,
Semantic Interoperability - Information Integration by
Using Ontology Mapping in Industrial Environment.
In 10th International Conference on Enterprise
Information Systems, June 12-16, Barcelona, Spain.
ikoff, I. and Allemang, D. 2003, Semantic Integration
Strategies and Tools, TQ TechnologyBriefing 2003,
TopQuadrant, USA.
lock, J.T., Hodgson, R., 2004. Adaptive informatio
Improving business through semantic interoperability,
grid computing, and enterprise integration, John
Wiley & Sons, Hobok
Ram, S., Park, J., 2004. Semantic Conflict Resolution
Ontology (SCROL): An Ontology for Detecting and
Resolving Data and Schema-Level Semantic Conflicts.
IEEE Transactions on
Engineering, 16(2), pp.189-202.
janoja, E. M., Helaakoski, H., and Peltomaa, I., 2008.
Semantic Interoperability in Industrial Environment.
In Modern Information Technology in the Innovation
Processes of the Industrial
November, Prague, Czech Republic.
hold, M., Gruninger, M., 1996. Ontologies: principles,
methods, and applications. Knowledge Engineering
Review 11(2), pp.93-155.
ske, M., 2007. Business Proces
SEMANTIC FRAMEWORK FOR INFORMATION INTEGRATION - Using Service-oriented Analysis and Design
69
