
INJECTING SEMANTICS INTO EVENT-DRIVEN
ARCHITECTURES
Jürgen Dunkel
Computer Science Depart., University of Applied Sciences and Arts, Ricklinger Stadtweg 120, 30459 Hannover, Germany
Alberto Fernández, Rubén Ortiz, Sascha Ossowski
CETINIA, University of Rey Juan Carlos, Calle Tulipán s/n, 28933 Mosteles (Madrid), Spain
Keywords: Event Models, Ontologies, Event-driven Architecture, Complex Event Processing, Rule-based Systems.
Abstract: Event-driven architectures (EDA) have been proposed as a new architectural paradigm for event-based
systems to process complex event streams. However, EDA have not yet reached the maturity of well-
established software architectures because methodologies, models and standards are still missing. Despite
the fact that EDA-based systems are essentially built on events, there is a lack of a general event modelling
approach. In this paper we put forward a semantic approach to event modelling that is expressive enough to
cover a broad variety of domains. Our approach is based on semantically rich event models using ontologies
that allow the representation of structural properties of event types and constraints between them. Then, we
argue in favour of a declarative approach to complex event processing that draws upon well established rule
languages such as JESS and integrates the structural event model. We illustrate the adequacy of our
approach with relation to a prototype for an event-based road traffic management system.
1 INTRODUCTION
A wide range of applications is characterized by
event-driven business processes. They must deal
with a huge amount of different events which
continuously arrive as streams (Luckham, 2002),
(Babu et al., 2001). Due to the high volume of
events and their complex dependencies, no
predefined workflow can be specified for business
processes. Current software architectures such as
service-oriented architectures (SOA) do not target
event-based systems, because they are based on a
process-oriented control flow, which is not
appropriate for event-driven systems.
In recent years, event-driven architectures (EDA)
have been proposed as a new architectural paradigm
for event-based applications (Luckham, 2002).
Processing events is the central architectural concept
of EDA: streams of events are analyzed using
Complex Event Processing (CEP) to initiate
downstream event-driven activities, which are
provided by software components and application
systems for implementing domain-specific event
handling. Event streams generated by sensors, RFID
tags or software components contain a large volume
of different events, which must be transformed,
classified, aggregated and evaluated. Examples for
EDA-based systems are logistic applications based
on RFID events (Wang et al., 2005), (Dunkel and
Bruns, 2008), financial trading (Adi et al., 2006),
business activity management (Coy, 2002), click
stream analysis in web portals (Coy, 2002) and
traffic control systems (Dunkel et al., 2008).
The main goal of CEP is to identify in a huge
event cloud those patterns of events which are
significant for the business domain. In traffic control
systems millions of sensor-emitted events are
analyzed to discover event patterns signifying
upcoming traffic problems.
Meanwhile, EDA have been used successfully
for event-based applications (Wu et al., 2006),
(Babcock et al., 2002) and several commercial
products supporting EDA are available (Coral8,
2008), (Espertech, 2008).
Unfortunately, event-driven architectures have
not yet the maturity of well-established software
architectures: there is still a lack of methodologies,
models and standards. Despite the fact that EDA-
70
Dunkel J., Fernández A., Ortiz R. and Ossowski S. (2009).
INJECTING SEMANTICS INTO EVENT-DRIVEN ARCHITECTURES .
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Databases and Information Systems Integration, pages 70-75
DOI: 10.5220/0001952600700075
Copyright
c
SciTePress

based systems are essentially built on events,
existing architectures does not use any formal event
modelling approaches. In this paper, we introduce
Semantic Event Models using ontologies to define
precisely the hierarchy of event types used in an
Event-Driven Architecture. Semantic Event Models
reflect the sequence of event processing steps and
constitutes the software architecture by identifying
the essential systems components and the main event
processing steps.
The paper is organized as follows: In the next
section the main deficiencies of existing EDA-based
systems are discussed. In section 3 we introduce
semantic event models based on ontologies and
show how they can be used subsequently in event
processing. Finally, we summarize the most
significant features of our approach and provide an
outlook on future lines of research.
2 EDA DEFICIENCIES
One of the main deficiencies of current EDA
approaches is the absence of decent software
architectures. A software architecture is described by
an abstract model defining the essential domain
concepts and mapping them on appropriate software
components (Evans, 2003), (SEI, 2008).
Obviously, events are the key domain concept of
EDA and should therefore be defined precisely by a
formal event model. An event model should provide
a complete understanding of the different event
types, its properties, constraints and dependencies;
and is therefore invaluable to derive the software
architecture of EDA-based systems.
Defining Events in Event Processing Languages.
Surprisingly, existing event-driven architectures do
not use any generic and comprehensive event model,
e.g. (Adi et al., 2006), (Rozsnyai et al., 2007),
(Wang et al., 2005), (Wu et al., 2006).
Instead, event processing languages (EPL) are
used, which intermingle the processing with the
definition of events. Mostly, proprietary SQL-like
event processing languages for continuous queries
(CQL) are used in academic approaches (Babu et al.,
2001), (Babcock et al., 2002), and available EDA
products (Coral8, 2008), (Esper, 2008). Event
definitions are hidden in the SQL-like low-level
code (Arasu et al., 2002). This approach causes the
following drawbacks:
Because CQL-based system doesn’t provide
any dedicated event model, an overview of the
given event types is missing, which makes the
understanding of event processing difficult.
Furthermore, there is a lack of explicit business
rules in form of event constraints. Due to this
deficiency, event processing rules can easily
violate inherent.
Benefits of Formal Event Models. A formal event
model is a key issue of EDA-based systems allaying
the above mentioned problems in providing detailed
semantics about the given events. Furthermore,
event models yield the basis for the overall system
architecture. The event hierarchy corresponds with
the sequence of event processing steps: simple
technical events are transformed into more abstract
and sophisticated application-specific events. Each
transformation step is processed by event agents
which building blocks of the software architecture
(Dunkel et al., 2008).
In summary, current EDA systems lack semanti-
cally rich event models which are indispensable for
understanding the key concepts of event-driven
systems and for deriving appropriate software
architectures.
3 SEMANTIC EVENT MODELS
In our approach we distinguish two different layers
of Event-Driven Architectures: the Structural Event
Model and Complex Event Processing see figure 1.
Structural Event Model
Complex Event Processing
event
type
event
type
event
type
constraint constraint
processing
rule
processing
rule
event data
Figure 1: EDA layers.
The Structural Event Model serves as a formal
event model as motivated in section 2. It defines the
different types of events and their relations. Further-
more, it specifies general constraints defining more
precisely the structure of events and their inter-
dependencies.
Note that the Structural Event Model determines
the business objects of EDA. Its task is to specify
the properties of events but not how they are
INJECTING SEMANTICS INTO EVENT-DRIVEN ARCHITECTURES
71

processed. In particular, the Structural Event Model
should meet the following requirements.
The Structural Event Model must be formally
defined and semantically rich to provide a
complete understanding of the given events. It
should define all constraints and interdepen-
dencies between events by declarative descrip-
tion mechanisms; i.e. by structural rules.
The specification of the Structural Event Model
should be based on an adequate formalism to
limit the room of interpretation and to allow
model-driven approaches.
Complex Event Processing is responsible for
processing streams of continuously arriving events.
It is based on event processing rules which define
correlations between events and are expressed by
event processing languages based on event algebras
(Schiefer, 2007). The rules consist of two different
parts: event patterns specify a certain situation of
events; and event actions are executed when the
event pattern is fulfilled. In particular, new events
can be generated within the event action part. CEP
relies completely on the Structural Event Model,
where all events used in the event processing rules
must be defined.
In summary, the two layers separate domain
knowledge: the structure of events is decoupled from
operational knowledge, i.e. the event processing
rules.
3.1 Formalisms for Event Models
Experience with EDA-based systems has led us to
the following requirements for formalisms aimed at
semantic event models:
sufficient expressiveness of the Structural
Event Model to describe all aspects and
interdependencies of events.
Complex Event Processing should integrate
smoothly the knowledge of the Structural
Event Model.
compatibility with standards to facilitate tool
support.
Structural Event Models. Most current EDA
approaches specify only the types of events by using
XML and XML Schema, as recently investigated in
(Rozsnyai et al., 2007). But XML is not suitable for
modelling semantics, as it lacks high-level language
constructs that support the declarative specification
of event interrelations and constraints.
Some other approaches use simple UML models
for defining event types and their relations (Coral8,
2008), (Esper, 2008). Common UML models are not
expressive enough, but they can be enriched by OCL
(Object Constraint Language) constraints (OMG,
2003) to specify more precise event models.
However a drawback of this approach is that OCL
cannot be easily integrated in standard rule engines
which perform complex event processing.
To comply with the above listed requirements,
we decided to apply ontologies for defining
semantically rich event models. Ontologies langua-
ges such as the Web Ontology Language (OWL)
provide sufficient expressiveness (W3C, 2004), and
may be easily integrated with classical rule engines
for further processing (Dunkel et al., 2006).
Furthermore, OWL is standardized by the W3C
and can be viewed as a semantic extension of XML,
RDF, and RDFS. We will use the OWL DL sub-
language that is based on description logic providing
an adequate degree of expressiveness while still
allowing automated consistency checking.
Complex Event Processing must integrate the
Structural Event Model with the event processing
rules. For instance, the constraints of the Structural
Event Model can be used as consistency rules for
checking the validity of incoming event data.
Because SQL-like continuous query languages
doesn’t support the concept of rules, it is much
easier to integrate a Structural Event Model with a
general rule based system like JESS (Jess, 2008) or
DROOLS (Drools, 2008). For instance, in (Dunkel
et al., 2006) we have shown how OWL models can
be mapped to facts and rules of a general inference
engine. In section 3.3 we will show how general rule
languages can be used for specifying event
processing rules.
3.2 Structural Event Models
In this section we show that OWL-DL is an
appropriate formalism for specifying Structural
Event Models. To illustrate our approach, we refer
to the prototype of a Decision Support Systems for
traffic management, which has been modelled using
an EDA (Dunkel et al., 2008).
In high capacity road networks, as the one of
Bilbao in Spain, sensors installed in the roads emit
events when cars are passing. The Decision Support
System transforms the sensor events into more
abstract and sophisticated domain events for
evaluating the actual traffic situation and initiating
appropriate traffic control actions.
In the following we will derive an ontology-
based event model for to illustrate how different
aspects of Structural Event Models can be modelled
in OWL. Figure 2 shows the simplified OWL event
ontology.
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
72
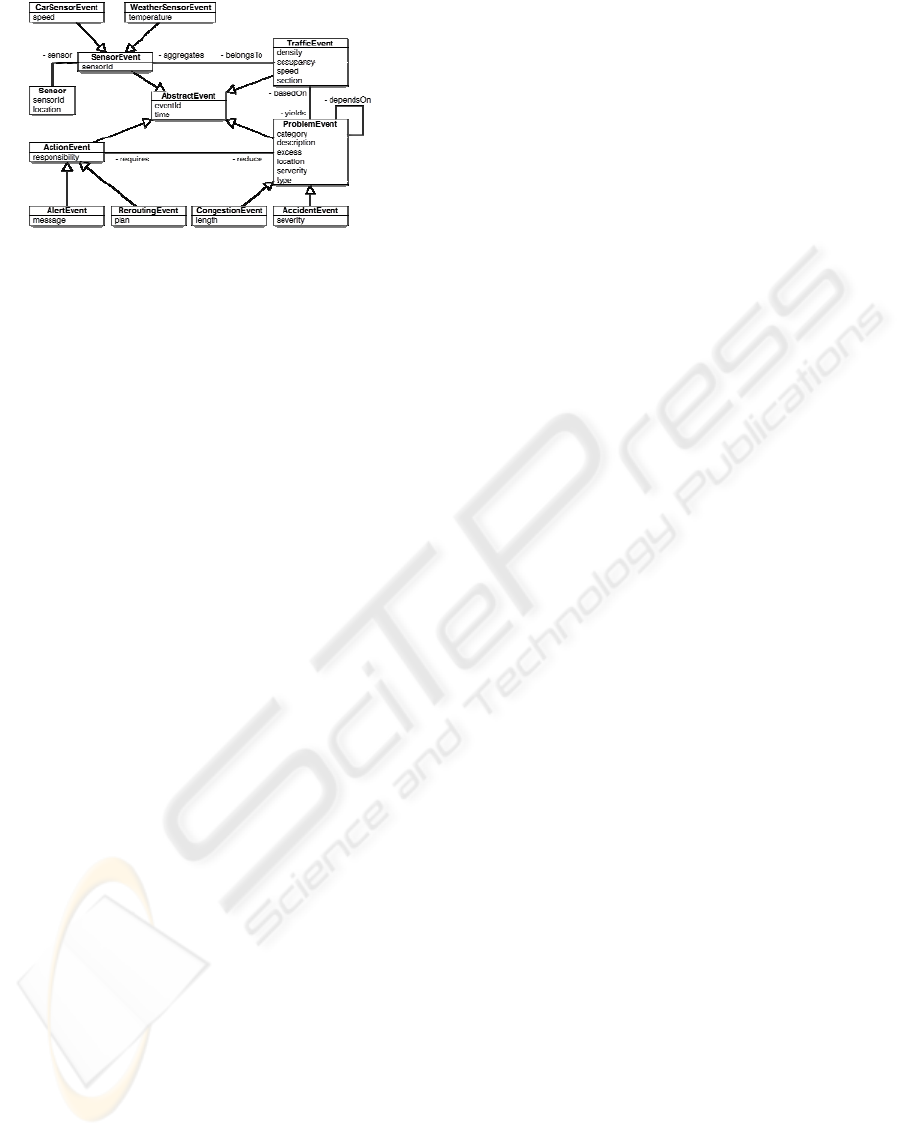
Figure 2: Part of the OWL event ontology.
Event Instances and Event Types. Every situation
that may require a reaction of the system forms an
Event Instance. An Event Instance is atomic and
instantaneous, i.e. bound to a certain point of time.
An Event Type classifies the event instances and
describes their conceptual features. Each Event
Instance belongs to a certain Event Type. The Event
Types reflect the event processing steps.
OWL already provides mechanisms for dealing
with Event Instances and Event Types: an OWL
classes provide an abstraction mechanism for
classifying individuals. An Event Instance is
represented by an OWL instance.
In Figure 2 each rectangle shows an OWL class
representing an Event Type, e.g. a
CarSensor-
Event
is emitted by a loop detector when a car
passes. The particular situation that a car passes the
sensor at a certain time forms an Event Instance. The
decision support system transforms the Sensor
Events into more meaningful Traffic and Problem
Events.
Event Hierarchies. Event Types usually constitute a
hierarchy – defining an Event Type as a subclass of
other types. (Note that OWL allows multiple inheri-
tance.) In figure 2 the
ProblemEvent has two
subtypes: a
CongestionEvent and an Accident-
Event.
Event Type Construction. Furthermore, OWL
offers some constructors to build classes out of other
classes, which are useful for event type definitions.
In particular, in OWL the operators
union,
intersection and complement are defined,
which represent the
AND, OR and NOT operators on
classes.
Event Context. Each Event Instance is
characterized by some data: general metadata (event
ID, time) is common to all Event Types; event-
specific data describes the context, in which the
event occurs. Because event data is type-specific, it
can be used to infer the Event Type. OWL allows
attributes of class instances: OWL data properties
describe event data, and OWL object properties
specify relationships between event instances.
In figure 2, a relation between
TrafficEvent
and
SensorEvent is defined by OWL object
properties. The
TrafficEvent aggregates some
SensorEvents: it calculates its attributes densi-
ty, (average) speed and occupancy using data
from the corresponding sensor events. Thus, the
TrafficEvent can be considered as a complex
event which aggregates correlated (sensor) events.
Event Constraints. With the hitherto presented
OWL language constructs the basic structure of an
event model can be specified. For defining events
more precisely, we need to inject further semantics
into our models.
The domain and the range of an object property
specify which classes are linked. In figure 2, the
property
yields has a TrafficEvent as range and
a
ProblemEvent as domain.
Additionally, logical restrictions can put more
semantics to the relations between Event Types.
OWL provides the symmetricProperty, inverseOf
and transitiveProperty constructs for logical
restrictions:
dependsOn is a symmetricProperty
between
ProblemEvents; requires and
eliminates are inverse; dependsOn is a
transitiveProperty.
Furthermore, OWL allows formulating con-
straints on Classes by so-called OWL class axioms.
For instance, two classes are
disjoint if they have
no instances in common, such as
SensorEvent and
ProblemEvent.
Notation of Time. Event Instances are (partially)
ordered according to their times of occurrence and
most event patterns define a certain sequence of
events. Therefore, the concept of time is a key issue
for event models. However, time is not explicitly
defined in OWL. A possible solution is modelling
time in a dedicated abstract type, here:
AbstractEvent. This class contains meta data
which is common to all events types, i.e. the
occurrence
time and an eventId. All Event Types
inherit from this class to provide them with these
concepts. Note that recently some work has been
proposed extending OWL with temporal aspects
(Marwaha et al., 2007).
In summary, OWL ontologies can be used to
develop semantically rich event models. Especially
OWL constraints can enrich event models with more
semantics.
INJECTING SEMANTICS INTO EVENT-DRIVEN ARCHITECTURES
73
3.3 Complex Event Processing
In this section we show how to use general rule
languages for specifying event processing on the
basis of the Structural Event Model. Note that the
Structural Event Model just represents the
knowledge about the event types and their
properties, but not how these events are processed.
CEP and Structural Event Model. Complex Event
Processing depends heavily on the Structural Event
Model: All event types and data used in the event
processing rules must be defined in the event
ontology as OWL classes or OWL properties.
Note that the expressiveness of OWL is not
sufficient for specifying processing rules: OWL
lacks the language constructs for formulating
complex event patterns and does not allow any data
processing as required in the action part.
A key issue of our approach is the smooth
integration of the OWL ontology with the event
processing rules. In (Dunkel et al., 2006) we have
outlined how OWL models can be mapped to facts
and rules of a general inference engine. In particular,
we used the OWL Inference Engine tool (OWL
inference engine, 2008) to load OWL ontologies and
OWL instances into a JESS knowledge base.
Event Patterns. In the following, we show how
general rule languages like JESS can serve as event
rule language. The key issue is their capability of
defining event patterns, which can be characterized
by the following elements (Zimmer et al., 1999):
Event Patterns are based on event types, i.e.
they define a sequence of event types that must
be matched. Events sequences can be defined by
some basic operators of an underlying algebra:
the sequential operator
E1 ; E2, a conjunction
operator
E1∧E2, the disjunction operator E1∨
E2 and a negation operator ¬E1.The following
example shows a pattern that identifies an
accident as the cause of a specific congestion.
(defrule Congestion_DependsOn_Accident
(AccidentEvent (time ?tacc) (location ?pos))
(CongestionEvent (time ?tcon)(location ?pos))
(test (> ?tcon ?tacc))
(not (and (ProblemEvent (time ?tprob))
(test (and (> ?tprob ?tacc)(< ?tprob ?tcon)))))
=> ...
)
Event Patterns contain context conditions, i.e.
restrictions on the data context of an event
instance. Context conditions are specified by
means of relational operators, which depend on
the data types of the corresponding event
properties. Data context allows the definition of
correlation sets, e.g. correlating all sensor
events belonging to one road segment. The next
rule is used to aggregate the speed measured by
the two sensors of a road section.
(defrule DataAggregation
(CarSensorEvent (sensorId ?sId1)(speed ?v1))
(CarSensorEvent (sensorId ?sId2)(speed ?v2))
(test (<> ?sId1 ?sId2))
(sensor (sensorId ?sId1)(location ?sec))
(sensor (sensorId ?sId2)(location ?sec))
=>
(assert (TrafficEvent (eventId (gensym*))(time (time))
(speed (/ (+ ?v1 ?v2) 2))(section ?sec)))
)
Finally, the event instance selection must be
determined: the event patterns just specify the
required event types. In the next example, we
need to select the last
AlertEvent to show its
message property in the information panel. The
first conditional pattern matches any alert event,
but the second requires the absence alert events
with a timestamp higher than the first one. So,
the rule only fires for the most recent Alert
Event, sending it to the panel.
(defrule SelectMessageToShow
(AlertEvent (time ?ta)(message ?m))
(not (and (AlertEvent (time ?tpre))
(test (> ?tpre ?ta))))
=>
(assert (sendMessageToPanel ?m))
)
Event Handling. If an event pattern is matched, i.e.
if a rule fires, a certain action is executed. The event
rules should allow defining arbitrary handling code.
In particular, the data of those event instances that
match the pattern must be processed and new event
instances must be created. Furthermore, actions must
be able to invoke business-level activities which
implement domain-specific event handling.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Though EDA-based systems are essentially built on
events, current approaches do not use formal event
models. Instead, event processing languages (EPL)
are used, which intermingle processing and
definition of events. Generally, there is a lack of
comprehensive and precise event models.
In this paper, we have put forward a semantic
approach to event modelling for EDA-based
systems. A Structural Event Model defines all event
types with their constraints and interdependencies
and can be described by ontology languages. We
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
74

showed how to use OWL to express semantically
rich event models that can be reused in subsequent
event processing steps straightforwardly. Complex
Event Processing defines the operational behaviour
of EDA on base of the Structural Event Model. For
instance, the constraints of the Structural Event
Model can be used as consistency rules for checking
the validity of incoming event data.
To integrate the structural with the operational
model we chose well established rule language as
JESS and showed how they can be used for
specifying event processing rules. Furthermore, we
have illustrated the adequacy of our approach with
relation to a prototype for an event-based road traffic
management system.
In contrast to other works (Adi et al., 2006),
(Rozsnyai et al., 2007), (Wang et al. 2005), (Wu et
al., 2006), we used a model-based approach for
deriving EDA, which separates the structural (i.e.
event types and constraints) from operational know-
ledge (i.e. event processing rules). The proposed
models yield the basis for the software architecture
and can be used for model-driven software
development approaches.
For the future, we intend to derive explicit
architectural guidelines and design patterns from the
semantic event models. For this purpose, we also
plan to integrate a reference architecture that we
have developed for structuring CEP reasoning
(Dunkel et al., 2008) into our approach.
Furthermore, we intend to explore the potential
benefits and drawbacks of combing OWL-based
ontologies with SQL-based EPLs. Finally, we want
to apply model-driven software development
approaches to generate event processing rules from
semantic event models and to simplify the
development of low-level event processing rules.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work has been partially supported by the
Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation through
projects CSD2007-0022 (Consolider-INGENIO
2010) and TIN2006-14360-C03-02 and the
European Community through project EFRE Nr. 2-
221-2007-0042.
REFERENCES
Adi, A., Botzer, D., Nechushtai, G., Sharon, G., 2006.
Complex Event Processing for Financial Services,
IEEE Services Computing Workshop.
Babcock, B. Babu, S., Datar, M., Motwani, R., and
Widom, J.. Models and issues in data stream systems.
In Proc. of the 21st Symp. on Principles of Database
Systems, pages 1-16, June 2002.
Babu, S., Widom, J., Continous Queries over Streams,
SIGMOD Record, 2001.
Coral8, http://www.coral8.com/, retrieved 10. June, 2008
Coy, D.: Business Activity Monitoring: Calm Before the
Storm, Gartner Research, LE-15-9727, 2002.
Drools, http://jboss.org/drools
Dunkel, J., Bruns, R., Ossowski, S.: Semantic E-Learning
Agents - Supporting E-Learning by Semantic Web and
agent technologies, in: Seruca, I. et al.. (eds.),
Enterprise Information Systems VI, Springer Verlag,
2006, pp. 237-244.
Dunkel, J., Bruns, R., Reference Architecture for event-
driven RFID applications, 2nd Intern. Workshop on
RFID Technology (IWRT), Barcelona, 2008, pp. 129-135.
Dunkel, J., Fernández, A., Ortiz, R., Ossowski, S., Event-
Driven Architecture for Decision Support in Traffic
Management Systems. Proc. of the 11th Intern. IEEE
Conf. on Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2008.
ESPERTECH: Esper Reference Documentation, Version
2.0.0. Technical Report, http://esper.codehaus.org,
retrieved 10. June, 2008.
Evans, E., Domain-driven Design: Tackling Complexity in
the Heart of Software, Addison Wesley, 2003.
Jess, the Rule Engine for the Java Platform,
http://herzberg.ca.sandia.gov/
Luckham, D: Power of Events. Addison-Wesley, 2002.
Marwaha, S., Bedi, P., Temporal Extensions to OWL
Ontologies, International Journal of Information
Technologies, Vol.4, No.1, pp 53-60, 2007.
Object Management Group (OMG), UML 2.0. OCL
Specification, http://www.omg.org/docs/ptc/03-10-
14.pdf, 2003.
OWL Inference Engine, http://mycampus.sadehlab.cs.-
cmu.edu/public_pages/OWLEngine.html
Rozsnyai, S., Schiefer, J., Schatten, A., Concepts and
Models for Typing Events for Event-Based Systems,
Proceedings of DEBS, pp. 62-70, 2007.
Schiefer, J., Rozsnyai, S., Rauscher, C., and Saurer, G.,.
Event-driven rules for sensing and responding to
business situations. Inaugural International
Conference on Distributed Event-Based Systems,
2007, pp. 198-205.
SEI – Software Engineering Institute (Carnegie Mellon
University, Software Architecture Definitions.
http://www.sei.cmu.edu/, 2008.
W3C, OWL Web Ontology Language Reference,
http://www.w3.org/TR/owl-ref/, , February, 2004.
Wang, F. and Liu, Peiya. Temporal management of RFID
data. VLDB, 1128-1139, 2005.
Wu, E., Diao, Y., Rizvi, S., High-performance complex
event processing over streams. Proceedings of the
2006 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on
Management of Data, 2006, pp. 407-418.
Zimmer, D., Unland, R. On the semantics of complex
events in active database management systems. ICDE,
1999, pp. 392-399.
INJECTING SEMANTICS INTO EVENT-DRIVEN ARCHITECTURES
75
