
MULTI-AGENT NEGOTIATION MODEL BASED-ON
ARGUMENTATION IN THE CONTEXT OF E-COMMERCE
Guorui Jiang , Yangwei Xu and Ying Liu
School of Economics & Management, Beijing University of Technology,100 Pingle Yuan, Beijing 100124, China
Keywords: Argumentation, Auto-negotiation system, Multi-agent, Negotiation model.
Abstract: In the e-commerce transactions, there are lots of commodities with the same name, but anyone of these
commodities have certain attributes which differ itself from others. During the traditional process of
multi-agent negotiation, only one commodity can be selected as the negotiation object from these
commodities with same name, if buyer agent want to find an appropriate commodity, the flexibility and
efficiency of multi-agent negotiation would be low. This paper studies the multi-agent negotiation model by
argumentation for a group of commodities. It firstly defines all kinds of negotiation elements, then
establishes a negotiation model based-on argumentation and describes the negotiation agreements and
strategies, and finally an example would be presented for testifying the effects of this model.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the 90s of last century, along with the
development of e-commerce, multi-agent
negotiation is becoming a hot research topic.
Multi-agent negotiation based-on argumentation is
an important kind of automatic negotiation, through
it agents can take part in the process of negotiation
more flexibility and affect other agent’s beliefs,
desires or objectives (Rahwan et al, 2003.
In the field of multi-agent negotiation based-on
argumentation, Jennings and others presented a
model based-on argumentation for multi-issue
negotiation (Jennings et al, 1998); Jing-hua Wu
studied the encouragement model in the multi-agent
negotiation(Wu et al, 2006). However, these papers
are almost concentrated in abstract models. In this
models, the negotiation object is always just one
commodity, and argumentation content is usually not
commodity’s attributes, such as threat and reward. In
the researches of multi-issue negotiation, all the
issues are defined in advance (Wu et al, 2008; Gu et
al, 2010). In the e-commerce transactions, there are
lots of commodities with the same name, but anyone
of these commodities have certain attributes which
differ itself from others. During the traditional
process of multi-agent negotiation, only one
commodity can be selected as the negociation object
Supported by Chinese National Science Fund (71071005,
70940005).
from these commodities with same name, if buyer
agent want to find an appropriate commodity, the
flexibility and efficiency of multi-agent negotiation
would be low.
This paper divides the pricing factors of these
commodities into two classes: main attributes and
secondary attributes. The main attributes is the
common attributes of these commodities and
determine the general price, and the secondary
attributes affect the range of price fluctuation of
these commodities. Secondary attributes would be
considered as argumentation objects, and agents
select certain commodity by argumentation. This
paper firstly defines all kinds of negotiation
elements, then establishes a negotiation model
based-on argumentation and describes the
negotiation agreements and strategies, and finally an
example would be presented for testifying the effects
of this model.
2 MULTI-AGENT NEGOTIATION
MODEL BASED-ON
ARGUMENTATION
2.1 Assumptions
This paper supposes that there are three participants:
seller, buyer and third-party. The third-party plays a
coordinating role and is responsible for the
422
Jiang G., Xu Y. and Liu Y..
MULTI-AGENT NEGOTIATION MODEL BASED-ON ARGUMENTATION IN THE CONTEXT OF E-COMMERCE.
DOI: 10.5220/0003176604220425
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2011), pages 422-425
ISBN: 978-989-8425-41-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

establishment of trading relations, the proposal
forwarding and the arbitration.
2.2 The Relevant Definitions
2.2.1 Definition 1
Set of Negotiation Participants:
,,SBA
, S
indicates the Seller Agent, B indicates the Buyers
Agent and A denotes the Third-party Agent.
2.2.2 Definition 2
Negotiation Issue:
0
,
k
I
II
, negotiation issue
consists of two sub-issues: the main issue and
argumentation issue. The main issue is price. The
argumentation issue
k
I
refers the secondary
attribute, and
11 12
, ,,,,,
kkn
I
II I I
.
2.2.3 Definition 3
Price Range and Bid Range: The Price Range is
min max
,
SS
PP
, it is given by the seller.
min
S
P
is the
seller's reservation value and not known to the
outside world; Bid Range is
min max
,
BB
PP
, it is
given by the buyer.
max
B
P
is the buyer's reservation
value and not known to the outside world.
2.2.4 Definition 4
Value of Argumentation Object: Argumentation
object is corresponding to the secondary attribute of
goods. Argumentation object is inherently valuable.
Value of argumentation object is
max min
()
k
PP
.
k
is the weight of secondary attribute of number k,
in addition
1
1
n
k
k
.
2.2.5 Definition 5
Utility: Utility is negotiating expectation or
assessment of opponent’s offer. The utility can be
divided into two classes: expectation utility and
negotiation utility. The expectation utility is
depended on three factors: Price Range, Bid Range
and argumentation. Negotiation utility is related to
times of negotiation. In round
t
, the negotiation
utility of seller is
min
max min
B
s
t
t
SB
PP
U
PP
, and the
buyer’s is
max
max min
S
B
t
t
SB
PP
U
PP
.
For a certain commodity with m argumentation
objects, the seller's expectation utility is:
12
ma x mi n ma x mi n
1
ma x mi n
()( )()
22
ˆ
SS
m
SS SS SB
ij ij
S
i
m
SS
PP PP
U
PP
(1)
Among them,
1
S
and
2
S
are the weights, in
addition
12
1
SS
.
S
ij
is the number
i
secondary attribute,
1
1
M
S
ij
i
,
1 mM
,
M
is
the amount of argumentation objects.
S
ij
is the
number
j
impact factor of the number
i
secondary attribute,
1
1,1 , 0
N
SS
ij ki
j
,
N
is the amount of values of the number
i
secondary
attributes.
For a certain commodity with m
argumentation objects, the buyer's expectation
utility is:
(2)
2.3 Model Description
Multi-Agent negotiation model based-on
argumentation is defined as a seven-tuple
,,,,,,,,
A
OIR TSPB
. In the seven-tuple, A
means negotiation agent, O means the negotiation
object, I is the negotiation issue, R is the range of
Agent’s price offer,
is the space of negotiation
issue, T indicates the times, S is the negotiation
strategy, P is the negotiation agreement, and finally
B is agent’s behavior.
12
maxmin maxmin
1
max mi n
()( )()
22
ˆ
B
B
m
BB BB S B
ij ij
B
i
m
BB
PP PP
U
PP
MULTI-AGENT NEGOTIATION MODEL BASED-ON ARGUMENTATION IN THE CONTEXT OF E-COMMERCE
423

3 NEGOTIATION AGREEMENT
Negotiation agreement is the standard of behavior
which agents must comply with when they
communicate with each other. This paper uses this
agreement as the following steps:
(1) The Buyer Agent and the Seller Agent send the
initial prices to the Third-party Agent at the same
time. The Third-part Agent forwards their prices and
determines a certain commodity at random, and then
informs the result to Buyer Agent and Seller Agent.
(2) Buyer Agent and Seller Agent evaluate the
opponent price and confirm that whether accept
opponent proposal or not, and send the their results
to the Third-party Agent; Third-party Agent
judges :if anyone of them accepts opponent proposal,
then process turns to the Sept 3, if there is no
acceptance, then process turns to the Sept 4.
(3) If there is only one acceptance, the Third-part
Agent informs that deal can be done; if there are two
acceptances, the Third-party Agent informs that deal
can be done according to the price offered by last
biding agent.
(4) If there is no acceptance, the Buyer Agent and
Seller Agent evaluate the commodities which have
different secondary attributes according to the
existing prices.
a. If no one has achieved the expectation utility,
both sides continue to offer new prices. Process
turns to the Step 1.
b. If one party achieved its expectation utility, that
is
ˆ
SS
tm
UU
or
ˆ
BB
tm
UU
, then the agent
will send initiative argumentation for the commodity
which has m secondary attributes. The
argumentation would be evaluated by the opponent
agent, if it be accepted, deal can be done, if not,
process turns to the Step 4. If both sides send
argumentations at the same time, the last
argumentation would be selected by Third-party
Agent.
(5) If deal is done, the negotiation is over, if any
agent refuses negotiation or the negotiation exceeds
maximum time, then the negotiation would be
stopped.
4 NEGOTIATION STRATEGY
Negotiation strategy is what behaviors should be
taken in the process of negotiation. By these
behaviors agent can achieve its max utility. In other
words, negotiation strategy is how to provide price
(Wang et al, 2009).
In this paper, concession strategies are adopted.
min
P
is minimum price offered by agents, and
max
P
is
the maximum price. T is the maximum time
negotiation allows, t is a time variable,
is an
index. Specific concession strategies are defined as
follows:
min max min
() ( )
t
Pt P P P
T
(
0
),The
smaller of attribute value, the better;
max max min
() ( )
t
Pt P P P
T
(
0
),The
bigger of attribute value, the better.
When
0 0.5
negotiation strategy belongs to
impatient type; when
0.5 2
, negotiation
strategy belongs to moderate type; when
2
negotiation strategy belongs to economical type (Li
et al, 2008).
5 EXAMPLES
There is a category of flash disk. Its brand is M, the
type belongs to N, and Type N has three kind of
color: red, blue and gray. M and N are the main
attributes, color is secondary attributes.
It is assumed that the Pricing Range of S is
[220,312], the impact factor of color
S
has
three values: 1, 0, -1, corresponding to red, blue and
gray, the weight of color is 0.1. The Bid Range of B
is [226,305], the impact factor of color
B
also
has three values: 1, 0, -1, corresponding to red, blue
and gray, the weight of color is 0.08. Negotiation
strategy of both sides is to take a moderate type, and
both the indexes
are 0.8. When B start to bid, it
select commodity in random. Now expectation
utility of both sides can be computed, results are
shown in the Table 1.
Table 1: Agent’s expectation utility.
Color
Participant
S B
Red 0.59 0.40
Blue 0.49 0.48
Gray 0.39 0.56
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
424
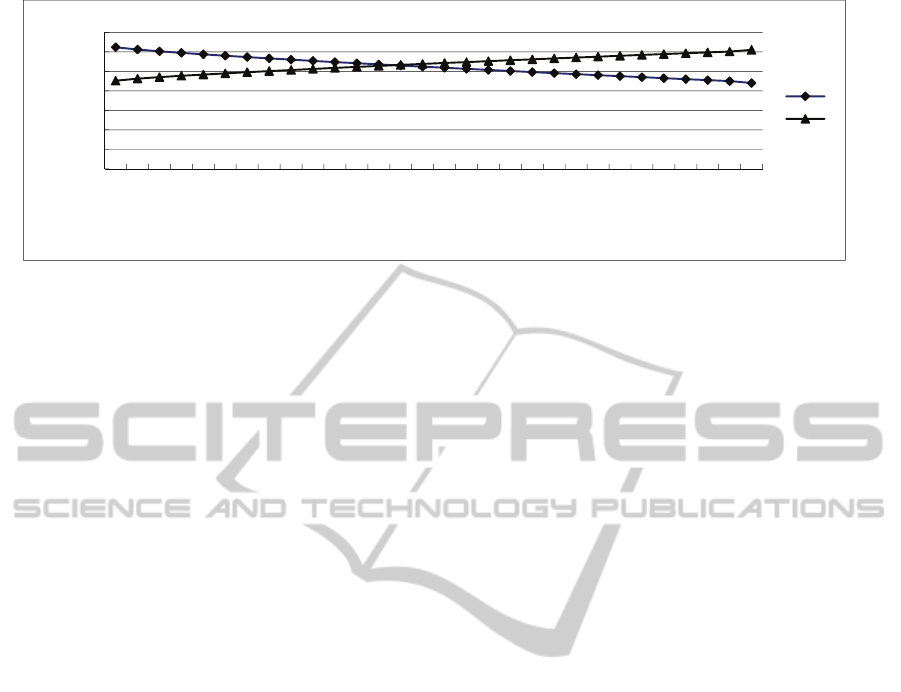
Figure 1: The bargaining process of negotiation.
The bargaining process is shown in Figure 1.
According to negotiate agreement, in the Round 9,
the pricings of B and S are 256.15, 276.89, deal can’t
be made. However,
9
0.41
B
U
,
9
ˆ
BB
red
UU
,
Pursuant to the agreement, B would send
argumentation initiatively.
SB (red, 276.89)
, in
this condition, the negotiation utility of S is 0.59
which is equal to expectation utility, so S would
accept the argumentation of B, deal can be
done.Conclusions can be got from analysis: if
argumentation is abandoned, deal can be done in
round 13. From here we can see that agents send
argumentation initiatively in appropriate time
according to their expectation utility, not only
satisfactory solution would be got as soon as
possible, but also a group of commodities can be
negotiated in one process.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In the field of multi-agent negotiation, very few
researches on negotiation based-on argumentation
are for groups of commodities. This paper researches
the multiple commodities negotiation by
argumentation mechanism, established negotiation
model and testifies it by an example. It proves that
blinding negotiation processes of many commodities
into a uniform multi-agent negotiation process by
argumentation is good selection. As the complexity
of commodity transactions, researches on
multi-agent negotiation based-on argumentation
need to be further excavated.
REFERENCES
Rahwan I, Ramchurn S D, Jennings N R, et al.
Argumentation-based negotiation [J]. The Knowledge
Engineering Review, 2003, 18(4):343-375.
Jennings N R, Parsons S, Noriega P, et a1. On
argumentation-based negotiation [A]. Proceedings of
the International Workshop on Multi-Agent Systems
(IWMAS98) [C]. Boston. MIT. 1998. 1-7.
Wu Jing-hua, Jiang Guo-Rui, Huang Ti-yun. Research on
Models of Reward in Argumentation-based
Negotiation of Agent [J]. Computer Engineering and
Applications, 2006, (36):172-175.
Wu Jing-Hua, Jiang Guo-Rui, Sun Hua-mei et
a1.Modeling and Implementing the Course of
Agent-based Argument-Negotiation [J]. Journal of
Industrial Engineering/Engineering Management. 2008,
(3): 69-74.
Gu Chuan-Long, Sun Hua-Mei, Jiang Guo-rui et a1.
Research on Collaborative Negotiation Model and
Prototype System in Supply Chain [J]. Journal of
Industrial Engineering/Engineering Management. 2010,
(01): 65-69.
Wang Ying, Jiang Guo-Rui, Huang Ti-yun.Two Stage
Negotiation Model for Multi-issue between
Multi-agent [J]. Application Research of Computers.
2009,(2): 573-576.
Li Ran-ran, Sun Hua-mei, Jiang Guo-rui et a1.A Research
on the One-to-many Automated Negotiation Model
Adopting Elimination System Based on Multi-agent [J].
China Journal of Information Systems. 2008, (5):
29-36.
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
1 3 5 7 9 11131517192123252729
Price
Time
S
B
MULTI-AGENT NEGOTIATION MODEL BASED-ON ARGUMENTATION IN THE CONTEXT OF E-COMMERCE
425
