
MOBILE IRIS RECOGNITION SYSTEM
A Low Cost Approach
Silvia Anton and Florin Daniel Anton
Department of Automation and Industrial Informatics, University Politehnica of Bucharesty
Spl.Independentei, 313, Bucharest, Romania
Keywords: Iris recognition system, Sensor systems, Wireless communication, Virtual private network, Mobile sensing
devices.
Abstract: Nowadays biometric data acquisition and processing systems for person identity verification and / or
identification are increasingly used (both in military applications – person identification in military
operations and war theatres, but also in civilian applications – mobile employee enrolment and accounting
systems). Such systems and especially mobile biometric iris recognition systems are expensive and also
brings big security issues (loosing such a mobile device can expose the company or can break the cover of a
military operation by exposing personal identification data of agents or informants). This paper presents a
functional architecture of a mobile, low cost system for biometric iris data type acquisition and processing
for personal identity verification. The particularity of this system is that it is a low cost, but in the same time
offers an acceptable performance and security level. The paper presents the hardware and software
architecture, but also shows how the device is connected with other systems in order to obtain processing
and storage capacity for the recognition process. The paper is structured on three chapters presenting the
hardware components, the software tools and programs, the connectivity and security issues, and ends with
some experimental data and conclusions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, the identification and verification of the
identity of persons becomes an increasingly
important factor, and mobile biometric data
acquisition and processing become increasingly
widespread and used (Zhai, 2009, Patnala, 2009,
Araghi, 2010, Matschitsch, 2008). A special place is
held by systems for person identity verification /
identification based on the iris, which were accepted
and used especially in military applications (see
Figure 1) (L-1 Identity Solutions Inc., 2010).
The biggest advantage of using the iris as a
biometric verification and recognition method is the
accuracy and reliability (Daugman, 2004) estimated
to be ten times more accurate than methods using
fingerprint, iris-based methods produce a false
match rate (or false acceptance rate – FAR) of 1/1-2
million samples, while fingerprint-based methods
produce a false match rate close to 1/100000
samples (Cao, 2005, Ganeshan, 2006). Due to this
aspect some countries have initiated the procedures
to integrate the iris biometric data into the
population identification cards.
While fingerprints are constantly exposed and
are likely to deteriorate, the iris is naturally protected
by the cornea (a transparent membrane covering the
eye) and its model seems to remain unchanged for
decades, being only affected by some eye diseases
which are more frequently found to elders
(population less active).
Unlike fingerprint scanners, which require direct
contact and must be kept extremely clean, iris scan
can perform safely and hygiene at some distance
from the eye. Disadvantages include the iris
scanning higher initial cost (few thousands of
dollars) and the fact that it is still a relatively new
technology that has not been tested enough.
This paper gives some solutions to the issues
presented and offers a low cost solution for
acquiring and processing information using iris
biometric type devices. In the next sections the
hardware and software architecture of the proposed
solution is described, followed by the presentation of
the connectivity method with the outside world in
order to obtain processing and storage capacity
needed for iris recognition. security issues are
presented and possible solutions are proposed, the
237
Anton S. and Anton F..
MOBILE IRIS RECOGNITION SYSTEM - A Low Cost Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0003400502370242
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems (PECCS-2011), pages
237-242
ISBN: 978-989-8425-48-5
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Figure 1: The military mobile iris based identification system HIIDE 5.
paper ends with a set of preliminary results and
conclusions
2 THE HARDWARE
ARCHITECTURE
The hardware architecture of the system is based on
an ARM processor SBC structure – Single Board
Computer (see Figure 2). The SBC is produced by
the company Gumstix and is based on the ARM
Cortex-A8 processor from Texas Instruments
OMAP3530. The processor runs at a frequency of
720 MHz and has up to 1200 Dhrystone
performance MIPS. SBC's is equipped with 256MB
RAM and 256MB Flash (which can be extended by
using an extension card up to 8GB), 2D and 3D
acceleration POWERVR SGX and the ability to
communicate wireless via Bluetooth and 802.11b/g
(Gumstix Inc., 2010).
Figure 2: The Single Board Computer System.
The SBC can work as is, but in order to use a
display an expansion card is required (see Figure 3).
The expansion card (Palo 35) offers the
possibility of using a touch screen 3.5 "LCD, USB
peripheral, and I/O audio lines, the expansion card
also features an integrated accelerometer.
The display is provided by a touch screen LG
3.5" LCD. The image acquisition is performed by a
webcam (Figure 4). The webcam is equipped with
built in LEDs for lighting (in the visible spectrum),
this system of lighting can not be used because the
human eye is embarrassed and also the light in the
visible spectrum negatively affects the acquisition
due to reflections that occur (Kim, 2005).
The camera was modified by replacing the existing
LEDs with IR LEDs, which has triggered also the
need to modify the lens, which contains an IR filter
that cancels the effect of the IR LEDs; this IR filter
was removed and replaced with one filtering the
visible light. The camera can be any camera with
USB connection and at least VGA resolution
(640x480) that has a reasonable picture quality, but
also which lens allows filter change.
Figure 3: The expansion card Palo 35.
The system is powered by a 5V battery that
allows up to 8 hours of continuous operation with
wireless connection and LCD screen active.
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
238

Figure 4: The modified camera.
The equipment also has an integrated power
saving system that disables the LCD display, and
switches the processor in the energy saving mode
after a certain period of inactivity detected by the
included accelerometer and the user interaction with
the graphical interface (which is also monitored).
This time can be preferentially set by the user. The
reverse operations are executed also based on the
user interaction.
3 THE SOFTWARE
ARCHITECTURE
In terms of software, the system is installed with
Angstrom Linux operating system, the graphical
interface is generated by a system application that
runs under the X window system. When the device
is started, the system automatically searches for a
specific access point (or list of access points) to
which it connects using the security protocol Wi-Fi
Protected Access II (WPA2) to establish an Internet
connection (Wong, 2009, Kizza, 2009). If the access
point has not been found, the device allows the user
to manually configure the wireless connection
through the user interface.
After the Internet connection was made, the
system connects to a processing infrastructure that
will provide processing power and a database used
to store information about the enrolled users and
also provide information for personal identity
verification and identification.
The connection to the processing structure is
created using a VPN network which is based on the
IPsec technology (Internet Protocol Security see
Figure 5) (Red Hat Inc., 2007). IPsec is a software
solution to securely connect to a WAN; this solution
is widely used by top companies like Red Hat and
offers a high level of security for network
communications. IPsec is used to connect the mobile
device and the processing infrastructure using a
secure tunnel on a common carrier network such as
the Internet. IPsec uses Internet Key Exchange
(IKE), a protocol implemented by the Internet
Engineering Task Force (IETF) and used for mutual
authentication and secure associations between
connecting systems.
IKE uses X.509 certificates for authentication
which are either pre-shared or distributed using DNS
(preferably with DNSSEC), and a Diffie–Hellman
key exchange to set up a shared session secret from
which cryptographic keys are derived. In addition, a
security policy for every peer which will connect
must be manually maintained.
The IKE protocol uses UDP packets, usually on
port 500, and generally requires 4-6 packets with 2-3
turn-around times to create a Security Association
on both sides. The negotiated key material is then
given to the IPsec stack. For instance, this could be
an Advanced Encryption Standard key, information
identifying the IP endpoints and ports that are to be
protected, as well as what type of IPsec tunnel has
been created. The IPsec stack, in turn, intercepts the
relevant IP packets if and where appropriate and
performs encryption / decryption as required.
Implementations vary on how the interception of the
packets is done—for example, some use virtual
devices, others take a slice out of the firewall (in our
case IPsec uses virtual devices).
An IPsec connection is split into two logical
phases. In phase 1, an IPsec node initializes the
connection with the remote node or network. The
remote node or network checks the requesting node's
credentials and both parties negotiate the
authentication method for the connection.
In our case the IPsec connection uses the pre-
shared key method of IPsec node authentication. In a
pre-shared key IPsec connection, both hosts must
use the same key in order to move to Phase 2 of the
IPsec connection.
Phase 2 of the IPsec connection is where the
Security Association (SA) is created between IPsec
nodes. This phase establishes an SA database with
configuration information, such as the encryption
method, secret session key exchange parameters,
and more. This phase manages the actual IPsec
connection between remote nodes and networks.
IR LEDs
Visible
Light
Filter
MOBILE IRIS RECOGNITION SYSTEM - A Low Cost Approach
239
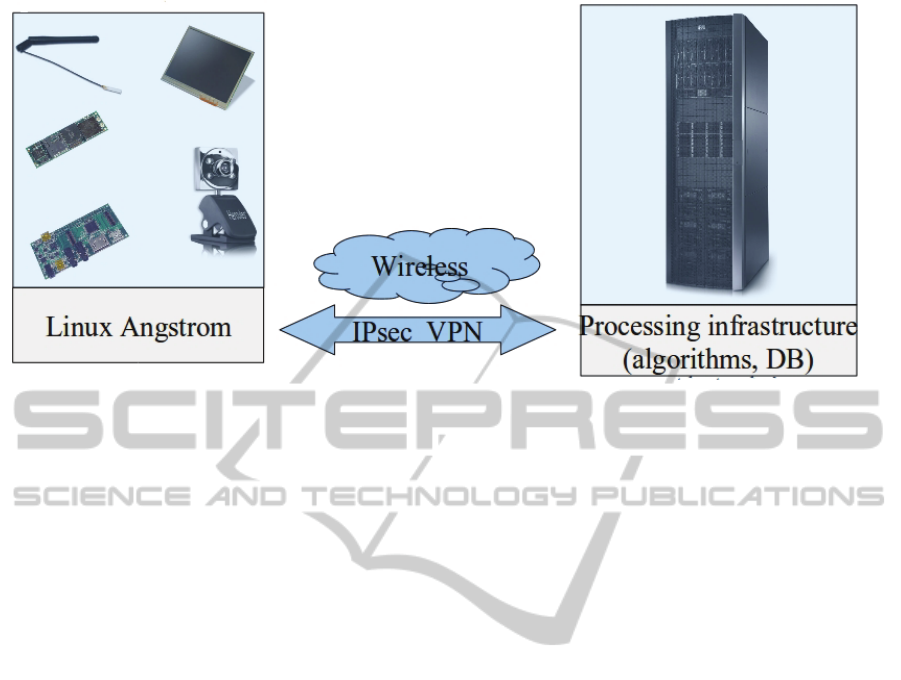
Figure 5: System connectivity.
Basically intensive computations and storage
space will be accessed remotely on the available
infrastructure, the mobile device having only the
role of acquiring and segmenting images (using long
Gabor filters) (Popescu-Bodorin, 2010, Xu, 2008,
Chen, 2010, Jeong, 2010, Perez, 2010) and to submit
further information and applications for enrolment,
verification and identification (recognition is done
using the Daugman’s algorithm) (Daugman, 2007,
Ren, 2008, University of Bath Iris Database, 2009).
The user can access the system using a user
friendly graphical user interface (He, 2008).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The proposed system is a low cost iris acquisition
and processing system for personal identification,
the overall cost of the components is under 500 US
dollars, which is considerable cheaper than the
existing systems on the market.
The system has low power consumption and a
power management system which allows the system
to run over 8 hours. The drawback of such a system
is the low processing (720 MHz, low power
processor) capability and a small and slow storage
(256 MB flash, which can be extended) area which
cannot be used to store the iris biometric information
in a local database.
In order to overcome this problem the system
must access the database and the recognition
algorithms remotely using a secured connexion
(IPsec). Storing and accessing the data remotely also
adds a plus of security because in the event that a
device will be lost the confidential data will not be
accessed by an unauthorized user because all the
biometric information is stored remotely in a secured
location.
Due to its low processing capacity the system
will only acquire the image and run a set of long
Gabor filters to segment the image. In Figure 6 the
graphical interface is presented, the interface has a
set of ambidextrous controls which makes this
device more ergonomic allowing the user to access
the interface in a natural manner. The image is
segmented and the iris area is searched (in the area
marked by the blue circle) and isolated (by the red
and green circles). The isolated iris data is then sent
remotely for further processing.
The presented system can be considered as a low
cost alternative to professional mobile iris
recognition systems, providing an acceptable
performance and a high level of security.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work has been co-funded by the Sectoral
Operational Programme Human Resources
Development 2007-2013 of the Romanian Ministry
of Labour, Family and Social Protection through the
Financial Agreement POSDRU/89/1.5/S/62557.
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
240
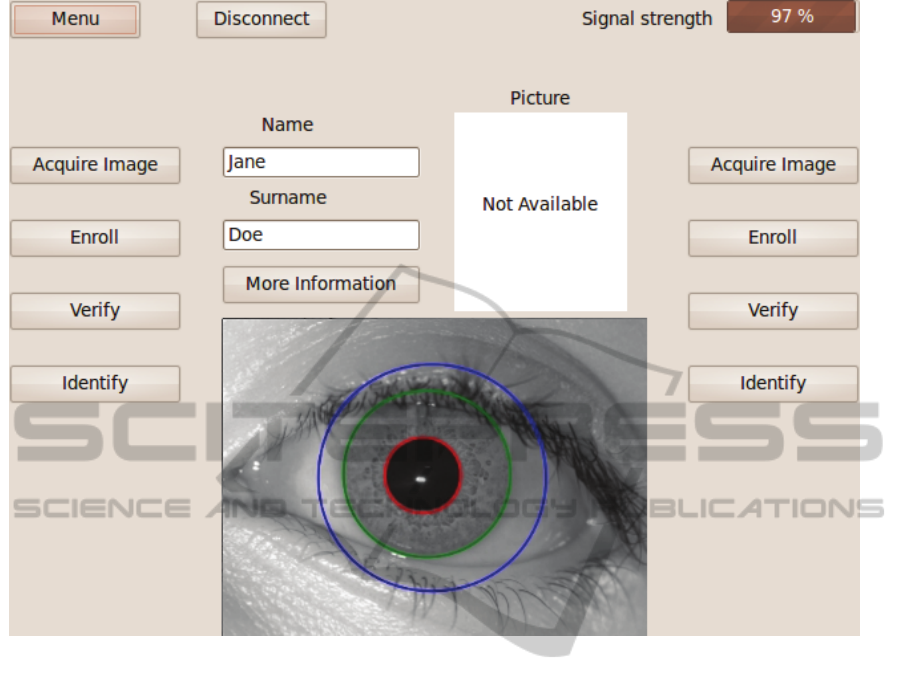
Figure 6: The user interface.
REFERENCES
Daugman, J. G., 2004. How iris recognition works, IEEE
Trans. On circuits and Systems for Video Technology,
vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 21-30.
Daugman, J. G., 2007. New methods in iris recognition,
IEEE Trans. On Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - part
B: Cybernetics, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 1167-1175.
Gumstix Inc., 2010. Overo: Setup and programming.
http://www.gumstix.net/Documentation/cat/Setup-
and-Programming/109.html.
L-1 Identity Solutions Inc., 2010. HIIDE 5 Solutions,
http://www.l1id.com/pages/774-hiide-5.
Popescu-Bodorin N., Balas, V. E., 2010. Comparing
Haar-Hilbert and Log-Gabor Based Iris Encoders on
Bath Iris Image Database. IEEE SOFA 2010.
(http://fmi.spiruharet.ro/bodorin/articles/ieee-sofa-
2010-bodorin-balas.pdf).
Red Hat Inc, 2007. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5
Deployment Guide. Deployment, configuration and
administration of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5, Edition
4.
University of Bath Iris Database. (2009)
http://www.bath.ac.uk/eleceng/research/sipg/iriswe/.
Wong, A., Yeung A., 2009. Network infrastructure secu-
rity. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, New York,
USA. ISBN: 978-1-4419-0166-8.
Kizza, J. M., 2009. A guide to computer network security.
Springer-Verlag London Limited, ISBN: 978-1-
84800-917-2.
Zhai, Y., Zeng, J., Gan, J., Xu, Y., 2009. A study of BPR
based iris recognition method. Proceedings of the
2009 International Symposium on Information
Processing (ISIP’09).
Patnala, S. R., Murty, C., Reddy, E. S., Babu, I. R., 2009.
Iris Recognition System Using Fractal Dimensions of
Haar Patterns. International Journal of Signal
Processing, Image Processing and Pattern
Recognition, Vol. 2, No.3.
Araghi, L. F., Shahhosseini, H., Setoudeh, F., 2010. Iris
Recognition Using Neural Network. Proceedings of
The International MultiConference of Engineers and
Computer Scientists 2010 Vol I, IMECS 2010, March
17-19, Hong Kong.
Xu, G., Zhang Z., Ma Y., 2008. An image segmentation
based method for iris feature extraction. The Journal
Of China Universities Of Posts And
Telecommunications, Vol. 15, Issue 1.
He, Z., Sun, Z., Tan, T., Qiu, X., 2008. Enhanced
Usability Of Iris Recognition Via Efficient User
MOBILE IRIS RECOGNITION SYSTEM - A Low Cost Approach
241

Interface And Iris Image Restoration, ICIP 2008, 978-
1-4244-1764-3/08/$25.00.
Matschitsch, S., Stogner, H., Tschinder, M., 2008.
Rotation-Invariant Iris Recognition Boosting 1d
Spatial-Domain Signatures To 2D, ICINCO 2008 -
International Conference on Informatics in Control,
Automation and Robotics.
Cao, W., Hu, J., Xiao, G., Wang, S., 2005. Iris
Recognition Algorithm Based on Point Covering of
High-Dimensional Space and Neural Network,
MLDM 2005, LNAI 3587, pp. 305 – 313, Springer-
Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2005.
Kim, J. O., Joung, B. J., Chung, C. H., Hwang, J., 2005.
Efficient Iris-Region Normalization for a Video
Surveillance System, HSI 2005, LNCS 3597, pp. 353–
356, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2005.
Ganeshan, B., Theckedath, D., Young, R., Chatwin, C.,
2006. Biometric iris recognition system using a fast
and robust iris localization and alignment procedure,
Optics and Lasers in Engineering 44 (2006) 1–24.
Chen, Y., Adjouadi, M., Han, C., Wang, J., Barreto, A.,
Rishe, N., Andrian, J., 2010. A highly accurate and
computationally efficient approach for unconstrained
iris segmentation, Image and Vision Computing 28
(2010) 261–269.
Jeong, D. S., Hwang, J. W., Kang, B. J., Park, K. R., Won,
C. S., Park, D. K., Kim, J., 2010. A new iris
segmentation method for non-ideal iris images, Image
and Vision Computing 28 (2010) 254–260.
Ren, X., Peng, Z., Zeng, Q., Peng, Q., Zhang, J., Wu, S.,
Zeng, Y., 2008. An improved method for Daugman’s
iris localization algorith., Computers in Biology and
Medicine 38 (2008) 111 – 115.
Perez, C. A., Aravena, C. M., Vallejos, J. I., Estevez, P.
A., Held, C. M., 2010. Face and iris localization using
templates designed by particle swarm optimization.
Pattern Recognition Letters 31 (2010) 857–868.
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
242
