
A METHOD PROPOSAL FOR IMPLEMENTING
ACCESSIBILITY IN DESKTOP APPLICATIONS
FOR VISUALLY IMPAIRED USERS
Livia Cristina Gabos Martins and Bruno Elias Penteado
MStech, Bauru, Brazil
Keywords: Accessibility, Flash, Desktop applications, WCAG.
Abstract: Currently, little is said about the accessibility-oriented desktop applications. In the case of this study,
problems related to the application structure, which has characteristics of a legacy software, brings
challenges that hinder the implementation of accessibility. This article shows an implementation of
accessibility by applying the concepts of web standards in desktop applications, addressing factors such as
controlling the events of Flash components to make data accessible to screen readers and communication
between the layers of user interface and business taking into account information accessibility through the
use of technology MSAA.
1 INTRODUCTION
In general, accessibility can be understood by
removing the barriers which prevents disabled
people to participate in activities of a social context,
including services, products and information
(Santarosa, L. M. C. et al., 2007). In a digital
context, accessibility means that people with
different kinds of disabilities can understand, browse
and interact with the web as well as with other
people, benefiting even those without any disability
(W3C, 2005).
The use of standards for developing accessible
applications emerged in 1997 with the creation of
HTML 4.0 (W3C, 1997) by W3C (World Wide Web
Consortium) - the international community where
associated organizations work together to develop
standards for the Web. In this version of HTML
some elements were introduced which facilitated the
distinction between structure and presentation of the
document. There was also improvement in the
semantics of documents, the addition of medias to
content formatting via the cascading style sheets
(CSS) towards Braille, among others.
Aimed at accessible Web development, the WAI
(Web Accessibility Initiative), a division of W3C,
established a standard known as WCAG 1.0 (Web
Content Accessibility Guidelines 1.0) (W3C, 1999)
for Web developers and designers This standard
defines techniques so that people with disabilities,
such as inability to see, hear, or move properly -
named visually, hearing and motor impaired,
respectively - can read and understand the
information available on the Internet.
Another standard established for this purpose
was the WAI-ARIA (Web Acessibility Initiative -
Accessible Rich Internet Applications) (W3C, 2008)
created to establish specifications of accessibility for
Web applications using Ajax, HTML, JavaScript
and other related technologies in its composition -
also known as rich Internet applications.
The standards described are meant to help the
communication with assistive technologies. This
term is used to identify resources and services that
contribute to provide or increase the functional
abilities of people with various types of impairments
(Sonza, 2008). As examples such resources, we can
highlight: the screen readers and magnifiers, much
used by the visually impaired; speech recognizers,
used to trigger commands by voice; data input
devices, as alternative to the keyboard and mouse;
among others.
Currently, to our knowledge, there is not a
specific standard for implementing accessibility for
desktop applications. We can find some studies on
best practices and observations to this issue (IBM
Corporation, 2009; The University of Wisconsin,
1997), but none declared as official. In general,
287
Gabos Martins L. and Elias Penteado B..
A METHOD PROPOSAL FOR IMPLEMENTING ACCESSIBILITY IN DESKTOP APPLICATIONS FOR VISUALLY IMPAIRED USERS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003495702870290
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2011), pages 287-290
ISBN: 978-989-8425-56-0
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

utility tools are used - the built-in assistive
technologies in operating systems, with no
equivalent standard for the Web.
According to the World Health Organization
(WHO) (WHO, 2009) about 314 million people
worldwide are visually impaired, of which 45
million are blind. In Brazil, according to the IBGE
(Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics),
16.6 million people have some degree of visual
impairment, with almost 150 thousand people
reported blind (IBGE, 2005).
According to Filho (2005), the visually impaired
are very prejudiced by the lack of accessibility on
the Web because, most of the time, it is one of the
few ways they obtain information. Hence the
importance of ensuring accessibility, not only to the
Web, but also to the desktop applications that
provides access to such information, sometimes even
getting information from the Web.
The problem to be addressed in this case study is
related to the use of a desktop application for
visually impaired people, using techniques and
standards originally established for Web applications
and its application in a legacy software.
2 SOFTWARE AND METHOD
The software used in this case study is blueControl,
created by the technology company MStech
(MStech, 2011). This is an application for computer
labs in schools, widely used in educational programs
in Brazil, responsible for managing (from the
computer of the technician responsible for the lab)
the access to computers for students or community
members who use the school computers. With
blueControl, one can provide access for use of lab
computers, block inappropriate software or websites,
print documents, report of events and use of
computers, among other features. It is usually
operated by a technician who manages all computers
connected to that network and where they can
perform the functions described above.
The blueControl is commonly used in
educational programs that provide access to
computer labs for classes, training and access to the
general public. The technicians responsible for the
school’s or institution’s labs are trained to use the
application in their jobs, such as how to turn on
computers in a room for a class. Impaired people are
hired by the government obeying the Brazilian Law
8213/91, also known as Law of Quota, which
guarantees a percentage of employment for impaired
people.
The inability to use the blueControl software for
the visually impaired entails the exclusion of these
people from everyday activities such as the
management of computer laboratories, usually
waiting for a resolution of the problem with the help
of others.
The use of this tool, as originally designed, in
day-to-day laboratory showed that most of its
features did not meet the needs of visually impaired
people responsible for the laboratory, demanding a
redesign of its user interface.
However, being an application also used by
people who have not visual impairment and being
also widely marketed, with manuals created and
distributed, one of the assumptions in the redesign of
the application was that its interface could not be
changed abruptly to meet the accessibility need.
When the blueControl software was firstly
designed, it was not pondered the possibility of
making it accessible for the visually impaired
people. Therefore, problems were faced by the
development team to adapt it.
The blueControl application was implemented in
three layers, using the C# language, the .Net
Framework 2.0 in the layers of business logic and
persistence to the database – Microsoft SQL Server
2005. The interface layer was implemented using
Flash Action Script 2.0 technology.
Normally, when best practices are applied in the
development of accessible websites using Flash
technology, screen readers can identify the website
information, due to MSAA technology (Microsoft
Active Accessibility) (Microsoft, 2000). MSAA is a
technology based on COM (Component Object
Model), which enables communication between
applications and operating system and exists only on
Windows.
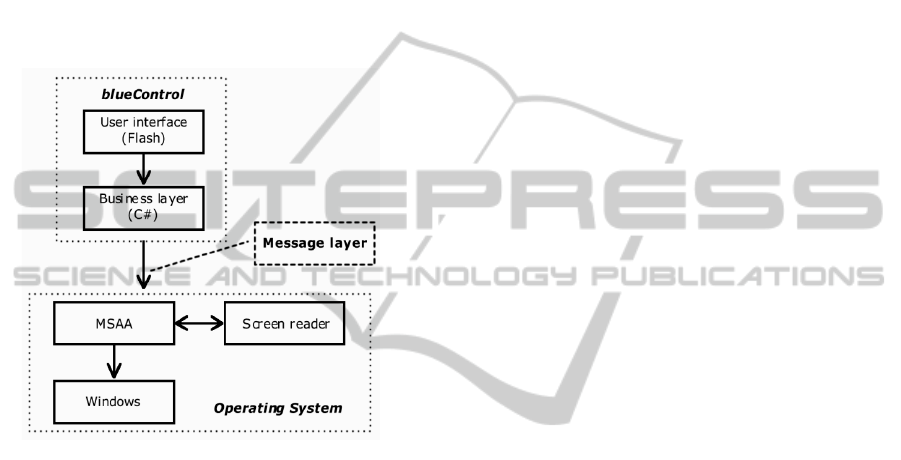
So that the interface could represent the state of
the inner logic an additional messaging service layer
was created. The messaging service layer helps
assistive technology interact with the operating
system. Due to this, browsers can send the
information, if any, for screen readers. As
blueControl was designed to run only on Windows,
a new service layer was created, to capture the
interface information and make it available to
assistive technology MSAA.
As the business layer was developed in C#, the
function of this new service layer is to pass the
accessibility information from Flash user interface to
the operating system, through MSAA, where screen
readers can identify the information (Figure 1).
To improve the user experience in using
blueControl, it was added a button that takes the
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
288
user to a help screen about the accessibility
implemented. On this screen the user finds all
information on how to operate blueControl by using
the shortcut keys.
The development team followed the WCAG 1.0
standard for the modifications. This standard is
divided in three levels of priorities, namely: i)
Priority 1 - should be fully satisfied, ii) Priority 2 -
should be met and iii) Priority 3 - can be met. In this
study, the three levels have been met, while
respecting the differences in concepts and
procedures between web and desktop.
Figure 1: Diagram of communication.
Thus, our method to enable accessibility in
desktop applications consists in the observance of
WCAG guidelines for desktop applications along
with the new service layer to help the
communication with assistive technologies.
3 METHOD EVALUATION
A small group of 3 people was selected to
preliminarily assess the blueControl application. The
group was restricted to visually impaired people, due
to the focus of this study. They were classified
according to the WHO definition regarding
blindness and low vision (WHO and DIMDI, 2007).
In this study we used the environment DOSVOX
(Borges, 2002) as assistive technology for testing. It
is a system only for Windows, which communicates
with the user via speech synthesis, enabling the use
of computers by the visually impaired. It is
considered an environment and not just a screen
reader, due to the many features it has and by letting
the user not navigate by operating system directly.
DOSVOX was chosen because it is a free
environment, widely used and distributed in
government programs in Brazil and has a good
support for Flash on desktop environment.
Another popular tools of assistive technology,
such NVDA and JAWS were not used in this case
study, since they were not distributed along with
blueControl. Thus, we used DOSVOX for
standardization of testing. Besides, for the tests with
blueControl a group who had training on its usage
was selected, providing equal knowledge in the
assessment.
In possession of the new software version, with
the changes implementing accessibility features,
users of the selected group were instructed to
perform their tasks as taught in their training for the
management activities of the laboratory.
After applying the suggested method in the user
interface redesign, the selected users were able to
perform their regular tasks. During the first use,
some delay was caused at first experience, as they
get accustomed to the software and its layout.
Further interactions with the software showed
natural to their experience, as they had previous
experience with screen readers.
There were some drawbacks though, in the
implementation: some components, like Calendar,
needed an alternative input, since it could not
provide direct access to the information needed (e.g.
a specific day in the future), making it difficult to
handle and time consuming to use it often. The
DataGrid component, used to display a table of
records, came up as a problem too. An alternative
and simplified version, merging the columns into a
single one was used. Also, the excess of explaining
texts in some forms made difficult the fluent
execution of some tasks. The broad solution to these
components was a proper navigation by keyboard.
Though the implementation had some issues, the
basic concepts of WCAG were met properly, with
minor adjustments.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Currently, little is disseminated on the issue of
accessibility in software, although the standards or
even the law regarding accessibility. Usually the
topic is bound to the development of Web
applications.
Although there is not a specific standard to the
implementation of accessibility in a desktop
application, this case study demonstrated the
A METHOD PROPOSAL FOR IMPLEMENTING ACCESSIBILITY IN DESKTOP APPLICATIONS FOR VISUALLY
IMPAIRED USERS
289

technical feasibility of implementing the concepts of
web accessibility in a desktop application using only
different methods of implementation, regarding
desktop specificities, which was possible due to the
similarity of elements and features.
Although there are some points where Flash
technology does not allow an implementation of
accessibility in a less laborious way, it is an
interesting technology for use in desktop
applications, since it offers the possibility of creating
richer interfaces.
With the adjustments implemented in this case
study it was possible to adapt a legacy desktop
application, already in market, to meet the
accessibility levels set for Web applications,
ensuring adherence to laws and inclusion of visually
impaired users in their everyday work.
Though this work has only used one screen
reader, DOSVOX, other tools from the most popular
screen readers must be tested to assess the
comprehensiveness of this approach.
As an ongoing project, we have as a next step the
application of surveys, based on WCAG
recommendations, to the visually impaired who
work on a daily basis with blueControl so that we
can evaluate what are the achievements of our
approach. In future, it could be extended to other
types of disabilities such as motor impairment.
REFERENCES
Santarosa, L. M. C. et al., 2007. Inclusão e Diversidade :
referenciais na construção da acessibilidade para
Ambientes Virtuais de formação de
Professores.In:Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na
Educação.São Paulo,Brazil 2007.Brasília:Sociedade
Brasileira de Computação.
Borges, J. A, 2002. O que é o Dosvox. Núcleo de
Computação Eletrônica da UFRJ – Universidade
Federal do Rio de Janeiro. Available at:
<http://intervox.nce.ufrj.br/dosvox/intro.htm>
[Accessed April, 2010].
Filho, L. P. P., 2005. Como a falta de acessibilidade na
web pode afetar os portadores de deficiência visual.
Graduation. Faculdade Integrada do Recife.
IBGE,2005. IBGE e CORDE abrem encontro
internacional de estatísticas sobre pessoas com
deficiência. (Hitting the headlines article)[online]
Available at: <http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/
presidencia/noticias/noticia_visualiza.php?id_noticia=
438&id_pagina=1> [Accessed May, 2010].
IBM Corporation, 2009. Software checklist.[online]
Available at:<http://www-
03.ibm.com/able/guidelines/software/accesssoftware.h
tml> [Accessed June, 2010].
Microsoft Corporation, 2000.Microsoft Active
Accessibility: Architecture. [online] Available at:
<http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-
us/library/ms971310.aspx#actvaccess_topic1>
[Accessed May, 2010].
MStech,2011. MStech. [online] Available
at:<http://www.mstech.com.br/>.[Accessed January,
2011].
Sonza, A.P., 2008. Ambientes virtuais acessíveis sob a
perspectiva de usuários com limitação visual.
Doctorate.Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul.
The University of Wisconsin, 1997.Requirements for
accessible software design. [online] Place: University
of Wisconsin-Madison. Available at:
<http://trace.wisc.edu/docs/ed_dept_software_guidelin
es/software.htm>. [Accessed June, 2010].
W3C, 1997. HTML 4.0 Specification. [online] Available
at: <http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40-971218/>
[Accessed June, 2010]
W3C, 1999. Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 1.0.
[online] Available at:
<http://www.w3.org/TR/WCAG10/>. [Accessed
March, 2010].
W3C, 2005. Introduction to Web Accessibility. [online]
(Updated September 2005) Available at:
<http://www.w3.org/WAI/intro/accessibility.php>
[Accessed January, 2011].
W3C, 2008. WAI-ARIA Overview. [online] (Updated 18
January 2011) Available at:
<http://www.w3.org/WAI/intro/aria.php> [Accessed
April, 2010].
WHO, 2009. World Health Organization - Visual
impairment and blindness – Fact Sheet no. 282.
[online] Available
at:<http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs282/e
n/> [Accessed March, 2010].
WHO,DIMDI, 2007. World Health Organization -
Chapter VII - Diseases of the eye and adnexa. [online]
Available at:
<http://apps.who.int/classifications/apps/icd/icd10onli
ne/?gH53.htm+h540> [Accessed December, 2010].
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
290
