
SEMANTICS AND KNOWLEDGE CAPITALIZATION IN
ONLINE COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE OF E-LEARNING
Lamia Berkani
1, 2
, Azeddine Chikh
3
and Omar Nouali
4
1
Department of Computer Science, USTHB University, Bab-Ezzouar, Algiers, Algeria
2
Higher National School of Computer Science, ESI, Oued Smar, Algiers, Algeria
3
Department of Information System, KSU University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
4
Department of Research Computing, CERIST, Algiers, Algeria
Keywords: Communities of practice, CoP, CoP of e-learning, Knowledge management, Knowledge capitalization,
Ontology-based framework, Semantic annotation.
Abstract: Knowledge management in Communities of Practice of E-learning (CoPEs) is challenged by several issues:
the complexity of knowledge, considered as interdisciplinary (psycho-cognitive, pedagogic, software-
oriented, and hardware-oriented), the difficulty to access and reuse that knowledge, and the complexity of
the knowledge capitalization process. Most of the knowledge exchanged is mainly tacit, based on direct
communication between members, and therefore needs to be elicited and represented in a formal way to be
capitalized. Explicit knowledge is generally shared and accessible through the CoPE’s repositories.
However, it is not always well elicited and organized. In this paper, we propose an ontology-based
framework for capitalizing knowledge for reuse in CoPEs. We show through an example of use how
semantics can contribute to the management of the tacit knowledge that the community members own and
therefore to the improvement of the learning process in CoPEs.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recent researches show that Communities of
Practice (CoPs) play an important role in the
management of the tacit knowledge that the
community members own (Wenger, 2004; Kimble
and Hildreth, 2004). A CoP has become associated
with knowledge management, in particular as a way
of transferring tacit knowledge. CoPs have several
characteristics that distinguish them from formal
organizations. In fact, according to Wenger (2004)
such communities are groups of people who share a
concern, a set of problems, or a passion about a topic
(the domain of the community), deepen their
expertise and practical knowledge (the practice of
the community), and interact on an ongoing basis
(the community itself).
Communities of Practice of E-learning (CoPEs)
(Chikh et al., 2007; 2008) are considered as a virtual
framework for exchanging and sharing techno-
pedagogic knowledge and know-how between actors
of e-learning (e.g. teachers, tutors, administrators,
etc.). Recently, we can see the emergence of CoPEs.
For example: the CoPe-L (CoP of e-learning at
Luxembourg), has been created in the framework of
Palette project (2006), and whose objective is to
share practices and promote e-learning activities;
CoP of tutors Learn-Nett (Learning Network for
Teachers and Trainers - http://learn-nett.org), is
focused on a shared course and aims at preparing
future teachers or trainers for educative uses of
Information and Communication Technologies.
By using advanced technology, online CoPEs
have the potential to bring members together
virtually, to learn from each other, collaborate and
share expertise and techno-pedagogic practices.
We address in this paper the problem of
capitalization of knowledge, both tacit and explicit,
in a way that facilitates its access and reuse. Due to
the informal character of learning within a CoPE,
most of the knowledge is mainly tacit, based on
direct communication between members, and then
needs to be elicited and represented in a formal way
to be capitalized. Moreover, explicit knowledge is
generally shared and accessible through the CoPE’s
repositories. But, it is not always well elicited and
organized and then needs to be more explicit, so as
to improve access, sharing and reuse of this
96
Berkani L., Chikh A. and Nouali O..
SEMANTICS AND KNOWLEDGE CAPITALIZATION IN ONLINE COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE OF E-LEARNING.
DOI: 10.5220/0003676500960104
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2011), pages 96-104
ISBN: 978-989-8425-81-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

knowledge.
We propose in this paper an ontology-based
framework for capitalizing knowledge for reuse in
CoPEs. Ontologies, generally defined as a
representation of a shared conceptualization of a
particular domain (Gruber, 1993), is a major
component of the semantic web. The role of
ontologies is to assist persons and organizations by
providing a common vocabulary, to achieve
interoperability between different environments, and
to improve consistency information retrieval. In our
context, the ontology-framework will provide a
common backbone for capitalization of knowledge,
both tacit and explicit, allow to annotate the CoPE’s
knowledge resources in order to facilitate their
retrieval and reuse; provide a shared understanding
between the different actors of e-learning; and
facilitate exchanges between the CoPE environment
and the Learning Management Systems (LMS).
2 RESEARCH PROBLEM
In a CoPE, members can openly discuss and
brainstorm about their problems and experiences,
related to the development and use of online
learning systems. The interactions are conducive to
developing new knowledge, stimulating innovation,
or sharing existing tacit and/or explicit knowledge
between e-learning actors.
On one hand, those actors have tacit techno-
pedagogic knowledge which they learnt from their
experience in different e-learning projects. However,
that knowledge is not always capitalized in the
memory. Sharing such knowledge is considered as a
big challenge: it must be efficiently and effectively
represented in order to be further exploited.
On the other hand, explicit knowledge, which
includes learning resources, is generally shared and
accessible through the CoPE’s repositories.
However, it is not well elicited and organized (e.g.
lack of information related to feedback use, validity
and assessment).
In the context of a CoPE, we distinguish two
types of knowledge reuse: the explicit knowledge
reuse (e.g. reuse of knowledge resources) and the
tacit knowledge reuse (e.g. reuse of some hints
provided by another member having more
experience). Our objective consists to make the
reuse explicit and to well organize it, so as to make
it more efficient.
Consequently, our main research question is:
“How to represent knowledge, tacit and explicit,
within the framework of a CoPE, so as to facilitate
its access and reuse?”
In this paper we try to answer the following sub-
questions:
How can we help members to formalize and
capitalize tacit knowledge?
How do we organize the CoPE memory in
order to enhance the reuse of its content by
members?
How do we enrich learning resources with
metadata in order to improve their reuse?
3 RELATED WORK
Recently, a lot of research works was interested to
knowledge management and capitalization within a
CoP, to name but a few: the Palette project (2006),
where several knowledge management services were
proposed to support CoPs. These services rely on a
semantic web-based approach using ontologies
(Tifous et al., 2007), for annotating knowledge in
order to facilitate their transfer and sharing. Other
works are based on the concept of organizational
learning memory to capitalize tacit knowledge
(Leblanc and Abel, 2008).
In the context of CoPEs, Quénu-Joiron and
Condamines (2009) developed a web community
platform dedicated to knowledge capitalization and
on-line know-how transfer between experienced
teachers and beginners. While Quénu-Joiron and
Leclet (2010), implemented a CoP dedicated to
project based pedagogy tutors using a case-based
reasoning approach.
4 KNOWLEDGE
CAPITALIZATION IN COPES
4.1 Knowledge Capitalization Process
The process of knowledge capitalization can be seen
as a cycle with several steps. Grundstein (1992)
summarizes this process in four steps: detection,
preservation, exploitation, and actualization. In
(Oladejo et al., 2010) the authors propose the
“Dynamic Capitalization” approach (see figure 1).
There are five major phases in this approach and
each phase is dynamic with respect to evaluation and
validation of knowledge resources by actors.
Knowledge can be elicited using the process of
declaration and annotation. Knowledge resources are
represented with the aid of a conceptual knowledge
model. The acquired knowledge resource is stored
SEMANTICS AND KNOWLEDGE CAPITALIZATION IN ONLINE COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE OF
E-LEARNING
97
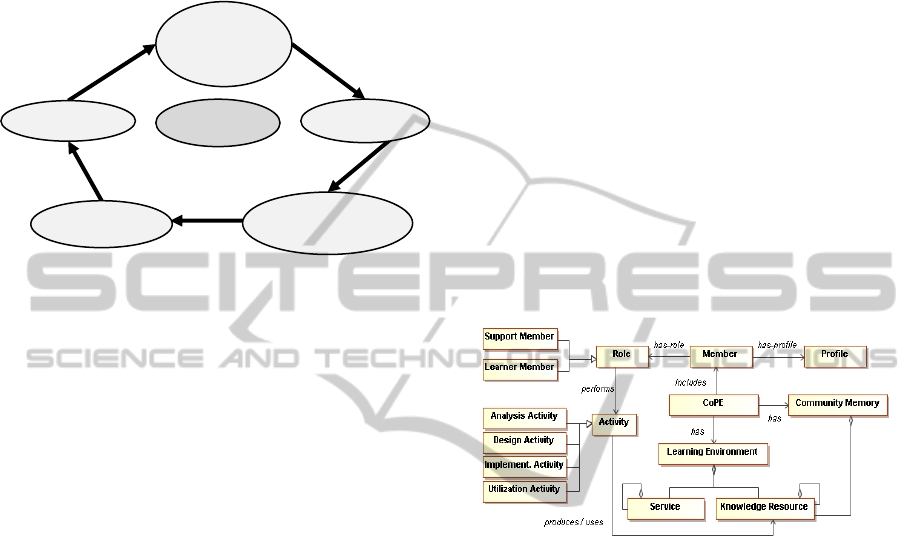
with temporal attributes, in a knowledge repository
(i.e. for dynamic and non-volatile capitalization).
The storage facilitates the reuse of knowledge
through exploitation process. Acquired and stored
knowledge resources can be exploited for reuse and
sharing.
Figure 1: Dynamic capitalization approach, from (Oladejo
et al., 2010).
The dynamic capitalization approach seems to be
well adapted for our context of study, as it proposes
a structure for knowledge reuse and encourages and
favours the collaboration between actors.
4.2 Knowledge Capitalization Process
in CoPEs
The capitalization process in a CoPE is considered
as the result of continuous update from knowledge
reuse and capitalization of lessons learnt by the
community members. We discuss below the
different steps of the dynamic capitalization
approach applied to the context of a CoPE:
Elicitation, Acquisition, Validation:
knowledge is elicited from members through
discussion using the annotation process (e.g.
analysis comments). This supports the
understanding and validation of knowledge
among them.
Representation: knowledge resources are
represented using ontologies, knowledge
models, etc.
Storage: an organizational learning memory is
used to store all the CoPE’s knowledge
resources.
Exploitation: refers to the reuse of knowledge
resources from the memory. For example, in
the case of problem-solving, knowledge
exploitation involves mining and visualization
of knowledge for new cases of problems.
Feedback exploitation strategy: members can
be guided to externalize the knowledge
derived from the reuse of knowledge
resources in form of feedback.
5 THE ONTOLOGY-BASED
FRAMEWORK
We present in this section, an ontology-based
framework for knowledge reuse in CoPEs.
5.1 OntoCoPE – An Ontology for
CoPEs
A general conceptual model for a CoPE, called
OntoCoPE ontology, is based on the O’CoP
ontology conceptual model for CoPs (Tifous et al.,
2007) defined in the Palette project (2006) and on
partial conceptual models for CoPEs proposed in
(Berkani and Chikh, 2009).
Figure 2: Main concepts of CoPEs.
5.2 Ontology-based Framework for
CoPE Memory
The organizational memory refers to the place where
the organization’s information and knowledge
resources are found. The use of ontologies helps the
organization to become a “semantic learning
organization”. MEMORAe project (Organizational
Memory Applied to the e-learning) illustrated the
importance of using ontologies to represent an
organizational learning memory in the context of an
e-learning training (Abel et al., 2004) and for a
community of learners (Leblanc and Abel, 2008).
To implement the CoPE memory, we propose an
ontology-based framework in order to define a
common vocabulary and to annotate the knowledge
resources, and we provide a means of storage and
indexing of knowledge resources. We propose to
structure the memory into three layers, as shown in
figure 3.
Elicitation
Acquisition
Validation
Feedback
Evolution
Storage with
temporal attribute
Exploitation
Representation
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
98

Figure 3: Ontology-based Framework for CoPE memory.
The CoPE memory is seen as a “semantic learning
organization”, described using an ontology-based
framework structured into three layers as shown in
figure 3. The framework provides a common
vocabulary between the CoPE’s members, a
semantic support to annotate the CoPE’s knowledge
resources in order to facilitate their retrieval and
reuse, and a means of storage and indexing the
different data. We describe in the following the three
layers:
5.2.1 The Ontology Layer
The ontology layer is based on several ontologies:
OntoCoPE, an ontology for CoPEs (Berkani
and Chikh, 2009), describes the main concepts
of a CoPE: “Community”, “Actor”, “Role”,
“Profile”, “Activity”, “Process”, “Resource”,
“Service and Tool”, “knowledge”,
“Competency”.
An e-learning ontology, describing the
concepts related to the domain of e-learning.
This ontology will facilitate exchanges and
transfer of knowledge between the CoPE
environment and LMS.
A knowledge model ontology, describes the
different kinds of knowledge models such as
lessons learnt and which can be developed for
example using patterns and case-based
reasoning.
An application domain ontology, concerns a
specific course (e.g. mathematics, software
engineering, etc.).
A specification languages, such as Learning
Object Metadata (LOM, 2002) for describing
learning objects, IMS Learning Design
specification (IMS-LD, 2003) for describing
learning designs, etc.
5.2.2 The Semantic Annotation Layer
Semantic annotations are generated automatically
and assign knowledge resources of the content layer
to concepts of ontologies included in the ontology
layer. Information is represented as a triplet
<Ontology concept, Annotation, Knowledge
resource>.
5.2.3 The Content Layer
The content layer includes several repositories to
store the different data:
Members’ profile: includes some attributes
such as: experience; cognitive characteristics;
communication skills; learning competences;
learning objectives.
Lessons learnt: correspond to positive or
negative lessons learnt, related respectively to
best or bad practices regarding the different
stages of the development lifecycle (analysis,
design, implementation and utilization) of an
e-learning product.
Learning Objects (LOs): are described using
the standard LOM (2002). A semantic
description of a LO using ontologies is
proposed in (Jovanović et al., 2007). In the
next sub-sections we present a model of LO in
the context of CoPEs, in order to depict the
specificities of a CoPE.
Learning Designs: also called learning
scenarios, are represented using the standard
IMS-LD (2003) by identifying the necessary
LOs
LDs
Lessons
learnt
Specification
Languages
(
LOM, IMS-LD…)
Knowledge model
Ontology
E-learning
Ontology
OntoCoPE
Ontology
Application domain ontology
“Content layer”
(Knowledge Resource)
Members’ profile
“Ontology layer”
(
Ontologies)
“Semantic annotation layer”
<Ontology Concept, Annotation,
Knowledge Resource>
Annotations
SEMANTICS AND KNOWLEDGE CAPITALIZATION IN ONLINE COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE OF
E-LEARNING
99
learning activities and assigning LOs to those
activities in order to achieve the specified
learning objective.
5.3 Annotation Model
We use the annotations in the CoPE for the
capitalisation of tacit knowledge. Annotations aim to
evaluate and improve the understanding about
knowledge resources, artefacts, processes, etc.
The model of the annotation is created on the
basis of some previous works on annotations:
DAML Ontology Library (2000) and (Fogli et al,
2005). We consider that an annotation may annotate
one or more knowledge resources, a part of a
knowledge resource or another annotation. An
annotation may be related to several other
annotations.
We have defined three kinds of annotations: (1)
the analysis annotation, where members can write
some comments highlighting their personal remarks
and understanding; (2) the evaluation annotation,
where members can evaluate the knowledge
resources according a scale (1-5), from a very good
one to a very bad one. Moreover, members can give
their personal feedback regarding the use of any
knowledge resource; and (3) the results annotation,
shows the lessons learnt from this use (i.e. positive
and negative lessons learnt).
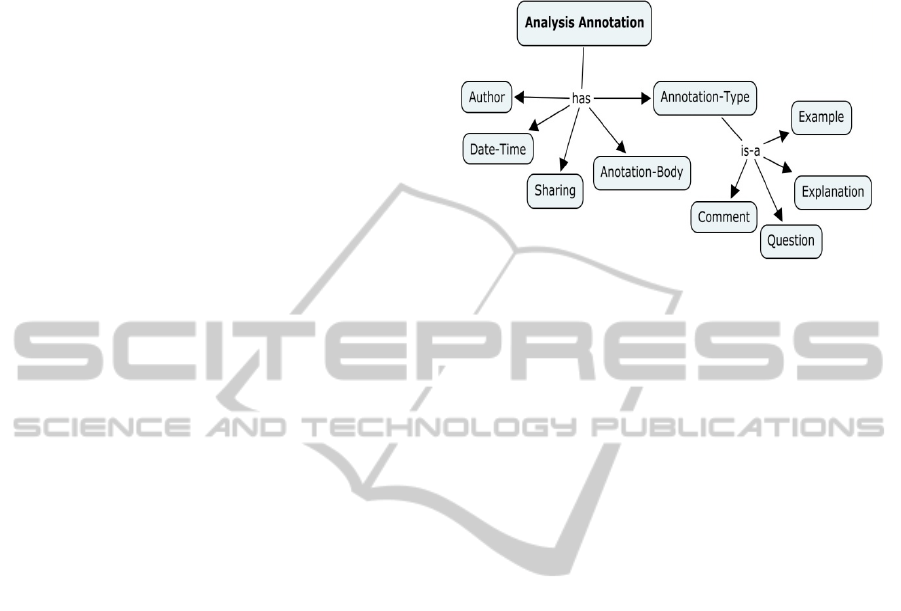
For the analysis annotation for example, we
propose the following annotation properties (see
figure 4):
Author: is the member who writes the
annotation.
Date-Time: corresponds to the date of creation
(or update) of the annotation.
Annotation-body: is the element concerned by
the annotation (a Knowledge resource, a part
of a knowledge resource or an annotation).
Sharing: the author may share or not his
annotation.
Annotation-type: which may be a “Question”,
asking for additional information; a
“Comment”, adding some remarks; an
“Explanation”, adding further clarification; an
“Example”, illustrating the annotation body,
Each annotation is associated to one or more
concepts of an ontology. This allows mapping of the
annotations to the elements of the ontology.
OWL-DL language may be used to implement
our ontology, as it offers the consistency checking of
our model and the querying which provides an
improved exploitation and knowledge retrieval from
complex knowledge bases. Thus, members can
formulate complex queries such as: ‘retrieve
knowledge resources of a given topic and having
high levels of score’.
Figure 4: Analysis annotation model.
5.4 LO Model in the Context of a CoPE
The adoption of the standard LOM (2002), promotes
exchange of LOs among different LMS, and offers
higher potentials for finding existing learning
content. However, decisions about reuse involve a
broad set of issues about content, context and
pedagogy that cannot be fully expressed in the
LOM’s metadata fields. The authors in (Jovanović et
al., 2007) developed an ontology-based framework
aimed at explicit representation of context-specific
metadata. The core part of the proposed framework
is a LO context ontology, that leverages a range of
other types of ontologies (e.g., user modeling
ontology and content structuring ontology to capture
the information about specific context of use of a LO
inside a learning design). Information of this kind
can be rather useful for personalization of learning
process in the LMS.
In the context of a CoPE, members need not only
to find and reuse LOs in their courses, but moreover,
to find the comments and feedback about LOs
expressed by members having used them; the results
of tests and experimentations in the LMS;
information about how to use the LO (i.e. the
context of use and contexts of possible reuse, etc.).
In our solution, we propose to adopt the standard
LOM (2002) and the existing ontologies to annotate
the LO. Moreover, we add a concept, called “LO-
Reuse”, to capture all the above mentioned
elements: members’ comments, their feedback,
results, and so on.
Figure 5 shows the description of a LO’s related
metadata. The proposed metadata concerns: the LO
information context, gives general information about
the origin of the LO (developed in the CoPE or
imported from any other source), its subject and
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
100
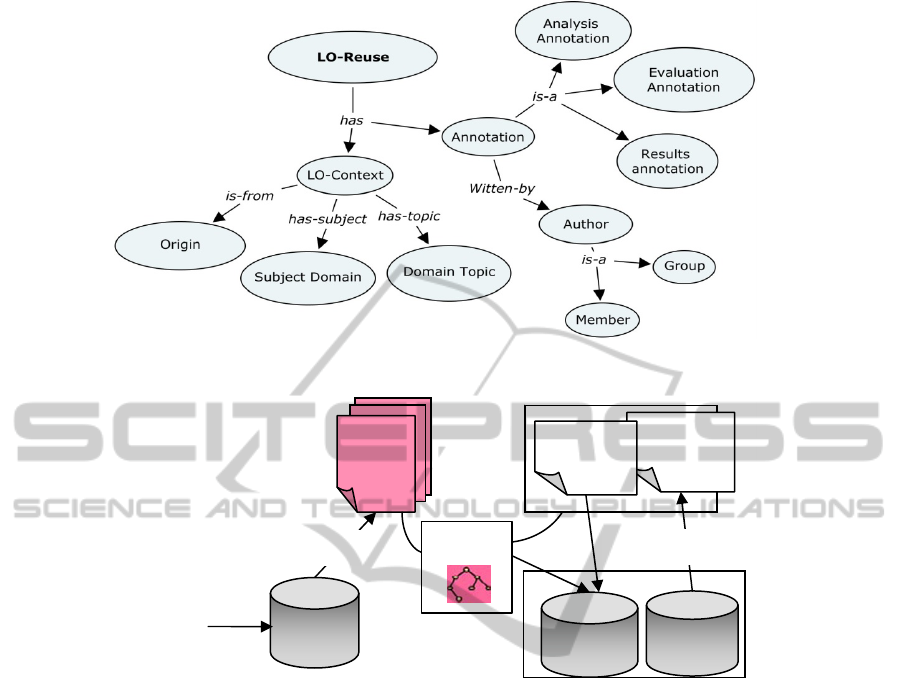
Member with
Profile “P1”
Figure 5: LO-Reuse metadata in the context of a CoPE.
Figure 6: Example of knowledge capitalization for reuse.
topic domain; and a set of annotations, analysis,
evaluation and results, provided by a member or
group of members who have used the LO.
Using this concept, allows us to recommend the
adequate LOs for members according to their
profiles and needs. Moreover, when a member is
seeking about LOs related to any subject and /or
topic domain, it is possible to recommend him
automatically LOs jugged as interesting (i.e.
evaluated with a high level score) by other members
having the same profile. The recommendation of the
relevant LOs will help members in their activities
and will improve their learning using the experience
and feedback of other members, through the
different annotations.
6 EXAMPLE OF USE
We consider a use case within Learn-Nett (Learning
Network for Teachers and Trainers), a CoPE
focused on a shared course and aims at preparing
future teachers or trainers for educative uses of
Information and Communication Technologies. The
ontology-framework proposed will be useful for
annotating the CoPE’s knowledge resources such as
LOs (e.g. a pedagogical and/or technical guide for
the course). We suppose one teacher member (M1)
of Learn-Nett having the profile (P1) wants to
prepare a course concerning Software Engineering.
As shown in figure 6, the teacher M1 can retrieve
LOs from the memory. The “knowledge resources
search service” uses the ontology framework to seek
about the relevant resources that meets the needs of
M1. One or more LOs can be found and displayed
for the member, who will have the possibility to
consult and/or download them. However, once using
those resources, the member will have the possibility
to annotate any of them using the “knowledge
resource annotation service” (AnnotatKR).
In the following, we’ll show through a series of
screenshots how members interact with AnnotatKR
to annotate a LO.
Annotation
Repository
Members
Repository
Learning
objects
(LOs)
Query
LOs
Repository
Store
Fetches
Member’s
Profile "P1"
Ontology-
Framework
Fetches
Annotation
SEMANTICS AND KNOWLEDGE CAPITALIZATION IN ONLINE COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE OF
E-LEARNING
101
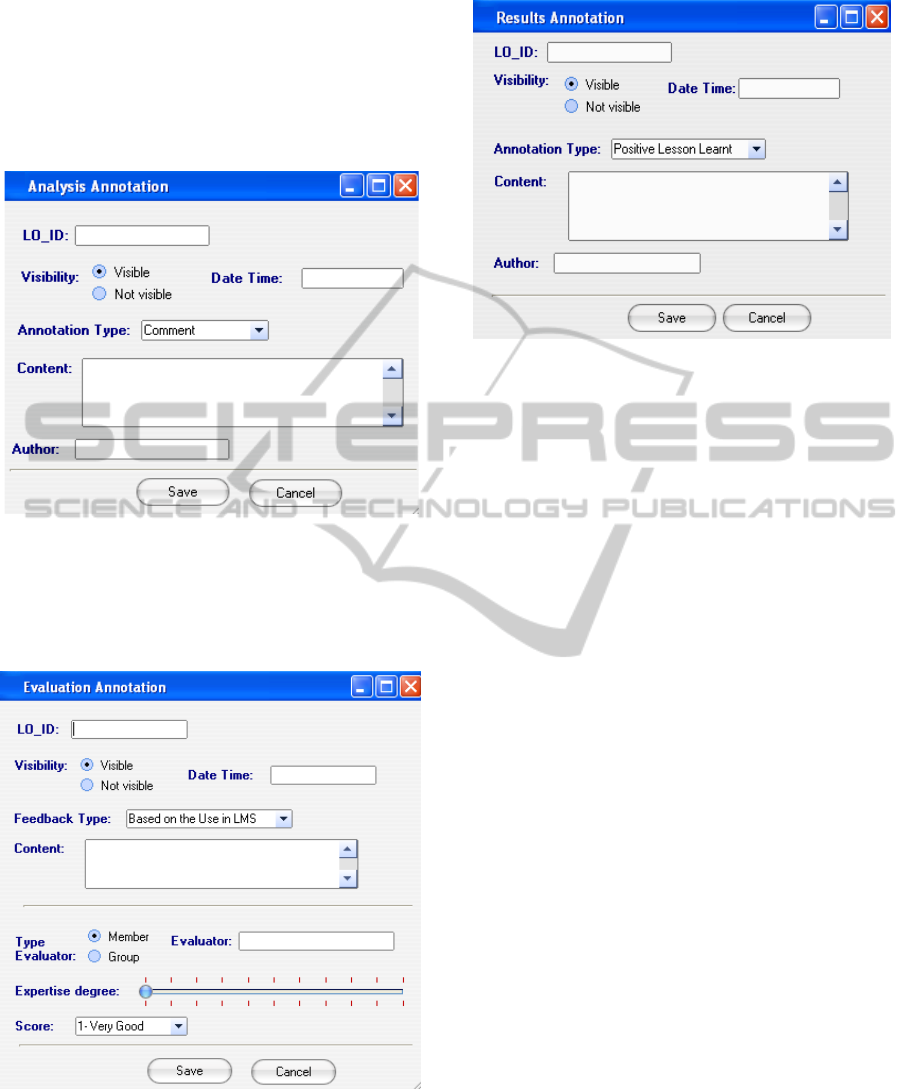
After using the LO in this course, the member
M1 can write some comments highlighting his
personal experience and analysis about it. He can
also give some comments that will serve to improve
it, ask a question, or give an example from his
practice, using the “Analysis annotation module”
(see figure 7).
Figure 7: Analysis annotation module.
Moreover, the member M1 can participate to the
evaluation of the LO by giving his own feedback
and score using the “Evaluation annotation module”,
as shown in the figure 8.
Figure 8: Evaluation annotation module.
Finally, the member M1 can use the “Results
annotation module” to note positive and/or negative
aspects from reflective analysis of the supervision
methods throughout his effective experience of
tutoring students (see figure 9).
Figure 9: Results annotation module.
Once the LO’s reuse-related metadata are fulfilled,
the anchoring information and the information on
the teacher are stored in the annotation repository.
Another teacher member (M2) can retrieve the
same LO, and then he will have the possibility to
reuse, not only the LO content but also the
comments found on it. Moreover, he will have an
idea about the degree of interest of the LO according
to the given scores. He will have access to the results
deduced from its use by other members. Finally, he
can also create annotations on that resource.
7 DISCUSSION
The work presented in this paper aims to capitalize
the tacit knowledge owned by members of a CoPE,
using semantic annotations. We focused in this
paper on LOs just in order to illustrate the process of
capitalizing knowledge using annotations. However,
this approach can be used to annotate all the
knowledge resources, artefacts and processes in the
CoPE. For instance, we can annotate the proposed
solutions during the problem-solving process.
Our main objective is to facilitate the
capitalization of tacit knowledge (know-how,
experience, feedback, etc.) of members when using
knowledge resources so as to facilitate the
knowledge access and reuse. We can summarise the
main results expected by this approach as follows:
Members can share and reuse their tacit
knowledge through the analysis annotation.
They can have an idea about the different
feedback and evaluations of other members
who have used the knowledge resources.
The knowledge resource search service can
use the scores of a knowledge resource from
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
102

the different evaluation annotations and then
recommend those having a high level of
scores to other members.
The service can refine the search process by
finding the resources that meet the needs of
members and for what members having the
same profile used them and evaluated them
with a high level of scores.
The manager of the CoPE can have an idea
about the utilisation of knowledge resources
by members and about the participation of
members too in the annotation process.
Members can learn from the experience of
others through the results annotations. This
will help them to improve their expertise and
practical knowledge.
Furthermore, in addition to this different forms
of knowledge acquisition and reuse, this initiative,
will help members to improve their engagement in
the CoPE. Indeed, this will motivate them to
collaborate and participate actively in the
community. The collaboration here concerns
especially the reification process of tacit knowledge
in the community memory. In addition, we can
consider the annotations as a trigger for other
activities in the community, as they can open further
discussions and exchanges among members.
8 CONCLUSIONS
The present paper described an ontology based-
framework for knowledge capitalization and reuse
within online CoPEs. The ontology allows to
annotate knowledge resources in order to facilitate
their retrieval and reuse by CoPEs’ members. Our
main objective is to organize the process of
capitalization of knowledge and to allow a
knowledge elicitation through manual and automatic
annotation of knowledge resources by capturing the
members’ experience and feedback. We have
proposed a model for manual annotation.
In our future work, we envisage to complete our
ontology, integrate a SPARQL engine to allow
querying of the knowledge base, and to allow an
automatic and semi-automatic annotation of
knowledge resources.
Finally, it is necessary to check the usefulness of
the framework and to describe the experience in the
members’ feedback and point of view.
To do so,
we’ll evaluate our approach in a CoPE to be created
in the University of Science and Technology
(USTHB) called A-CoPE (Algerian CoP of E-
learning), and whose main objective is to promote e-
learning in higher education context.
REFERENCES
Abel, M. H., Barry, C., Benayache, A., Chaput, B., Lenne,
D., Moulin, C., 2004. Ontology-based Organizational
Memory for e-learning. In Educational Technology &
Society, vol.7.
Berkani, L., Chikh, A., 2009. Towards an Ontology for
Supporting Communities of Practice of E-learning
"CoPEs": A Conceptual Model. In U. Cress, V.
Dimitrova, and M. Specht (Eds.) EC-TEL 2009. LNCS
5794, pp. 664–669. Springer, Heidelberg,
Chikh, A., Berkani, L., Sarirete, A., 2007. Modeling the
communities of practice of e learning – CoPEs. In 4th
Annual Conference proceedings of Learning
International Networks Consortium, pp. 428-441,
Jordan
Chikh, A., Berkani, L., Sarirete, A., 2008. Communities of
Practice of E-learning “CoPE” – Definition and
Concepts. In International Workshop on Advanced
Information Systems for Enterprise, pp. 31-37.
DAML Ontology Library, 2000. http://www.w3.org/
2000/10/annotation-ns#
Fogli, Fresta, G., Mussio, P., Marcante, A., Padula, M.,
2005. Annotation in cooperative work: from paper-
based to the web one” In: International Workshop
Annotation for Collaboration, pp. 24-25, Paris France.
Gruber, T.R., 1993. A Translation Approach to Portable
Ontology Specifications. In Knowledge Acquisition,
vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 199-220.
Grundstein, M., 1992. Knowledge Engineering within the
Company: An Approach to Constructing and
Capitalizing the Knowledge Assets of the Company”.
In Proceedings of 3
rd
Annual Symposium of the
International Association of Knowledge Engineering,
Washington DC.
IMS-LD, 2003: IMS Learning Design specification,
http://www.imsglobal.org/learningdesign/index.cfm
Jovanović, J., Gašević, D., Knight, C., Richards, G., 2007.
Ontologies for Effective Use of Context in e-Learning
Settings. In Educational Technology & Society, vol.
10, no. 3, pp.47-59.
Kimble, C., Hildreth, P., 2004. Communities of practice:
Going one step too far? In AIM, pp. 1-7, 2004
Leblanc, A., Abel, M.H., 2008. E-MEMORAe2.0: an e-
learning environment as learners communities support.
In International Journal of Computer Science &
Applications. Vol. 5, pp. 108-123
LOM, 2002: Learning Object Metadata, http://ltsc.
ieee.org/wg12/
Oladejo, B. F., Odumuyiwa, V. T., David, A. A., 2010.
Dynamic capitalization and visualization strategy in
collaborative knowledge management system for EI
process. In International Conference of Knowledge
Economy and Knowledge Management, France.
SEMANTICS AND KNOWLEDGE CAPITALIZATION IN ONLINE COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE OF
E-LEARNING
103

PALETTE IST project, 2006. Pedagogically sustained
Adaptive Learning through the Exploitation of Tacit
and Explicit Knowledge, http://www.ecrim.palette.org
Quénu-Joiron, C., Condamines, T., 2009. Facilitate On-
Line Teacher Know-How Transfer Using Knowledge
Capitalization and Case Based Reasoning. In 4th
European Conference proceedings on Technology
Enhanced Learning: Learning in the Synergy of
Multiple Disciplines.
Quénu-Joiron, C., Leclet, D., 2010. How to Instrument a
Community of Practice Dedicated to Project Based
Pedagogy Tutors: A Solution Based on Case Based
Reasoning. In 10th IEEE International Conference
proceedings on Advanced Learning Technologies, pp.
344-348.
Tifous, A., El Ghali, A., Dieng-Kuntz, R., Giboin, A.,
Evangelou, C., Vidou, G., 2007. An ontology for
supporting communities of practice. In: 4th
International Conference on Knowledge Capture,
Canada.
Wenger, E., 2004. Knowledge management as a doughnut:
Shaping your knowledge strategy through
communities of practice. In Ivey Business Journal.
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
104
