
Enterprise Integrity Constraints Management using Production
Rules and Conceptual Schema
Nattawut Vejkanchana, Jane Saetent and Suphamit Chittayasothorn
Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut’s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang,
10520, Bangkok, Thailand
Keywords: Integrity Constraint, ORM, Production Rules.
Abstract: Enterprise software maintenance has been an important issue for over a decade. In conventional software
development, integrity constraints including business rules are integrated as parts of application programs.
These rules are frequently changed naturally, posing some difficulties for rules and applications
maintenance. In fact, it has long been presented that rules are a discrete part of business and technology
models and should be separated from processes, not contained in them. Based on the Business Rules
Approach and ISO 100% principle, this paper presents an integrity constraint management solution using a
combination of Object-Role Modeling (ORM) as conceptual schema and a production rules system for
integrity constraint modeling and implementation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Business rules are statements that define or constrain
some aspects of the business and always resolve to
either true of false (The Business Rules Group,
1997).In enterprise applications, a major problem is
these business rules keep changing naturally and
considerable efforts to maintain application
programs are required. The fact that rules are
normally combined with the program control logic
exacerbates the situation. In fact, this problem can
be easily solved by centralized control and
maintenance of business rules. According to the
Business Rules Manifesto presented by the Business
Rules Group (The Business Rules Group, 2012),
Rules must be excluded from processes and
procedures and implemented as a separated part
from them. This notion also supported by the 100%
principle conceived by the International
Organization for Standardization (van Griethuysen,
1982) as the approach will ease the way for
programmers to modify the rules without modifying
the program code.
Providing almost all the constraints classified in
Taxonomy of integrity constraints in conceptual
models (Miliauskaite and Nemuraite, 2005), Object-
Role Modeling (ORM/NIAM) (Halpin and Morgan,
2005), one of the prevalent conceptual modeling
method, has been a focus of interest in modeling an
information system. However, most of the
constraints which are clearly declared on an ORM
model are lost when the ORM model is transformed
into relation database schemas. In addition, ORM is
prone to enforces only on constraint on entity types.
Therefore, some techniques are needed in order to
maintain these rules in the system as well as define
constraints on entity instances.
Regarding integrity constraints definition and
modeling, the Object Constraint Language (OCL,
2011), a formal language used to describe
constraints that apply to the Unified Modeling
Language (UML, 2011) model, and now part of the
UML standard, has been adopted by the Object
Management Group (OMG, 2011), provides the
standard for declaring constraints on conceptual
models. OCL is an unambiguous language that
remains easy to understand and is completely
programming language independent which makes it
possible to transform the integrity constraint defined
by OCL into any language depending upon the
user’s desire. Saetent, Vejkanchana, and
Chittayasothorn (2011) present a combined Object
Constraint Language (OCL) and Object Role Model
(ORM) for integrity constraints modeling, and
demonstrate an implementation which enforces them
by using a commercially available DBMS. In this
paper, an open source rule-based system Drools
150
Vejkanchana N., Saetent J. and Chittayasothorn S..
Enterprise Integrity Constraints Management using Production Rules and Conceptual Schema.
DOI: 10.5220/0003986601500155
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2012), pages 150-155
ISBN: 978-989-8565-11-2
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
Expert (JBoss Community, 2012) is used to describe
the integrity rules as an alternative approach.
However, the conceptual schema is still the ORM.
This paper presents a method for managing
enterprise integrity constraints using ORM
constraints combined with the Drools Expert to
model a domain conceptual schema and its relevant
business rules. These rules are stored separately
from the applications. Other rules which are not
already modeled in ORM conceptual schema can be
defined using separate production rules. In order to
encourage more users to adopt this approach in
practice, we present some mapping from ORM
constraints to production rules as well as
implementation details of the rules in the Drools
environment.
2 OBJECT-ROLE MODELING
(ORM)
Object-Role Modeling (ORM) is a method used to
model information systems at the conceptual level.
For simplicity, it uses natural language to build a
formal model of universe of discourse (UoD) of the
application area. In addition, in the ORM model, the
information is expressed in elementary relationships
(fact types or reference types) which cannot be split
up into two or more simpler relationships without
information loss. Therefore, transformation from
ORM model into Fifth Normal Form (5NF) of
relational schemas is guaranteed (Halpin and Carver,
2008). There is no explicit use of attributes in ORM
model. For example, the relationship type “Supplier
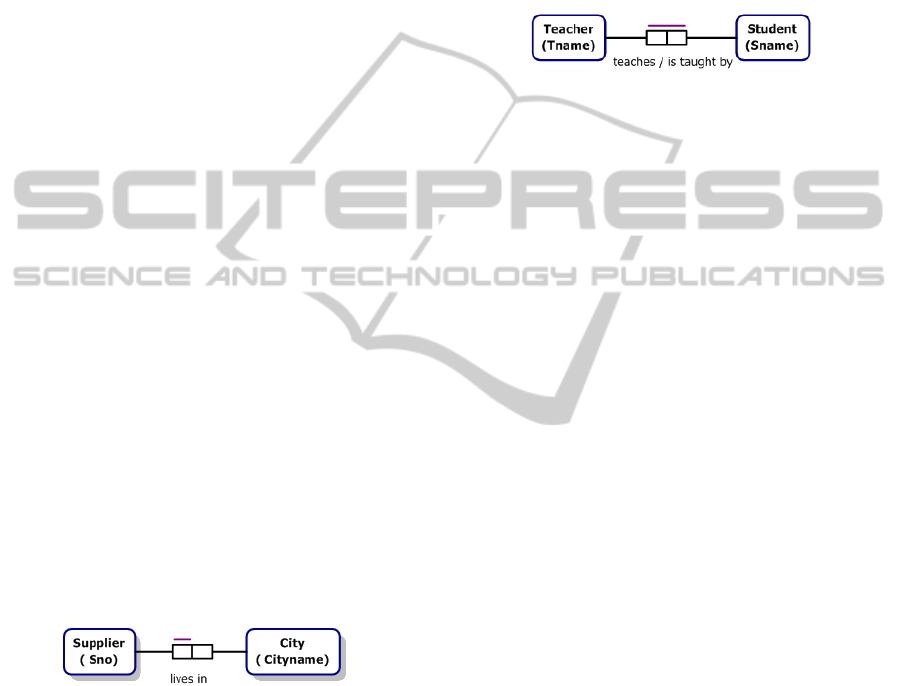
lives in City” (Figure 1) is used instead of using City
as an attribute of the entity type Supplier.
Figure 1: An ORM model for the relationship type
“Supplier lives in City”.
In ORM model, object types are classified into
entity types and value types. An entity type, depicted
as a named soft rectangle, is the set of all possible
instances, meanwhile a value type, represented by a
named dotted soft rectangle, is used to denote a
lexical object type such as a number or a character
string. There are two kinds of relationship type in
ORM diagram; fact type and reference type. Fact
types are relationships between entity types.
Reference types, on the other hand, are the
relationships between entity types and value types.
A predicate is simply a declarative sentence with
object holes which are filled by object terms. Each
role is represented by one object hole; n role(s) (n>0)
equals a sentence with n object hole(s) are called n-
ary predicates. The value of n is the degree or the arity
of the predicate. Any arity is allowed in ORM
diagram. Each object type has at least one predicate
reading which can be forward or inverse predicate
reading or both. Figure 2 shows a fact type with
binary predicate and two directions predicate reading.
Figure 2: A binary associated fact type with forward and
inverse predicate reading.
A way to identify an instance of an entity type is
required. A basic 1:1 reference scheme consists of a
reference predicate between an entity type and a
value type, where each entity is associated with
exactly one value, and vice versa. This particular
kind of reference type is called a unique identifier.
Reference mode or manner in which the value type
relates to the entity type is parenthesized next to the
entity type name to represent this kind of scheme.
For instance, Teacher(Tname) means Tname is the
unique identifier of Teacher. It is shown in Figure 2.
In this paper, our major focus is dedicated to
ORM constraints. According to the role-based
notation characteristic of the ORM diagram, a rich
variety of constraints can be specified.
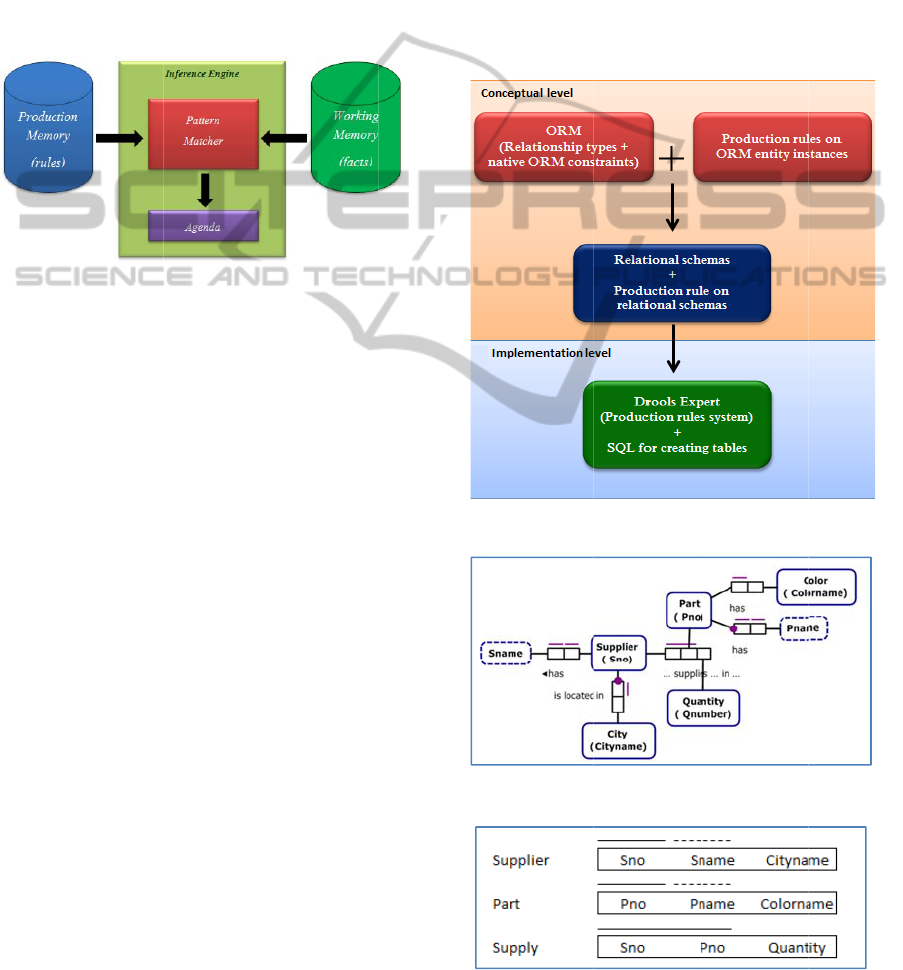
3 DROOLS EXPERT
Drools (JBoss Community, 2012) is an open source
business rule management system (BRMS) with a
number of components. Drools Expert, one of the
Drools’ components, is a business rule engine that
uses the rule-based approach to implement an expert
system and is more correctly classified as a
production rules system. It uses the Rete algorithm
and Drools Rule Language (DRL) to perform
reasoning.
A production rules system expresses a set of
rules in a concise, non-ambiguous and declarative
manner. The inference engine matches facts and data
against production rules to infer conclusions which
lead to actions. A production rule consists of two
parts; the condition (when) and the action (then). In
Drools, the inference engine uses the Rete algorithm
to perform the process of matching the new or
existing facts against production rules called pattern
matching.
EnterpriseIntegrityConstraintsManagementusingProductionRulesandConceptualSchema
151
Figu
r
p
roducti
o
p
roducti
o
engine
m
working
current
f
rule’s a
c
system
w
result in
assertio
n
executio
conflict
r
Fig
u
Rule
s
b
usiness
p
roducti
o
separati
o
simpler
t
and the
y
distinct
r
knowle
d
b
usiness
as docu
m
4 P
R
C
O
A main
constrai
n
transfor
m
databas
e
transfor
m
ORM i
n
relation
a
ORM c
o
not on i
n
on entit
y
well. F
i
transfor
m
and the
i
Ther
e
native
t
r
e 3 depicts
h
o
n rules syst
e
o
n memory
w
m
atches agai
n
memory. If
f
act, then th
e
c
tion is exec
u
w
ith a huge
n
many rules
b
n
. An agen
d
n order of th
e
r
esolution str
a
u
re 3: High-lev
e
s
are easy t
o
peo
p
le to r
e
o
n rules sys
o
n, which
m
t
o maintain i
f
y
can all be e
a
r
ules files. F
u
d
ge is centr
a
policy. Thes
m
entation.
R
ODUCT
I
O
NSTRA
I
objective of
n
ts declared
o
m
ation int
o
e
schemas.
T
m
ORM co
n
n
tegrity const
r
a
l schemas
w
o
nstraints en
f
n
stances. We
y
instances
w
i
gure 4 pres
e
m
ation in tw
o
i
mplementati
o
e
are many
i
t
o ORM. I
n
h
igh-level vi
e
e
m. All rules
w
hile the facts
n
st the rules
a rule’s con
d
e
production
u
ted, it is sai
d
n
umber of ru
l
b
eing trigger
d
a is neede
d
e
se conflictin
g
a
tegy.
e
l view of Droo
o
express an
d
e
ad than pro
tem provide
s
m
eans the lo
g
f
there are ch
a
a
sily organiz
e
u
rthermore, b
y
a
lized as a
e readable ru
l
I
ON RUL
E
I
NTS
our work is
o
n a concept
u
o
correspo
n
T
herefore, ou
r
n
ceptual sch
e
r
aints on the
w
ith product
i
f
orce only on
therefore int
r
w
ritten in pr
o
e
nts the rul
e
o
levels; the
o
n level.
i
ntegrity con
s
n
this pape
r
e
w of the Dr
o
are stored i
n
that the infer
e
are kept in
d
ition matche
s
is triggered.
d
to have fire
d
l
es and facts
for the same
d
to manage
g
rules by usi
n
ls’ rule engine.
d
much easie
r
g
ram codes.
s
logic and
g
ic can be
m
a
nges in the f
u
e
d in one or
m
y
using rules
,
single point
l
es can also s
E
S ORM
to retain al
l
u
al model aft
e
n
ding relati
r
approach i
e
ma with n
a
schema int
o
on rules. N
a
entity types
r
oduce constr
a
o
duction rule
declaration
conceptual
l
s
traints whic
h
r
, due to s
p
o
ols’
n
the
e
nce
the
s
the
If a
d
. A
may
fact
the
ng a
r
for
The
data
m
uch
u
ture
m
ore
,
the
for
s
erve
l
the
e
r its
i
onal
s to
a
tive
o
the
a
tive
and
a
ints
e
s as
and
l
evel
h
are
p
ace
li
m
ex
a
Su
p
Fig
rel
a
of
c
co
n
an
d
tra
n
p
re
ke
y
de
c
co
m
Fig
u
Fig
u
Fig
u
dia
g
itation, we
o
a
mple ORM
c
p
plie
r
-Part sy
u
re 5. The
m
a
tional schem
a
c
onstraints ar
e
n
straint, the
m
d
the mandato
r
n
sformed in
t
s
ented in Fig
u
y
s in relation
a
c
lared as keys
m
mands.
u
re 4: The 2-le
v
u
re 5: The OR
M
u
re 6: Transfo
r
g
ram in Figure
o
nly illustrat
e
c
onceptual s
c
s
tem (Date,
C
m
odel is the
n
a
as shown i
n
e
presented h
e
m
any:many
u
r
y constraint.
o
productio
n
u
re 7. Note th
a
a
l database a
n
using databa
s
v
el rules declar
a
M
diagram for t
h
r
med relational
5
.
e
some of t
h
c
hema for th
e
C
. 2004) is
s
n
transforme
d
n
Figure 6. T
h
e
re; the 1:1 u
n
u
niqueness
c
The constrai
n
n
rules in
h
at these cons
t
n
d can altern
a
s
e manageme
n
r
ation and trans
f
h
e Supplie
r
-Par
t
schemas fro
m
h
em. An
e
popular
s
hown in
d
into the
h
ree types
n
iqueness
c
onstraint,
n
ts can be
DRL as
t
raints are
a
tively be
n
t system
f
ormation.
t
example.
the ORM
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
152
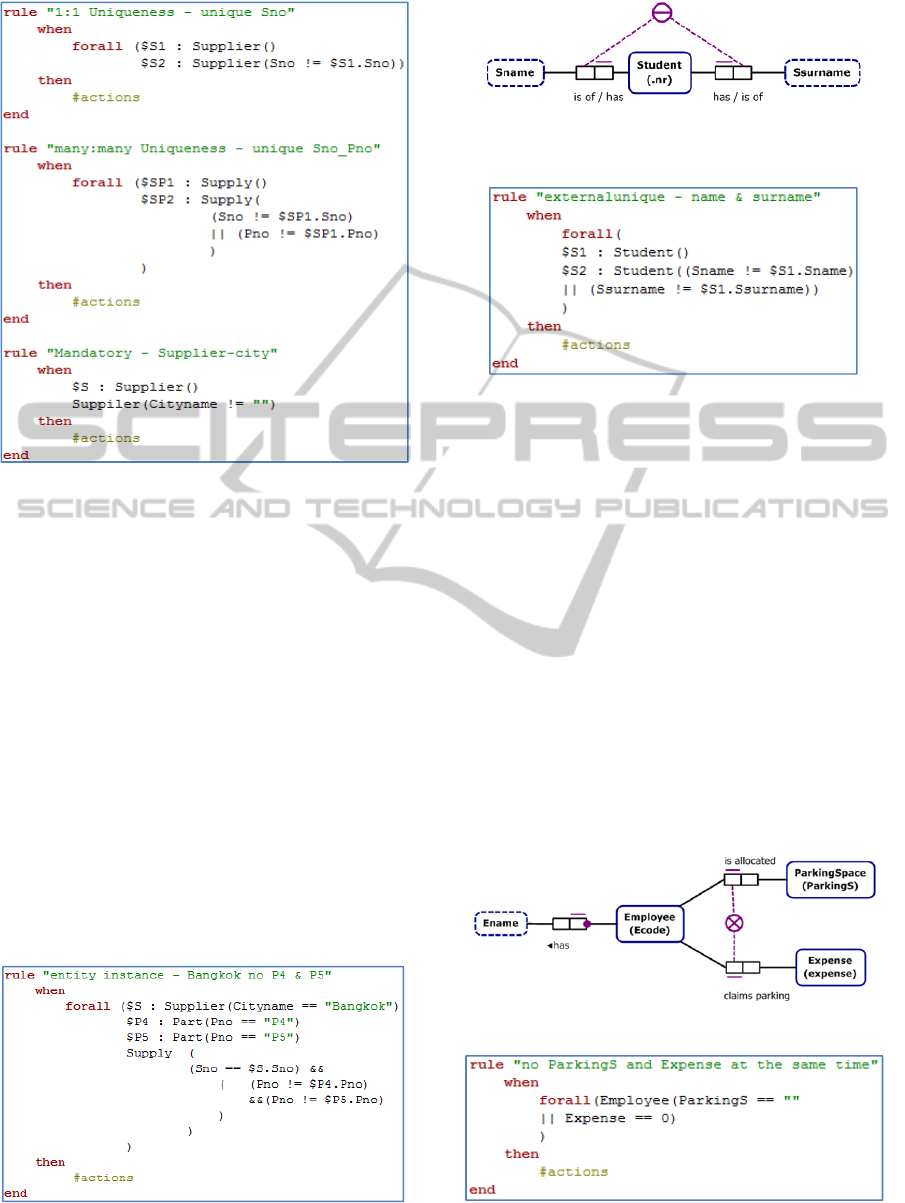
Figure 7: Some production rules in DRL for the Supplier-
Part example.
Apart from production rules which are
transformed form native ORM constraints; production
rules on entity instances are also introduced. In the
Supplier-Part example, a constraint enforces that any
instances of the entity type Supplier playing the role
“is located in” with an instance of the entity type City
that has Cityname “Bangkok”, must not play the role
“supply” with the instances of the entity type Part
having Pno “P4” or “P5”. In other words, any supplier
located in the city Bangkok must not supply the parts
P4 or P5. The constraint can be defined with the
production rules as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 9 shows an example of ORM model which
contains an external uniqueness constraint. The
constraint specifies that at most one student has that
name and surname combination. The constraint can
be written in a DRL production rule as depicted in
Figure 10.
Figure 8: A production rule which refers to entity
instances.
Figure 9: An ORM diagram illustrates an external
uniqueness constraint.
Figure 10: A production rule in DRL for an external
uniqueness constraint.
Another example demonstrates the use of
exclusion constraint which enforces that each
employee must not be allocated some parking space
and claims parking expenses at the same time. An
ORM conceptual schema for the constraint is shown
in Figure 11 while Figure 12 describes the
production rule written to enforce this constraint.
The next example focuses on a subset constraint.
In this example, the constraint indicates that the set
of instances of the entity type “Member” which
plays the role “booked” must be a subset of the set
of instances of the entity type “Member” which
plays the role “play”. In other words, fitness club’s
members will be able to book hour slots if they play
some sports. An ORM diagram for the constraint is
presented in Figure 13 and the related production
rule is shown in Figure 14.
Figure 11: ORM diagram for an exclusion constraint.
Figure 12: A production rule in DRL for an exclusion
constraint.
EnterpriseIntegrityConstraintsManagementusingProductionRulesandConceptualSchema
153
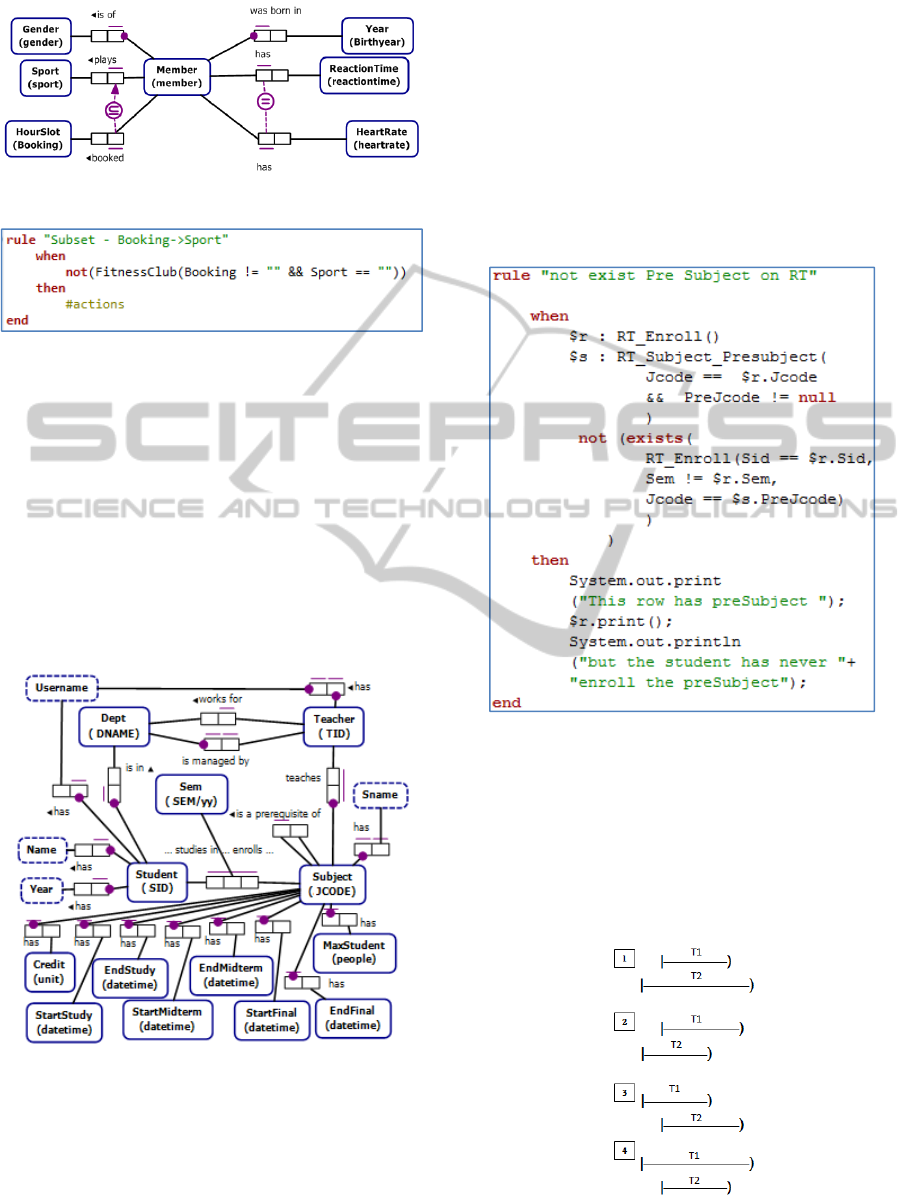
Figure 13: An ORM diagram for a subset constraint.
Figure 14: A production rule in DRL for a subset
constraint.
5 DYNAMIC AND TEMPORAL
CONSTRAINTS
A real-world application was developed to verify the
concepts presented in this paper. The application is a
students’ registration system of a university. A part
of the application’s conceptual schema is shown in
Figure 15. Some ORM constraints are presented
together with relationship types.
Figure 15: A partial ORM conceptual schema diagram for
the developed application.
Apart from these ORM constraints as shown in
the conceptual schema, there are other constraints
that cannot be modeled directly on the conceptual
schema. Two very common constraints that cannot
be modeled by ORM include the dynamic or state
transition constraints, and the temporal constraints.
The dynamic constraint states that an entity
instance must be in a state before it is allowed to
move to the next state. In our student registration
system, a student has to pass a prerequisite subject
of the subject he or she intends to enroll. In this case,
the constraint has to be written by the application
developer explicitly. This constraint written in DRL
is shown in Figure 16. Note that the constraint is
coded on relationship types as presented in the
conceptual schema; not on the underlying relational
database tables.
Figure 16: A dynamic integrity constraint.
Temporal constraints in this application include
the validation of overlapped lecture time, midterm
and final examination time. These constraints need
to be written explicitly as well. The overlapped time
has four possible cases as shown in Figure 17. This
is the classic cases of temporal join as presented in
(Snodgrass, 1998). Since DRL does not have special
Figure 17: The four possible cases for checking
overlapped time.
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
154

temporal support or temporal operators, explicit
checking of all the four cases has to be done. They
are tedious but necessary.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The idea of separating integrity constraints from
application processes in order to reduce the software
maintenance cost has long been introduced and well
accepted. Leading DBMSs have explicit integrity
constraints declaration which are triggered by
application events and enforced by the DBMS. The
UML has the class diagram which mainly describes
object classes and their associations. Integrity
constraints are separately declared using the Object
Constraint Language (OCL). Instead of separating
constraints from the conceptual database structure,
our previous work (Saetent et al., 2011) introduces
the use of OCL together with the Object Role Model
(ORM) which has rich native integrity constraints as
parts of the conceptual schema to reduce the
integrity constraints coding efforts in OCL. Native
ORM and OCL constraints are transformed to
Oracle (Oracle, 2012) integrity constraints
declarations and PL/SQL (Oracle, 2012) codes.
Based on the same concept, the combination of
ORM conceptual schema and production rules in
Drools Expert, is presented in this paper. Native
ORM constraints are automatically transformed to
production rules written in DRL on ORM
relationship types. They are then further transformed
to be rules on relational database schemas.
Additional integrity constraints on entity instances
are also implemented. This implementation
approach is economical and flexible since Drools
Expert is an open source system which can
accommodate most commercial DBMSs.
REFERENCES
The Business Rules Group. (1997). GUIDE Business
Rules Project Final Report.
The Business Rules Group, (2012). The Business Rules
Group home page. Retrieved February 15, 2012, from
http://www.businessrulesgroup.org
Carver, A. and Halpin, T. (2008). Proceedings from
EMMSAD’2008: Atomicity and Normalization.
Date, C. (2004). An Introduction to Database Systems
(8th ed.). Boston: Addison Wesley.
Forgy, C. (1982). Proceedings from Artificial
Intelligence’82: Rete: A Fast Algorithm for the Many
Pattern/Many Object Pattern Match Problem.
Halpin, T. and Morgan, T. (2007). Information Modeling
and Relational Databases (2nd ed.). CA: Morgan
Kaufmann.
JBoss Community, (2012) Drools business community
platform. Retrieved February 22, 2012, from
http://www.jboss.org/drools/drools-expert.html
Miliauskaite, E. and Nemuraite, L. (2005). Proceedings
from IADIS’2005: Taxonomy of integrity constraints
in conceptual models.
OCL. (2011). Unified Modeling Language: OCL Version
2.3 – beta 2, OMG document ptc/2010-11-42.
OMG (2011). “OMG,” http://www.omg.org/, August 25,
2011.
Oracle. (2012). http://www.oracle.com/us/products/data
base/index.html, April 20, 2012.
Price, J. (2007). Oracle database 11g SQL. New York:
McGraw-Hill.
Saetent, J., Vejkanchana, N. and Chittayasothorn, S.
(2011). Proceedings from ICITST’2011: A thin client
application development using OCL and conceptual
schema.
Snodgrass, R. (1998). Managing Temporal Data A Five
Parts Series, Technical Report TR28, TimeCenter,
University of Arizona.
UML (2011). Unified Modeling Language Superstructure
Specification Version 2.4, OMG document ptc/2010-
11-16.
van Griethuysen, (Ed.). (1982). Concepts and
Terminology for the Conceptual Schema and the
Information Base, International Organization for
Standardization, ISO TC97/SC5/WG3.
EnterpriseIntegrityConstraintsManagementusingProductionRulesandConceptualSchema
155
