
An Empirical Study on the Factors Influencing Usage Intention of
IPTV in Korea
Dong-Man Lee, Hyun-Sun Park and Sung-Hee Jang
Business School of Administration, Kyungpook National University, Buk-gu, Daegu, Korea
Keywords: IPTV, Information Quality, System Quality, Service Quality, Media Quality of IPTV, Usage Intention.
Abstract: This study examines the factors influencing IPTV (internet protocol television) usage intention. Using
Davis's technology acceptance model (TAM) and DeLone and McLean's model of information system
success, this study investigates the effects of information system quality (information quality, system
quality, and service quality) and media quality on IPTV use in terms of perceived usefulness, perceived ease
of use, and usage intention. We examined the proposed model by employing structural equation modeling
and survey data from 222 IPTV users. The results indicate that information quality, service quality, and
media quality had significant effects on perceived usefulness and that information quality and media quality
had significant effects on perceived ease of use. However, system quality had no effect on perceived
usefulness and perceived ease of use. In addition, perceived ease of use influenced perceived usefulness,
and perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use influenced of IPTV usage intention. Further, the stability
and reliability of IPTV services induced IPTV use, and successful IPTV services showed high media quality.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recently, IPTV (internet protocol television) has
emerged as a new broadcast medium, following
terrestrial, satellite, and cable broadcast networks,
and has become a basis for the convergence of
broadcasting and communications based on Web 2.0.
IPTV, unlike traditional broadcast media, generally
faces no bandwidth limitations, which allows it to
provide large numbers of channels.
Given the rapidly increasing number of IPTV
subscribers and the expansion of the IPTV market,
there has been growing research interest in IPTV. A
number of studies have examined customer
satisfaction and usage intention with respect to IPTV
services. In addition, some studies have analyzed the
effects of government policies on the acceptance of
IPTV, and others have examined the activation of
IPTV services. These studies have typically focused
on the quality of IPTV services, and thus, little is
known about the media properties of IPTV.
The objective of the present study is to identify
the factors that induce users to adopt IPTV,
including information quality, system quality, and
service quality. In addition, the study examines the
effects of these factors and media quality on
perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and
usage intention with respect to IPTV services. For
this, the study employs Davis's technology
acceptance model (TAM) and DeLone and
McLean's model of information systems success.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 IPTV
IPTV is an internet-based TV service providing all
the services of traditional media (e.g., data, videos,
songs, and TV programs) through the IP.
The International Telecommunication Union
defined IPTV as “multimedia services such as
television/video/audio/text/graphics/data delivered
over IP based networks managed to provide the
required level of quality of service and experience,
security, interactivity and reliability." In commercial
environments, IPTV has been widely deployed for
live TV, video channels, and VOD (video on
demand) through LAN/WAN IP networks based on
QoS control. Due to the technical requirements of
IPTV, security robustness is needed to ensure the
quality, reliability, and availability of IPTV services
(Bilgehan and Matthews, 2008); (Jang and Noh,
2011).
320
Lee D., Park H. and Jang S..
An Empirical Study on the Factors Influencing Usage Intention of IPTV in Korea.
DOI: 10.5220/0004096003200323
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2012), pages 320-323
ISBN: 978-989-8565-11-2
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
2.2 TAM
The technology acceptance model (TAM), an
information system (IS) framework proposed by
Davis (1989), is one of the most influential
extensions of Ajzen and Fishbein’s theory of
reasoned action (TRA). TAM replaces many of the
TRA’s attitude measures with two technology
acceptance measures: ease of use and usefulness
(Ajzen and Fishbein, 1980).
Davis et al. (1989) proposed perceived
usefulness and perceived ease of use as important
prerequisites for inducing the actual use of computer
systems and defined perceived usefulness as "the
degree to which a person believes that using a
particular system would enhance his or her job
performance" and perceived ease of use as "the
degree to which a person believes that using a
particular system would be free from effort." A
number of studies have examined and expanded
TAM, and thus perceived usefulness and perceived
ease of use are well known to be important
explanatory variables for information technology
acceptance (Davis et al., 1989).
2.3 Information System Quality
With the development of information technology,
previous studies have examined IS quality from
various perspectives.
DeLone and McLean’s (1992) seminal study of
IS quality provided the key factors in IS success.
According to their model of information system
success, IS quality includes system quality,
information quality, and service quality, and these
factors have considerable influence on usage
intention, user satisfaction, and the total effect (net
income) (DeLone and McLean, 1992).
2.4 IPTV Media Quality
Katz et al.’s (1974) uses and gratifications theory is
a popular framework for understanding mass
communication (Jarvenpaa and Todd, 1966); (Lin
and Lu, 2000).
This theory focuses more on consumers or
audiences than on actual messages by asking “what
people do with media,” not “what media does to
people” and suggests that people’s needs influence
what media they choose; how they use certain
media; and what gratification they find in media.
First, audiences are conceived as active participants,
i.e., an important part of mass media use is assumed
to be goal-oriented. Second, media compete with
other sources of customer satisfaction. Third, people
are sufficiently self-aware and are thus able to
verbally report their interests and motives in
particular cases (or at least to recognize them) when
confronted with them in an intelligent and familiar
manner. Fourth, value judgments about the cultural
importance of mass communication should be
suspended while the audience’s orientation is
explored on their own terms.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Model
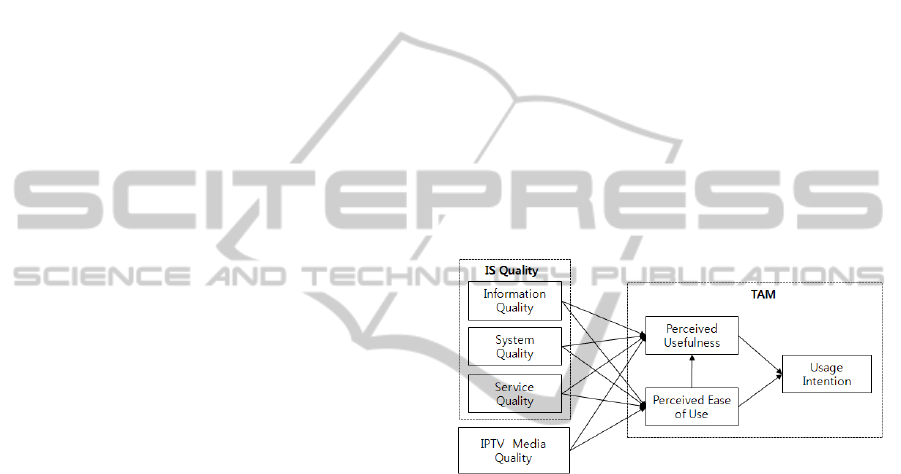
This study examines the effects of IS quality and
media quality on IPTV usage intention. For this, the
study proposes a research model based on Davis’s
TAM and DeLone and McLean's model of IS
success.
Figure 1: Research model.
3.2 Research Hypotheses
To identify the factors influencing IPTV usage
intention, this study uses Davis's TAM and DeLone
and McLean's model of IS success. In addition, this
study investigates the effects of IS quality and media
quality on IPTV use in terms of perceived
usefulness, perceived ease of use, and usage
intention (Shin, 2009); (Venkatesh and Davis, 2003).
In this regard, we propose the following hypotheses:
H1.1: Information quality has a positive effect on
perceived usefulness.
H1.2: Information quality has a positive effect on
perceived ease of use.
H2.1: System quality has a positive effect on
perceived usefulness.
H2.2: System quality has a positive effect on
perceived ease of use.
H3.1: Service quality has a positive effect on
perceived usefulness.
AnEmpiricalStudyontheFactorsInfluencingUsageIntentionofIPTVinKorea
321
H3.2: Service quality has a positive effect on
perceived ease of use.
H4.1: Media quality has a positive effect on
perceived usefulness.
H4.2: Media quality has a positive effect on
perceived ease of use.
H5: Perceived ease of use has a positive effect on
perceived usefulness.
H6: Perceived usefulness has a positive effect on
usage intention.
H7: Perceived ease of use has a positive effect on
usage intention.
4 RESULTS ANALYSIS
4.1 Sample and Survey Research
Methods
For the determination of factors influencing IPTV
use, users with IPTV experience were selected for
the survey. The questionnaire items, which were
based on previous research, were modified by
professionals (headquarters, technical and sales staff
members at KT, a major IPTV service provider in
Korea) with knowledge of IPTV systems. For the
reliability and validity of the questionnaire items, a
pretest was conducted with 32 individuals who used
IPTV services for at least six months.
Of the 300 questionnaires distributed, 252 were
returned. However, 30 were not complete or lacked
a sufficient understanding of IPTV services, and
thus, they were excluded, resulting in a total of 222
respondents.
Among the 222 respondents, 129 (58.1%) were
males; approximately 60% were in their twenties
and thirties; 63 (28.4%) were students; and majority
(63.5%) of respondents had a bachelor’s degree. In
terms of the representative IPTV operators in Korea
(KT, SK Broadband, and LG Telecom), most
respondents (56.3%) used KT. In addition,
approximately 74% used IPTV for less than 6
months.
4.2 Reliability and Validity Analysis
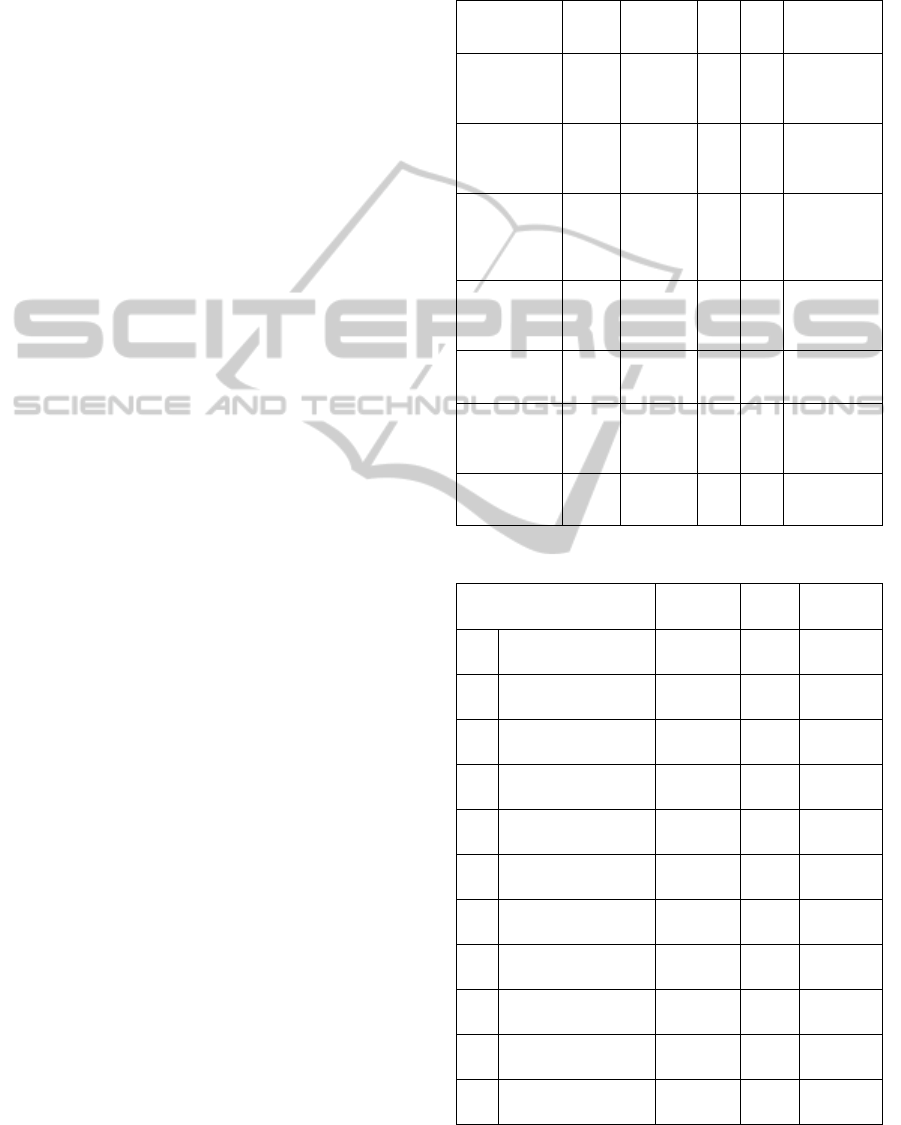
As shown in Table 1, we analyzed the measurement
items for their reliability and validity.
4.3 Hypothesis Testing
We tested each hypothesis by using PLS Graph and
examining the path coefficients. The estimated path
effects, together with their level of significance, are
given. Table 2 summarizes the results.
Table 1: Reliability and validity analysis.
Variables Item
Factor
Loading
AVE ICR
Cronbach’s ⍺
Information
Quality
IQ1
IQ2
IQ3
IQ4
.832
.876
.789
.791
.677 .893 .841
System
Quality
SYQ1
SYQ2
SYQ3
SYQ4
.795
.847
.741
.743
.613 .863 .788
Service
Quality
SEQ1
SEQ2
SEQ3
SEQ4
SEQ5
.785
.818
.823
.748
.761
.621 .891 .847
IPTV Media
Quality
MQ1
MQ2
MQ3
MQ5
.724
.822
.815
.607
.558 .833 .732
Perceived
Usefulness
PU1
PU2
PU3
.871
.883
.727
.689 .868 .773
Perceived
Ease of Use
PE1
PE2
PE3
PE4
.821
.857
.846
.837
.706 .906 .862
Usage Intention
INT1
INT2
INT3
.805
.911
.905
.765 .907 .845
Table 2: Hypothesis test results.
Channel
Path
Coefficient
t value
Test
Results
H1.1
Information Quality ->
Perceived Usefulness
0.200 2.846
***
Supported
H1.2
Information Quality ->
Perceived Ease of Use
0.206 2.462
***
Supported
H2.1
System Quality ->
Perceived Usefulness
0.027 0.355 Rejected
H2.2
System Quality ->
Perceived Ease of Use
0.083 0.840 Rejected
H3.1
Service Quality ->
Perceived Usefulness
0.261 3.018
***
Supported
H3.2
Service Quality ->
Perceived Ease of Use
0.039 0.312 Rejected
H4.1
IPTV Media Quality ->
Perceived Usefulness
0.394 4.746
***
Supported
H4.2
IPTV Media Quality ->
Perceived Ease of Use
0.240 3.014
***
Supported
H5
Perceived Ease of Use->
Perceived Usefulness
0.179 2.857
***
Supported
H6
Perceived Usefulness->
Usage Intention
0.486 8.444
***
Supported
H7
Perceived Ease of Use->
Usage Intention
0.366 6.184
***
Supported
Significance level:
***
: p<0.01
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
322

5 CONCLUSIONS
We examined the factors influencing IPTV use by
employing Davis's TAM and DeLone and McLean's
model of IS success, which are widely used in IS
research. Based on these models, we considered a
research model including media quality, and with a
sample of 222 IPTV users, we tested a set of
hypotheses about IPTV use. The results are
summarized as follows.
First, information quality, service quality, and
media quality had significant effects on perceived
usefulness, but system quality had no such effect on
perceived usefulness. Second, information quality
and media quality had significant effects on
perceived ease of use, but system quality and service
quality did not influence perceived ease of use.
Third, perceived ease of use influenced perceived
usefulness, and perceived usefulness and perceived
ease of use influenced usage intention. These results
indicate that the stability and reliability of IPTV
services can induce IPTV use and that high media
quality can facilitate IPTV success.
The results have a number of important
implications. First, we examined the factors
influencing IPTV use by combining the media
attributes of IPTV with Davis's TAM and DeLone
and McLean's model of IS success. Second, media
quality was most likely to influence perceived
usefulness and perceived ease of use. Unlike
traditional media, IPTV is based on a wide range of
new and unique elements, particularly in terms of its
interactivity, content diversity, ease of use, and
multitasking capability. Therefore, IPTV service
providers should pursue aggressive customization.
Third, information quality had a positive effect on
perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use,
suggesting that IPTV service providers should
continuously update their content and provide
accurate information to ensure customer satisfaction.
Finally, service quality had a significant effect on
perceived usefulness. Thus, IPTV providers should
provide reliable after-sales as well as before-sales
service and facilitate collaboration between relevant
departments (e.g., sales and technical support) to
provide informal and technical aspects based on
prompt service and appropriate expertise.
This study has some limitations. First, IPTV syst
em were studied using only DeLone and McLean (2
003)’s variables and IPTV media quality with extern
al variables (DeLone and McLean, 2003). In this re
gard, future research should examine the relationship
between the characteristics of potential users of IPT
V and their acceptance of IPTV. Second, system qua
lity had no significant effects on perceived usefulnes
s and perceived ease of use, which indicates a need f
or developing items that could better reflect the attri
butes of IPTV system quality. Third, for more practi
cal strategies for inducing IPTV use, future research
should emphasize the strategic aspects of study.
REFERENCES
Bilgehan, E., Matthews, E. P., 2008, “Analysis and
realization of IPTV service quality,” Bell Labs
Technical Journal, 12(4), pp.195–212.
Davis, F. D., 1989, “Perceived usefulness, perceived ease
of use, and user-acceptance of information
technology,” MIS Quarterly, 13(3), pp. 319-340.
Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., Warshaw, P. R., 1989, “User
acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of
two theoretical models” Management Science, 35(8),
pp. 982-1003.
DeLone, W. H., McLean, E. R., 1992, “Information
system success: The quest for the dependent variable,”
Information Systems Research, 3(1), pp. 319-340.
DeLone, W. H., McLean, E. R., 2003, “The DeLone and
McLean Model of information success: A ten-year
update,” Journal of Management Information System,
19(4), pp. 9-30.
Jang, H. Y., Noh, M. J., 2011, “Customer acceptance of
IPTV service quality,” International Journal of
Information Management, 31(6), pp.582-592.
Jarvenpaa, S. L., Todd, P. A., 1997, “Consumer reactions
to electronic shopping on the World Wide Web,”
International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 1(2),
pp. 59-88.
Katz, E., Blumler, J. G., Gurevitch, M., 1974, Utilization
of Mass Communication by the Individual, In Blumler,
J. G. and Katz, E.(eds), The Use of Mass
Communication, Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Lin, J. C. C., Lu, H., 2000, “Towards an understanding of
the behavioral intention to use a web site,”
International Journal of Information Management,
20(3), pp. 197-208.
Shin, D. H., 2009, “An empirical investigation of a
modified technology acceptance model of IPTV,”
Behavior & Information Technology, 28(4), pp. 361-
372.
Venkatesh, V., Davis, F. D., 2000, “A theoretical
extension of the technology acceptance model: Four
longitudinal field studies,” Management Science,
46(2), pp. 186-204.
AnEmpiricalStudyontheFactorsInfluencingUsageIntentionofIPTVinKorea
323
