
How to Design Good Educational Blogs in LMS?
Ahmed Mohamed Fahmy Yousef and Guido Rößling
Dept. of Computer Science, TU Darmstadt, Hochschulstr. 10, 64289 Darmstadt, Germany
Keywords: e-Learning, Web Page Design, Educational Blogs, LMS, Blogs Criteria.
Abstract: Social communication tools in E-Learning have seen monumental growth in the last decade. Blogs as one of
the most important tools have a huge contribution in social communication in Learning Management
Systems (LMS), and the majority of research incorporating blogs in LMS reveals the effectivity of them.
Thus, the quality of blog design becomes the main factor that determines the success of educational blogs.
Although a literature review of guidelines and web page standards contain a variety of categories to cover
most features of web page design, not all of them can be used to create an effective blog. There is a need to
further explore these technologies in educational contexts and identify the criteria of combining them in unit
design. The main purpose of this paper is identifying the educational blogs criteria by analysing the
literature, research and the reviews of experts in the field. The study outcomes include the final list of blogs
criteria which are classified into 6 categories and 80 indicators.
1 INTRODUCTION
A weblog is defined in short as a personal website
that usually provides the opportunity to discuss
topics with historical entries that are as a rule brief
and often include subjects’ summaries and links on
the blog as well as personal opinions and
recommended references. Photo and video blogs are
blogs with posts of pictures and videos, respectively,
supported by text (Vaezi et al., 2011); (Shih, 2010);
(Tekinarslan, 2008). Pedagogical blogs have many
advantages, such as self-editorship, free space to
present students’ view, quick and easy updates, free
access to the discussion topics and indexing (Ko and
Pu, 2011); (Farmer et al., 2008). Moreover, students
can be encouraged to discuss what interests them,
and can post their personal comments on other
students' blogs. (Ozkan, 2011); (Reupert and
Dalgarno, 2011); (Farmer et al., 2008).
On the one hand, some researchers focus on
exploring the factors influencing blogging
interaction (Ko and Pu, 2011); (Kuzu, 2011); (Vaezi
et al., 2011); (Wu and Wu, 2011); (Hourigan and
Murray, 2010); (Al-Ani et al., 2008); (Burke and
Oomen-Early, 2008); (Chong, 2008). All results
support the new trend in e-learning and effective
blogging as communicative tools for both individual
self-expression and provide free space for students
to learn and interact.
On the other hand, Saeed and Yang (2008),
reported that, 40.7% of the students never
participated in blogging activity, and 70% of all
participations shared only one post per week. Stone
(2012), were analyzed 505 blogs results indicates
that not all students completed each of the 15 blogs
task requested of them, only 57.1% of the total
entries (885) were actually posted by students. The
purpose of this paper is identifying a set of blog
criteria based on web page design guidelines and
blog literature. These criteria will assist students in
improving interaction among themselves and will
help e-learning designers in developing more
effective blogs in LMS. We present the details of a
study conducted to identify educational blog criteria
in LMS. This study consisted of three phases. The
first phase was a thorough literature research to
collect the initial list of blogs criteria. The second
phase was the classification of the blogs criteria in
six categories with specific indicators. The last
phase was to conduct a survey with experts in
instructional technology and e-learning to evaluate
the importance of the proposed blogs criteria.
2 EDUCATIONAL BLOGS
Educational blogs are quite different from traditional
web pages, and they need more specific criteria to
70
Mohamed Fahmy Yousef A. and Rößling G..
How to Design Good Educational Blogs in LMS?.
DOI: 10.5220/0004351500700075
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2013), pages 70-75
ISBN: 978-989-8565-53-2
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
ensure that can be used effectively in an e-learning
platform (Tan et al., 2010). We conducted a detailed
literature review to collect blog criteria. These
criteria are then classified in six main categories that
we discuss in some detail in the next sections.
2.1 Blog Design
Design features refer to how blog look and feel. This
study found three elements for design: font, color
and frames. Font is one of the main factors affecting
blog design. Font should be visible without having
to install new fonts. Moreover, color in educational
blogs is used not only to make blogs more attractive,
but also to improve readability and focus on the
specific information in the blog (Vaezi et al., 2011);
(Tarasewich, 2008); (Viehland and Zhao, 2008);
(Yousef, 2008); (Powell, 2002); (Nielsen, 2002);
(Nielsen and Tahir, 2001); (Gibbs et al., 2000); (Lee
and Boling, 1999).
2.2 Navigation
The navigation style helps students to achieve their
blog objective. It is important that students are able
to find the navigation feature easily (Wu and Wu,
2011). Good design of navigation tools help students
to find the important topics and discussion via blog
effectively. In this study identified three components
links, menu and search box (Tan and Tan, 2010).
2.3 Media Use
Multimedia is an extra option for students and
teacher (Derry, 2007). It can be defined as the
incorporation of communication media such as
image, audio and video in the blogging to present
information (Crozat et al., 2007); (Hartsell and
Yuen, 2006); (Bijnens et al., 2004); (Leidig, 1999).
2.4 Usability
According to the International Standards
Organization (ISO) web usability is defined as "the
extent to which a site can be used by a specified
group of users to achieve specified goals with
effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a
specified context of use" (Wu and Wu, 2011); (Tse
et al., 2010);
(Whitehead, 2006); (Nielsen, 2002).
2.5 Content
A good content design not only improves the
learners’ attention and increases their performance,
but also improves their knowledge and skills
(Schoneboom, 2010); (Krunić and Ružić-
Dimitrijević, 2008); (Rieh, 2002); (Lee et al., 1996).
2.6 Accessibility
The purposes of accessibility are that students can
perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with the
blog, and that they can browse all content available
on the blog and meet different technical needs to
support loading speed, download ability and
compatibility with major browsers (Ozkan, 2011);
(Ha et al., 2007); (Hassan and Li 2001).
3 STUDY RESULTS
AND DISCUSSION
In this study, we grouped the list of 80 indicators in
6 categories and 19 main criteria. We then
conducted a survey in which we asked 19 e-learning
and instructional technology experts to rate each
indicator on a 5-point Likert scale from not
important (1) to very important (5). The evaluators
could also use a decimal value like (3.75). The
statistical results of this survey show that the most
important categories were accessibility and
navigation, while the least important ones were blog
design and content. In the following sections, we
discuss the results of this study based on each
category.
3.1 Blog Design
Blog design category included three main criteria
with 13 indicators. See Table 1.
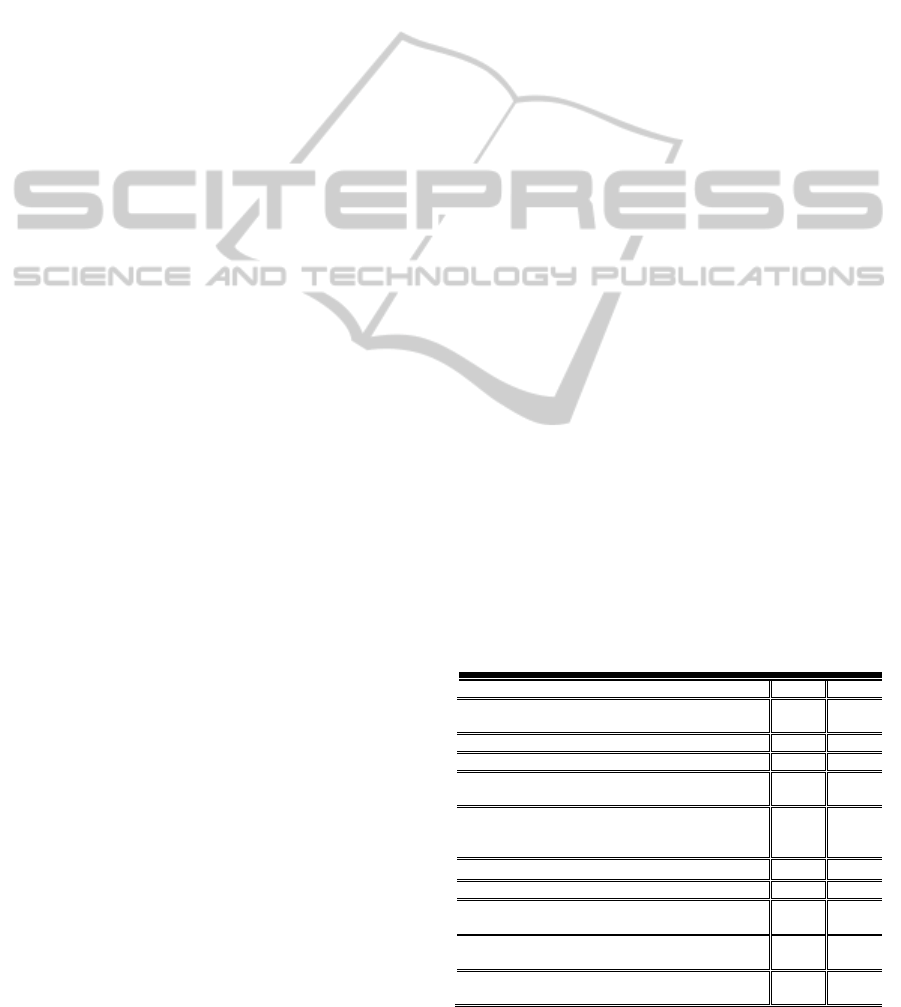
Table 1: Blog design category (N=19).
Blog Design Indicators M SD
1. Use commonly-supported font styles (e.g., Times
New Roman, Arial, Calibri, and Arial Black).
3.54 0.926
2. Titles/Headings font size (16 to 24) Bold. 3.29 0.783
3. Body text font size (14 to 20) Normal. 3.45 0.872
4. Don’t use more than 3 font types in the same
Blog.
3.89 0.792
5. Use high-contrast text and background colors
so that type is as legible as possible. For Ex
(Black text with White Background).
4.34 0.726
6. Using mixture of upper and lower case for text. 3.62 1.158
Font Indicator means average
3.69
7. Sharp color contrast between background and
foreground.
3.86 0.843
8. Use color for different functional area (Title,
Menu and hyperlinks).
3.63 0.915
9. Use of light color (white / yellow) for
background.
3.25 1.070
HowtoDesignGoodEducationalBlogsinLMS?
71
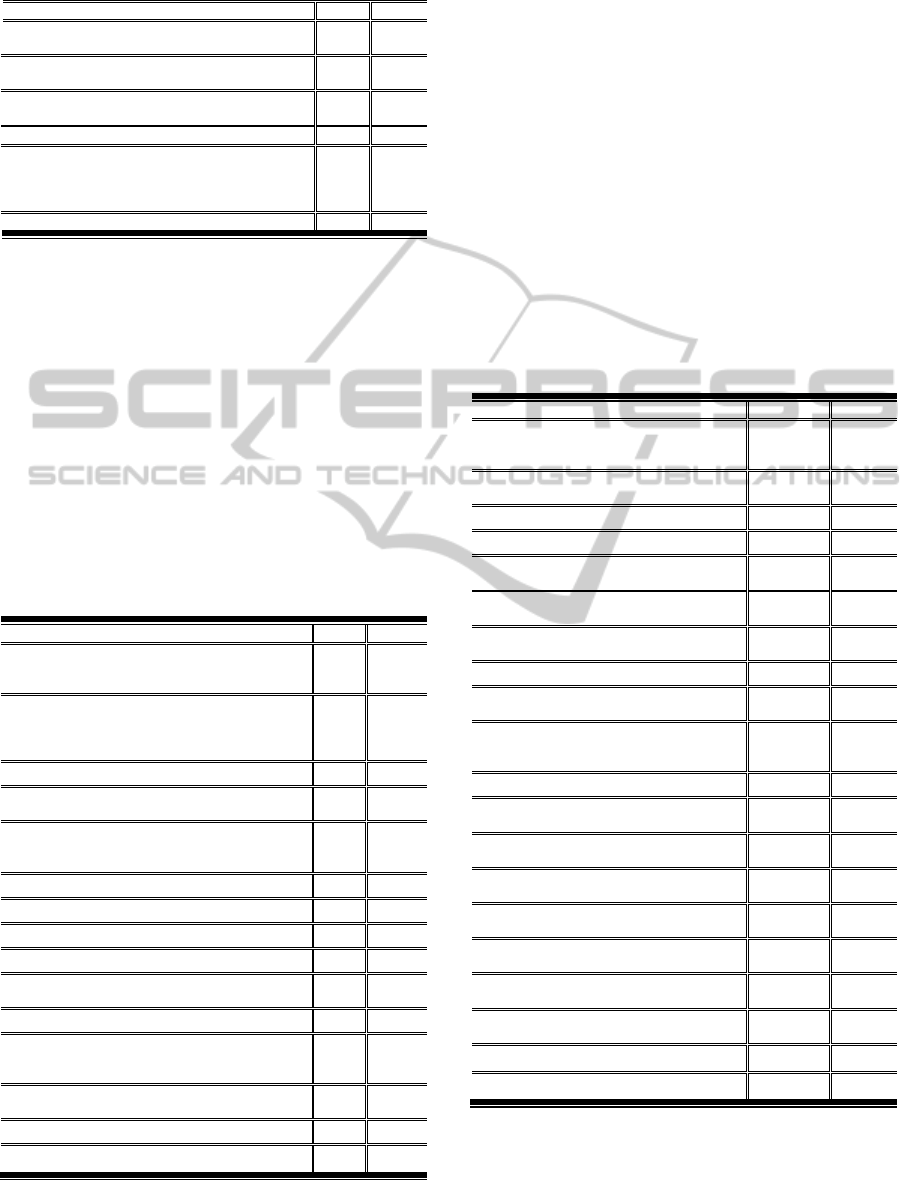
Table 1: Blog design category (N=19) (Cont.).
Blog Design Indicators M SD
10. Minimum 2 color, Maximum 4 color except for
photo and graphic.
3.71 0.680
11. Color can be used to highlight text or graphics to
make them stand out.
3.68 0.798
12. Avoid the use of complementary colors (e.g.,
blue/orange, red/green, violet/yellow)
3.50 1.054
Color Indicator means average
3.60
13. Use templates rather than frames to avoid
confusing users, or if frames are used, be sure to
title and label them to identify areas of changing
information
3.39 1.021
Blog Design Indicator Average means 3.63
In the statistical results font is ranging between
M=3.29 and 4.34 which indicate that experts
accepted these indicators. High contrast between text
and background is a critical issue that may influence
the value of blog. The second high mean of this
category is Color and Background with a range of
M=3.25 to 3.86. As well as, the third criteria frames
obtain M=3.39.
3.2 Navigation
The navigation category included three main criteria
with 11 indicators. See Table 2.
Table 2: Navigation category (N=19).
Navigation Indicators M SD
14. Begin links with the information-carrying
word, because users often scan through the first
word or two of links to compare them.
3.61 0.926
15. Clearly identify items that are links by using
visual cues (e.g., underlining, a change of item
color when cursor is hovered, or a change of
cursor image on hover, etc.
4.18 0.831
16. Accurate and up-to-date links.
4.64 0.548
17. Links should lead directly to the detailed
page for the discussion topic.
4.42 0.765
18. Input boxes should be wide enough: Allow
enough space for at least 30 characters in the
font size used by most of the users.
4.05 0.705
Links Indicator means average 4.18
19. Menu / List of contents on each page of blog.
4.08 0.765
20. Menu includes blog map.
3.37 1.179
21. Using simple design for menu.
4.22 0.815
22. Navigation located in the same place of
each page of blog.
4.68 0.436
Menu Indicator means average
4.09
23. Give users an input box on the blog to enter
search queries, instead of just giving them a link
to a search page.
3.97 1.019
24. Search box should be placed at the top of
page, left or right of the blog.
3.89 0.981
Search Box Indicator means average
3.93
Navigation Average 4.10
According to the results in this table, it can be
clearly seen that indicators 16, 17, 15 and 18
obtained the highest mean scores of 4.64, 4.42, 4.18
and 4.05, respectively, which indicated that experts
give the helpful links high level to support students
to be able to find more information and navigation
feature easily. The second point to note is indicators
22, 21 and 19 obtained the highest mean scores of
4.68, 4.22 and 4.08 respectively that referred to
importance of a menu design features such as simple
design, including a list of content to improve the
students, navigation.
3.3 Media Use
The media use category included three main criteria
with 16 indicators. See Table 3.
Table 3: Media use category (N=19).
Media Use Indicators M SD
25. Control features for audio file where
appropriate, for example, Play, repeat,
volume, stop and pause.
3.89 0.897
26. The sound shall be audible and
intelligible.
4.24 0.978
27. Easy to download.
4.00 1.076
Audio Indicator means average 4.04
28. Minimum Video resolution (Pixels) 320
* 240.
3.68 0.892
29. Standard Video format be offered as a
“HTML5-compatible video”.
3.89 0.804
30. Use short video clips, No more than 15-
minute clips.
4.08 0.799
31. Avoid rapid cuts or changes of scenery.
3.29 1.092
32. Keep videos small for easier transfer,
e.g., to up to 10 M.B.
3.92 0.892
33. Control features for video clip where
appropriate, for example, Play, repeat,
full screen, slowdown, stop and pause.
4.21 0.713
Video Indicator means average 3.85
34. Use graphics / Images for
emphasizing the information.
4.50 0.688
35. Use graphics / Images for attracting
attention.
3.87 0.856
36. Using “thumbnails” for showing large
images.
3.95 0.816
37. Using small images to be easy to
loading.
3.91 0.648
38. Make sure all the key components of
the graphical images are labeled.
3.76 1.002
39. Use simple and clear images; avoid
images with too much detail.
3.61 1.008
40. Use graphics to show real content,
not just to decorate blog.
4.51 0.588
Image Indicator means average 4.01
Media use means average 3.96
Audio indicator 26 and 27 obtained a high mean
score of 4.24 and 4, respectively, indicating that
audible and intelligible sound is a pivotal indicator
that may influence the effectiveness of audio blogs
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
72
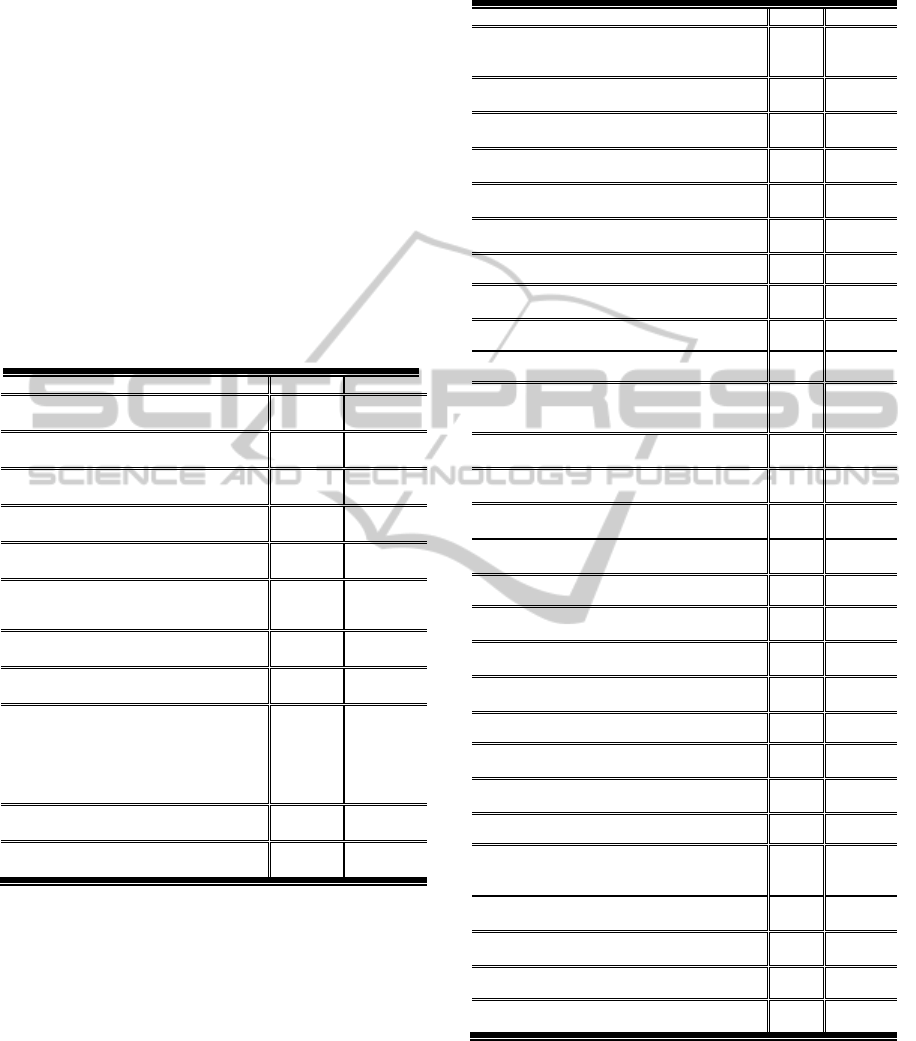
in LMS. Moreover, Image criteria indicators 40 and
34 obtained a high main score of 4.51 and 4.5,
respectively, indicating that image can be a source of
information, learning and present every bit as
powerful as the written text. Furthermore, Video
indicators 33 and 30 obtained a high mean score
4.21 and 4.08, respectively, that refers to the
importance of control features for video clip and
using short video clips is a crucial indicator that may
influence the effectiveness of video blog learning.
3.4 Usability
The usability category included two main criteria
with 8 indicators. See Table 4.
Table 4: Usability category (N=19).
Usability Design Indicators M SD
41. Include some information how to use
this blog.
3.76 1.105
42. Include some recommendation about
search and old posting finding. 3.82 0.831
43. Help link should be available.
3.97 1.175
Help Indicator means average
3.85
44. Blog length should be no longer than
2 screens. 3.38 1.013
45. Make sure the important content is
visible at a 800 * 600 resolution without
having to scroll.
3.87 1.024
46. Design should be simple and
uncluttered.
4.50 0.743
47. Include a tag line that explicitly
summarizes what the blog does.
4.14 0.792
48. Avoid horizontal scrolling at
1024x768. Horizontal scrolling
invariably causes usability issues, the
biggest being that users don't notice
the scrollbar and miss seeing content
that is scrolled off of the screen.
4.08 0.831
Layout Indicator means average
4.0
Usability Design Indicator Average
3.94
The most noticeable thing is that blog layout
indicators 46, 47 and 48, obtained the high mean
scores of 4.50, 4.14, and 4.08, respectively, which
indicate the importance of a simple and uncluttered
of blog.
3.5 Content
The content category included five main criteria
with 22 indicators as listed in Table 5.
Blog authority obtained high mean scores
ranging from M= 4.16 to 4.58, which indicate that
the important of copyright issue for the content.
Moreover, blog information indicators 64, 62 and 63
Table 5: Content category (N=19)
Content Indicators M SD
49. Blog title should attract the audience and be
easy to understand, and clearly convey the purpose
of the blog.
4.34 0.563
50. Include a short description of the topic in
blog title.
3.98 0.729
51. Blog information should be depth of subject
coverage.
3.67 0.833
52. Blog should be intrinsic value of
information.
3.86 1.008
Blog Scope means average
3.96
53. Blog must give references or sources of the
information.
4.58 0.591
54. Copyright holder statement.
4.18 0.935
55. Comments should be reviewed and ensured
that they are correct.
4.16 0.859
Authority means average
4.31
56. Blog should be standing clearly goals /aims.
4.18 0.782
57. Invite students to set their own goals for
blog usage - above and beyond a quantity
measurement.
3.95 0.999
58. Information should be presented in an
objective manner.
3.53 1.045
59. Use the “Bloom Taxonomy” instructional
objective design.
3.38 0.853
60. Each blog should have at most three
objectives.
3.18 1.003
61. Each objective should focus on only one
task.
3.00 1.136
Objective means average
3.54
62. Blogs content must be free from spelling,
grammatical, syntax errors, and typos.
4.21 1.068
63. Sequence of lessons information and
instruction are logical and clear.
4.14 0.880
64. Blog must be written at a level appropriate
to the reader of the content.
4.29 0.878
65. The content is informative.
4.00 0.960
66. Separation between information and
opinion content.
3.93 0.772
67. Choices of media type for information, for
example, text only, audio or video.
3.79 1.058
Information means average
4.06
68. Blogs body should be a goal, not a fixed
rule: a paragraph should preferably not have more
6 sentences.
3.03 0.950
69. Heading and bulleted lists are used so that
content can be easily scanned.
3.84 0.862
70. Use the typography and skimming layout,
for example, bold font and highlighted words.
3.76 0.996
Scanability means average
3.45
Content means average
3.75
obtained a high score mean of 4.29, 4.21 and 4.14,
respectively, indicating that content of a blog should
be free from spelling, grammatical, or syntax errors,
and typos. The blog scope indicator 49 obtained a
high mean score (M= 4.34) which indicating that,
the important of clear title. Furthermore, the blog
objective indicator 56 obtained a high score mean
HowtoDesignGoodEducationalBlogsinLMS?
73
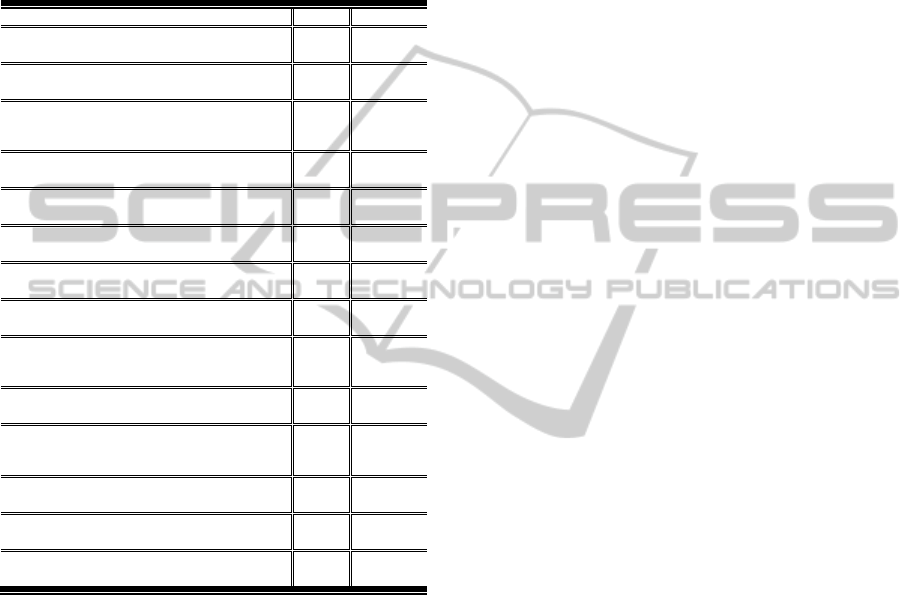
M= 4.18 indicating the importance of clear blog
aims to increase the influence of blog content value.
3.6 Accessibility
The accessibility category included three main
criteria with 11 indicators as listed in Table 6.
Table 6: Accessibility category (N=19).
Accessibility Indicators M SD
71. Blog does not take a long time to load.
4.39 0.836
72. Blog provides a "help feature" or
instructions on its use.
3.74 1.093
73. Blog does not require special "plug-ins"
or other types of special viewing helpers. If
it does, this is clearly indicated.
4.16 1.001
74. Ensure there is adequate technical support
available.
4.00 1.088
Loading speed means average
4.07
75. Student should be easily downloading the
materials from the blog. 4.01 1.077
76. Use hyperlinks to access the files in LMS.
3.95 0.887
Download ability means average
3.98
77. Ensure that equivalents for dynamic content
are updated when the dynamic content
changes.
4.14 0.677
78. Provide the ability to refresh the blog.
4.00 0.918
79. Compatible contents for all main
browsers (Internet Explorer, Opera,
Firefox, Safari and Google Chrome).
4.87 0.318
80. Clearly identify the target of each link.
4.34 0.828
Browsing means average
4.34
Accessibility means average
4.16
The first and most important indicator 79
obtained the highest mean score in the survey of M=
4.87, indicating that compatible content for all main
browsers is a critical indicator that may influence the
effectiveness and dissemination of the educational
blog. Furthermore, download ability indicator 71
obtained (M= 4.39) indicated that the time of
uploading blog page is a very important indicator to
increase the interaction between students.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The purpose of this paper was identifying
educational blogs criteria to improve the student’s
interaction and communication. According to results
the accessibility criteria scored 4.16 out of 5. In the
second priority, came navigation category criteria
that scored 4.10 indicated that navigation style helps
students to achieve their blog objective. followed by
category criteria of media use and usability.
However, it is surprising thing to note that the
amount of importance for learning objective in the
literature and research, but was rated low means
score of M= 3.54 except, only indicator 56 obtained
a mean score M= 4.18 this was the most outstanding
that was noted in this study.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We wish to thank the experts and professors who
participated in the study. The support was funded by
DAAD.
REFERENCES
Al-Ani, Ban; Mark, Gloria & Semaan, Bryan (2008).
Blogging through Conflict: Sojourners in the Age of
Social Media. ICIC’10, August 19–20, 2010,
Copenhagen, Denmark, ACM 978-1-4503-0108-
4/10/08.
Bijnens, Marie; Vanbuel, Mathy; Verstegen, Soetkin &
Young, Clive (2004). Handbook on digital video and
audio in education: Creating and using audio and
video material for educational purposes. Education
and culture Socrates Minerva.
Burke, Sloane & Oomen-Early, Jody (2008). That’s blog
worthy: ten ways to integrate blogging into the health
education classroom. American Journal of Health
Education, Vol 39, No. 6, 362-364.
Chong, Eddy K. M. (2008). Harnessing distributed
musical expertise through edublogging. Australian
Journal of Teacher Education, 24(2), 181-194.
Crozat, Stephane; Trigano, Philippe & Hu, Olivier (2007).
Set of criteria for evaluation and design of multimedia
applications in instructional context.UMR CNRS 6599
Heudiasyc.
Derry, Sharon J. (Editor), (2007). Guidelines for video
research in education: Recommendations from an
expert panel. Data Research and Development Center
(NORC at the University of Chicago).
Farmer, Brett; Yue, Audrey & Brooks, Claire
(2008).Using blogging for higher order learning in
large cohort university teaching: A case study.
Australasian Journal of Educational Technology,
24(2),123-136.
Gibbs, William J.; Graves, Pat R. & Bernas, Ronan S
(2000).Identifying important criteria for multimedia
instructional courseware evaluation.Journal of
Computing in Higher Education, Vol. 12(1), 84-106.
Ha, Kiryong; Park, Inho; Lee, Jeonwoo & Lee, Doheon
(2007). Automated Blog Design System with a
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
74

Population-Based Artificial Immune Algorithm. L.N.
de Castro, F.J. Von Zuben, and H. Knidel (Eds.):
ICARIS 2007, LNCS 4628, pp. 324–335, 2007.
Hartsell, Taralynn; & Yuen, Steve Chi-Yin(2006).Video
streaming in online learning. AACE Journal, 14, 1 31-
43.
Hassan, Shahizan; & Li, Feng (2001).Identifying web
usability criteria: the “scanmic” model.Mangment
science theory, method and practice, research paper
No: 2001\3.
Hourigan, Tríona & Murray, Liam (2010). Using blogs to
help language students to develop reflective learning
strategies: Towards a pedagogical framework. .
Australian Journal of Teacher Education, 26(2), 209-
225.
Ko, Hsiu-Chia & Pu, Hung-Jen (2011). Understanding the
Impact of Bloggers’ Self-disclosure on
Resilience.ICUIMC ‘11, February 21–23, 2011, Seoul,
Korea, ACM 978-1-4503-0571-6.
Krunić, Tanja & Ružić-Dimitrijević, Ljiljana (2008).
Online Privacy Analysis and Hints for Its
Improvement. Informing Science and Information
Technology, Volume5.
Kuzu, Abdullah (2011). Views of pre-service teachers on
blog used for instruction and social interaction.
Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, Vol 8,
3, 34-51.
Lee, Sung Heum & Boling, Elizabeth (1999). Screen
Design Guidelines for Motivation in Interactive
Multimedia Instruction: A Survey and Framework for
Designers. Educational technology. 39, 19-26.
Lee, Sung Heum; Choi, Wook & Byun, Hoseung
(1996).Criteria for evaluating and selecting
multimedia software for instruction. National
convention of the association for educational
communication and technology (18
th
, Indianapolis),
ERIC IR: 018000.
Leidig, Paul M. (1999) Designing “usable” web sites.
JCSC, 15, 31-38.
Nielsen, Jakob & Tahir, Marie (2001). Homepage
Usability: 50 Websites Deconstructed. New Riders
Indianapolis, Available at http://www.useit.com/
homepageusability/.
Nielsen, Jakob (2002). Top Ten Guidelines for Homepage
Usability. Available on line at
http://www.useit.com/alertbox/20020512.html.
Ozkan, Yonca (2011). Blogging in a teaching skills course
for pre-service teachers of English as a second
language. Australasian Journal of Educational
Technology, 27(4), 655-670.
Powell, Thomas A (2002). Web Design: The Complete
Reference. 2nd edn.Osborne/McGrawHill Berkeley,
CA.
Reupert, Andrea and Dalgarno, Barney (2011). Using
Online Blogs to Develop Student Teachers’ Behaviour
Management Approaches. Australian Journal of
Teacher Education, Vol. 36: Iss. 5, 48-64.
Rieh, Soo Young (2002). Judgment of information quality
and cognitive authority in the Web. Journal of the
American Society for Information Science and
Technology, Vol 53, 2145–161.
Saeed, Nauman & Yang.Yun (2008).Incorporating blogs,
social bookmarks, and podcasts into unit teaching.
Tenth Australasian Computing Education Conference
(ACE2008), Wollongong, Australia, 2008, 113-118.
Schoneboom, Abby (2010).Web Design
Criteria.LaGuardia Center for Teaching and Learning,
available at http://faculty.lagcc.cuny.edu/ctl.
Shih, Ru-Chu (2010). Blended learning using video-based
blogs: Public speaking for English as a second
language students. Australasian Journal of
Educational Technology, 26(6), 883-897.
Stone, Jeffrey A (2012).Using reflective blogs for
pedagogical feedback in CS1.SIGCSE '12 Proceedings
of the 43rd ACM technical Symposium on Computer
Science Education, 259-264.
Tan, Shuyan; Ladyshewsky, Richard & Gardner, Peter
(2010).Using blogging to promote clinical reasoning
and metacognition in undergraduate physiotherapy
fieldwork programs. Australian Journal of Teacher
Education, 26(3), 355-368.
Tan, YuhHuann & Tan, Seng-Chee (2010).A
metacognitive approach to enhancing Chinese
language speaking skills with audioblogs. Australian
Journal of Teacher Education, Vol. 26, 7, 1075-1089.
Tarasewich, Peter (2008). An Investigation Into Web Site
Design Complexity and Usability Metrics. Quarterly
Journal of Electronic Commerce, Northeastern
University.
Tekinarslan, Erkan (2008). Blogs: A qualitative
investigation into an instructor and undergraduate
students’ experiences. Australasian Journal of
Educational Technology, 24(4), 402-412.
Tse, ShekKam; Yuen, Allan Hoi Kau; Loh, Elizabeth Ka
Yee; Lam, Joseph WaiIp& Ng, Rex Hung Wai (2010).
The impact of blogging on Hong Kong primary school
students’ bilingual reading literacy. Australian Journal
of Teacher Education, 26(2), 164-179.
Vaezi, Reza; Torkzadeh, Gholamreza & Chang, Jerry Cha-
Jan (2011).Understanding the Influence of Blog on the
Development of Social Capital.
The Data base for
Advances in Information Systems, Vol 42, 3, August,
34-45.
Viehland, Dennis & Zhao, Fei (2008).An Empirical
Analysis of Homepage Design in New Zealand.
International Journal of Principles and Applications of
Information Science and Technology, Vol.2, 1, 49-63.
Whitehead, Christopher C (2006). Evaluating web page
and web site usability. ACM SE’06, Melbourne,
Florida, USA March, 10-12, 788-789.
Wu, Hui-Ju & Wu, Pai-Lu (2011). Learners’ Perceptions
on the Use of Blogs for EFL Learning. US-China
Education Review A 3 323-330.
Yousef, Ahmed Mohamed Fahmy (2008). The effect of
synchronous and asynchronous communication in co-
operative learning across the web to develop students’
of instruction technology skills of communication
through the network. Master thesis, Ain shams
university, Egypt.
HowtoDesignGoodEducationalBlogsinLMS?
75
