Improving Usability of EHR Software through Design for Progressive
Enhancement
With a Case Study of Anfani Open Source EHR Software
Timi Ogunjobi
CISTD FOUNDATION, Cognisci Information Systems and Technologies for Development, Ibadan, Nigeria
Keywords: EHR, EMR, Software, Usability, Functionality, Features, Progressive Enhancement, Anfani.
Abstract: EHR software are the way of the future for healthcare delivery. They can help recognize and contain
epidemics, cut healthcare administration costs and enable doctors to search records more rapidly or share
patient data with remotely located specialists. However, the typical EHR package is seen as an intrusive
addition to the workflow of many established healthcare establishments, primarily because they are usability
deficient. This paper takes an alternative look at the design of EHR software from the perspective of
usability and with a focus on progressive enhancement in terms of available functionality. An insight to how
this model works is shown as a case study of the open source Ànfàní EHR.
1 INTRODUCTION
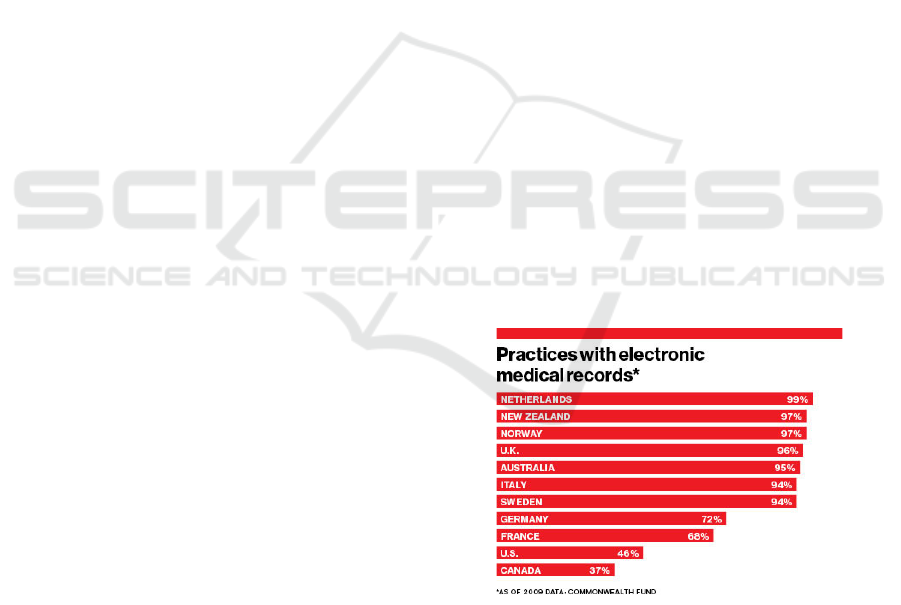
Statistics on the use of EHR systems in developed
countries are quite impressive and attest to the
recognition of the catalyzing role that such
technology play in the global improvement of
workflow in healthcare establishments.
Nevertheless, there still remains resistance to
adoption, from many health professionals primarily
for reasons relating to following:
Start Up Cost - The typical cost of switching to
electronic medical records may often be enormous.
These will include for the purchase of equipment to
record and store patient data, as well as for
converting all existing data to electronic form.
Training Cost - Further, staff have to be trained,
and while being trained they must be paid for non-
productive time.
2 DESIGNING THE PERFECT
EHR
Basically an EHR should be able to provide easy to
read clinical summaries of all active patient
problems, visits, medications, and lab results. But
many EHR salesmen believe in the “perfect” EHR,
which must contain all possible features including
records, laboratory, medication, radiology, health
Figure 1: EHR comparative usage.
information exchange, and automated export to
databanks.
3 USABILITY AND DESIGN
OF EHR SOFTWARE
Usability traditionally describes the interactive
experience associated with the user interface, of the
software application. Usability determines how easy
it would be to use the software, whether the software
will be engaging and satisfying to use, and whether
it will effectively support users’ goals ,tasks and
expectations.
While striving to create a “more perfect” EHR
417
Ogunjobi T..
Improving Usability of EHR Software through Design for Progressive Enhancement - With a Case Study of Anfani Open Source EHR Software .
DOI: 10.5220/0004362904170420
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2013), pages 417-420
ISBN: 978-989-8565-37-2
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

than the competitor, many vendors eventually create
“bloatware” , containing a multitude of features,
and technological capabilities which seek to amaze,
and probably do very little else . Many contain
superfluous features that do not support the goals
and tasks of the typical user, but which they must
nevertheless pay for and spend money to learn.
Above all they require users to adapt their attitudes
and behavior in order to get synchronized with the
new system. Thereby, rather than support its
intended users’ existing beliefs, attitudes, and
behaviors as they relate to the tasks that the system
is being designed to support very many HER
software tend to be distractive..
3.1 Defining Usability
The typical parameters which may be used to define
software usability and especially as it concerns
EMR/EHR are explained in the document, Defining
and Testing EMR Usability: Principles and
Proposed Methods of EMR Usability Evaluation and
Rating; which was created by HIMSS EHR
Usability Task Force. These parameters include:
Simplicity - which is defined as lack of visual
clutter and concise information as well as
inclusion of only functionality that is needed to
effectively accomplish tasks.
Naturalness - refers to how automatically
“familiar” and easy to use the application feels
to the user.
Consistency - how does the application’s
structure, interactions and behaviors match a
user’s experience with other software
applications. ?
Minimizing Cognitive Load - which could
negatively impact patient safety as a result of
an extra addition to the multiple demands for
the attention of the typical clinician
Efficient Interactions - by minimizing the
number of steps it takes to complete tasks.
Effective Information Presentation - in a user
friendly and not overtly technical manner.
Usability and Ease of Learning
Software usability reveals in improved ease of
learning or learnability. The use of consistence
concepts, behaviors, layout, and such features all
effectively lower the learning curve of software.
The ease of learning can be evaluated in terms of the
time it takes the user to reach a specified level of
proficiency and in terms of the time it takes a user
who has never seen the system interface to
successfully accomplish basic tasks. Consistence is
here also described as a similarity with previous data
storage and retrieval methods and workflows
4 DESIGNING EHR FOR
PROGRESSIVE
ENHANCEMENT
Most EHR design typically tend to be focused on
functionality. A user-centered design (UCD) on the
other hand engages a design process from the
perspective of how the software will be understood
and used by a human user. The result of employing
UCD to EHR design is a product that offers a more
efficient, satisfying, and user-friendly experience for
the user. Our model of the perfect EHR lacks
usability because it contains too many bundled
features employ a system that initially makes the
bare essentials available in an easy-to-use form and
then enables optional addition of more functionality
if the need arises. This design philosophy of
“progressive enhancement” is a current best-practice
trend in creating multi-user software, and which
originally relates to web technologies. It basically
describes the art of "separating document structure
and contents from presentation, and behavior. This
principle could also find use in the development of
software intended for use by several classes of
professionals each with a different need.
The principle, applied to the design of EHR will
suggest that:
Basic functionalities (patients’ record form)
should be accessible to all users
Enhanced behavior (e.g. prescription,
accounting, charts) should be provided by add-
on modules.
5 CASE STUDY: ÀNFÀNÍ EHR
Ànfàní EHR was from the onset designed with the
major tenets of usability in mind. Simplicity and
naturalness were highly desired features. It was
initially created as a research tool for consultants at
the University of Ibadan Teaching Hospital
(Nigeria) and later released as free and open source
software. The initial objective of the Ànfàní EHR
project was to make free and easy-to-use EHR
software available to health establishments in
developing countries Ànfàní is a Yoruba word which
means “beneficence”.
HEALTHINF2013-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
418

5.1 Architecture
The basic backbone of the Ànfàní-EHR system is a
Drupal framework. Drupal is a PHP development
software which has over the years shown superior
capabilities in the creation of web-based application.
Ànfàní-EHR as well as other related add-on modules
sits on top of this Drupal stack as a distribution of
the original framework.
Figure 2: The Anfani-EHR architecture.
5.2 Platform
The Ànfàní EHR was developed with PHP/AJAX
and to run on a Linux server environment.
Nevertheless, many users have successfully run it on
a Windows PC by using emulation software such as
WAMP or XAMPP to simulate the Linux server
environment. The software may also be successfully
run from a flash drive. Additionally, because the
biggest promise of the Drupal base is its versatility
as a web programming framework, Ànfàní-EHR
naturally lends itself to cloud hosting
5.3 Features and Functionality
Ànfàní-EHR is a database application consisting of
patient record forms piggybacked on the Drupal
framework. In summary Ànfàní EHR offers
following basic features
Editable electronic patients records forms
File and image uploads (documents, image,
audio, video)
Internationalization - Interface translation in
English, French, Spanish, Portuguese, and
Arabic.
This basic functionality may be progressively
enhanced by adding more modules such as for
accounting, drug prescription and several others as
the need arises.
5.4 Usability Assessment
On the basis of the previously enumerated
parameters for evaluation of usability, the following
is a brief examination of how Anfani EHR measures
up:
Simplicity - The basic demographic records,
including of visits, condition, and associated media
are entered and accessed from a single screen.
Naturalness - The record forms are intuitive and
built in the way clinicians are already used to
entering data on paper forms. With little technical
knowledge the basic form can be edited to
requirement of the health establishment.
Consistency – User interfaces are intuitive and
include search functions with a natural feel.
Usability and Ease of Learning - Most users
achieve 90% proficiency within 2 hours.
Figure 3: Typical patient record page.
5.5 Road Map
The focus ahead for Ànfàní EHR still remains to be
able to achieve the functionalities of the “perfect”
EHR, albeit in a different way- through a path of
enabling progressive enhancement. The preferred
method is to make more functionalities available as
add-on modules for specific users rather than as
unwanted features bundled in together.
Connectivity – The connectivity issue naturally
arises with EHR due to difference in database
structure across different software. Presently it is
possible to run isolated instances of Ànfàní-EHR on
widely distributed computers and have their
database records uploaded to populate a larger
database. This would be an inexpensive way to build
national health records databases especially in
developing countries. Alternatively the entire system
can be naturally cloud hosted for real-time records
ImprovingUsabilityofEHRSoftwarethroughDesignforProgressiveEnhancement-WithaCaseStudyofAnfaniOpen
SourceEHRSoftware
419

management, though this will require avoidable
infrastructure maintenance costs.
Prescription – One of the greatest challenges of
the Ànfàní –EHR system remains the development
of add-on modules relating to drug database for
running the prescription functionality. This is for the
reason that such data differ from one country to
another. But naturally as this is an open source
project, the code is freely modifiable for creating
new drug database modules for users in a specific
country.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper looked at the problems relating to the
design and use of electronic records management
software. It especially looks at how factors such as
optimistic design for functionality and poor usability
have become the bane for the use of EHR . It further
looked at how this can be improved by the process
of building functionality into EHR software through
the technique of progressive enhancement. The case
study for the propositions enumerated in the paper is
the open source Ànfàní EHR, which demonstrates
simplicity, scalability, and low integration costs as
the main features of a highly usable EHR software.
REFERENCES
Devin Leonard and John Tozzi.Why Don't More Hospitals
Use Electronic Health Records? - Businesswek
www.businessweek.co Jun 21, 2012
Anne Zieger. What Do Patients Need From EMRs? ,
Hospital EMR and EHR (www.hospitalemrandehr.
com) Nov 14, 2012
John D. Halamka, M. D., M. S.; Designing the Ideal
Electronic Health Record - http://
geekdoctor.blogspot.com Apr 23, 2008
Medflow Inc. Making the Transition from Paper Based
Medical Records to Electronic Health Records (EHR)
– Medflow . September 29, 2011
Usability First .User-centered design - www.
usabilityfirst.com
Wikipedia . Progressive enhancement – Wikipedia.org
James Bell Associates. Electronic Health Record Usability
AHRQ Publication - October2009
HIMSS EHR Usability Task Force, Defining and Testing
EMR usability: Principles and Proposed Methods of
EMR Usability Evaluation and Rating -, June 2009
CISTD Anfani EHR Users Manual, CISTD , September
2012.
HEALTHINF2013-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
420
