
How to Equip Students with Methodologies and Tools for Capturing
Rapidly Changing Environments through Computer
Supported Education
Ushio Sumita and Jun Yoshii
Graduate School of Systems and Information Engineering, University of Tsukuba,
1-1-1 Tennoudai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8573, Japan
Keywords: Matured Market Economy, Customer Segmentation, The 70-30 Principle, Intermediary DB, Profile Vectors.
Abstract: In the midst of the global mega-competition, the most competitive battle fields of economy, often referred to
as the tripod consisting of the United States, EU and Japan, has entered the matured market economy where
consumers are interested in acquiring goods and services to fit their particular needs, demanding a variety of
products and services in small quantities. Accordingly, corporations now have to deal with segmented
submarkets which change quite rapidly. For achieving the leading competitiveness in this new environment,
it is no longer sufficient to capture the entire market as a whole. Instead, it is necessary to trace and analyze
the segmented submarkets separately. In order to overcome this difficulty, methodologies and tools are
needed for extracting effective managerial implications from the massive data collected through the Internet
with speed and accuracy. The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate how to equip students with such
methodologies and tools through computer supported education.
1 INTRODUCTION
The growing market economy may be characterized
by the fact that consumers share the sense of lacking
goods and services for consumption and are eager to
possess what others have. In contrast, in the matured
market economy, consumers tend to pursue
individual tastes in consumption so as to maximize
their own sense of satisfaction. In other words,
consumers are interested in acquiring goods and
services that others may not have but fit their
particular needs. Naturally, this trend results in a
variety of products and services in small quantities
and the market segmentation becomes extremely
important. A typical successful R&D strategy in this
stage would be the market-in strategy, where a
variety of products are introduced into the market in
small quantities in response to particular needs in
particular market segments. Such products in the
matured market economy would have much shorter
life cycles than those in the growing market
economy, causing rapid changes in the segmented
submarkets.
As long as the real economy is concerned, the
economies of scale is always present. Since the
matured market economy requires more detailed
marketing strategies for individual segmented
submarkets, the efficiency resulting from the
economies of scale tends to diminish. In other words,
if corporations have to deal with separate segmented
submarkets in a one-on-one manner, the profit
margins would inevitably decrease. In order to
overcome this difficulty, methodologies and tools
are needed for extracting effective managerial
implications from the massive data collected through
the Internet.
The central approach for achieving this goal
would be to apply the 70-30 principle, proposed by
the authors in (Sumita and Yoshii, 2012), to the
information processing procedures, where such
procedures for separate segmented submarkets are
designed 70% in common with remaining 30% for
customization so as to cater for peculiarities of
individual submarkets. This observation would be
valid across many different industrial sectors.
Accordingly, from a pedagogical point of view, it is
very important to familierize students with the 70-30
principle applied to information processing, no
matter what industrial segment they plan to enter
after graduation.
493
Sumita U. and Yoshii J..
How to Equip Students with Methodologies and Tools for Capturing Rapidly Changing Environments through Computer Supported Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0004367904930496
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2013), pages 493-496
ISBN: 978-989-8565-53-2
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate how to
equip students with methodologies and tools for
implementing the 70-30 principle in information
processing through computer supported education.
In this paper, we focus on dynamic customer
segmentation in e-marketing for enhancing CRM
(Customer Relationship Management). A
pedagogical training scheme is illustrated explicitly
through computer supported education. Furthermore,
we clearly outline the procedures for extracting
managerial implications from the massive data
collected through the Internet.
2 DYNAMIC CUSTOMER
SEGMENTATION IN
E-MARKETING FOR
ENHANCING CRM
More than a decade has passed since the Internet
gained its significant presence in the world. It has
penetrated into many aspects of business practices
and has been drastically changing the traditional
business models in almost every industry. In the
retail chain business, for example, it is now possible
to collect and accumulate massive data from the
market via a POS (Point of Sales) system and utilize
them so as to develop effective marketing strategies
for enhancing sales of products. An extensive
literature exists for analyzing consumer purchasing
behaviors based on POS data, represented by
(Taguchi, 2010; Eugene, 1997; Ishigaki et al., 2011;
Yada et al., 2006) to name only a few.
The problem we face here is the excessive
computational burden, where the tremendous
amount of POS data collected from the market has to
be analyzed repeatedly in a timely manner. In order
to overcome this difficulty, we introduce the concept
of profile vectors as an intermediary information
base between various analytical engines and the DB
of POS data.
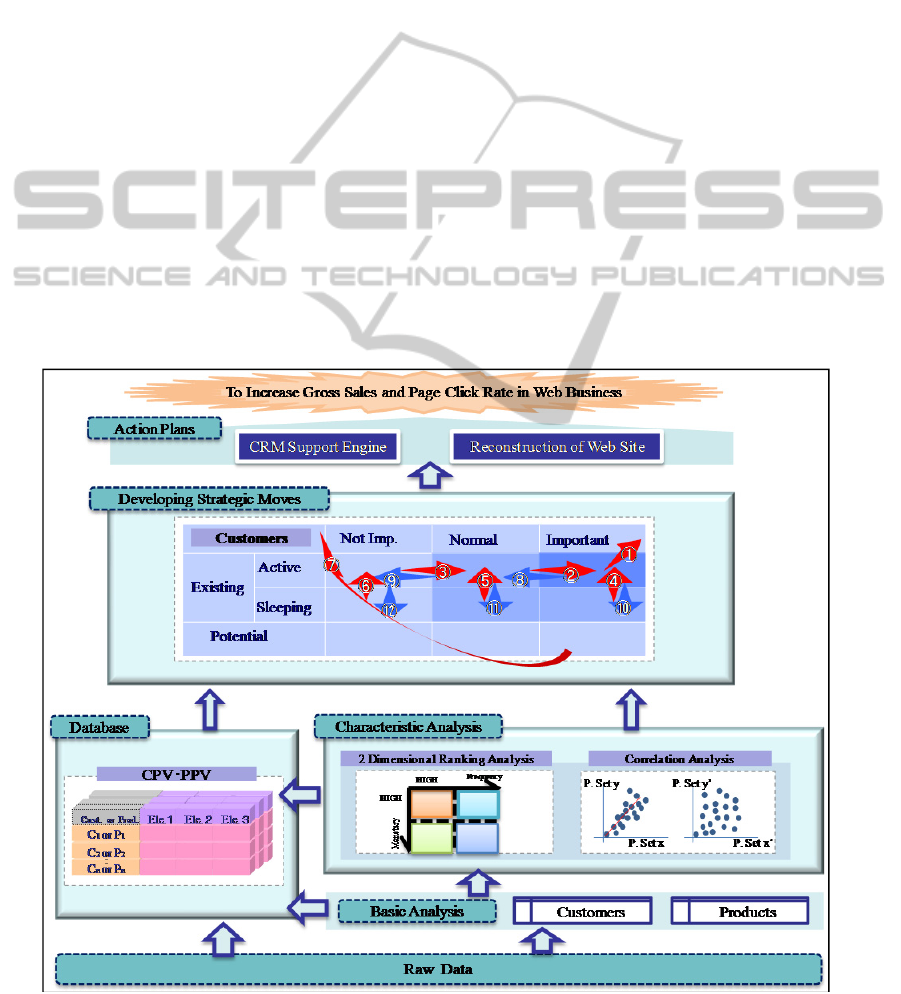
Figure 1 depicts the basic framework for
implementing dynamic customer segmentation. Here,
a variety of profile vectors, such as CPV (Customer
Profile Vector), PPV (Product Profile Vector) and
SPV (Store Profile Vector), are automatically
constructed and updated periodically from the DB.
These profile vectors are then used by different
analytical engines, producing the standard reports
Figure 1: Dynamic customer segmentation for enhancing CRM.
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
494

from the basic analysis as well as some ad hock
reports derived from characteristic analyses
specified by a manager through the graphic interface.
Furthermore, these results are used to update
customer segments dynamically so as to yield
different marketing strategies applied to different
customer segments.
CRM typically means that the lifetime value of a
customer is to be maximized by maintaining two
way communications between the customer and the
company through the Internet. This concept is
limited in that the potential customers are not
addressed explicitly. By combining POS data with
transaction data on the Internet, not necessarily
linked to purchasing, it is now possible to capture
the entire market as depicted in Figure 1, where the
market is decomposed into 9 segments: (Existing-
Active, Existing-Sleeping, Potential) × (Not
Important, Normal, Important). The arrows (1)
through (7) indicate the desirable changes of the
market for the company, whereas the arrows (8)
through (12) represent the changes of the market to
be avoided. The new marketing approach for
enhancing CRM would then be to devise strategic
moves so as to promote the moves along favorable
arrows and prevent the moves along unfavorable
arrows. Since such customer segments have to be
updated dynamically, the profile vector approach
becomes crucial for containing the underlying
computational burden. This example demonstrates
the importance of the 70-30 principle in e-Marketing.
For establishing a base for computer supported
education through this example, where students can
learn how to develop and maintain the dynamic
customer segmentation system illustrated in Figure 1
based on the 70-30 principle, a computer simulator
for the dynamic customer segmentation system is
installed in a server at Sumita Research Laboratory
in parallel with the system developed at the
collaborating e-business company through the joint
research project. Real data collected from the
Internet are fed into the simulator once a week. This
simulator enables students to actively get involved in
the decision process for development and analysis of
e-marketing strategies.
3 CONCLUSIONS
In the matured market economy, consumers are
interested in acquiring goods and services that others
may not have but fit their particular needs so as to
maximize their own sense of satisfaction. Naturally,
this trend results in a variety of products and
Figure 2: Customer profile vector.
Figure 3: Product profile vector.
services in small quantities and the market
segmentation becomes extremely important. Such
products introduced in response to segmented
submarkets would have much shorter life cycles,
causing rapid changes in the segmented submarkets.
In this paper, we propose a general scheme
involving methodologies and tools for capturing
such rapidly changing environments.
The proposed general scheme is based on the 70-
30 principle, proposed by the authors in (Sumita and
Yoshii, 2012), applied to the information processing
procedures, where such procedures for separate
segmented submarkets are designed 70% in common
with remaining 30% for customization so as to cater
for peculiarities of individual submarkets. The key
success factor for development of the general
scheme is to introduce profile vectors as an
CPV (Customer Profile Vector)
Part I
Customer ID
Sex
Age
…
Pa rt II
Time Period X(1) [ Tota l Quantity,
Total Monetary Amount,
Tota l Qua ntity of Ca tegory (1),
…
Tota l Qua ntity of Ca tegory (K),
Tota l Monetary Am ount of Ca tegory (1),
…
Tota l Monetary Am ount of Ca tegory (K),
… ]
Time Period X(2) [ Tota l Quantity,
Total Monetary Amount,
Tota l Qua ntity of Ca tegory (1),
…
Tota l Qua ntity of Ca tegory (K),
Tota l Monetary Am ount of Ca tegory (1),
…
Tota l Monetary Am ount of Ca tegory (K),
… ]
…
PPV (Product Profile Vector)
Part I
Product ID
Product Name
Category
…
Part II
Time Period X(1) [ Total Quantity,
Total Monetary Amount,
… ]
Time Period X(2) [ Total Quantity,
Total Monetary Amount,
… ]
…
HowtoEquipStudentswithMethodologiesandToolsforCapturingRapidlyChangingEnvironmentsthroughComputer
SupportedEducation
495

intermediary DB, where the majority of necessary
information for running analytical engines can be
extracted from such profile vectors without going
back to the DB, achieving the necessary speed.
In order to describe the general scheme clearly,
one concrete application area is discussed: dynamic
customer segmentation in e-marketing for enhancing
CRM (Customer Relationship Management). A
pedagogical training scheme is illustrated explicitly
through computer supported education. Furthermore,
we clearly outline the procedures for extracting
managerial implications from the massive data
collected through the Internet. It is expected that the
70-30 principle applied to massive information
processing for capturing rapidly changing
environments provides a general guidance to
enhance the strategic flexibility and the business
agility in other areas to be competitive in the midst
of the global mega-competition in the 21st century.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
In relation to the joint research project described in
this paper, the authors wish to express their sincere
gratitude to a corporate partner which prefers to
remain anonymous.
REFERENCES
Eugene J., 1997. An Analysis of Consumer Food
Shopping Behavior Using Supermarket Scanner Data:
Differences by Income and Location, American
Journal of Agricultural Economics, 79 (5), 1437-1443.
Ishigaki T., Takenaka T. and Motomura Y., 2011.
Improvement of Prediction Accuracy of the Number
of Customers by Latent Class Model, The 25th Annual
Conference of the Japanese Society for Artificial
Intelligence.
Sumita U and Yoshii J., 2012. Strategic Flexibility in
Exploiting Economies of Scope on 70-30 Principle –
A Case Study of Japanese Electronics Industry,
International Conference on Flexible Systems
Management.
Taguchi M., 2010. Analysis of Consumers’ Food Buying
Behavior Using Scanner Data. (in Japanese), Food
System Research, 16 (4), 25-31.
Yada K., Washio T. and Motoda H., 2006. Consumer
Behavior Analysis by Graph Mining Technique, New
Mathematics and Natural Computation, 2 (1), 59-68.
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
496
