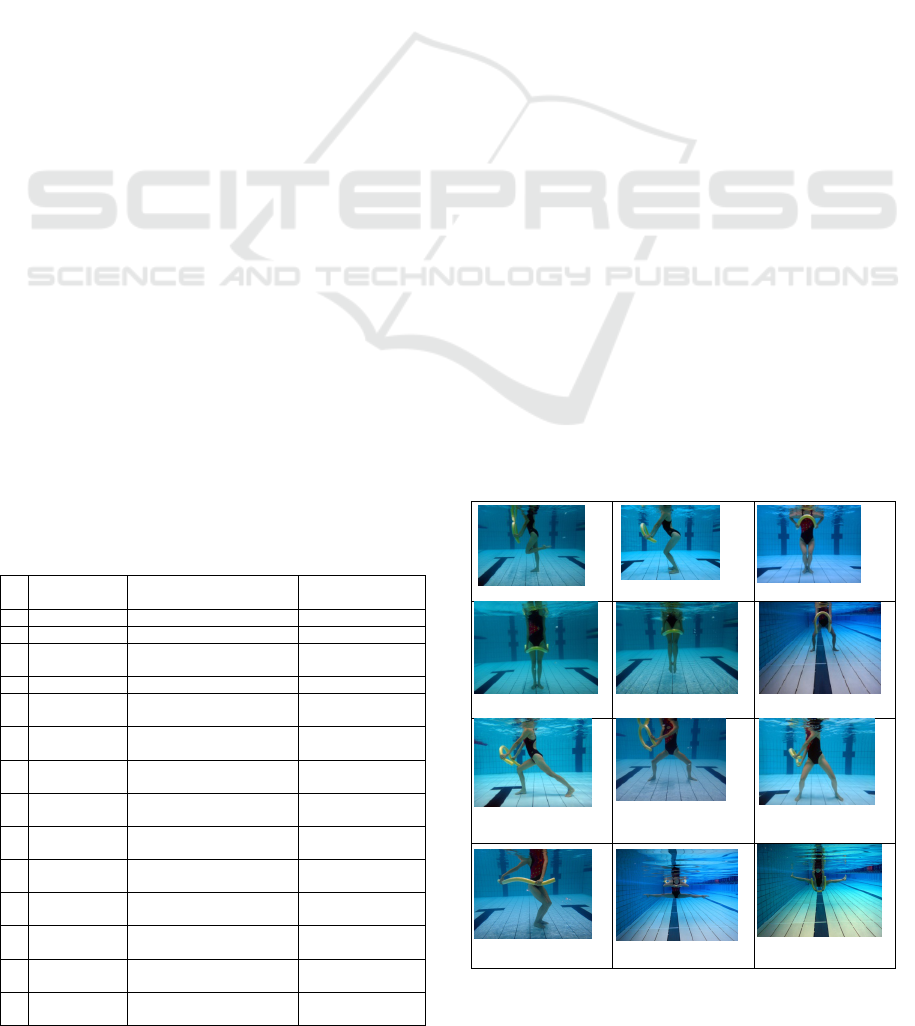
A Study on the Intensity of Water Noodle Aerobic Exercise for Adults
Yuhong Wen, Lijun Long and Yiming Zhang
Swimming Section, Beijing Sports University, Beijing, China
1 OBJECTIVES
Water aerobics are considered to be a fine way to
improve people’s fitness level without risk of injury
(Steve Tarpinian, Brian J. Awbrey,1997.). Noodle is
one of the commonly used equipments in water
aerobics. Noodle is made from foamed polyethylene
with the features of light, flexible, cushioning and
buoyant. It is usually used to improve exerciser’s
strength by adding resistance (
Michael De Toia, etc.
2004). It can also be facilitated as buoyancy
equipment to help exerciser floating or suspending
in the water for some special works.
Heart rate is a noninvasive, instant, practical and
easy index for intensity, cardiovascular and
metabolism. In order to reveal the load intensity of
different noodle works, 14 different movements are
designed based on the noodle’s feature of buoyancy
and length, as well as water characteristics and
human being’s anatomy.
2 METHODS
Table 1: Brief introduction of the 14 selected noodle
exercises.
No. Motion
Upper limbs (hold noodle
with hands)
Lower limbs
1 push jogging Push the noodle forward jogging
2 push squatting Push the noodle forward squatting
3 push jumping Push the noodle forward
squat and jumping
high
4 press squatting Press the noodle down squatting
5 press jumping Press the noodle down
squat and jumping
high
6
circle part
jumping
Press the noodle down then
push forward
Part jumping
7 circle lunges
Press the noodle down then
push forward
Lunging
8 scooping
Sweeping the noodle side to
side
Standing
9 waving
Sweeping the noodle from
left down up to the right
Standing
10 bunny jumping Holding the noodle
Jumping while
turning
11 lifting legs
Leaning the noodle with
chest
Lifting and
separating legs high
12 Press lifting Press the noodle down
Lifting and
separating legs high
13 circle lifting
Press the noodle down then
push forward
Lifting and
separating legs high
14
scissors
kicking
Leaning the noodle with
back and armpit
Suspending and
scissoring
In order to reveal the load intensity of different
noodle works, 14 different movements are designed
based on the noodle’s feature of buoyancy and
length, as well as water characteristics and human
being’s anatomy. 8 adults subjects aged from 18 to
40 are recruited to do water exercise 90 minutes for
3 times a week through 8 weeks period. 2 tests are
executed in the 6
th
and 8
th
week. Subjects maximum
heart rates are tested by porlar rs 400 when they do
each movement for 5 minutes continuously with 3
minutes interval between the movements so that HR
recovered almostly.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
HR is considered to be a sensitive and noninvasive
index for exercise intensity and metabolism level.
HR of water exercise is usually lower than land
exercise because of the buoyancy and resistance of
water and the speed of movement (MaryBeth Pappas
Baun,2007).
1
2
3
4 5 6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Figure 1: Diagram Sketch of the the 14 selected noodle
exercises.
Wen Y., Long L. and Zhang Y..
A Study on the Intensity of Water Noodle Aerobic Exercise for Adults.
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
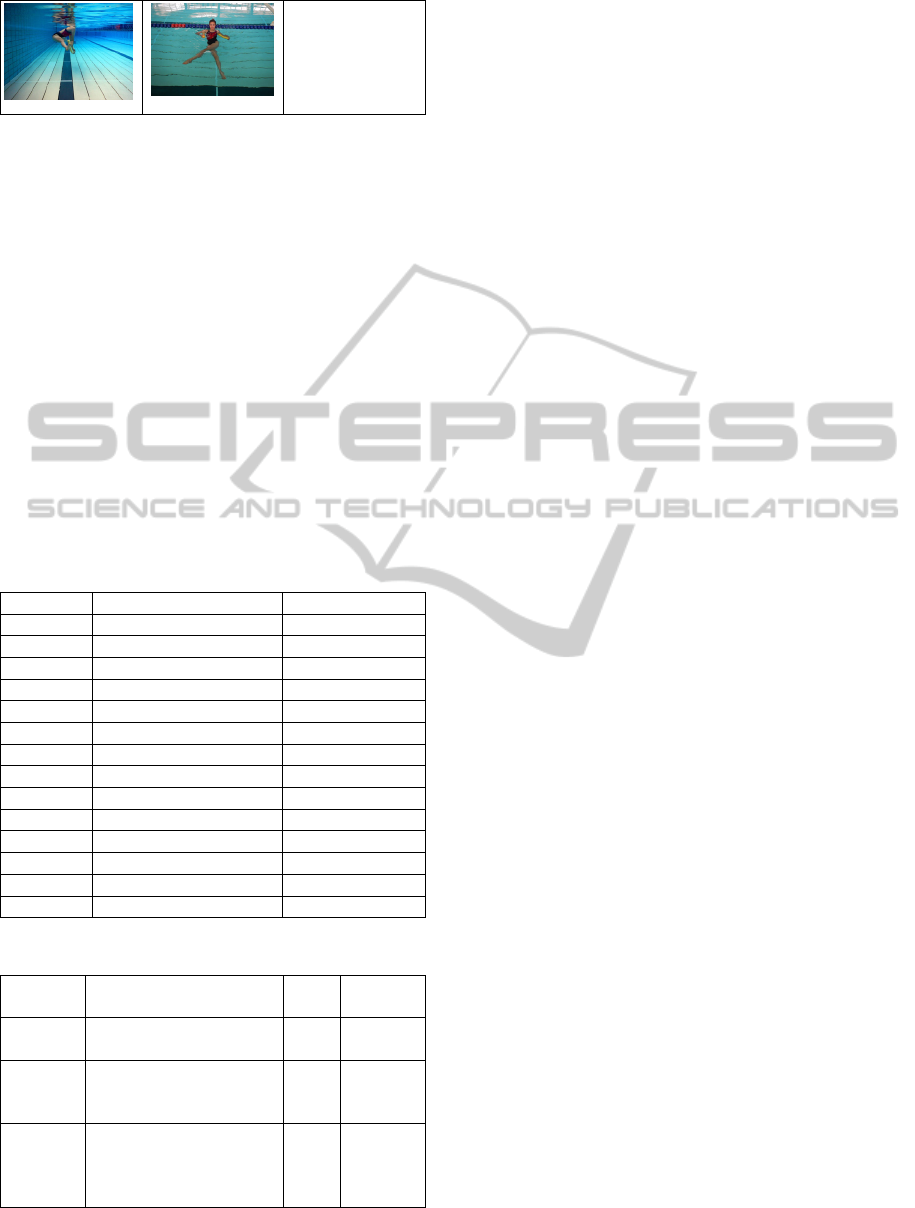
13
14
Figure 1: Diagram Sketch of the the 14 selected noodle
exercises. (cont.).
HR for the 14 movements range between
108±11.40 to 138±15.40 beat/min, which indicates
all the exercises are under aerobic intensity and are
beneficial for cardiovascular fitness. The highest HR
happened when subjects jumping in large range and
pressing down or pushing forward noodles with
arms, with mean HR located above 130 beat/min.
When the subjects press noodles while striding or
running, mean HR are between 120 to 130 beat/min.
When subjects press noodles with standing or
floating position, HR range from 110 to 120
beat/min. All the works can be divided into 3
groups, high intensity group, medium intensity
group and low intensity group.
Table 2: Subjects’ mean HR during the test for 14
works(N=8).
No. motions HR
1 Press lifting 138±15.40
2 circle lifting 136±12.37
3 press jumping 134±13.92
4 circle lunges 128±12.51
5 circle part jumping 127±20.53
6 bunny jumping 122±17.91
7 push jogging 121±17.08
8 push jumping 119±17.35
9 lifting legs 118±11.83
10 waving 116±10.07
11 scooping 116±10.36
12 scissors kicking 114±11.33
13 press squatting 110±14.28
14 push squatting 108±12.61
Table 3: Classification of the 14 movements.
movements
HR
zone
feature
High
intensity
Press lifting; circle
lifting; press jumping
A
b
ove
130
Jumping
vigorously
Medium
intensity
circle lunges; circle part
jumping; bunny jumping;
push jogging
120-
130
Striding
or jogging
Low
intensity
push jumping; lifting
legs; waving; scooping;
scissors kicking; press
squatting; push squatting
110-
120
Standing
or
floating
5 CONCLUSIONS
Intensity of water noodle exercises increases when
leg jumping vigorously with arm pressing noodles.
Intensity of exercises in floating position is
relatively low but good for injury prevention and
rehabilitation. All the pressing and pushing
movements are executed by pectoralis major and
bending muscles of arm, where latissimus dorsi and
extension muscle are not recruited thoroughly,
which indicates that further attention should be paid
in designing exercises.
REFERENCES
Steve Tarpinian, Brian J. Awbrey,1997. Water Workouts.
The Lyons Press.
MaryBeth Pappas Baun,2007. Fantastic Water Workouts.
Human Kinetics Publishers.
Jane Katz,2003. Your Water Workout: No-Impact Aerobic
and Strength Training From Yoga, Pilates, Tai Chi,
and More. Harmony.
Michael De Toia, etc. 2004.Water Exercises: Workouts
with the Aqua Noodle. Meyer & Meyer.
Terry-Ann, Wener Hoeger., 2002. Water Aerobics for
Fitness and Wellness. Wadsworth Publishing Co Inc.
Janna Lowell., 2012. Noodles for Dumbbells: Water
Exercise, Weight Management & More. America Star
Books.
