
Research on Dominant Process of Intellectual Resources in
Knowledge Service Project
Chen Chi and Chen Li
School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, 100044, China
Keywords: Knowledge Service, Intellectual Resources, Dominant Change.
Abstract: The work built a model of dominant process of knowledge service in intellectual resources using systematic
engineering method, modern knowledge management theory and method for the dominant change of
recessive resource. Furthermore, the structure, principle and elements of the model were descripted.
Besides, the dominant process of intellectual resource was divided into requirement elicitation, intelligence
processing and knowledge diffusion. Its links are further subdivided and studied.
1 INTRODUCTION
Knowledge service, especially consulting item,
always has strong casualness for its non-predictable
service process. Therefore, the dominant expression
of knowledge service becomes the core issue in the
development and application of intellectual
resources. The GPD (Gain-Process-Diffuse) model
constructed in this work aims to improve dominant
level in the process, thus studying knowledge
service process.
2 GPD MODEL OF THE
DOMINANT PROCESS OF
RECESSIVE INTELLECTUAL
RESOURCE
In GPD model of the dominant process of recessive
intellectual resource, knowledge service project is
abstracted and the service process of intellectual
resource is divided into three dominant change
stages (Qin Tiehui, Cheng Ni, 2006). Through
association, elements are integrated to a logical
description with comprehensive system, which is
complete and independent. Then, a simple means to
seek dominant change method for recessive resource
can be found. Fig.2-1 shows the GPD model.
Compared with traditional intellectual resource
study, the difference of GPD model is that the
dominant change method of recessive resource is
divided into requirement elicitation, intelligence
processing and knowledge diffusion. Moreover, the
operation mechanism of each node and stage as well
as the junction between them are studied.
3 REQUIREMENT ELICITATION
The first stage of knowledge service is requirement
elicitation, which can also be subdivided into the
communication, observation and internalization of
knowledge.
3.1 Communication
Consulting service is the convective reconstruction
process between explicit and implicit knowledge.
The dynamic transformation and updating of
recessive intellectual resources can only be achieved
through communication (Zhang Keying, Zhu Aihui,
Huang ruihua, 2007). The exchange in the beginning
of service process is a broad concept, including not
only the direct conversation and material transfer
between customer and facilitator, but also the formal
exchange about responsibility and obligation
between customers and facilitator experts. In
addition, this process also includes the informal
exchange, like private intercourse between
knowledge subjects, or even the participation and
communication among the cooperative alliance of
third-party and fourth-party. In terms of mode,
service process includes face-to-face
communication, such as conference interviews and
data transfer. Sometimes advanced information
330
330
Li C. and Chi C.
Research on Dominant Process of Intellectual Resources in Knowledge Service Project.
DOI: 10.5220/0006025503300333
In Proceedings of the Information Science and Management Engineering III (ISME 2015), pages 330-333
ISBN: 978-989-758-163-2
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

network tools and facilities will be used to organize
virtual dialogues across geographical boundaries. In
terms of content, during face-to-face communication
and virtual exchange dialogue, the most transmitted
in exchange is the explicit knowledge that is visual,
audible and perceptible.
3.2 Observation
From the perspective of system engineering theory,
the information of exchange links mostly belongs to
Wuli and Shili, while the primary task of
observation is Renli. Explicit knowledge is well
known and it is relatively easy to use it. However,
the acquisitions of recessive knowledge rely more on
subtle observation and perception. Experts,
professors and consultants tend to have a more acute
sense and richer means for recessive knowledge
acquisition than others. That is one of the elements
in recessive intellectual resources.
3.3 Knowledge Internalization
During knowledge internalization, attention should
be paid to two aspects to gradually clarify the
effectiveness. The first is customers’ requirements
expressed by words, and second is deep analysis of
the problems that need solving. Besides the
differences in their explicit-implicit degree, two
aspects are also interrelated. From the logical
relationship, the gap between subjective demand and
objective reality is the most urgent problem. But the
needs cannot be regarded as an equivalent to
problems, sometimes the real needs of customers are
gradually developed until emerge. Then what is the
exact and specific definition of effectiveness? A
simple question can be used to identify that. That is
the reflection of whether given effectiveness has
solved specific problems. Meantime, several
questions should be asked, such as what is the exact
problem that needs solving, what is the difference
compared to current situation and whether the
solving problem is the one stakeholders hoped.
4 INTELLECTUAL PROCESSING
After completing requirement elicitation, providers
of knowledge service will start internal operation,
namely performing intelligence processing to the
information and knowledge from collection and
internalization.
4.1 Idea
Idea is the view or opinion for specific problem. It
can be simple desires to reach certain goals, or
coming up with some means to solve problems. The
products of knowledge service often generate from
some immature thoughts, opinions and conceptions.
However, the confusion is that there are many initial
ideas while few are of innovation, significance and
value. Good ideas, after presented, are often able to
reach the presupposed effectiveness through
practice. Therefore, processing intellectual products
should not inhibit the generation of various ideas,
but should encourage the collision of thinking
sparks, free association of knowledge and passionate
confrontation of opinions. Even the consultants,
professors and scholars, it is impossible for them to
propose completely correct solutions at the
beginning of projects. That is because the final
solution is born during the process not at the
beginning.
4.2 Sketch
Idea is the first step of intelligence processing,
because the idea existing in brain is in a state of
imagination, which is vague, transitory and
fragmented. When consulting experts have captured
the ephemeral thoughts in brain, they should
immediately transform it into a visual preliminary
result, the sketch.
Sketch is a general description of things, ideas
and issues, or a visualization of them. In terms of its
content and form, sketch includes: thinking sketch,
conceptual sketch, report sketches, technical sketch
and emotional sketch.
4.3 Logic Model
Model method is one of the core methods of modern
science. Through preliminary discussion, the initial
idea can be stereotyped as sketch, which can be used
to build logic model. Although sketch is the
dominant result through thinking to some extent, but
the overall framework, structure and design of
elements are very rough. So sketch still needs further
refinement, namely to build logic model. Logic
refers to introducing the law of reasonable
conclusions from certain known conditions.
Therefore, logic model mainly focus on the analysis
of the relationship between various elements, and
describing the purpose and procedures of sketch
using reasonable forward-backward correlations. In
the construction of logic model, thinking forms of
Research on Dominant Process of Intellectual Resources in Knowledge Service Project
331
Research on Dominant Process of Intellectual Resources in Knowledge Service Project
331

summarizing, reasoning and judging, as well as
methods of analyzing, comparing, generalizing,
abstracting and integrating are needed.
4.4 Physical Model
Physical model describes the practice process of
how to achieve. If logical model was considered as
the engineering design plan of building, then
physical model should be the girders and
architectures. This is the key point of transforming
ideas into practice. The main work is as following:
(1) Stock assessment
The existing resource should be estimated based
on the business requirements of logic model design
as well as past experience. That includes the
personnel, information, technology, relationship and
capital, as well as all the recessive and explicit
resources.
(2) Service design
This step is the integration of problems and
solutions in logical model. That is, designers should
make full use of resources and plan the business to
refine measures and countermeasures of logic
model. Such design business should seriously
consider the effectiveness and executive personnel.
Besides, it should consider the requirements of
implementation as well as various existing
resources.
4.5 Practical Plan
Even the best model and design, it can only exert its
effect in practice. The bridge between model and
practice is scheme, the design and implementation of
which is the last step of visualizing the products of
intellectual processing. Scheme is the specific plan
of actual operations. In a broad sense, the
arrangement and layout of specific can also be called
scheme. Scheme establishing is to further manifest
recessive knowledge in physical model. Therefore,
the schemes in this work should be executable and
practicable. What’s more, they should also embody
the relations of Wuli, Shili and Renli.
5 KNOWLEDGE DIFFUSION
Knowledge service providers offer the processed
new knowledge to customers as consulting product.
This is the diffusion of knowledge. But it should be
noted that knowledge diffusion is not simply "you
release, I receive", but the dense interaction of new
knowledge between providers and customers, which
needs the socialization of expression, evaluation and
knowledge.
5.1 Expression
Expression is to present knowledge service products
to customers. In this process, recessive knowledge
will be transformed into explicit knowledge that
customers can perceive. The mission of consultants
is to clearly express the processed recessive
knowledge in intellectual product, thus making it be
easily understood by customers. Then, the service
objects can be achieved, and the value of intellectual
resource be realized.
For consulting project, the expression form of
knowledge product is more important. Sometimes
different expression forms could seriously affect the
degree to receive knowledge by customers, or even
lead to the contrary results. In the rapid rhythm
modern society, the extensively spread information
people faced requires the results expression of
consulting projects should be concise, have strong
wallop and can quickly move customers. Therefore,
the thinking of One Page Project Manager (OPPM)
can be used to design the expression forms of
knowledge products, namely drafting the elements
within the range of one paper. To make full use of
the structures, sharps and colors to show unitedly the
products, then customers can quickly and correctly
understand the products, thus acquiring knowledge
and making decisions accurately and efficiently.
5.2 Evaluation
The knowledge product supplied by knowledge
service providers is different from general
commodities, because it’s not a disposable deal.
Besides, unlike other services that provide
standardized services, it has strong interaction. In
commercial consulting industry, consulting experts
should repeatedly adjust solutions based on the
evaluation of customers, so as to truly meet
customers’ requirements. This is a custom-oriented
service process. Therefore, during the consulting
process, knowledge transfer between service
providers and customers is bidirectional with
continuous feedback. That is, both sides of
knowledge service are the providers and recipients
of knowledge, and the evaluators of knowledge
value. Consulting service is the circulation flow of
knowledge. Throughout the service process, both
two sides are continuously exchanging to transfer
knowledge until the end of consulting service.
ISME 2015 - Information Science and Management Engineering III
332
ISME 2015 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
332
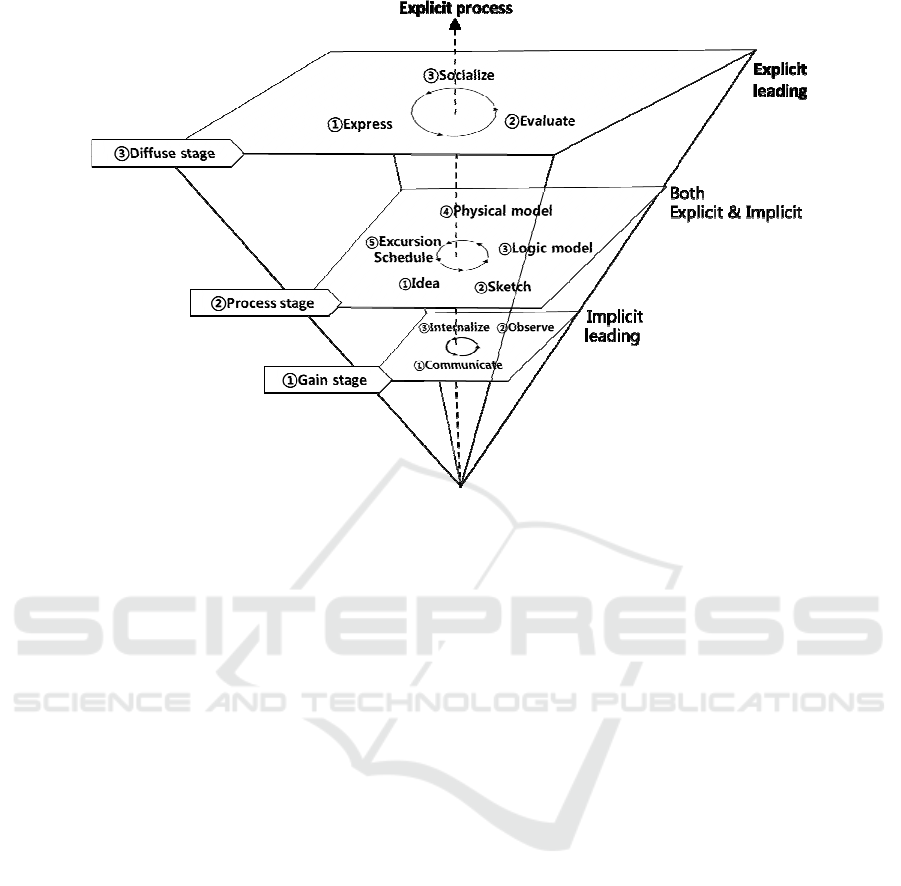
Figure 1: Model of the intellectual resource explicit process of the knowledge service project (GPD Model).
5.3 Knowledge Socialization
When knowledge service projects finished, part of
the explicit knowledge in knowledge product has
been transferred to customers by expression and
evaluation. Furthermore, there is also the
transmission between recessive knowledge and
recessive knowledge, called the knowledge
socialization. Knowledge socialization is the process
of transforming experiences into a new kind of
recessive knowledge, namely the transformation of
one kind of recessive knowledge to another. Because
the recessive knowledge should be adapted to certain
situation, so it is difficult to express it using formula
yet it can be obtained through personal experience.
Such knowledge conversion process is automatically
formed among subjects in their social behaviors. For
example, during the communication and sharing,
customers will be influenced by consultants’
working environment, or comprehend some methods
applied by consultants. These are all the content of
knowledge socialization.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Standing on the point of dominant development of
recessive knowledge, this work studied the model of
transformation and dominant process of recessive
knowledge in knowledge service projects. Based on
previous studies, the dominant process of intellectual
resource is divided into requirement elicitation,
intelligence processing and knowledge diffusion, the
links of which are further subdivided and studied. In
this way, the invisible and unspeakable process can
be visually presented to the mass.
REFERENCES
Qin Tiehui, Cheng Ni, Intelligence Communication in the
Knowledge Transformation Model SECI, Library and
Information Service, 2006 (7) .82-84.
Zhang Keying, Zhu Aihui, Huang ruihua, Research of
SECI Subdivision Mode Based on Main Body of
Knowledge Sharing, Journal of Intelligence, 2007 (7)
.5-7.
Research on Dominant Process of Intellectual Resources in Knowledge Service Project
333
Research on Dominant Process of Intellectual Resources in Knowledge Service Project
333
