
Analysis of Coastal Sea Reclamation Changes over Years and
Sustainable Development Capacity of Liaoning Province
Peng Wang, Xia Lin and Kai Jia
National Marine Environment Monitoring Center, Dalian 116023, China
Keywords: Liaoning Province, Coastal Zone, Sea Enclosure and Reclamation, Capacity of Sustainable Development.
Abstract: By collecting and collating related information of coastal sea enclosure and reclamation activities of Liaoning
province, this article did trend study on changes of coastal sea enclosure and reclamation activities over years
and environmental impact of Liaoning Province. The study showed that from 1990 to 2009, the area of sea
enclosure and reclamation in Liaoning Province had increased year by year, natural shoreline diminished with
the sea enclosure and reclamation activities year by year, total area of major bay decreased 18.4%. This article
did the quantitative evaluation of six coastal cities’ sustainable development level in Liaoning, result showed
generally poor sustainable development capacity of Liaoning coastal areas and mean evaluation score of
regional sustainability was 0.49, was non- sustainable development. Scores of Huludao City and Dalian City
were greater than 0.6, on basic level of sustainable development; score of Yingkou was greater than 0.5 and
less than 0.6, on low level of sustainable development; scores of Panjin, Dandong, Jinzhou were less than 0.5,
belonged to the level of non-sustainable development basically.
1 RESEARCH BACKGROUND
Coastal zone is the area natural process very active, in
terms of stability, the coastal zone is relatively
vulnerable geographical unit (Wang Jin, 2005). As
the socio-economic development, sea enclosure and
reclamation activities impacted the coastal
environment a lot, especially the damage to the
mangroves, coral reefs, estuaries, wetlands and other
ecosystems, according to the data of the Marine
Environment Quality Bulletin, coastal reed, swamps,
lagoons and other coastal wetlands lost by about 50%
(Chen Jiyu and Chen Shenliang, 2002). In 1840 the
area of Macau was just 2.78km
2
, currently it had
reached 23.5km
2
, 8.5 times as the original, and had
negative effect (Yang Chaoqun, 2000).
Research of Coastal Sustainable Development
also had some progress in our research and
implementation. Sheng Kerong et al., (2003) studied
the capacity and controlling measures for sustainable
development of Liaoning Province; Xiong Yongzhu
(2007) constructed a set of coastal sustainable
development evaluation model taking comprehensive
coordination degree, sustainability and sustainable
development as evaluation objectives, and did case
study as Guangdong Province; Han Jiwu et al., (2007)
studied coastal sustainable development evaluation
taking seven cities in China's coastal areas for
example; Qiu Yunfeng et al. (2007) studied
sustainable development of China's coastal province
based on GIS. Such studies mainly raised the
integrated management and development issues of
the coastal zone, which was important but easily
overlooked, to an understanding height, learning
from foreign experience (Abul-Azm et al., 2003;
Gladstone et al., 1999; Cave et al., 2003), pointed out
some of the problems and proposed solutions for
management and Sustainable Development of our
coastal zone.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
This paper used "Pressure - State - Response" (PSR)
model to build the coastal environment sustainable
development evaluation index system in Liaoning
province, and applied composite index method to
quantitative zoning evaluate the sustainable
development level of coastal six cities in Liaoning.
PSR model was established based on a causal
relationship that human activities pressured the
environment and would also change the number and
status of the resources. Society responded to these
changes by environment, economics and department
402
402
Jia K., Lin X. and Wang P.
Analysis of Coastal Sea Reclamation Changes over Years and Sustainable Development Capacity of Liaoning Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0006027304020406
In Proceedings of the Information Science and Management Engineering III (ISME 2015), pages 402-406
ISBN: 978-989-758-163-2
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
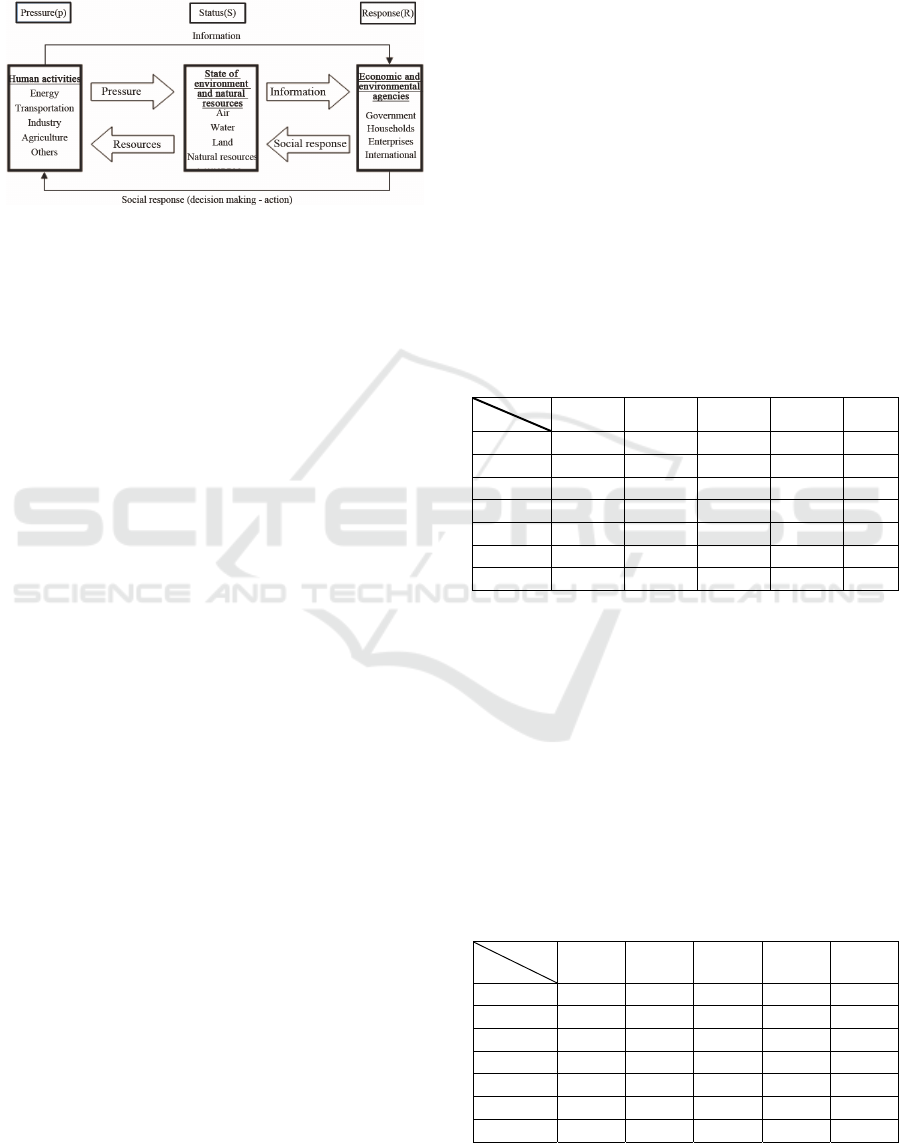
policies. These reactions formed a reverse circulation
pressuring human activities. The PSR framework
revealed a linear relationship between human
activities and the environment, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Pressure - state - response system and its indicator
type.
3 OVERVIEW OF STUDY AREA
Liaoning Province is one of ocean provinces in China,
across Huanghai and the Bohai. Coastal east began
from the Yalu River, west ended at the coast
demarcation point of Liaoning and Hebei. Its
mainland coastline was 2 292.4 km, had 506 islands,
reefs and lumps. There were 266 islands more than
500m
2
, 10 rivers were more than 5 000 km
2
, the
island coastline was 627km, mudflat resources were
1973.33 km
2
(Zhang Yaoguang and Cui Lijun, 2001).
Coastal prefecture-level cities are Huludao, Jinzhou,
Panjin, Yingkou, Dalian and Dandong. Seas vast,
coastline long, the huge potential of the oceans and
marine resources and other advantages had become
the carrier of Liaoning Province developing
production space, ecological space and living space.
In recent years, Liaoning Province increased the
input into the marine industry continuously, and the
ocean economic had developed lastingly and rapidly,
sea enclosure and reclamation activities also showed
development trend of fast, large area and wide range.
But in the process of seeking growth of ocean
economic, blind development and excessive use were
serious, causing serious environmental pollution in
coastal waters, deteriorating state of resources and
environment.
4 CHANGES OF SEA
ENCLOSURE AND
RECLAMATION OVER YEARS
AND ITS ENVIRONMENTAL
IMPACT OF LIAONING
PROVINCE
4.1 Changes of Sea Enclosure and
Reclamation over Years
In this paper, we used remote sensing images of 1990,
2000, 2005, 2008, 2009, combining with field
reconnaissance as well as data collecting in places,
got data of sea enclosure and reclamation over years
of Liaoning Province, and the results were shown in
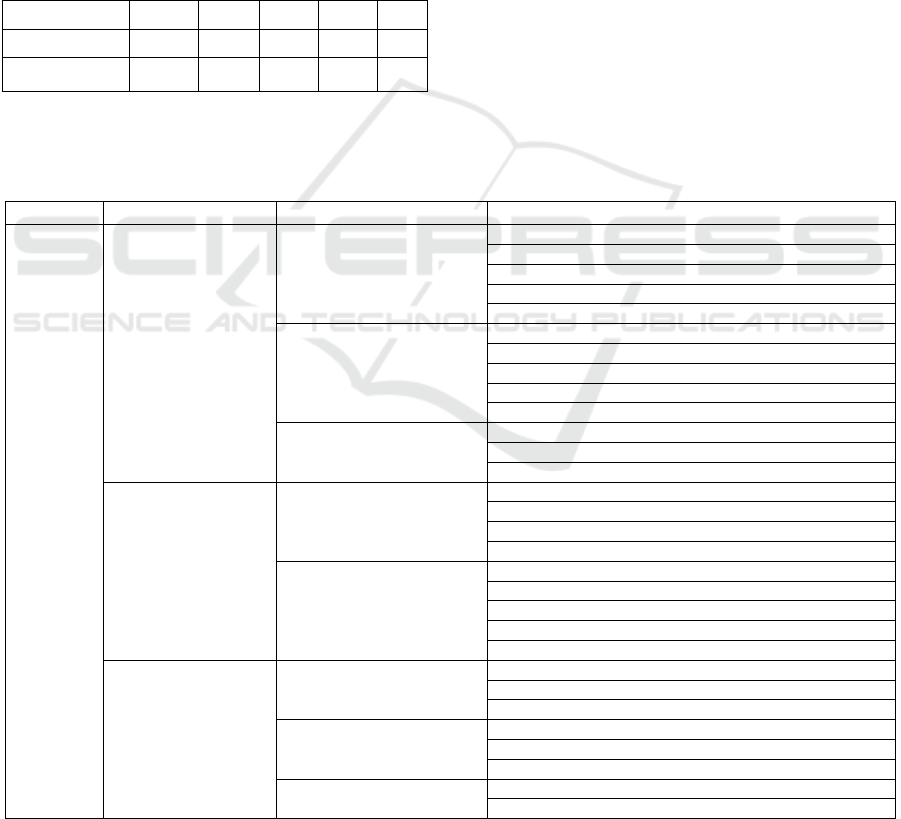
Table 1.
Table 1: Statistics of regional sea enclosure and
reclamation situation over years of Liaoning Province
(Unit: km
2
).
Year
Region
1990 2000 2005 2008 2009
Huludao 32.81 59.59 64.61 74.31 92.08
Jinzhou 86.43 178.9 193.49 201.63 213.82
Panjin 78.99 137.85 142.5 162.85 168.41
Yingkou 272.14 274.01 285.56 293.89 312.13
Dalian 428.73 669.75 740.27 824.69 884.47
Dandong 118.46 123.04 126.21 131.85 131.85
Total 1017.56 1443.14 1552.64 1689.22
1802.7
6
4.2 Sea Enclosure and Reclamation
Occupying Continental Natural
Shoreline
Due to the development and utilization of the coast,
natural shoreline changed into artificial shoreline
continuously in mainland coastline. In accordance
with the method determining natural shoreline in the
technical regulations of coastline resurvey, extracted
natural shoreline from remote sensing images over
years, and the results were shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Change statistics of mainland natural shoreline
over years of Liaoning Province (KM).
Year
Region
1990 2000 2005 2008 2009
Huludao 177.04 152.13 137.42 128.66 127.04
Jinzhou 26.81 20.18 19.88 18.43 18.43
Panjin 76.76 52.37 51.35 45.86 45.86
Yingkou 50.44 49.53 45.17 41.41 37.19
Dalian 579.40 536.69 488.02 442.73 437.48
Dandong 12.55 12.35 10.21 10.21 10.21
Total 923.00 823.24 752.05 687.30 676.20
Analysis of Coastal Sea Reclamation Changes over Years and Sustainable Development Capacity of Liaoning Province
403
Analysis of Coastal Sea Reclamation Changes over Years and Sustainable Development Capacity of Liaoning Province
403
4.3 Sea Enclosure and Reclamation
Occupying Bays
In this paper, we selected Jinzhou Bay, Taiping Bay,
Fuzhou Bay, Hulushan Bay, Dongjiakou Bay,
Pulandian Bay, Jinzhou Bay, Yingchengzi Bay,
Dalian Bay, Dayao Bay, Xiaoyao Bay, Changjiangao,
qingduizi Bay, 13 bays in total as evaluation objects
in bay log (Zhang Zongshu, 2002) of Liaoning
province.Taking outside boundary of sea enclosure
and reclamation in 1990 as coastline, analyzed the
bay area and sea enclosure and reclamation type in
bays, the results were shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Situation of sea enclosure and reclamation
occupying bays over years of Liaoning Province (km
2
).
1990 2000 2005 2008 2009
Area of bays 1367.31 1271.74 1214.72 1170.82 1115.6
Area of sea enclosure
and reclamation
0 95.59 152.09 195.77 234.39
5 CAPACITY FOR SUSTAINABLE
DEVELOPMENT OF LIAONING
PROVINCE COAST
Coastal area of six cities in Liaoning Province as the
research objectives, according to evaluation
objectives and situation of information acquisition,
based on P-S-R model framework and analytic
hierarchy to establish evaluation index system of
coast area sustainable development capacity,
including three subsystems: pressure, state and
response, four levels: objective layer, criteria layer,
elements layer and indicator layer.The data to
calculate the pressure indicator, status indicators,
response index were coastal six cities’
socio-economic statistic data at the end of 2006.
Using GIS spatial overlay and statistical analysis to
calculate the various space utilization ratio involved,
based primarily on the using status quo of sea,
distribution situation of water quality, space
distribution of sea and land resources in Liaoning
Province. Table 4 was shown below.
Table 4: Sustainable development evaluation index system of Liaoning Province.
Target layer Criteria layer Elements layer Index layer
level of coastal
sustainable
development
pressure subsystem
level of socio-economic
Year-end population density
GDP per unit area
Investment in fixed assets per unit area
Per unit output value of marine fishery
Per unit output value of mariculture industry
Level of resource utilization
Utilization rate of land space
Number of domestic tourists per unit shoreline
Artificial rate of shoreline
Utilization rate of sea space
Net deadweight of shipping tools per unit sea area
Direct environmental pressure
Emissions of industrial waste water per unit area
Emissions of domestic sewage per unit area
Emissions of industrial solid waste per unit area
State subsystem
resource utilization
Proportion of available land space
Proportion of available shoal space
Proportion of available sea space
Proportion of natural shoreline
Ecological environment
Proportion of clean water
Proportion of water worse than grade IV
Red Tide Frequency
Nekton density
Benthos density
Response subsystem
management policies
Criteria price valuation of sea area use
Sewage discharge rate reaching standard
Proportion of protected marine areas
Relevant inputs
Employment number of ocean management per unit area
Funding for ocean management per unit area
Pollution control investment per unit area
Other humanities response
Proportion of employed population above the high school education
Proportion of higher education population
ISME 2015 - Information Science and Management Engineering III
404
ISME 2015 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
404
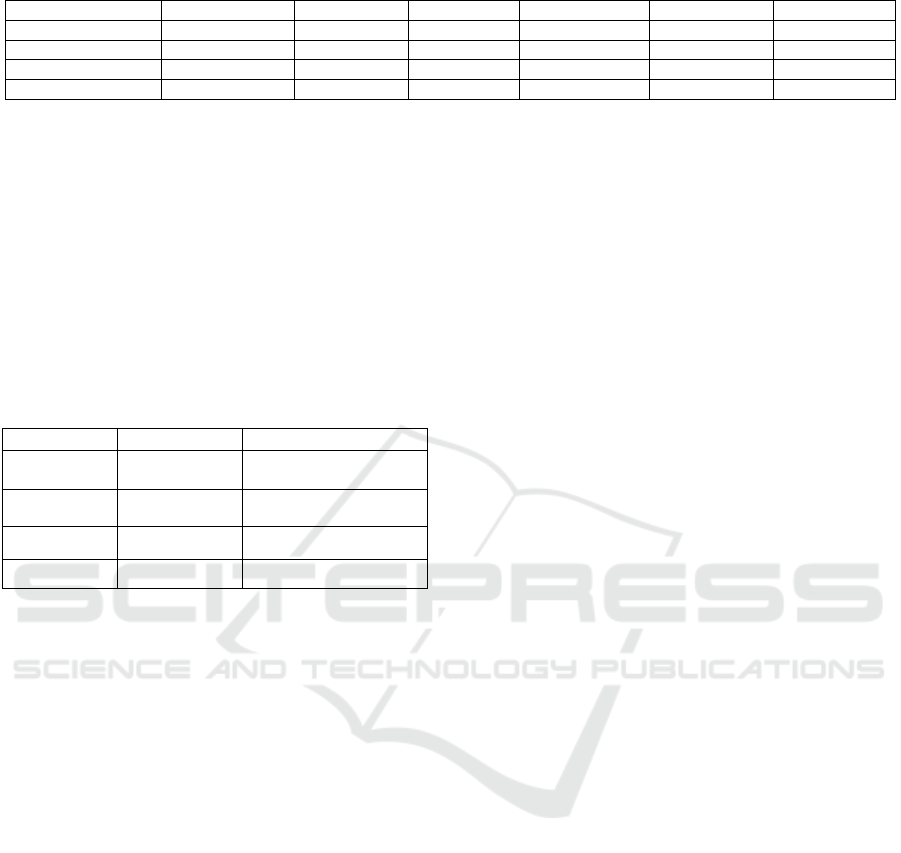
Table 5: Evaluation results list of six coastal cities’ sustainable development in Liaoning.
City of Dandong City of Dalian City of Panjin City of Yingkou City ofHuludao City of Jinzhou
ressure system 0.16 0.12 0.17 0.15 0.20 0.11
State system 0.05 0.07 0.04 0.06 0.09 0.06
Response system 0.13 0.48 0.18 0.37 0.40 0.09
Sustainability score 0.35 0.68 0.38 0.58 0.69 0.27
Using composite index method, based on the
weight above to evaluate the sustainable
development capacity of the coastal six cities in
Liaoning Province comprehensively, the evaluation
results were shown in Table 5.
Reference on the research results related to
sustainable evaluation of Zhang Zongshu (2002), Wu
Dun et al., (2005) composite index classification of
sustainable development of Liaoning Province’s
coast were in Table 6 below.
Table 6: Grading standard of composite index.
Classification Index value Grading standard
i 0.8<I<1
strong sustainable
development
ii 0.6<I<0.8
basic sustainable
development
iii 0.5<I<0.6
weak sustainable
develo
pm
ent
iv I<0.5
non-sustainable
development
On the score of each index, land area of Jinzhou
City was small, high density population, had the
maximum pressure on coastal, and the lowest score of
0.11; whether waters or land resources were
abundant in Huludao City, it had smaller population
density, lower economic development level, the
minimum pressure on coastal ecological
environment, the score of 0.20.
6 CONCLUSION
(1) Environmental Impact of the Coastal Zone
Development Activities in Liaoning Province. In
1990-2009, sea enclosure and reclamation area
increased year by year in Liaoning Province, the
accumulated area was 1797.13 km2 in 2009,
especially in 2008 and 2009, it increased 108km2.
Natural shoreline declined with sea enclosure and
reclamation activities year by year in Liaoning
Province, from 1990 to 2009, natural shoreline
decreased 246.8km, in which sea enclosure farming
occupied the most, in sea reclamation activities,
urban construction occupied the most. Since 1990,
the main bay area reduced from 1367km2 to
1116km
2
,
decreased by 18.4%.
(2) Capacity for Sustainable Development of
Liaoning Province Coast Zone. Synthesized scores of
main system indicators, getting the evaluation results
of coastal six cities’ sustainable development
capacity in Liaoning Province: with the descending
order Huludao 0.69, Dalian 0.68, Yingkou 0.58,
Panjin 0.38, Dandong 0.35 , Jinzhou 0.27.Overall,
Liaoning had poor sustainable development capacity
in coastal areas and mean evaluation score of regional
sustainability was 0.49, was non- sustainable
development. Scores of Huludao City and Dalian
City were greater than 0.6, on basic level of
sustainable development; score of Yingkou was
greater than 0.5 and less than 0.6, on low level of
sustainable development; scores of Panjin, Dandong,
Jinzhou were less than 0.5, belonged to the level of
non-sustainable development basically.
REFERENCES
Abul-Azm, AG, Abdel-Gelil, Ibrahim, Integrated Coastal
Zone Management in Egypt: The Fuka-Matrouh
project, Journal of Coastal Conservation, 9, pp.5- 12,
2003.
Chen Jiyu, Chen Shenliang, Challenges China’s Estuarine
and Seacoast facing, Trend of Marine Geology,18 (1),
pp.1-5, 2002.
Han Jiwu, Wu Wei, Li Jian, Research on Sustainable
Development Evaluation of Coastal zone: Seven Cities
of coastal China as example, Environmental Protection
Science, 22 (5), pp.58-60, 2007.
Qiu Yunfeng, Qin Qiming, Cao Bao, etc. Research on
Sustainable Development Evaluation of China's coastal
provinces based on GIS, Population • Resources and
Environment in China, 17 (2), pp.69-72, 2007.
RR Cave, L. Ledoux, K. Turner, The Humber catchment
and its coastal area: from UK to European perspectives,
The Science of the Total Environment, 7, pp.314-316,
2003.
Sheng Kerong, Zhang Pingyu, Ma Yanji, Research on
Sustainable Development Capacity and Mitigation
Countermeasures of Liaoning Province, Population •
Resources and Environment in China, 13 (3), pp.74-80,
2003.
W. Gladstone, N. Tawfiq, D. Nasr, I. Andersen,
Sustainable use of renewable resources and
Analysis of Coastal Sea Reclamation Changes over Years and Sustainable Development Capacity of Liaoning Province
405
Analysis of Coastal Sea Reclamation Changes over Years and Sustainable Development Capacity of Liaoning Province
405

conservation in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden: issues,
needs and strategic actions, Ocean & Coastal
Management, 42, pp.671-697,1999.
Wu Dun, Using Analytic Hierarchy Process to Evaluate
Sustainable development situation of Hohhot city,
Inner Mongolia Normal University (Natural Science
Chinese Edition), 34 (2), pp. 237-240, 2005.
Wang Jin, Research on Synthesized Management Model
and its Management Countermeasures of Typical
Coastal Zone, 2005, 5.
Xiong Yongzhu, Research on Sustainable Development
Evaluation Model of Coastal Zone and Its Application,
Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, pp.164, 2007.
Yang Chaoqun, Negative Effects of reclamation in
Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao and
Countermeasures, Guangdong Geology, 15 (2), 2000.
Zhang Yaoguang, Cui Lijun, Resources basic research of
marine economic development of Liaoning, Liaoning
Normal University Journal (Natural Science), 24 (3),
pp. 308-313,2001.
Zhang Zongshu, Research on Regional Sustainable
Development Evaluation Index System and Method –
Sichuan’s Sustainable Development Evaluation as
Example, Leshan Teachers College Journal, 17 (4),
pp.79-82, 2002.
ISME 2015 - Information Science and Management Engineering III
406
ISME 2015 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
406
