
Information Driven Cyber Security Management
through LinDA
Panagiotis Gouvas
1
, Eleni Fotopoulou
1
, Spyros Mouzakitis
2
and Anastasios Zafeiropoulos
1
1
UBITECH Ltd., 15231 Chalandri, Athens, Greece
2
Decision and Support Systems Laboratory, National Technical University of Athens,
15780 Zografou, Athens, Greece
{pgouvas, efotopoulou, azafeiropoulos}@ubitech.eu
smouzakitis@epu.ntua.gr
Abstract. The continuous evolution and adaptation of cybercrime technologies
along with their impact on a set of services in various business areas make nec-
essary the design and development of novel methodologies and tools for pro-
tecting public organizations and businesses’ infrastructure as well as end users.
Such methodologies and tools have to exploit the massive power that can be
provided through the available data collected in organizations’ perimeter, net-
working and infrastructure level as well as data collected via endpoint devices.
However, the available data, in order to be easily exploitable have to be repre-
sented in standardized formats or be easily interlinked and being analyzed. To-
wards this direction, linked data technologies can be used towards the appropri-
ate interconnection of available entities/concepts among different cyber security
models. In the current manuscript, we describe an approach for supporting in-
formation driven cyber security management through exploitation of linked data
analytics technologies, as they are developed within the framework of the Lin-
DA FP7 project. A cyber security data model is designed for cyber-attacks data
representation, while a set of insights are produced upon data analysis over data
collected in a small enterprise environment.
1 Introduction
Over the last years, the evolution of the Internet along with the emergence and adop-
tion of novel ICT technologies and the development of a portfolio of online services
have led to the appearance of a wide set of online threats, risks and vulnerabilities that
are handled mostly per case upon their appearance. The arisen security issues impact
significantly the daily operation of enterprises and public sector organizations as well
as the overall economic growth indicators.
Taking into account the continuous evolution and adaptation of cybercrime tech-
nologies as well as the huge number of people that they affect, advanced methodolo-
gies and operational tools have to be developed for protecting businesses’ and public
organizations’ infrastructure and citizens. Threats have to be faced at their creation
while the overall complexity in the threat management and remediation process has to
be minimized. The emergence of cyber security management methodologies and tools
Mouzakitis S., Gouvas P., Fotopoulou E. and Zafeiropoulos A.
Information Driven Cyber Security Management through LinDA.
DOI: 10.5220/0006163300030016
In The Success of European Projects using New Information and Communication Technologies (EPS Colmar 2015), pages 3-16
ISBN: 978-989-758-176-2
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
3

has also to be combined with an increased level of collaboration and exchange of
information among enterprises and public organizations, targeting at the increase of
their awareness with regards to the design and implementation of cyber security solu-
tions as well as the facilitation of the specification of effective policies for handling
cyber threats.
Towards this direction, a set of challenges is identified. These challenges regard (i)
the efficient processing of the available cybersecurity-oriented information from inter-
nal and external sources within an enterprise/organizational environment (e.g. raw
data with regards to incidents, vulnerabilities, weaknesses etc.), (ii) the extraction of
advanced knowledge upon the available cyber security information based on the ap-
plication of a set of knowledge-extraction and management algorithms, (iii) the appli-
cation of effective and efficient mechanisms for cyber-security management by mak-
ing use of the available information flows and taking in parallel into account con-
straints with regards to peculiarities imposed by the provided services, (iv) the design
of user-friendly tools for information driven cyber security management that facilitate
timely and efficient response to incidents without the need for actions from cyber-
security specialised personnel and (v) the promotion of unified open cyber security
data publication schemes along with interoperability mechanisms to be used/consumed
by enterprises and public organizations.
Processing of the available cybersecurity-oriented information has to be realised
from internal and external sources within an enterprise/organizational environment –
through cyber security monitoring tools- as well as over raw data or data available in
heterogeneous formats. Processing of such information can lead to efficient decision
making in real time as well as a posteriori with regards to the implementation of
cyber-security solutions. In order to deploy efficient information processing schemes,
advanced techniques have to be applied for information representation as well as con-
cepts interconnection processes. Efficient representation necessitates the exist-
ence/usage/extension of commonly used cyber security meta-models, as well as the
application of mapping mechanisms for transformation of the available data to formats
that can be easily and commonly processed. Such a mapping can be realised through
the development of an ontology (or group of ontologies) of the cyber security domain,
expressed in a specific language (e.g. OWL language), that will enable data integra-
tion across disparate data sources. Formally defined semantics will then make it possi-
ble to execute precise searches and complex queries and support semantically align-
ment processes among datasets represented by different models.
Towards this direction, linked and open data technologies can be exploited. The
term linked data refers to a set of best practices for publishing and interlinking struc-
tured data on the Web. By following these practices, data from diverse sources can use
the same standard format that allows them to be combined and integrated. Linked data
specify that all data will be represented based on the Resource Description Framework
(RDF) specifications. Conceptual description of data is realized based on specific
vocabularies (and thus semantics) accessible over HTTP, allowing the user to interpret
data from multiple vocabularies and query them in a uniform manner. By adopting
linked data principles, a set of advantages are provided towards the production of
advanced analytics and insights. Combination of data from multiple and in many cases
distributed sources, as well as from publicly available data (e.g. open governmental
data) or privately owned data maintained by enterprises, can help businesses enhanc-
4
EPS Colmar 2015 2015 - The Success of European Projects using New Information and Communication Technologies
4

ing their experience of managing and processing of data, in ways not available before.
Actually, linked data provide the capacity for establishing association links among
concepts in different datasets, producing high-quality interlinked versions of semanti-
cally linked web datasets and promoting their use in new cross-domain applications by
developers across the globe. Such interlinked datasets constitute valuable input for the
initiation of an analytics extraction process and can lead to the realization of analysis
that was not envisaged in the past.
In the cyber security domain, linked data can be used towards the appropriate inter-
connection of available entities/concepts among different cyber security models.
Linked data analysis provides cyber experts and incident responders a way to quickly
identify the important assets, actors, and events relevant to their organization, accen-
tuating the natural connections between them and providing contextual perspective.
With this added context, it becomes much easier to see abnormal activity and assess
the blast radius of an attack [1]. However, the power of linked data can be fully ex-
ploited, given the existence of significant amount of data, made available by public
organizations and enterprises. Open data publication and consumption schemes have
to be adopted and widely used for the aggregation of cyber security associated data in
open repositories. Over such repositories, queries on the available open data or inter-
linking of data for advanced queries can be applied. The wide adoption of open data
technologies can facilitate the appropriate dissemination of information with regards
to new threats and vulnerabilities, the realisation of advanced analysis taking into
account available data from other sources as well as the shaping of communities of
practice and the engagement of “non-experts” in the cyber security domain.
Extraction of knowledge and management of the available information upon the
mapped/interlinked data can be realised through the application of novel analysis
techniques as well as the development of user-friendly analytics and visualisation
tools. Novel analytic and visualisation approaches have to be introduced and provided
to end users through user-friendly tools. Analysis has not only to focus on extraction
of conclusions and results based on experiences from previous threats, attacks and
risks. A set of analytics for identification of malicious behaviours, anomaly detection,
identification of epidemiological incidents etc. has to be supported even for decisions
that have to be made in real time. This is not to say that preventive measures are use-
less, but instead that organizations must arm themselves with proficient detection and
response practices for readiness in the inevitable event that prevention fails [1].
Going one step further, such tools have to support functionalities for the extraction
of linked data analytics [2], given that analytics are in most cases related with the
processing of data coming from various data sources that include structured and un-
structured data. In order to get insight through the analysis results, appropriate input
has to be provided that in many cases has to combine data from diverse data sources
(e.g. data derived from endpoints in different geographical areas). Thus, there is in-
herent a need for applying novel techniques in order to harvest complex and heteroge-
neous datasets, turn them into insights and make decisions.
Taking into account the afore-mentioned challenges and enabling technologies for
overcoming part of them, it could be claimed that there is open space for the design,
development and validation of novel information driver cyber security management
solutions that can unleash the potential of the processing of huge amount of the avail-
able information. In the current manuscript, such an approach is presented based on
5
Information Driven Cyber Security Management through LinDA
5

the realisation of linked data analysis through the workbench that is developed within
the framework of the FP7 project LinDA (http://linda-project.eu/). A cyber security
data model is designed for cyber-attacks data representation, while through the usage
of the LinDA workbench, data transformation to RDF format and data analysis is
supported. Available data stem from data collected through monitoring of cyber-
attacks in a small enterprise environment. The produced insights of the analysis, along
with the definition of the cyber security data model, constitute outcomes that can be
the basis for further extensions and more advanced analyses in the future.
In more detail, the structure of the paper is as follows: in section two, the LinDA
project including its main objectives, the LinDA workflow and the developed LinDA
workbench is described; in section three a pilot application scenario in the cyber secu-
rity domain is presented along with the analysis results and the produced insights,
while section four concludes the paper by referring to the exploitable outcomes of the
presented work and plans for future work.
2 The LinDA Project
LinDA [3] aims to assist SMEs and data providers in renovating public sector infor-
mation, analysing and interlinking with enterprise data by developing an integrated,
cross-platform, extensible software infrastructure, titled as the “LinDA workbench”
[4] that handles the end-to-end the transition of a data-powered enterprise to a linked
data-powered organisation. The LinDA workbench allows for the transformation of
various formats of data into arbitrary RDF graphs, the construction of linked data
queries through user friendly interfaces addressed to SMEs, included intuitive visuali-
sation methods and charts, while it is in a position to perform further statistical analy-
sis to the queries results based on the R framework [5]. The LinDA workbench can be
used either as a service, or be deployed and operated as a standalone solution, while
users are in a position to make use of its sub-modules in a distinct manner also.
The overall realisation of the LinDA project has been achieved through the realisa-
tion of the following objectives:
• enhance the ability of data providers, especially public organisations to provide
re-usable, machine-processable linked data.
• provide out-of-the-box software components and analytic tools for SMEs that of-
fer the opportunity to combine and link existing public sector information with
privately-owned data in the most resourceful and cost-effective manner.
• deliver an ecosystem of linked data publication and consumption applications that
can be bound together in dynamic and unforeseen ways.
• demonstrate the feasibility and impact of the LinDA approach in the European
SMEs Sector, over a set of pilot applications.
• achieve international recognition and spread excellence for the research undertak-
en during the LinDA implementation towards enterprises, scientific communities,
data providers and end-users. Diffuse and communicate readily-exploitable pro-
ject results, of a pro-normative nature. Contribute to standardisation and educa-
tion.
6
EPS Colmar 2015 2015 - The Success of European Projects using New Information and Communication Technologies
6

2.1 The LinDA Workbench
The LinDA workbench [4] concerns an open-source package of linked data tools for
enterprises to easily publish data in the linked data format, interlink them with other
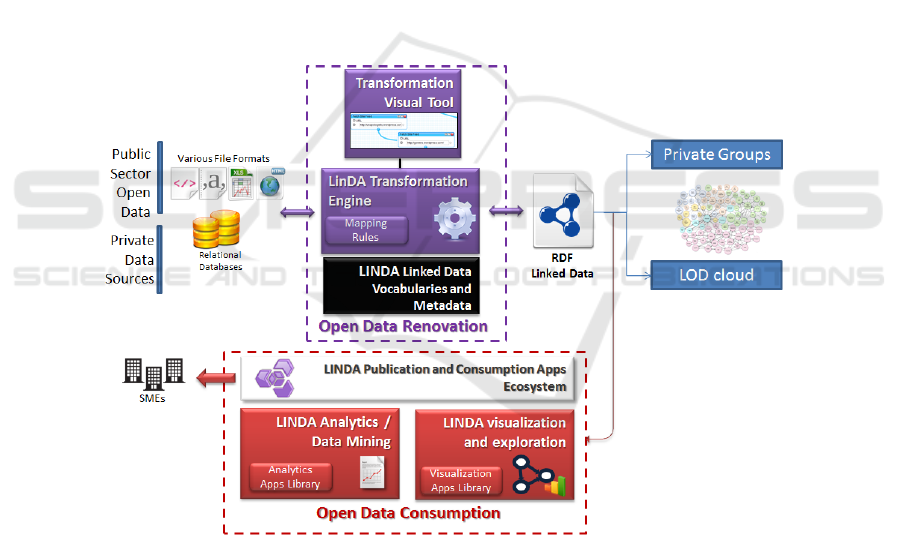
data, analyze them and create visualizations. The main components of the LinDA
workbench (Figure 1) are the following:
• The LinDA Transformation Engine, a data transformation solution that provides a
simplified workflow for renovating and converting a set of common data contain-
ers, structures and formats into arbitrary RDF graphs. The Transformation Engine
can be used to develop custom solutions for SMEs and public sector organisations
or be integrated into existing open data applications, in order to support the auto-
mated conversion of data into linked data. The overall platform allows the export
of arbitrary RDF graphs as tabular data, supporting SMEs to store the final results
of data linking into relational databases or process further with spreadsheet and
data analysis software.
• The LinDA Vocabulary Repository, a repository for accessing and sharing linked
data that can be linked to the Linked Open Data (LOD) cloud. The system allows
SMEs to reference and enrich metadata shared by well-established vocabulary
catalogues (e.g. LOV, prefix.cc, LODStats), thus contributing to easy and effi-
cient mapping of existing data structures to the RDF format as well as to increas-
ing the semantic interoperability of the SMEs datasets.
• The LinDA Query Designer and the Query Builder tools that enable non-experts
to formulate a SPARQL query and explore open datasets in an innovative and
easy way, to use graphical methods to interactively build a simple or complex
query over multiple data sources and view the results in a SPARQL editor. The
Query Designer follows the paradigm and quality of SQL Query designers of
popular relational database management systems where, with simple drag’n’drop
functionality, users can perform complex SPARQL queries, while the Query
Builder offers similar functionality through a wizard-like guided list procedure.
• The LinDA Visualization engine that can help enterprise users gain insight from
the linked data that the company generates. With this engine users can visualize
data in linked data format taking into advantage their semantics. The LinDA visu-
alization provides a largely automatic visualization workflow that enables SMEs
to visualize data in different formats and modalities. In order to achieve this, a
generic web application is being developed based on state-of-the-art linked data
approaches to allow for visualizing different categories of data, e.g. statistical,
geographical, temporal, arbitrary data, and a largely automatic visualization work-
flow for matching and binding data to visualizations.
• The LinDA Analytics and Data Mining component [2] supports the realization of
analysis based on the consumption and production of linked data. A library of
basic and robust data analytics functionality is provided through the support of a
set of algorithms, enabling organizations and enterprises to utilize and share ana-
lytic methods on linked data for the discovery and communication of meaningful
7
Information Driven Cyber Security Management through LinDA
7
new patterns that were unattainable or hidden in the previous isolated data struc-
tures. The analytics and data mining component is based on an extensible and
modular architecture that facilitates the integration of algorithms on a per request
basis. The development of the component is based on open-source software while
integration of algorithms is based on open-source analytics projects (mainly, the
R statistics project).
• An ecosystem of linked data consumption applications, which can be bound to-
geth+er in a dynamic manner, leading to new, unpredicted insights. The consump-
tion applications regard a set of applications that are developed aiming to provide
to end users (including pilot users) functionalities that are not provided through
the LinDA Workbench. The objective is to facilitate, through specific applica-
tions, the daily business processes of the SMEs based on the redesigned work-
flows that take into account the usage of the LinDA tools. As such, the consump-
tion applications can be considered as small tailor made solutions, easy-to-
implement and of low-cost, serving the specific needs of the LinDA end-users that
occurs while interacting with LinDA workbench. In this way, the LinDA work-
bench can be considered as a complete, end-to-end solution for the incorporation
of the linked data concepts within the SMEs.
Fig. 1. The LinDA Overall Concept.
2.2 The LinDA Workflow
From a user perspective, the main LinDA workflow can be summarized in three sim-
ple steps, as illustrated in Figure 2.
8
EPS Colmar 2015 2015 - The Success of European Projects using New Information and Communication Technologies
8

STEP 1
Explore datasets / Turn
data into RDF
STEP 2
Query / Link your Data
STEP 3
Visualize / Analyze your Data
RDF Data
Dump
SPARQL
Endpoint
Fig. 2. The LinDA Workflow.
More specifically the three workflow steps are:
• Step 1 – Explore Datasets/Turn Data into RDF: Using the LinDA toolset, us-
ers can publish their data as linked data in a few, simple steps. In cases where the
data are not available in RDF format, the users can simply connect to their data-
base(s), select the data table they want and make their mappings to popular and
standardized vocabularies. LinDA assists even more by providing automatic sug-
gestions to the mapping process. Based on the defined mappings, transformation
from various formats (e.g. csv, relational database) to RDF is realised.
• Step 2 - Query/Link your Data: With the LinDA toolset, users can perform
simple or complex queries through an intuitive graphical environment that elimi-
nates the need for SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language (SPARQL) syn-
tax. In addition to the submission of queries, interlinking of instances is support-
ed, where the designer lets the end user ignore its instance's data source and han-
dle instances as if they were defined in the same data source. The possible types
of interlinking vary according to the interlinking element that is used. More spe-
cifically, classes and object/datatype properties can be combined in a versatile
way, during the interlinking procedure. Hereinafter, for the sake of homogeneous
representation, all interlinking endpoints will be referred as interlinking types.
The interlinking of instances of the types [A] and [B] can occur in several ways:
(i) instances can be interlinked directly to each other, in which case an entity
(URI) is fetched in the query results if belongs to both types [A] and [B] at the
same time; (ii) an instance of type [A] can be interlinked to an instance of type
[B] via a property, where [A].p is bound to be an instance of type [B] (“owl:same-
as" interlinking) and (iii) instances can be interlinked by their properties, where
[A].p = [B].q, given that [A].p and [B].q refer to the same URI or that [A].p and
[B].q are literals (strings, numbers, dates etc.) with the same value.
9
Information Driven Cyber Security Management through LinDA
9

• Step 3 - Visualize/Analyse your Data: the LinDA toolset can help enterprise us-
ers gain insights from the data that the company generates or consumes through
the support of a set of visualization and analytics services. LinDA supports visual-
isations over different categories of data, e.g. statistical, geographical, temporal,
arbitrary data, as well as a largely automatic visualization workflow for matching
and binding data to visualizations. As far as the analytics services are concerned,
they are presented in detail in the following subsection.
According to this workflow, the user can utilize either external public data or internal,
private sources. If the initial data source is in RDF format, the user can directly insert
the data source to the available data sources of the LinDA Workbench. If the initial
data source is in another format (relational database, csv, etc.), the LinDA Workbench
guides the user to the toolset responsible for transformations in order to transform the
data into the RDF format, with the utilization of popular linked data vocabularies.
Once in RDF, the user can then visit the list of data sources and activate one of the
available LinDA services. More specifically, the user has the option to a) visualize the
selected RDF data source, b) analyse it, c) query it and d) edit/update/delete it.
3 Information Driven Cyber Security Management
3.1 Scenario Description and Implementation at LinDA Workbench
In the examined case, information based on a set of attacks in a small enterprise envi-
ronment is collected based on the installation of a honeypot. The information regards
different type of attacks such as authentication abuse, sql injections etc. The attacks
have been recorded for 11 months using raw packet interception mechanisms. Each
connection attempt that was classified as malicious was analyzed in a near-time man-
ner. The endpoint-ip of the attacker was submitted to several third-party services in
order to infer the location (using a GeoIP resolution service), the size of the originat-
ing subclass (using WHOIS services), the possible existence of DNS entries that are
associated with the IP (using reverse IP services) and the blacklisting level (using ~40
open lists). In addition each IP was port-scanned and checked for vulnerabilities. The
results of this analysis had to be represented in a common format. In order to support
common representation of the collected data and support their re-usability and inter-
connection, a specific cybersecurity oriented ontology is designed. This ontology (see
Figure 3) describes the main artefacts of a cyber-attack and specifically:
- the networking environment of the attacker including its IP address, the net-
work size, range and name;
- the hosting environment of the attacker including information regarding the
hosting operating system and its vulnerabilities, the open ports detected, the
blacklisting level of the considered host based on its IP address, the number of
virtual hosts;
- the type of the enterprise/organization where the attack is produced as well as
locality information (location of the host including geospatial coordinates);
10
EPS Colmar 2015 2015 - The Success of European Projects using New Information and Communication Technologies
10
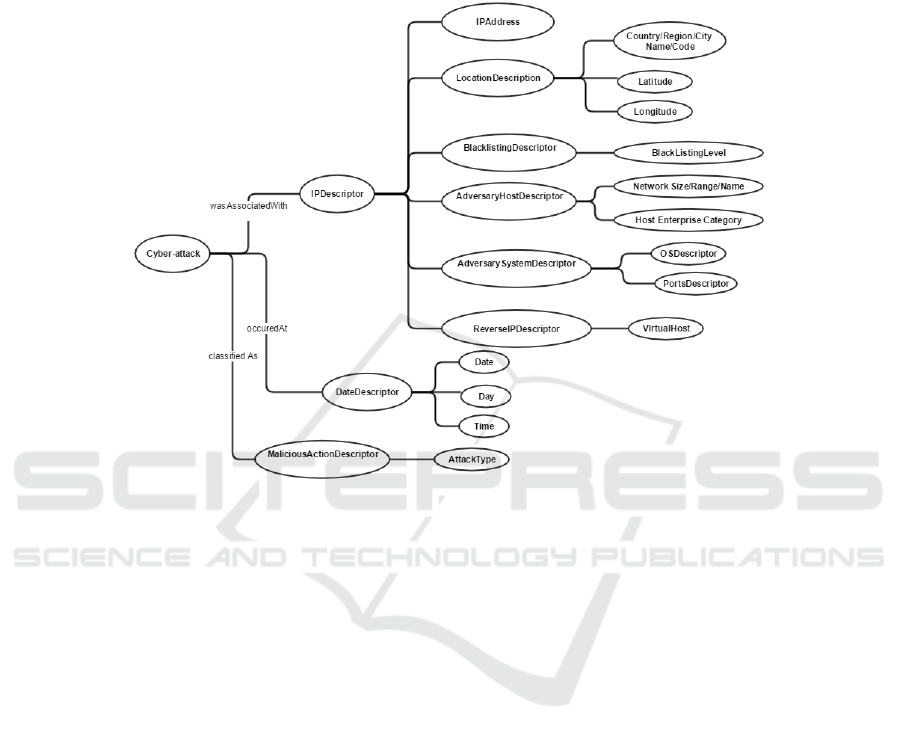
- the type of the attack based on its classification according to existing cyber-
attacks vocabularies, such as CAPEC (https://capec.mitre.org/);
- the date, day and time of the attack taking into account the time zone of the at-
tacking host.
Fig. 3. The Cybersecurity Ontology.
Upon the collection of the cyber-attacks data, their integration in the LinDA Work-
bench in raw format is taking place. Following, the LinDA Transformation Engine is
being used for mapping of the collected raw data into the defined cybersecurity ontol-
ogy and the production of the RDF data for further analysis. Following, the LinDA
Query Designer is being used for design of a set of queries over the available data as
well as the definition of possible interlinking of data. An indicative query produced
through the Query Designer is depicted in Figure 4.
Next, the produced queries may trigger the initiation of visualization or analytic
process through the LinDA visualization tool and the LinDA analytics and data min-
ing tool accordingly. The overall analysis realized is described in the following sub-
section.
3.2 Analysis Overview
The first step of our analysis regards the production of a set of descriptive statistics,
aiming at getting some insights about the available data through monitoring of the
variation of selected parameters as well as the production of a set of visualisations.
In Table 1, the number of cyber-attacks from the top 10 countries (in terms of num-
ber of cyber-attacks) is detailed, while Figure 5 provides a geomap of the distribution
11
Information Driven Cyber Security Management through LinDA
11

Fig. 4. Indicative Query by LinDA Query Designer.
of the cyber-attacks adversary hosts location. Following, Figure 6 provides a bar plot
of the number of attacks per country combined with the average blacklisting index per
country, aiming at examining the potential severity of attacks, especially from coun-
tries where this number is large (the higher blacklisting index, the more epidemic can
be considered an attack).
Table 1. Cyber-attacks per country (top 10).
Country
Number of attacks
China
9715
Hong Kong
2072
Unknown
1577
Malaysia
383
United States
380
Netherlands
138
Germany
61
Republic of Korea
43
Spain
39
India
33
In Table 2, a summary of the number of attacks based on the network range of the
network that the IP address of the adversary host is coming from is provided. Larger
networks possibly regard home devices that have acquired IP addresses through large
telecom operators’ networks, while smaller networks may refer to public or private
organizations and enterprises that have their own IP address pool.
Following, the cyber-security analyst is interested to have an overview of the trend
followed with regards to the daily number of monitored cyber-attacks, aiming at the
identification of periodical patterns that could lead to immediate protection actions in
the future. Figure 7 is produced for this purpose, depicting the evolution of cyber-
attacks monitored in the enterprise’s environment for a nine months period.
12
EPS Colmar 2015 2015 - The Success of European Projects using New Information and Communication Technologies
12
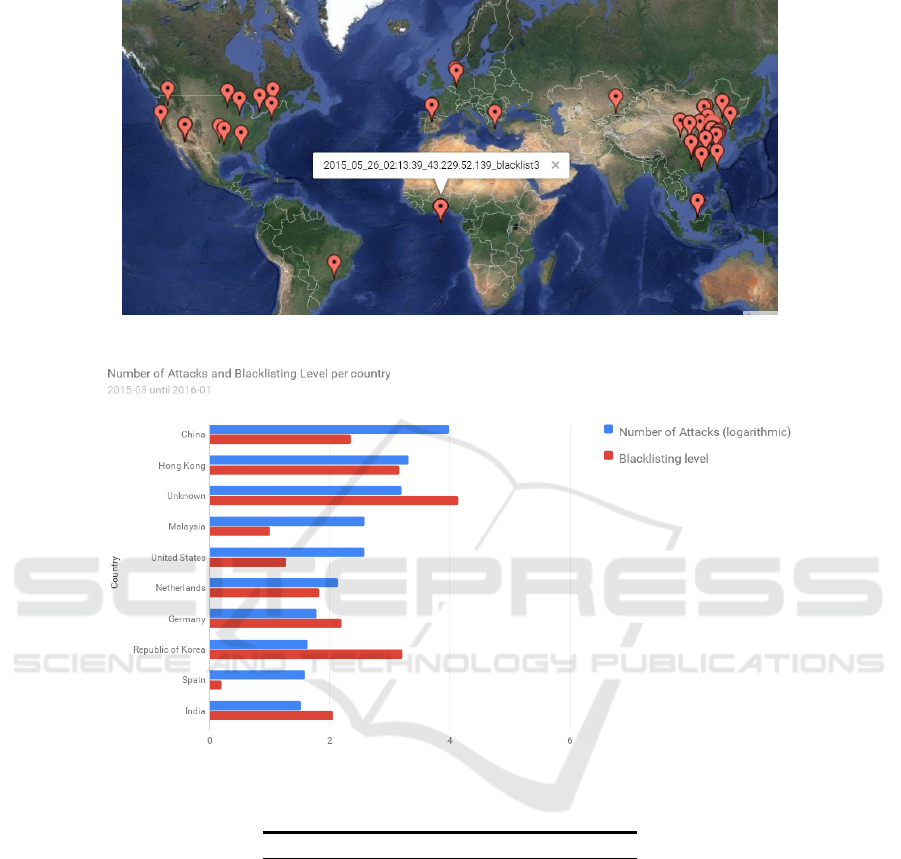
Fig. 5. Geomap of cyber-attacks adversary hosts location.
Fig. 6. Number of attacks and blacklisting index per country.
Table 2. Number of attacks per network size.
Netmask
Number of attacks
255.0.0.0
14459
255.255.0.0
308
255.255.255.0
45
255.255.255.240
34
Finally, a clustering analysis is realized over the available data, targeting at the
identification of clusters taking into account the variation of the number of virtual
hosts, number of exposed ports and blacklisting index parameters. The clustering
analysis results are provided in Table 3, while the produced clusters are also depicted
in Figure 8. Upon the interpretation of the clustering analysis, it could be argued that
cluster 1 regards possibly compromised hosts that are used for botnet-expansion or
13
Information Driven Cyber Security Management through LinDA
13
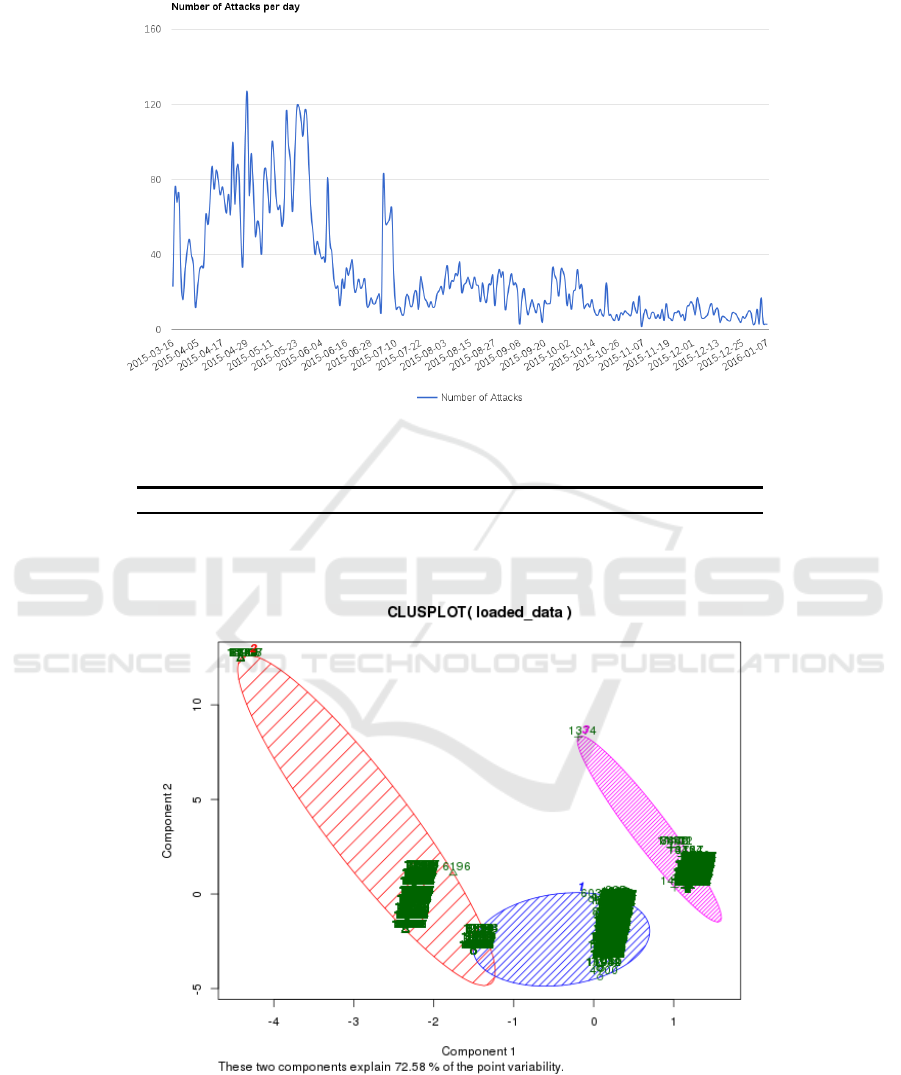
Fig. 7. Variation of number of cyber-attacks during the monitored time period.
Table 3. Clustering Analysis Results.
Cluster
#of virtual hosts
#of exposed ports
#blacklisting index
1
-0.01686813
-0.5667083
-0.6397090
2
-0.02852310
-0.5409678
0.8961126
3
0.07096821
1.7396984
-0.3635785
Fig. 8. Variation of number of cyber-attacks during the monitored time period.
14
EPS Colmar 2015 2015 - The Success of European Projects using New Information and Communication Technologies
14

dedicated attacks or DDOS attacks, while cluster 2 regards less focused attacks, pos-
sibly from mature botnets which the control and command server is not taken down.
However, these interpretations have to be further examined and validated based on
updated versions of the acquired datasets.
4 Conclusions and Future Work
By taking into account the continuous evolution of cyber threats and the need for
design of novel solutions for supporting information driven cybersecurity manage-
ment, an approach for producing and exploiting linked data from cyber-attacks to-
wards the production of added-value analytics and insights has been provided.
The proposed information driven cyber security management approach aims at en-
abling effective decision making, threat and risks management through the efficient
processing of heterogeneous information flows. The approach is targeting at the provi-
sion of a set of information management, analysis and visualisation tools to end users
responsible for the deployment, monitoring and management of cyber security solu-
tions (including improved information processing, analysis and, where necessary,
exchange functionalities), based on the workbench that is already developed within the
framework of the LinDA project.
Prior to the provision of information management functionalities, the approach fa-
cilitates the effective collection and harmonization of internal and external information
sources related to cyber security management, based on the design of a cyber-attacks
representation model. Linked and open data technologies are being used for mapping
of the collected information to the developed model and publication/consumption of
the available data that can be openly published to commonly used repositories or data
that have to be kept in private repositories within the boundaries of an enter-
prise/public organization.
Based on the deployment and operation of a small-scale scenario upon data collect-
ed on a small enterprise environment, indicative analysis is realized leading to a set of
insights and validating the efficiency and applicability of the proposed approach. It
could be argued that the proposed approach can help enterprises enhancing their expe-
rience of managing and processing cyber-attacks data, in ways not available before. It
can provide them the potential to produce advanced knowledge, leveraging the power
of linked data analytics, for effective information driven cyber security management.
However, in order to be able to easily adopt and integrate the usage of such an ecosys-
tem in their daily processes, they have also to take into account the need for an initial
learning curve as well as the involvement of data scientists in the specification of the
analysis and the interpretation of the analysis results.
With regards to plans for future work, a set of open issues are identified. These in-
clude the need for extending the designed cyber security model in order to be more
descriptive and applicable to a wider number of cyber threats, the need for interlinking
information collected within an enterprise with information openly available in the
web for realization of analysis that can lead to more advanced insights and the need
for tackling of challenges related to the management of big data and the adoption of a
distributed nature of the execution mode.
15
Information Driven Cyber Security Management through LinDA
15

Acknowledgement. This work has been co-funded by the LinDA project, a European
Commission research program under Contract Number FP7-610565.
References
1. Sqrrl report: Linked Data For Cyber Defense – Available Online: http://sqrrl.com/media/
linked-data-cyber.pdf
2. Fotopoulou, E., Hasapis, P., Zafeiropoulos, A., Papaspyros, D., Mouzakitis, S. & Zanetti,
N., Exploiting Linked Data Towards the Production of Added-Value Business Analytics
and Vice-versa, DATA 2015 Conference, Colmar, Alsace, France, 20-22 July 2015.
3. The LinDA Project, Available Online: http://linda-project.eu/
4. The LinDA Workbench, Available Online: http://linda.epu.ntua.gr/
5. The R Project, Available Online: https://www.r-project.org/
16
EPS Colmar 2015 2015 - The Success of European Projects using New Information and Communication Technologies
16
