
Decision Criteria for the Payment of Technical Debt in Software
Projects: A Systematic Mapping Study
Leilane Ferreira Ribeiro
1,2
, Mário André de F. Farias
3,4
, Manoel Mendonça
4
and Rodrigo Oliveira Spínola
1,5
1
Graduate Program in Systems and Computer, Salvador University, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
2
Federal Institute of Bahia - IFBA, Jequié, Bahia, Brazil
3
Federal Institute of Sergipe, Lagarto, Sergipe, Brazil
4
Federal University of Bahia, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
5
Fraunhofer Project Center for Software and Systems Engineering at Federal University of Bahia, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
Keywords: Technical Debt, Technical Debt Management, Decision-making Criteria, Software Maintenance,
Systematic Mapping.
Abstract: The term Technical Debt (TD) is used to describe the debt that a development team incurs when it takes
shortcuts in the software development process, but that may increase the complexity and maintenance cost in
the long-term. If a development team does not manage TD, this debt can cause significant long-term
problems such as high maintenance costs. An important goal of the management of the debt is to evaluate
the appropriate time to pay a TD item and to effectively apply decision-making criteria to balance the short-
term benefits against long-term costs. However, although there are different studies that have proposed
strategies for the management of TD, decision criteria are often discussed in the background and,
sometimes, they are not even mentioned. Thus, the purpose of this work is to identify, by performing a
systematic mapping study of the literature, decision-making criteria that have been proposed to support the
management of TD. We identified 14 decision-making criteria that can be used by development teams to
prioritize the payment of TD items and a list of types of debt related to the criteria. In addition, the results
show possible gaps where further research may be performed.
1 INTRODUCTION
The term Technical Debt (TD) is used to describe the
debt that a development team incurs when it takes
shortcuts in the software development process, but
that may increase the complexity and maintenance
cost in the long-term (Brown et al., 2010) (Kruchten
et al., 2012). In this work, we use the term “TD item”
to refer to an instance of TD.
According to Brown et al. (2010), if a
development team does not manage a TD item, this
debt can cause significant long-term problems such
as high maintenance costs. In this sense, effective
management of TD is an important step to achieve a
good quality in the software maintenance (Guo et al.,
2014).
Management strategies have been proposed in
order to minimize negative impacts of management
of debt. The main goal of these strategies is to
evaluate the appropriate time to pay a TD item, i.e.
the time for the development team change the system
and eliminate the debt. Thus, knowing decision
criteria used to choose the most suitable time for the
payment of TD items is important to balance their
short-term benefits against long-term costs.
Although there are different studies that have
proposed strategies for the management of TD
(Snipes et al., 2012) (Seaman et al., 2012) (Power,
2013) (Codabux and Williams, 2013) (Guo et al.,
2014) (Mamun et al., 2014), none of them provides a
deep discussion on decision-making criteria for the
payment of TD. On these works, decision criteria are
often discussed in the background, sometimes they
are not even mentioned. Thus, despite their
importance, there is not a comprehensive view on the
existing criteria.
In this context, this paper presents a systematic
mapping study over studies published up to 2014
that focus on management strategies of TD. This
allowed us to investigate how researches are being
conducted in this field and to address the following
research questions:
572
Ribeiro, L., Farias, M., Mendonça, M. and Spínola, R.
Decision Criteria for the Payment of Technical Debt in Software Projects: A Systematic Mapping Study.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 1, pages 572-579
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

• RQ1. What decision-making criteria have
been proposed for the payment of TD?
• RQ2. What are the types of TD related to the
decision-making criteria for the payment of
TD?
• RQ3. Which empirical evaluations have been
performed to evaluate the criteria?
We held searches in three digital libraries (ACM
Digital Library, IEEE Xplorer, and Scopus). 38
studies were considered relevant to answer the
research questions. The results provide a list of 14
criteria that can be used to support decision-making
on the payment of TD, and a list of types of TD that
have been considered in approaches that focus on the
payment of debt.
Besides this introduction, this paper has six other
sections. Section 2 discusses some related work.
Section 3 details the systematic mapping method.
Next, in section 4, the results of the mapping study
are presented. Some implications of this work for
researchers and practitioners are discussed in section
5. Next, Section 6 shows the threats to validity.
Finally, Section 7 presents the conclusions and
directions for future researches.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section, we present other secondary studies in
the TD area.
The study performed by Tom et al. (2013)
reported an exploratory case study that involves
multivocal literature review, supplemented by
interviews with software practitioners and academics
to consolidate understanding of the nature of TD and
its implications for the software development. The
results of this study included the creation of a useful
theoretical framework, consisting of a set of TD
dimensions, attributes, precedents and outcomes, as
well as the phenomenon itself and a taxonomy that
describes and encompasses different forms of TD.
Villar and Matalonga (2013) performed a
systematic mapping study in order to understand the
feasibility of using the TD metaphor as a tool for
project management. The main purpose was to
identify the current state of TD definitions. The
results show that there is no agreed definition of the
technical debt term.
In another systematic review, Ampatzoglou et al.
(2015) investigated how the financial aspects are
defined in the context of TD and how they are related
to the concepts of software engineering. The results
indicate: (i) the most common financial terms used in
TD researches: principal and interest, and (ii) the
financial approaches that have been more frequently
applied for managing TD: real options, portfolio
management, cost-benefit analysis, and value-based
analysis. Furthermore, the authors emphasize that the
application of such approaches lacks consistency,
i.e., the same strategy is differently applied in
different studies, and in some cases lacks a clear
mapping between financial and software engineering
concepts.
In another work in this area, Li et al. (2015)
conducted a systematic mapping in order to obtain a
comprehensive understanding of TD and an overview
of the current state of research on its management.
The results pointed out 10 types of TD, 8 TD
management activities, and 29 tools for TD
management.
In this same sense, Alves et al. (2016) performed
a systematic mapping study. Their results include an
initial taxonomy of types of TD, a list of indicators
that was proposed to identify TD, management
strategies, and an analysis of the current state of the
art, which allows to identify possible gaps and
research topics.
These studies are different from the mapping study
presented in this paper. They provide a broad view of
the TD management through different perspectives.
This work focuses on identifying a set of criteria to be
used in the decision-making on the payment of TD
items. Therefore, our mapping study and the works
discussed above are complementary to each other.
3 SYSTEMATIC MAPPING
METHOD
Systematic mappings are used to evaluate and
interpret relevant works relating to a research
question, an area or a phenomenon of interest
(Kitchenham and Charters, 2007). A systematic
mapping study follows a set of well-defined steps,
according to a protocol, to reduce the bias inherent
in an informal review of the literature (Petersen et
al., 2008). We chose to conduct a mapping study
because it allows accessing and analyzing the
primary studies aiming to summarize the evidences
related to our research questions and carry out future
researches. We describe the steps of the mapping
method below.
3.1 Research Questions
Our general purpose is to better understand the
decision-making criteria on the payment of TD
Decision Criteria for the Payment of Technical Debt in Software Projects: A Systematic Mapping Study
573

through a systematic mapping study. Thus, we
defined three research questions which guide this
study and reflect our goals. These questions and
their motivations are described at the following:
RQ1. What decision-making criteria have been
proposed for the payment of TD?
In order to achieve the software quality, a TD
item must be effectively managed. In this sense,
evaluating whether a TD must be paid and the
suitable time for this may reduce the negative
impacts of debt on the quality of the software
project. Knowing decision criteria used to choose
the appropriate time to pay off the debt may support
this task.
This question intends to identify and classify
these decision criteria.
RQ2. What are the types of TD related to the
decision-making criteria for the payment of TD?
A TD item can be inserted at any moment in the
software development life cycle and may be related
to several immature artifacts such as bad design,
incomplete documentation, and missing tests. These
immature artifacts may be seen as a type of debt that
may burden software maintenance in the future
(Alves et al., 2016).
Different types of debt can bring different
consequences to the software project, influencing
what we need to consider when deciding if a debt
should be paid and when.
In order to effectively manage TD, it is important
to know the relation between types of debt and
decision criteria. Thus, the purpose of this question
is to identify types of TD that have been studied in
the works that focus on debt payment criteria.
RQ3. Which empirical evaluations have been
performed to evaluate the decision criteria?
Alves et al. (2016) reported that most of the
proposals in the TD management area still require
more empirical evaluation. In this context, this
question investigates which types of validation have
been used in studies that focus on decision criteria
for the payment of TD. This information is
important to analyze the level of the maturity of the
proposed approaches.
3.2 Search Strategy
In consonance with Petersen et al. (2008), the first
step in conducting the mapping study is to look for
primary studies into the defined scope. To define the
search string, we considered the following aspects
and keywords:
• Population: Technical Debt;
• Intervention: management of TD;
• Results: methods, criteria, and process to
support decision on payment of TD.
We used these keywords and OR and AND
operators to assemble the terms. Table 1 presents the
complete search string used in this work. We applied
the search string to titles and abstracts in some digital
database. We did not use full text search because full
text search resulted in a very large number of studies
from domains other than software projects. The
search covered papers published up to 2014.
3.3 Databases and Study Selection
We chose three digital libraries to the search process:
(i) ACM Digital Library, (ii) IEEE Xplore, and (iii)
Scopus. We selected these databases because,
according to Alves et al. (2016), they have a large
concentration of studies in the TD area.
To support the study selection process, we defined
the following inclusion and exclusion criteria:
• Inclusion Criteria: the study needs to explore
a theory, a practice, or an approach related to
the management of TD.
• Exclusion Criteria: we excluded studies that
do not address management of TD. Surveys
and secondary empirical studies were
removed, since they report approaches from
others. Challenges, showcases, and abstracts
were also excluded, such as Tamburri et al.
(2013) and Shah et al. (2014).
The selection of papers was divided into three
steps. Figure 1 shows the selection process. After the
search, we had 450 studies, published between 1991
and 2014. In the first step, we removed the duplicate
studies. Next, we read the titles and abstract of
resulting selection in order to analyze if the papers
were into our scope. Finally, in the last step, we
completely read each study in order to analyze it.
The first step returned 332 studies. The second
step reduced the list to 61 papers. Our final step
resulted in 38 studies, published between 2010 and
2014, to be further analyzed and classified. A whole
list of the studies is available at
https://goo.gl/RivQ16. Table 2 shows the number of
papers by publishing type.
Table 1: Search String.
Population (("Technical Debt")
AND
Intervention (Management OR Monitoring OR
Control)
AND
Results (Criteria OR Method OR Process))
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
574
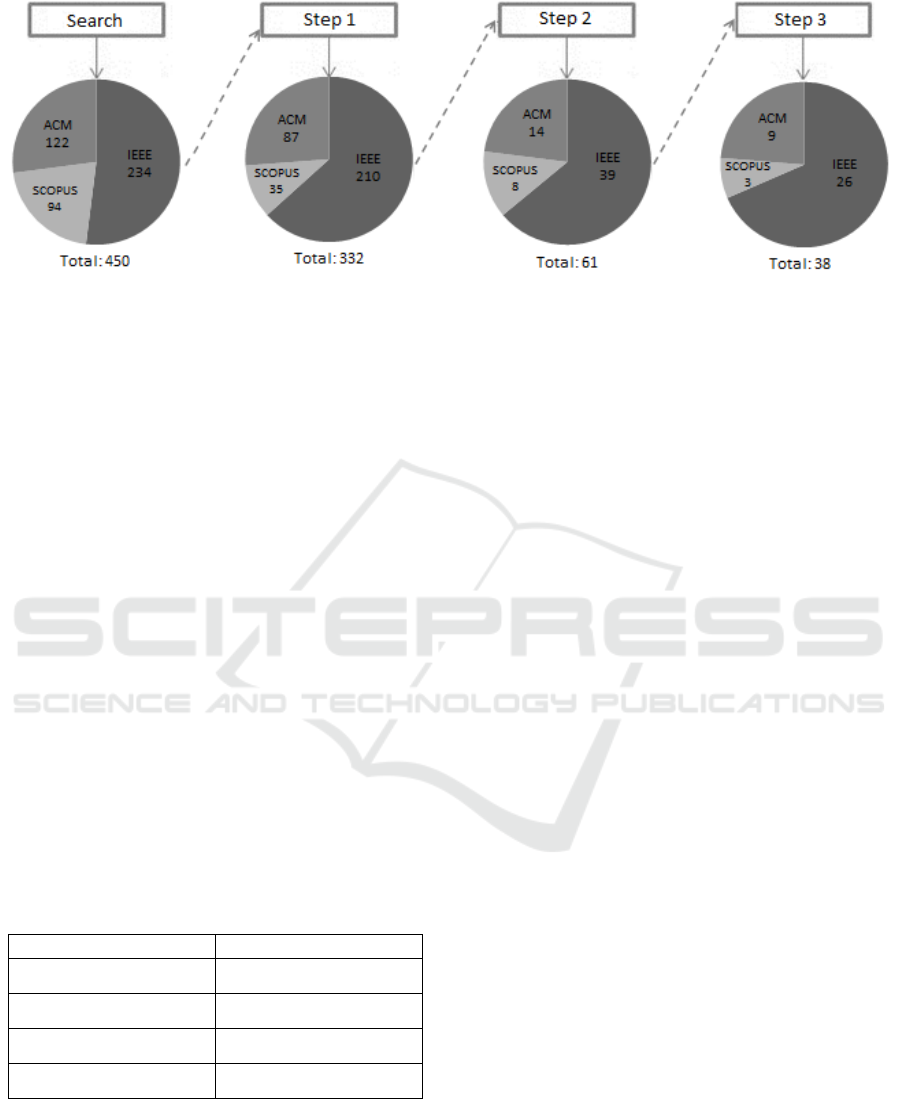
Figure 1: Study selection process.
3.4 Classification Scheme
We defined three categories to classify the papers
and answer the research questions:
• Decision-making Criteria on Payment of TD
(RQ1): in order to classify the criteria, a
researcher collected the decision-making criteria
and their definitions following the terminology
straight from the studies. We assumed as a
criterion the strategy that supports decisions
about when and if a TD item should be paid;
• Types of TD Related to the Decision-making
Criteria (RQ2): this category lists the types of
TD that were related to any criterion in the
studies. We used the types of debt proposed by
Alves et al. (2014);
• Empirical Evaluation (RQ3): we verified
whether the proposed criterion has been
evaluated through empirical methods and, if so,
which method was used. We considered that a
study has an empirical evaluation if it brings at
least one section with some discussion dedicated
to this topic.
Table 2: Number of papers by publishing type.
Type Number of papers
Conference 18
Journal 9
Symposium 1
Workshop 1
4 RESULTS
This section presents the main results of the data
extraction activity. The extracted data were recorded
on a spreadsheet that is available at
https://goo.gl/Akdu8r. We analyzed the extracted
data in an effort to answer our research question
.
4.1 Decision-making Criteria (RQ1)
In this section, the decision-making criteria found in
the literature and their definitions will be presented.
We classified them into four categories:
• Nature of the TD: criteria that are related to the
TD’s properties, such as their severity and time
when the debt was incurred;
• Customer: criteria into this category concern
about the impact that debts have on the
customers;
• Effort: criteria that are related to the cost of TD,
such as the impact of the TD on the project and
what effort will be applied to pay the TD item.
• Project: criteria that are related to the projects’
properties, such as their lifetime and their
possibility of evolution.
These categories may help the development team
on better understand the decision criteria and decide
the suitable time to pay off a TD item. For instance,
in a specific situation, it may be more important for
the team to prioritize the customer category. Thus,
criteria related to the category customer may be
applied in order to perform the management of TD
items. On the other hand, whether the cost to pay a
TD item is more important than its impact on
costumer, criteria related to category effort will be
more relevant to decide which and when a TD will
be paid.
We identified 14 decision-making criteria to
support the choice of the suitable time for the
payment of debt. Table 3 presents criteria found in
this mapping study (sorted by category), as well as
their definitions, and the papers that discussed each
one.
Decision Criteria for the Payment of Technical Debt in Software Projects: A Systematic Mapping Study
575
Figure 2 shows criteria distribution over the
investigated years. From this figure, we highlight
two outcomes:
(i) Debt impact on the project and Cost-Benefit
are the most explored criteria by the analyzed studies
(both studies had 8 citations). Moreover, they appear
nearly every years covered by this mapping. This
may indicate that the biggest concern at the moment
of decision-making on payment of a TD item is the
impact and extra cost that a debt may cause on the
project;
(ii) most criteria have clearly been not much
explored. Five criteria were approached by two
studies and other four only by one study. In this
same sense, decision-making criteria were covered
in less than 50% (17 from 38 papers) of the studies
that focused on management of TD. This set of
results indicates that these criteria need further
investigation in order to improve their maturity.
4.2 Types of TD Related to
Decision-making Criteria (RQ2)
In order to answer this question, we identified types
of TD that were discussed with regards to the
decision-making criteria. Table 4 presents the
relation between types of TD and criteria. We can
see that although many types of TD had already been
discussed in several researches, only Defect Debt and
Design Debt were related to criteria. As different
types of debt can bring different consequences to the
software project, influencing what we need to
consider when deciding if a debt should be paid and
when, the lack of relation between other types of
debt and decision criteria provides us the following
open question: “Are criteria independent of types of
TD or there is some kind of influence between
them?”. We do not have evidences to answer this
question. This gap needs to be explored by
academics in further researches.
Table 3: Decision-making criteria.
Category Criteria Definition Studies
Nature of the TD
Severity of the Debt Debt items with high level of severity should be paid. S1, S9
Existence of
workaround
The payment of debt items that have a workaround may be
delayed.
S1, S14, S9
Existence time of debt
items in the project.
Debt items that are a long time in the project should be paid. S9
Localization of TD If the debt is located in a resource that will change due to a
development or maintenance activity, the software engineer
should take advantage of the change to pay the debt.
S38
Customer
Visibility The visible debt must be paid. S5
Analysis when the
refactored part will be
used
Pay debt items that are in widely used parts of the system. S4, S33
Debt impact on
customer
Debt items that impact directly on the customer should be
prioritized.
S1, S9
Effort
Debt impact on the
project
Debt items that offer the greatest impact on the project should
be paid.
S2, S3, S5,
S8, S9, S1,
S24, S38
Scope of tests Debt items with smaller scope of tests to validate their
adjustment should be prioritized.
S1, S9
Cost-Benefit Debt items with good cost-benefit should be paid. If the cost
of the debt is less than the cost of paying it off, the payment
can delayed.
S1, S14, S4,
S10, S23, S9,
S24,S28
Effort to implement the
proposed correction
Debt items that require less effort to be paid must be removed
first.
S1, S3, S9
Project
Nature of the project Debt items of critical projects must be paid quickly. S11, S24
Lifetime of the system Debt items in projects that will be discontinued soon should
not be paid.
S12, S14, S24
Need of evolution of
the system or features
Debt items of systems or modules that will stop evolving or is
stable and will not be affected by future changes should not be
paid.
S21
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
576
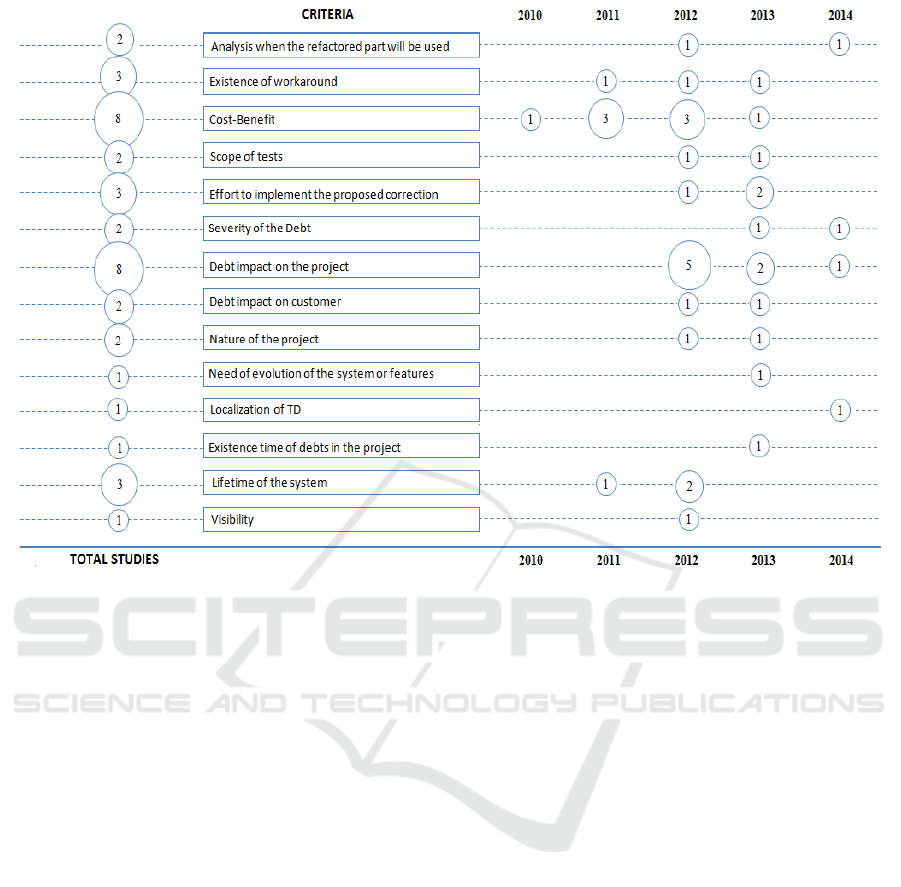
Figure 2: Criteria distribution over the investigated years.
4.3 Empirical Evaluations (RQ3)
We analyzed whether the papers investigated in this
mapping study have conducted some type of
empirical evaluation to validate the proposed
criteria. Despite we identified different criteria in 17
papers, none of them has been evaluated through an
empirical study.
According to Novais et al. (2013), empirical
evaluation of technologies has increased
significantly in the software engineering domain
over the last years. However, we cannot observe this
regarding studies that focus on decision-making
criteria for the payment of TD. This implies that
proposed criteria still require empirical
investigation, so that their benefits and limitations
can be known with increased confidence.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Implications for Practitioners and
Researchers
The results of this mapping study point to the
following implications for practitioners:
• We identified 14 decision criteria that can be
used to decide and/or prioritize the payment
of TD items incurred in software projects.
After identifying TD items, developers can
apply the criteria to each of them and decide
on the payment of that item;
• We defined 4 categories to facilitate the
understanding and using of the criteria: nature
of TD, customer, effort, and project. Software
engineers can use these categories in the
initial phases of a strategy for managing the
TD in their projects.
For researchers, the findings of this mapping
study point to the following implications:
• Different criteria were mapped, however, we
did not identified any empirical study to
assess them. This indicates that the criteria
still require evaluation, so that their benefits
and limitations could be known;
• Although there are many types of TD, only
two of them have been discussed with respect
to decision-making criteria. Thus, the results
were not conclusive as regards to the relation
between decision criterion and types of TD.
This gap needs to be further investigated.
Decision Criteria for the Payment of Technical Debt in Software Projects: A Systematic Mapping Study
577
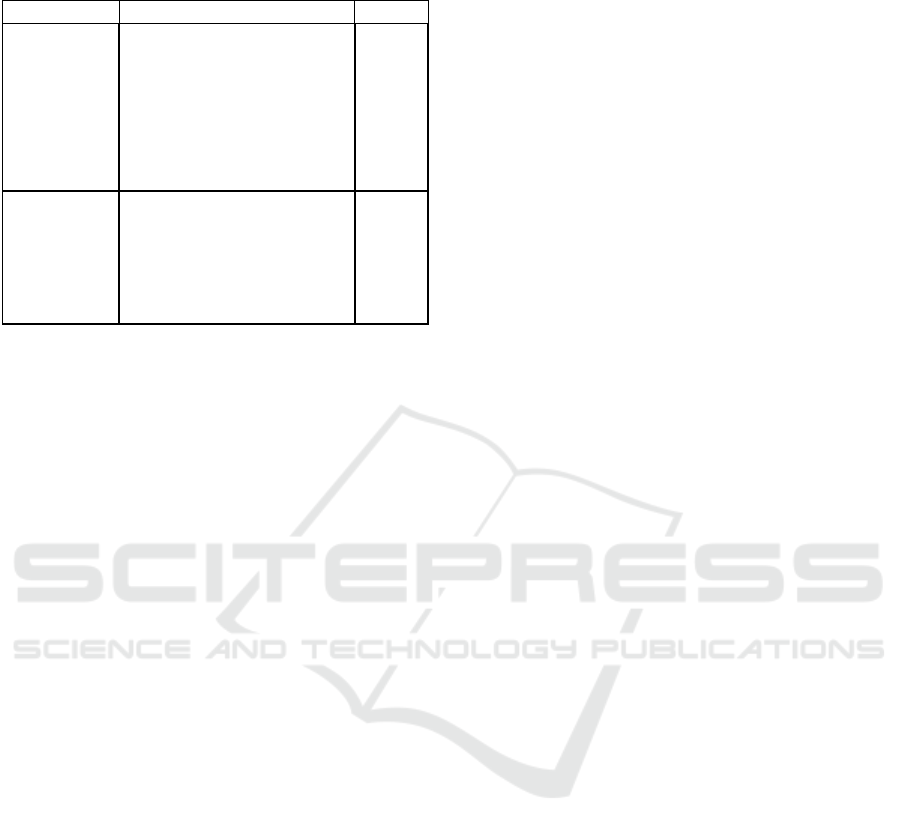
Table 4: Relation between types of technical debt and
decision criteria.
Types of TD Criteria Studies
Defect Debt
- Severity of the Debt
- Existence of workaround
- Debt impact on customer
- Debt impact on the project
- Scope of tests
- Cost-Benefit
-Effort to implement the
proposed correction
S1,
S16, S6
Design Debt
- Debt impact on the project
- Analysis when the refactored
part will be used
- Cost-Benefit
S2, S4,
S25
6 THREATS TO VALIDITY
Our study has some threats to validity. We present
them below with the strategies for its mitigation.
Selection Bias: we selected each study based on
the judgment of the inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Thus, we cannot guarantee that all relevant primary
studies were selected. With the intention of mitigate
this threat, we discussed the study protocol among
the researchers to guarantee a common
understanding and searched the studies into the main
digital libraries in our field.
Data Extraction: bias or problems on data
extraction from selected studies can affect their
classification. In order to reduce this bias, we
discussed deeply the definitions of data items and
the classification scheme.
External Validity:
we carried out a systematic
mapping study over studies published up 2014 that
focused on TD management. This implies that we
might have missed some relevant studies. Thus, we
cannot generalize our conclusions for whole TD
management approaches. However, our outcomes
allow us to draw insights to guide further
investigations.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The goal of this work was to conduct a systematic
mapping study of the literature in order to identify
criteria to support the decision on the payment of
existent TD items in software systems. We focused
on studies published up 2014 and selected 38 primary
works that discuss TD management strategies.
The main contribution of this work was the
identification of 14 decision criteria that can be used
by development team to decide and/or prioritize the
payment of TD items. In addition, we identified that
only two types of TD were related to decision-
making criteria. In this sense, we cannot recognize
whether: (i) decision criteria are independent of
types of TD, or (ii) there is some kind of influence
between decision criteria and types of TD.
Considering evaluation methods, we identified
that none of analyzed studies has performed any kind
of empirical evaluation. This may indicate a low
level of maturity of the decision-making criteria for
payment of TD.
In general, the results provide some evidence and
motivation for continuing to study decision criteria
for TD payment. As future work, we will investigate
the gaps identified in this mapping study. In
particular, continuing to explore decision criteria in
order to answer the following question: Are criteria
independent of types of TD or there is some kind of
influence between them?. We also intend to work on
the development of a TD management strategy based
on the identified criteria and their combinations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by CNPq
Universal 2014 grant 458261/2014-9.
REFERENCES
Alves, N.S.R., Ribeiro, L.F., Caires, V., Mendes, T.S. &
Spínola, R.O., 2014. Towards an Ontology of Terms
on Technical Debt, In the Sixth International
Workshop on Managing Technical Debt, Victoria,
British Columbia.
Alves, N. S., Mendes, T. S., de Mendonça, M. G., Spínola,
R. O., Shull, F., & Seaman, C, 2016. Identification and
management of technical debt: A systematic mapping
study. Information and Software Technology, 70, 100-
121.
Ampatzoglou, A., Ampatzoglou, A., Chatzigeorgiou, A.,
Avgeriou, P. 2015. The financial aspect of managing
technical debt: A systematic literature review,
Information and Software Technology, Volume 64,
Pages 52-73, ISSN 0950-5849.
Brown, N., Cai, Y., Guo, Y., Kazman, R., Kim, M.,
Kruchten, P., Lim, E., MacCormack, A., Nord, R.,
Ozkaya, I., Sangwan, R., Seaman, C., Sullivan, K. &
Zazworka, N., 2010. Managing Technical Debt in
software-reliant Systems, a, Proceedings of the 18th
FSE/SDP Workshop on Future of Software
Engineering Research, 47-5.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
578

Codabux, Z. & Williams, B., 2013. Managing technical
debt: An industrial case study. In: 4th International
Workshop on Managing Technical Debt (MTD).
Guo, Y., Spínola, R. O. and Seaman, C., 2014 . Exploring
the costs of technical debt management – a case study
on Empirical Software Engineering, v. 1, p. 1-24.
Kitchenham, B. A. & Charters, S. 2007. Guidelines for
performing systematic literature reviews in software
engineering. Tech. Rep. EBSE-2007-01,
KeeleUniversity.
Kruchten, P., Nord, R. L., Ozkaya, I., 2012. Technical
Debt: From Metaphor to Theory and Practice. IEEE
Software, 29(06), 18-21.
Li, Z., Avgeriou, P. & Liang, P., 2015. A systematic
mapping study on technical debt and its management.
In Journal of Systems and Software, Volume 101,
Pages 193–220.
Mamun, M. A., Berger, C. & Hansson, J., 2014.
Explicating, Understanding and Managing Technical
Debt from Self-Driving Miniature Car Projects, In:
30th IEEE International Conference on Software
Maintenance and Evolution (ICSME).
Novais, R.L. et al. 2013. Software evolution visualization:
A systematic mapping study. Information and
Software Technology. 55, 11 (Nov. 2013), 1860–1883.
Petersen, K., Feldt, R., Mujtaba, S. & Mattson, M., 2008.
Systematic mapping studies in software engineering,
In the Proceedings of the 12th International
Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software
Engineering, University of Bari, Italy.
Power, K., 2013. Understanding the impact of technical
debt on the capacity and velocity of teams and
organizations: Viewing team and organization
capacity as a portfolio of real options. In: Managing
Technical Debt (MTD).
Seaman, C., Guo, Y., Zazworka, N., Shull, F., Izurieta, C.,
Cai, Y. & Vetro, A., 2012. Using technical debt data
in decision making: Potential decision approaches,
Third International Workshop on Managing Technical
Debt (MTD).
Shah, S. M. A., Torchiano, M., Vetrò, A. & Morisio, M.,
2014. Exploratory testing as a source of technical
debt, IT Professional, vol. 16, no. 3, Article ID
6475929, pp. 44-51.
Snipes, W., Robinson, B., Guo, Y. & Seaman, C., 2012.
Defining the Decision Factors for Managing Defects:
A Technical Debt Perspective. In: 3th International
Workshop on Managing Technical Debt (MTD).
Tamburri, D.A., Kruchten, P., Lago, P. & Van Vliet, H.,
2013. What is social debt in software engineering?, In:
6th International Workshop on Cooperative and
Human Aspects of Software Engineering (CHASE),
pp. 93-96.
Tom, E., Aurum, A. & Vidgen, R. B., 2013. An
exploration of technical debt, Journal of Systems and
Software 86(6), 1498-1516.
Villar, A. & Matalonga, S., 2013. Definiciones y tendencia
de deuda técnica: Un mapeo sistemático de la
literatura. Anais do CIBSE13 - Congresso Ibero-
Americano em Engenharia de Software, Montevideo,
Uruguai, Abril 8, 9 e 10, pp 33-46.
Decision Criteria for the Payment of Technical Debt in Software Projects: A Systematic Mapping Study
579
