
A Pervasive Business Intelligence Solution to Manage Portuguese
Misericordia
Danilo Coelho, Filipe Portela, Manuel Filipe Santos, José Machado and António Abelha
Algoritmi Research Centre, University of Minho, Guimarães, Braga, Portugal
Keywords: Business Intelligence, Misericórdia, Data Mart, Pervasive HealthCare, Dashboards.
Abstract: Currently, the healthcare system is one of the main pillars of any society. Given the economic crisis in
Portugal and poor healthcare system in need of profound improvements, the need to increase the efficiency
of resource management and services is imperative. With the increasing use of Business Intelligence (BI) in
organisations and the proven effectiveness of this, comes the desire to use BI in healthcare, specifically in
the healthcare of Misericórdia. One of the purposes of this article is to present the results obtained through
the development of the dissertation whose theme is "Prototyping of Business Intelligence component to
support the management in the health area of a Misericórdia". So, in this work, some concepts associated
with the use of BI in Misericórdias were addressed, and the Pervasive BI architecture of the developed
solution was designed. It is also important to emphasise that the solution presented is pervasive, available
anywhere at any time. Furthermore, a set of metrics were developed and the data presented in the form of
dashboards, for later use by the users. Through this work, it was possible to gather all the data into a single
structure (Data Mart), to identify a set of aspects that can be improved and to have a generalised view of the
state of operation of the organisation, as far as health care is concerned.
1 INTRODUCTION
Currently, the national health system is one of the
main pillars of any society. It is almost mandatory to
increase the efficiency of the management of
resources and services in the provision of health
care. In this way, the present article aims to present
the results obtained through the dissertation
"Prototyping of Business Intelligence component to
support the management in the health area of a
Misericórdia" whose objective is to develop a
pervasive functional prototype of Business
Intelligence(BI) in the health area of a Misericórdia.
The use of BI in health organisations, particularly
not-for-profit organisations, increases efficiency and
effectiveness in care delivery. Nonprofits have
always been present in society, playing a critical role
in it. These organisations, defined in 1982 as
"Private Institutions of Social Solidarity" (PISS), are
organisations that have established non-profit goals
by private initiative, to give organised expression to
the moral responsibility of solidarity and justice. In
other words, the PISS is a response of civil society
to a set of social problems, developing an economic
activity based on the principles of solidarity,
cooperation and equity (
Decreto-Lei n
o
.172-A/2014).
In a health organisation, the volume of data is
high and complex. Most of the time the data is
stored in several sources which make it difficult to
analyse it for later decision making. This situation
instead of facilitating the decision-making process
makes it an extremely complex process with a high
degree of uncertainty (Vuori, 1984). Consequently,
recognising the importance of decision making in
healthcare and the existence of BI solutions that
facilitate the work of health professionals is an
improvement for the organisation. One of the
purposes of this paper is to present the results
obtained and consequent advantages and
disadvantages of applying a BI platform in the
health area of an organisation, to understand the
extent to which a sustained decision-making process
is important in an organisation.
This work is divided into several sections. A
brief introduction is initially exposed. Next, in
section 2 a background is presented to present the
background in which the article is found. Then in
Section 3 is stated the methodologies used to
developed the Pervasive BI platform. In Section 4 is
Coelho, D., Portela, F., Santos, M., Machado, J. and Abelha, A.
A Pervasive Business Intelligence Solution to Manage Portuguese Misericordia.
DOI: 10.5220/0006382301170123
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2017), pages 117-123
ISBN: 978-989-758-251-6
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
117

presented the BI architecture and in Section 5 the
main results of the dissertation development. Section
6 address a short discussion of the results and final,
in Section 7 the future work.
2 BACKGROUND
Today, health is one of the pillars of any society.
Since health is an area that affects every citizen, the
quality of health care delivery is important. In this
way, the need for a more sustainable decision-
making process arises, as well as the need to identify
possible aspects to be improved. Therefore, the
optimisation of healthcare delivery involves the
computerization of clinical procedures, with a
transition from paper-based processes to electronic
processes, using Information Systems (IS) or
reorganising the IS. The health professionals are
based on the analysis and monitoring of the clinical
information of each user to obtain and sustain a
correct clinical diagnosis. Nowadays, with the
technological and economic advances, all this
clinical information is available and distributed by
different SIs. According to Marins (Marins, 2013),
hospital information systems (SIH) are "systems
responsible for acquiring, processing and presenting
all information about all the participants (patients,
doctors, nurses, among others) and all services,
among others)".
In the current context, due to the pressure exerted
on organisations, given the current economic crisis,
their management focuses on the decision-making
process through the Business Intelligence (BI)
component. They need to make quick and effective
decisions in any of the areas of the organisation, be
they tactical, strategic or operational, and this is one
of the critical success factors. However, a correct
decision-making from the organisational point of
view is based on a large amount of data that allows
us to perceive the best option.
This article addresses health issues using BI in
the health area of a Misericórdia. This presents the
results obtained through the development of a BI
functional prototype. On Misericórdias, these are
characterised as non-profit institutions, whose
purpose is to express the moral duty of solidarity and
justice (Andrade, 2014). Also, they play a
considerable role in Portuguese society,
characterised by the wide range of areas in which
they work, with special emphasis on health.
Therefore, since the Misericórdias are not-for-profit
institutions and given the need for more and more
organisations to require sustained and effective
decision-making, it is concluded that the need for a
well-defined basis for decision-making is
imperative.
On the article, this one presents the results
obtained through the development of a functional BI
prototype developed through the dissertation which
theme is "Prototyping of a Business Intelligence
component to support the management in the health
area of a Misericórdia ". This work also can help to
answer the research question "How can the use of
Business Intelligence contribute to decision making
in a Misericórdia?".
Thus, the solution developed throughout the
dissertation and presented in the article meets the
needs of organisations because it allows for
sustained decision making and as it is hosted in the
cloud then allows remote access on any device.
During this process, open-source tools also were
explored (Brandão, et al., 2016).
2.1 Portuguese Misericórdias
The Misericórdias have always played a very
important role in Portuguese society.
According to the Decree-Law 172-A / 2014 of 14
November the Ministry of Solidarity, Employment
and Social Security, Misericórdias are "associations
recognised in canon law, to meet social needs and
acts of Catholic worship, by its traditional spirit,
informed by the principles of doctrine and Christian
morality". In spite of they have performed different
roles in society, they have always been associated
with the provision of health care (
Decreto-Lei n
o
.172-
A/2014
). According to the Decree-Law 172-A/2014,
Misericórdias may provide goods and develop social
intervention activities, which includes the area of
health. Misericórdias can promote health, disease
prevention and care in curative perspective,
rehabilitation and reintegration. Also, Penteado
(Penteado, 2004) defines Misericórdias as
associations of believers who, according to the
country's legislation, have the status of IPSS, which
was granted to them in 1979. The same author,
Penteado (Penteado, 2004), states that Misericórdias
are non-profit institutions, whose purpose is to
express the moral duty of solidarity and justice
between individuals and the provision of services in
the field of social security.
In Decree-Law no. 138/13 of October 9 of the
Ministry of Health, these institutions play an
important role in the health system, being
increasingly recognised in Portuguese society. The
same decree (Decree-Law no. 138/13 of October 9
of the Ministry of Health, 2013) states that the
ICT4AWE 2017 - 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
118

Misericórdias have been associated with the
provision of health care, although they have
different roles in society (
Decreto-Lei n.
o
138/2013).
2.2 Pervasive Business Intelligence
In health, the access and presentation of medical
information are identified as a major concern for
health professionals. This concern is because
caregivers need to make sustained decisions because
the patient's health is at stake. Currently, one of the
main problems in health facilities is that all medical
information is dispersed by several data sources, the
result of the use of various tools. In this way,
accessing, crossing and querying the data when
necessary becomes a complicated task to perform
promptly, which may lead to less correct decisions
on the part of the professionals. To solve this
problem, the need to use a pervasive system arises.
The main objective of a pervasive system in
health is to achieve a quality care service, to anyone
and at any time, regardless of their location or
position (Pereira et al., 2016).
A pervasive health system is characterised by a
set of heterogeneous information, a set of
stakeholders, and ubiquitous computing that
connects digital infrastructures to our daily lives. It
gathers, processes and distributes "any kind" of
personal information and contextual data anywhere
(Pereira et al., 2016).
Pervasive Healthcare is considered a key factor
in the reduction of expenses and is known for
allowing improvements in disease management and
advances in communication technologies and
wireless networks providing the acquisition,
transmission and treatment of critical medical
information in real time (Pereira et al., 2016).
For Larburu et. Al (Larburu et al., 2015), the
Pervasive Healthcare systems apply information and
communication technologies to allow the use of
omnipresent clinical data by authorised medical
personnel.
Pervasive Business Intelligence (BI) systems are
a future area whose goal is to support decision-
making by health professionals.
2.3 Related Work
As a related work, we continue the work presented
in the dissertation "Use of process-oriented
methodologies in the implementation of Business
Intelligence systems - application in the health area"
(Miranda, 2015). This work arose from the need of
exploring the process-oriented potentialities, such as
Business Process Management (BPM), Mlearn, and
Balanced Scorecard, to clearly and objectively
identify the information needed to support decision
making. The objective, according to the author João
Miranda (Miranda, 2013), was to "develop a
Business Intelligence System (BI) that guarantees its
alignment with the organisation's mission and
strategy, using process-oriented methodologies and
supporting the function of analysing and
Organisational performance, enhancing the
continuous improvement of its processes ".
After the work mentioned above was completed,
the dissertation discussed in the introductory chapter
was developed and serves as the basis for this
article. This work is divided into several phases,
according to the methodologies used. In an initial
phase (information research) a survey of concepts
associated with the theme and of the tools used by
the Misericórdias in their daily life was carried out
with the objective of perceiving the characteristics of
these, at a later stage, to develop a differentiating
solution capable of interacting with Existing
information systems. Throughout the development
of the dissertation and with the intention to present
the work developed an article whose was written
about "Towards a Business Intelligence Platform to
Portuguese Misericórdias" (Coelho et al., 2016). Its
purpose is to show the surgical process dimensional
model, the BI architecture and the Strengths,
Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats (SWOT)
analysis of the solution proposed to health area of
Portuguese Misericórdias.
In addition, the same article presents the key
concepts, tools used by Misericórdias and process
architecture.
3 METHODOLOGIES
The present chapter describes the characteristics of
each of the methodologies used throughout the
development of the dissertation and consequently
the development of the functional prototype as well
as its different phases, interconnecting each one of
the phases to what was being done in the course of
the work. The methodology used for research is the
Design Science Research (DSR), and for the
practical component, the Kimball methodology was
used. The DSR methodology consists of a set of
principles, practices and procedures for conducting
research, through the design of artefacts and the
analysis of their use/performance, in order to solve
problems (Peffers et al., 2007).
A Pervasive Business Intelligence Solution to Manage Portuguese Misericordia
119
The main tasks of DSR are the identification of
the problem and motivation; Definition of the
objectives of the solution; Design and development;
Demonstration and finally evaluation and
communication (Peffers et al., 2007).
Briefly, the use of this methodology allowed the
entire development of the project to be oriented
correctly and rigorously. Through the Several phases
of the DSR, we are able to identify and describe the
problem, showing the importance of this in order to
clarify any doubts about the importance of the
project development. This methodology served to
assist in all project planning and development. As in
any type of project, there is a need for the
stakeholders to have a theoretical basis to fill
potential knowledge gaps in the area of the project
and, therefore, it is necessary to use a methodology
that guides the entire research process and Concept
documentation.
Regarding Kimball's methodology, also known
as the business dimensional life cycle, it was
conceived in the mid-1980s by members of the
Kimball group. This methodology has been used in
projects related to Data Warehouse and Business
Intelligence (DW / BI) in the various organisational
areas (Kimball, 1998).
The main phases of this methodology are project
planning; Analysis of business requirements;
Dimensional modelling and design of the technical
architecture; Selection of tools; Design and
development of the Staging Area and finally
installation and start-up and maintenance and
evolution. It should be noted that throughout the
development of all these phases of the project, a
project management is carried out simultaneously,
aiming at monitoring the entire development of the
solution, deadlines, duration and so on (Kimball,
1998). Through the use of these methodologies, it
was possible to develop the solution always in a
phased and rigorous way, without forgetting any
phase.
4 PERVASIVE BUSINESS
INTELLIGENCE
ARCHITECTURE
The development of the Pervasive Business
Intelligence (BI) prototyping component was based
on an architecture composed of 3 levels, data
sources, Data Mart and finally Dashboards and
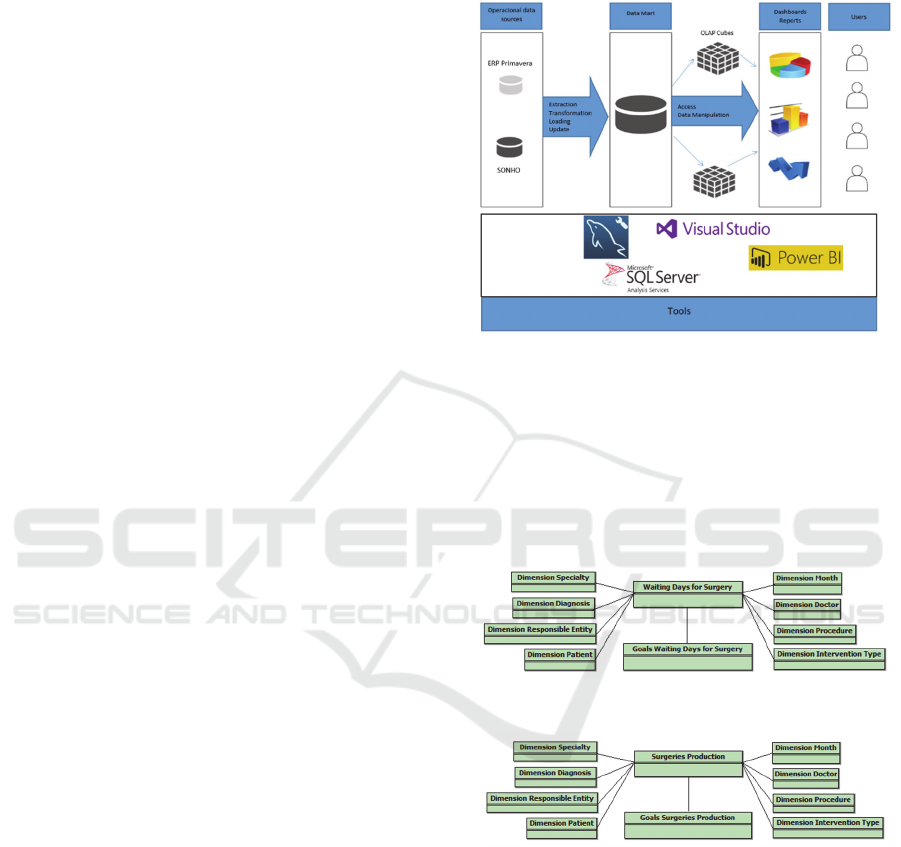
Reports. As can be seen in Figure 1, two operational
data sources and a set of tools were used to support
the development of the whole process. The
Misericordia defined this architecture and all the
features associated with it.
Figure 1: Pervasive BI Architecture.
In an initial phase data were extracted,
transformed, loaded, and updated to Data Mart.
Next, OLAP cubes were developed through access
and manipulation of data and metrics created to meet
the needs of users. Finally, panels with dashboards
and reports were developed to present the data to the
final user(s).
Figure 2: Star schema for waiting days for surgery.
Figure 3: Star schema for surgeries production.
The entire process was developed using the tools
shown in the architecture: MySQL
Workbench where Data Mart, Microsoft Visual
Studio and Microsoft SQL Server Analysis Services
are located where the metrics and OLAP cubes were
developed and finally the Microsoft Power BI
Desktop where the panels were developed and
therefore presented the data. The fact that the data
can be accessed in both the desktop and cloud tools
indicates that it is a pervasive platform because the
ICT4AWE 2017 - 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
120

data can be queried and the panels changed if
necessary anytime, anywhere.
The development of Data Mart was based on a
constellation scheme designed per data type of the
operational sources. This consists of two tables of
facts, waiting days for surgery and surgeries
production and eight dimensions in common (date,
speciality, doctor, intervention, diagnosis,
intervention type, users and responsible financial
entities). Given the complexity of the scheme and to
a better perception in the article, the scheme was
divided into 2 diagrams: Waiting days till surgery
(Figure 2) and Production of surgeries (Figure 3).
The Data Mart is already deployed, and it is
prepared to be used.
5 RESULTS
The multidimensional analysis using facts and
dimensions of Data Mart allows a set of
functionalities available to the user, among which:
Ad-hoc creation and access to queries;
Registration of queries for future use, which may
be provided to one or more users;
Performing Roll-up actions to aggregate the data
from a more detailed perspective on a more
generalised one;
Selection detail level in the query, that is, allow the
data to be explored for a more detailed perspective,
performing drill-down;
Definition the criteria of the data query;
Show results of data analysis through graphs,
tables and maps.
Table 1: Metrics, types in each table.
Name Type Used table
Total surgeries Record count
Fact table: Waiting
days for surgery
Maximum number of
waiting days for
surgery
Maximum
Minimum number of
waiting days for
surgeries
Minimum
Total surgeries
production
Record count Fact table:
surgeries
production
Quantity of patients Record count Dimension:
Patients
Quantity of
interventions
Record count Dimension:
Interventions
Quantity of doctors Record count Dimension:
Doctors
Over OLAP cube development were defined a
set of metrics to allow greater analysis capacity in
data presentation.
Table 1 presents the developed
metrics, where it is possible to verify which type of
metric and what dimension or table of facts each
metric is based on it.
The presentation of the data was done using
panels in the PowerBI Desktop tool. Each panel
consists of a set of dashboards.
Figure 4 is one of the several examples of the use of
the cube. As you can see in figure 4, it is possible to
analyse the data with different levels of detail. In
this case, it is possible to analyse the production of
surgeries by month (mês), a quarter (trimester),
semester (semester) and year (ano), which allows
obtaining knowledge regarding which periods of
time the production of surgeries is more and less. In
addition, it is possible to select only one or more
specialities (especialidades) as well as the type of
surgery (tipo de cirúrgias) that is intended,
Ambulatory (ambulatório) and Normal (normal).
This type of information helps the manager to make
decisions regarding, for example, what times of the
year a larger / smaller amount of hospital material
and a larger / smaller amount of health professionals
are required. In this way, it is possible to tailor
resources to hospital needs based on sustained
decision making.
6 DISCUSSIONS AND
CONCLUSIONS
Throughout the article, the central theme is health.
This theme is very important since it directly
influences the quality of life of each citizen. This
leads to the need to contribute to significant
improvements in this area, for example, in the
decision-making by professionals. It is known that
one of the main problems that a manager of a health
organisation is facing is the difficulty in perceiving
which aspects can be improved. What has been
verified is that the high variety of tools used leads to
the stored data are dispersed, which makes it
difficult to access the data. With this, the use of the
data stored by the different tools becomes quite
complicated. In this way, one of the possible
contributions to health would be to help those in
charge of managing the organisation in their
decision-making, through Business Intelligence (BI)
applications.
Based on the BI functional prototype developed
throughout the dissertation, the data stored in the
various sources are extracted, processed and stored
in one place and then easily manipulated according
to the needs of Misericórdia. As shown in the
A Pervasive Business Intelligence Solution to Manage Portuguese Misericordia
121
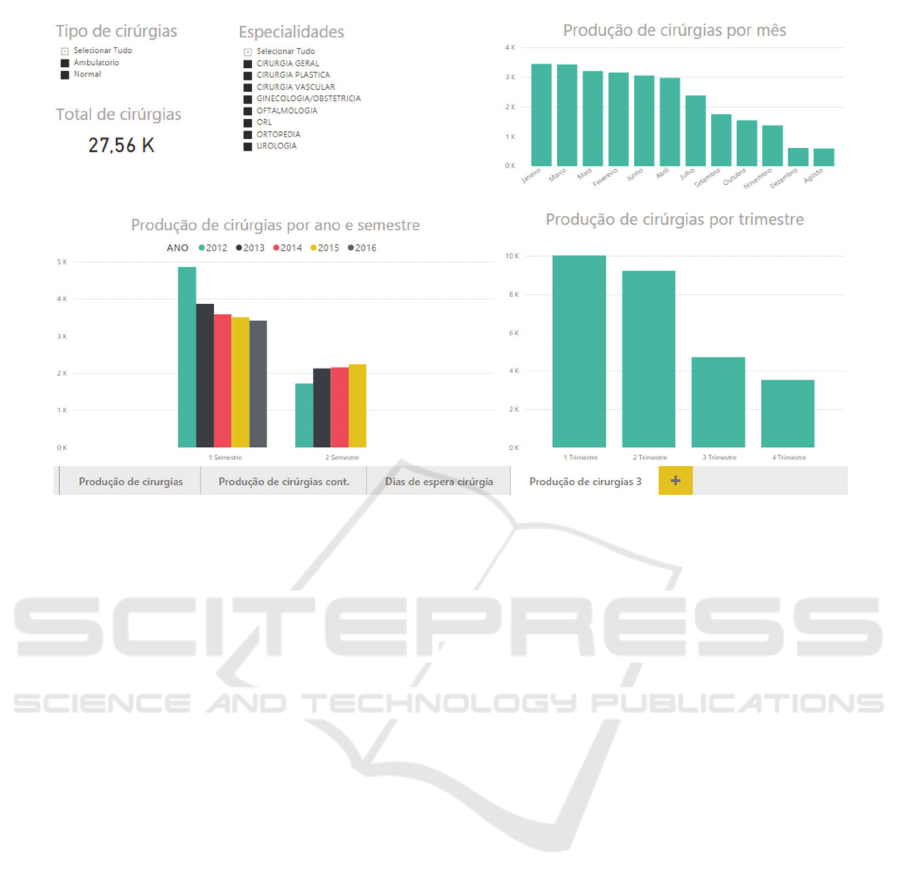
Figure 4: Surgeries Production panel example.
Results section, the displayed pane is just an
example of data presentation. Having said this, the
end user can easily access the dashboard in real time
and make sustained decisions, which until then was
a complex process.
In summary, the use of BI in the Misericórdia
healthcare sector brings many benefits. In this
article, the solution proposed by the BI architecture
allows a Misericórdia sustainable decision-making
in the surgical procedure. This architecture requires
a complete process of data storing and processing
tasks to the data being converted into
information/knowledge later. When the user makes
queries, the system can help the decision-makers in
their task by providing them new insight able to help
to make the right choices leading it to a positive
impact on their patients. In brief, this BI solution can
provide concrete information regarding the trends
and needs of the Misericórdia.
The main contribution of this paper is to show a
BI architecture of functional prototype which can be
reused in others Misericórdias, to improve the
quality of healthcare and patient satisfaction. This
architecture is a new approach and the first
architecture to this market segment. During this
phase, Misericordia participated actively in the
process, namely in requirements elicitation.
7 FUTURE WORK
As a future work and according to Kimball's
methodology, the phase of installation and start-up
of the solution would be a possible phase to be
developed in the future, and in an initial phase, it
would be important to proceed with the survey of the
requirements of the solution according to the needs
of the organisation. After the implementation of the
solution it is important to study the Maintenance of
the platform without leaving aside possible
adjustments to the platform as new features arise
and/or new tools.
In addition, other challenges could be
considered: to provide improvements to ensure the
success and usefulness of BI systems, management
function, responsible for organisational performance
assessment and monitoring; Disseminate the project
to other organisational processes, starting from the
identified organisational process architecture.
Explore other tools to verify what is indicated for the
development and presentation of dashboards,
multidimensional reports, according to the
organisation needs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by COMPETE:
POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007043 and FCT –
ICT4AWE 2017 - 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
122

Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia within the
Project Scope: UID/CEC/00319/2013
REFERENCES
Decreto-Lei n
o
.172-A/2014 de 14 de Novembro do
Ministério da Solidariedade, Emprego e Segurança
Social. , Portugal (2014).
Vuori, H.: Primary health care in Europe—problems and
solutions. J. Public Heal. . 6, 221–231 (1984).
Marins, F. de A.: Monitorização e prevenção em
plataformas de interoperabilidade hospitalar. (2013).
Andrade, S.A. da C.: Inovação nos serviços de saúde das
Misericórdias da região norte de Portugal. (2014).
Penteado, P.: A Investigação em sistemas de arquivo
organizacionais: algumas reflexões sobre o caso das
Misericórdias de Portugal. Actas do Colóquio “Do
Doc. à informação” e das Jornadas sobre Sist.
Informação Munic. 141–163 (2004).
Decreto-Lei n.
o
138/2013 de 9 de Outubro do Ministério
da Saúde. , Portugal (2014).
Pereira, A., Portela, F., Santos, M.F., Machado, J., Abelha,
A.: Pervasive Business Intelligence: A New Trend in
Critical Healthcare. Procedia Comput. Sci. 98, 362–
367 (2016).
Larburu, N., Bults, R.G.A., Van Sinderen, M.J., Hermens,
H.J.: An ontology for telemedicine systems resiliency
to technological context variations in pervasive
healthcare. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Heal. Med. 3, 1–10
(2015).
Miranda, J.: Utilização de metodologias orientadas a
processos na implementação de sistemas de Business
Intelligence – aplicação na saúde, (2013).
Peffers, ken, Tuunanen, T., Rothenberger, M., Chatterjee,
S.: A Design Science Research Methodology for
Information Systems Research. J. Manag. Inf. Syst.
(2007).
Kimball, R.: The Data Warehouse Lifecycle Toolkit:
Expert Methods for Designing, Developing, and
Deploying Data Warehouses. Wiley (1998).
Miranda, João "BI nas Misericórdias", Mestrado em
Sistemas de Informação.2015
Brandão, A., Pereira, E., Esteves, E., Portela, F., Santos,
M.F., Abelha, A., and Machado, J. A Benchmarking
Analysis of Open-Source Business Intelligence Tools
in Healthcare Environments. Information. Volume 7,
Issue 4. ISSN: 2078-2489. MDPI. 2016.
Coelho, D., Miranda, J., Portela, F., Santos, M., Machado,
J., Abelha, A. Towards of a Business Intelligence
Platform to Portuguese Misericórdias. Procedia
Computer Science - HCIST 2016 - Healthy and Secure
People. Volume 100, pp 762-767. ISSN: 1877-0509.
Elsevier- 2016.
A Pervasive Business Intelligence Solution to Manage Portuguese Misericordia
123
