
Teachers’ Work Performance Seen from Work Circumstance, Work
Motivation, and Headmaster’s Leadership Style
Sulistyo Sulistyo and Suprehatin Niingtyas
Universitas Kanjuruhan, East Java, Indonesia
Keywords: Work circumstance, Teachers’ work motivation, Headmaster’s leadership style, Teachers’ work performance.
Abstract: This research aims to know the effect of work circumstance, teachers’ motivation and headmaster leadership
style on teachers’ work performance both partially and simultaneously. Some of the previous research have
similar variables and became reference to show teachers’ work performance is influenced by work
circumstance, teachers’ motivation and headmaster leadership style. It also used saturated sampling technique
which took all of teachers in State Senior Islamic High School Gondanglegi. This research used quantitative
method with double linear regression analysis. The result of this research showed teachers’ work performance
could be affected from work circumstance, teachers’ motivation, and headmaster’s leadership style both
partially and simultaneously.
1 INTRODUCTION
Teachers’ work performance in school has important
role in achieving the goal of school. According to
Wahab & Umiarso (2011:119), teachers’ work
performance is an ability shown by teachers in
implementing their duties or works. “Teacher
performance is the ability to apply its competence in
the performance of its duties which include learning
to plan, implement learning and assess learning
outcomes”.(Kempa & Herenz, 2016). In a work to
realize a good work performance it is needed to have
work performance scoring.
The scoring of teachers’ work performance is
meant as scoring in every teachers’ main activity in
career coaching framework rank and position
(Regulation of the Minister of Administrative Reform
(Permen PAN) No.16 in 2009). There are three types
of aspect scored in the scoring of teachers’ work
performance (Kemdiknas Ditjen PMPTK, 2010:5-8)
that is, the related aspect with learning process,
guidance process, and additional task
implementation. In this research, teachers; work
performance is measured from work circumstance,
teachers’ motivation and headmaster’s leadership
style.
According to Nitisemito (2001:183) he stated that
work circumstance is everything around workers that
can influence themselves to do the tasks given to
them. For example, cleanness and etcetera.
Sedarmayanti (2001: 21) states that, generally
speaking, the type of work environment is divided
into two namely, a) physical work environment, b)
Non-physical work environment. (Muchtar, 2016).
“The domain of work environment contains two
parts: physical and psychosocial working conditions
(Arsalani et al., 2011).” (Thushel Jayaweera, 2015).
“Motivation is defined as a driving force that
compels an individual to take some actions in order
to achieve certain goals. Motivational level of
everyone is different like perception, attitude of
everyone is different. Motivation also takes part in an
important role for teachers because it helps to achieve
the target in an efficient way. Teacher motivation is
very important because it improves the skills and
knowledge of teachers because it directly influences
the student’s achievement (Mustafa, and Othman,
2010). If in schools, the teachers do not have
sufficient motivation then they are less competent
which directly influence the students and the
education system.” (Inayatullah & Palwasha, 2013).
“Teacher motivation is much related to the do
with teachers' attitude to work and work environment,
classroom climate. Teacher motivation could be
referred to as those factors that operate within the
school system which if not made available to the
702
Sulistyo, S. and Niingtyas, S.
Teachers’ Work Performance Seen from Work Circumstance, Work Motivation, and Headmaster’s Leadership Style.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 702-706
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
teacher could obstruct performance, cause stress,
unhappiness and frustration all of which would
subsequently reduce classroom effectiveness and
student quality output. The issue of teacher
motivation is important because of its correlation with
the quality of education.” (Selvam &
Chamundeswari, 2015).
Leadership is a basic of structure or new
procedure to gain purposes and organization’s target
to change purposes and targets of organization (James
Lipham in Ngalim Purwanto, 2007: 27).
“Leadership style is the manner and approach of
providing direction, implementing plans, and
motivating people (Clark, 2010). Three main
leadership styles have been identified as autocratic,
democratic and delegate (Newstrom & Davis, 1993)
as well as laissez-faire and paternalistic (Foster,
2002)”. (Husna, 2015). Lewin et al (1939) concluded
that democratic style of leadership is the most
effective. (Nadeem Bhatti et all, 2012). The
leadership style in this research used as the basis is
the style of democratic leadership.
2 METHODS
This research used quantitative research which can be
described as a research method based on positivism
philosophic, which is used to observe on certain
population and sample (Sugiyono, 2010:14). The
population in this research were all teachers in MAN
Gondanglegi. The technique used in taking the
sample was saturated sample, data collection by using
questionnaire as the instrument, the analysis was
quantitative or statistically to examine the hypothesis.
This research used descriptive analysis where the data
gained was accumulated and analyzed by using SPSS
22.00 for windows with significant level of 0.05.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Double linear regression analysis by using SPSS
version 22.00 for windows was accumulated through
several steps to know the effect among independent
variables consist of: work circumstance, work
motivation, and headmaster’s leadership style on
dependent variables which was teachers’ work
performance, thus the double linear regression can be
seen on the table 1, table 2, table 3.
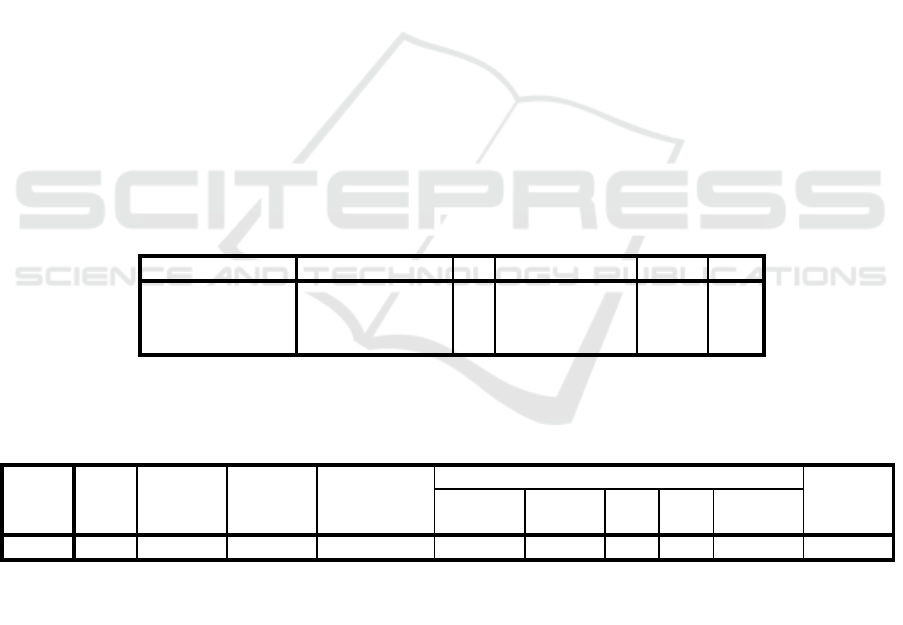
Table 1: ANOVA
b
Model
Sum of Squares
df
Mean Square
F
Sig.
1
Regression
81850.250
3
27283.417
11.068
.000
a
Residual
140505.062
57
2465.001
Total
222355.311
60
a. Predictors: (Constant), Work Environment, Work Motivation, Style Leadership of
the Principal
b. Dependent Variable: Teacher Performance
Table 2: Model Summary
b
Model
R
R Square
Adjusted
R Square
Std. Error of
the Estimate
Change Statistics
Durbin-
Watson
R Square
Change
F Change
df1
df2
Sig. F
Change
1
.607
a
.368
.335
49.64878
.368
11.068
3
57
.000
2.425
a. Predictors: (Constant), Work Environment, Work Motivation, Style Leadership of the Principal
b. Dependent Variable: Teacher Performance
The basic decision to examine the hypothesis is as
follow: the anova-test was F-count of 11.068 with
significant level 0.000 since the significant is less
than 0.05 and Rsquare was 0.368, thus the result of
this research rejects hypothesis Ho and accepts
research hypothesis Ha that: there was effect on work
circumstance, work motivation and headmaster’s
leadership style on teachers’ work performance in
State Senior Islamic High School Gondanglegi.
Teachers’ Work Performance Seen from Work Circumstance, Work Motivation, and Headmaster’s Leadership Style
703
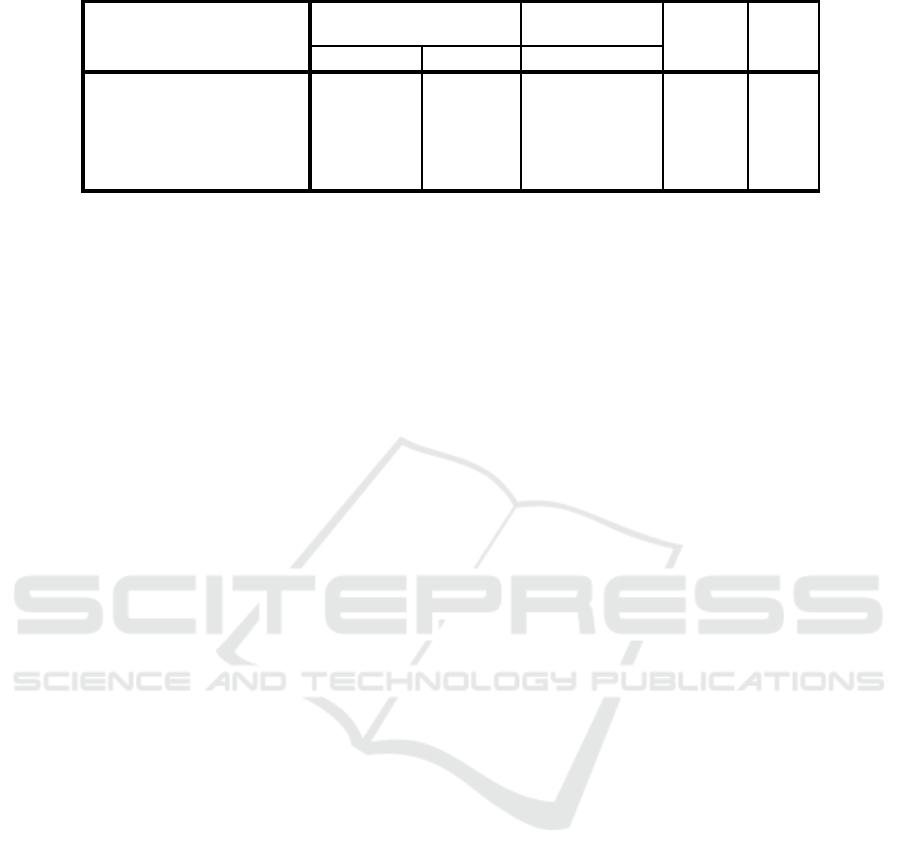
Table 3: Coefficients
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t
Sig.
B
Std. Error
Beta
1
(Constant)
39.595
89.756
.441
.661
Work Environment
-.2311
.881
-.289
-2.625
.011
Work Motivation
.2719
1.106
.364
2.459
.017
Style Leadership of the
Principal
.3094
1.454
.312
2.128
.038
a. Dependent Variable: Teacher Performance
Table 3 shows the significant effect level on each
independent variable which consist of work
circumstance, work motivation and headmaster’s
leadership style with dependent variables that is
teachers’ work performance as follow:
Decision making for proposed hypothesis
examination was: based on Table 3 above, t-
count score for variable X1 (work circumstance)
was -2.625 with significant level of 0.011. Since
the significant level is less than 0.05, thus
variable X1 (work circumstance) influenced
variable Y (teachers’ work performance).
Hence, Ha is accepted and Ho is rejected, it
means there is effect of work circumstance on
teachers’ work performance in State Senior
Islamic High School Gondanglegi.
Decision making for proposed hypothesis
examination was: based on Table 3 above, t-
count for variable X2 (work motivation) was
2.459 with significant level of 0,017. Since the
significant level is less than 0.05, thus variable
X2 (work motivation) influenced variable Y
(teachers’ work performance). Hence, Ha is
accepted and Ho is rejected, it means there is
effect of work motivation on teachers’ work
performance in State Senior Islamic High
School Gondanglegi.
Decision making for proposed hypothesis
examination was: based on Table 3 above, t-
count for variable X3 (headmaster’s leadership
style) was 2.128 with significant level of 0.038.
Since the significant level is less than 0.05, thus
variable X3 (headmaster’s leadership style)
influenced variable Y (teachers’ work
performance). Hence, Ha is accepted and Ho is
rejected, it means there is effect of headmaster’s
leadership style on teachers’ work performance
in State Senior Islamic High School
Gondanglegi.
3.1 The Effect of Work Circumstance
on Teachers’ Work Performance
Based on the t-test statistical analysis, t-count or
variable X1 (work circumstance) is -2.625 with
significance of 0.011. Since the significance is
smaller than 0.05, thus variable X1 (work
circumstance) affects or influence variable Y
(teachers’ work performance) with indicators of
physical and non-physical circumstances. The results
of this study are in line with research conducted by
Dewi Rahmawati (2013), Chandra & Priyono (2015)
and Thushel Jayaweera (2015) stating that there is an
influence of work environment on performance. It
means, a good work circumstance affect teachers’
work performance but a very good work circumstance
will make teachers too comfortable and their work
performance will decrease.
3.2 The effect of Work Motivation on
Teachers’ Work Performance
Based on the t-test statistical analysis, t-count for
variable X2 (work motivation) is 2.459 with
significance level of 0.017. Since the significance is
less than 0.05, thus variable X2 (work motivation)
influenced on variable Y (teachers’ work
performance) with indicators intrinsic and extrinsic
motivations. The results of this study are in line with
research conducted by Dewi Rahmawati (2013),
Selvam & Chamundeswari (2015) dan Inayatullah &
Palwasha (2013) which concludes that there is a
positive influence both simultaneously and partially
between work motivation and performance. It means
with a high motivation the teachers’ work
performance will rise, and A teacher should grow
motivation from their inside soul, because inner
motivation works longer than from outside which is
easy to lost.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
704

3.3 The Effect of Headmaster’s
Leadership Style on Teachers’
Work Performance
Based on t-test statistical analysis, the t-count for
variable X3 (headmaster’s leadership style) is 2.128
with significant level of 0.038. since the significant
level is less than 0.05, thus variable X3 (headmaster’s
leadership style) influenced variable Y (teachers’
work performance) with indicators of democratic
leadership of: decision making by discussion with
other staffs, task dividing is appropriate with ability,
discipline in implementing the task and its function,
two ways open communication. The results of this
study are in line with research by Kempa & Herens
(2016), Muchtar (2016) and Chandra & Priyono
(2015) which concluded that there is a positive
influence between leadership style and teacher
performance. . It means, the headmaster’s success in
managing his duty depends on his leadership style.
Headmaster’s leadership style can raise teacher’s
work performance because of two ways open
communication, task dividing is appropriate with
ability, discipline in implementing his duties and
responsibilities can be guidance to be followed by
teachers, students and staffs, the decision taken is
based on discussion, these are things that help
teachers to increase their work performance.
3.4 The Effect of Work Circumstance,
Work Motivation and
Headmaster’s Leadership Style on
Teachers’ Work Performance
Based on F test from three free variables in this
research overall is simultaneous that it gives
contribution of 11.068 with R square of 0.368 it can
be described that work circumstance variable (X1),
teachers’ work motivation (X2), and headmaster’s
leadership style (X3) give very little contribution to
teachers’ work performance (Y) which is 36.8% and
a bigger contribution effect of 63.2% is affected from
other factors. The result of this research shows there
is effect between work circumstance, teachers’ work
performance and headmaster’s leadership style on
teachers’ work performance in State Senior Islamic
High School Gondanglegi. Other factors which is
possible to influence are ability, skill, personality,
work experience, family background, salary,
facilities, and family condition.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Work circumstance, teachers’ work motivation, and
headmaster’s leadership style have significant effect
on teachers’ work performance in State Senior
Islamic High School Gondanglegi. Thus, to improve
teachers’ work performance the headmaster should
involve teachers in most activities for school needs,
which is sure must be adjusted with the abilities of
teachers. Headmaster is expected to re-review the
policy which can be used to arrange further strategies,
to actualize school’s hope to create optimal quality
human resources. The increase of optimal human
resource can be supported by fixing school’s
circumstance to fulfil higher standard that will make
teachers feel comfortable and raise their motivation
also to work more optimally.
REFERENCES
Arsalani, N., Fallahi-khoshknab, M., Ghaffari, M.,
Josephson, M., Lagerstrom, M., 2011. Adaptation of
Questionnaire Measuring Working Conditions and
Health Problems Among Iranian Nursing Personnel.
Asian Nursing Research, 5 (3), 177-182.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2011.09.004
Chandra, T., Priyono. 2016. The Influence of Leadership
Styles, Work Environment and Job Satisfaction of
Employee Performance—Studies in the School of
SMPN 10 Surabaya. International Education Studies;
Vol. 9, No. 1: 131-140.
http://dx.doi.org/10.5539/ies.v9n1p131
Clark, D. R., 2010. Leadership Styles. Instructional System
Design Concept Map.Retrieved May 6, 2015, from:
http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/leader/leadstl.html
Foster, D.E., 2002. A Method of Comparing Follower
Satisfaction with the Authoritarian, Democratic, and
Laissez-faire Styles of Leadership. Communication
Teacher, 16 (2): 4–6.
Husna, Salma Binti Abu Kusin. 2015. Leadership Style of
Lecturer Influence on Academic Performance of TVET
Student. Journal of Resources Development and
Management. Vol.9: 20-23
Inayatullah, A., Palwasha Jehangir. 2013. Teacher’s Job
Performance: The Role of Motivation. Abasyn Journal
of Social Sciences Vol. 5 No. 2: 78-99
Jayaweera, T., 2015. Impact of Work Environmental
Factors on Job Performance, Mediating Role of Work
Motivation: A Study of Hotel Sector in England.
International Journal of Business and Management.
Vol.10 No.3: 271-278.
http://dx.doi.org/10.5539/ijbm.v10n3p271
Kemdiknas PMPTK, 2010. Pembinaan dan Pengembangan
Profesi Guru, Pedoman Pelaksanaan Penilaian
Kinerja Guru (PK Guru). Kementrian Pendidikan
Teachers’ Work Performance Seen from Work Circumstance, Work Motivation, and Headmaster’s Leadership Style
705

Nasional, Ditjen Peningkatan Mutu Pendidik dan
Tenaga Kependidikan. (Online), (http://dirjen-pmptk-
kementrian-pendidikan-nasional.htmldiakses 28
November 2015).
Kempa, R., Herens Edy Luturmas. 2016. Leadership
Behavior, Organizational Culture, and Teacher
Performance. International Journal of Science and
Research. Vol. 5 Issue 10: 552-555.
www.ijsr.net/10.21275/ART20162045
Muchtar. 2016. The Influence of Motivation and Work
Environment on the Performance of Employees.
SINERGI, Vole 6 No2: 27-40.
Mustafa, M., Othman, N., 2010. The effect of work
motivation on teacher’s work performance in
pekanbaru senior high schools, Riau Province,
Indonesia. SOSIOHUMANIKA, 3 (2), 259-272
Bhatti, Nadeem. Ghulam Murtza Maitlo, Naveed Shaikh,
Muhammad Aamir Hashmi, Faiz. M. Shaikh., 2012.
The Impact of Autocratic and Democratic Leadership
Style on Job Satisfaction. International Business
Research, Published by Canadian Center of Science
and Education Vol.5 No.2:192-201.
www.ccsenet.org/ibr
Newstrom, J.W., Davis, K. 1993. Organizational Behavior:
Human Behavior. Work. New York: Mc Graw-Hill.
Nitisemito, A. S. 2001. Manajemen Personalia. Jakarta:
Ghalia Indonesia
Peraturan Menteri Negara Pendayagunaan Aparatur Negara
dan Reformasi Birokrasi Nomor 16 Tahun 2009.
Tentang Jabatan Fungsional Guru dan Angka
Kreditnya.
Purwanto, N., 2005. Administrasi dan Supervisi
Pendidikan. Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Rahmawati, D., 2013. Pengaruh Lingkungan Kerja dan
Motivasi Kerja terhadap Kinerja Guru GTT. Skripsi
tidak di terbitkan. Malang: Fakultas Ekonomika dan
Bisnis, Universitas Kanjuruhan
Selvam. P., S. Chamundeswari. 2015. Motivation, Job
Satisfaction and Performance of Teachers at the
Secondary Level. International Journal in
Management and Social Science, Vol.3 Issue 7: 705-
719. http://www.ijmr.net.in
Serdamayanti. 2001. Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia,
Revormasi Birokrasi dan Manajemen Pegawai Negeri
Sipil. Bandung: PT Revika Aditama
Sugiyono. 2010. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
706
