
The Improvement Writing Explanation Text through the
Implementation of Text Structure Mapping Strategy
Lilik Binti Mirnawati
University Muhammadiyah of Surabaya. Indonesia
lilikbintimirnawati@fkip.um-surabaya.ac.id
Keywords: Writing Explanation Text, Text Structure Mapping Strategy.
Abstract: This research is attempted is to describe the implementation of teaching writing explanation text by using text
structure mapping strategy learning and to investigate the improvement of students’ skills in writing
explanation text through the implementation of text structure mapping strategy. This research is conducted in
CAR with two cycles: cycle I and cycle II. Each cycle focuses on the learning process of writing explanation
text using a text structure mapping strategy. Each cycle consists of several stages, namely the stage of
planning, implementation, observation, and evaluation. The data are collected through observation and
learning achievement test. Based on the observation result, the percentage of the implementation of learning
activity in the first cycle is 94,17% and the second cycle is 97,08%. The percentage of both cycles indicates
that the implementation of learning is very good or optimal. Based on the test results, there is an increase in
students’ skills in writing explanation. This improvement can be seen from the average score obtained by
students at the end of each cycle. In the initial test the average score of writing explanation text is 65.71%.
The average score in the cycle I is 70%, and the cycle II is 77.14%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Language learning are very important to be taught to
children, one of which is Bahasa Indonesia. Bahasa
Indonesia is a compulsory subject in elementary
school. There are 4 language skills that must be
mastered by students, namely speaking, writing,
reading, and listening. Nurgiyantoro (2009: 296)
states that compare to the other three skills, writing
skills are more difficult to be mastered by native
speakers because writing involves various skills that
require mastery of language elements, the ability to
compose feelings and thoughts by using words in
sentence form to produce cohesion and coherent
paragraph in accordance with the rules of grammar.
There are several supporting factors of the success
of language learning process on writing skills, such as
teacher and student. Teacher factor includes the
teaching method implemented by teacher in teaching
writing while student factor includes the lack of
students’ motivation in learning appropriate writing
skills.
Based on the results of observations conducted on
Monday, July 10, 2017 at SDN Rangkah VII
Surabaya, especially in grade V, there are several
causes of an ineffectiveness of the learning process of
Bahasa Indonesia especially in writing skill. The first
cause is the lack of learning innovative models and
strategies implemented by Bahasa teacher. The
second cause is the lack of students’ interest in
writing class particularly the students in grade V. This
can be seen from the results of pre-test done by
researcher to measure students' writing skills about
explanation text. From the pre-test results, it is
obtained that 61.90% of 42 students have not met the
standard KKM (the minimum standard of learning
achievement) of the Bahasa subjects. The standard
score of KKM for Bahasa subjects is 70.
Based on these rising problems, researcher
conducts a Classroom Action Research (CAR).
According to Arikunto (2010: 135), classroom action
research is an action research conducted by teacher
aimed to enhance or improve the process and the
quality of learning. This research is conducted as an
effort to improve students’ writing skill in grade V at
elementary level. The title of the research is "The
Improvement Writing Explanation Text through the
Implementation of Text Structure Mapping Strategy”.
122
Mirnawati, L.
The Improvement Writing Explanation Text through the Implementation of Text Structure Mapping Strategy.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences (ICES 2017) - Volume 1, pages 122-126
ISBN: 978-989-758-314-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
The research problems in this study are: (1) how
is the implementation of the text structure mapping
strategy in improving students’ skills in writing
explanation text at elementary school grade V? and
(2) Does the implementation of text structure
mapping strategy improve students’ skills in writing
explanation text at elementary school grade V? The
purpose of this research is to know the learning
process during an effort to improve students’ skills in
writing explanation text through the implementation
of text structure mapping strategy in grade V of
elementary school and to know improvement of skills
in writing explanation text through the
implementation of text structure mapping strategy of
students in grade V of elementary school.
Writing is a communication activity in terms of
delivering written message (information) to others by
using written language as tool or media (Dalman,
2014: 3). Writing is an activity of expressing feelings
in written language in order to entertain, convey,
explain, or tell something to someone. There are
several kinds of text, one of which is explanation text.
Explanation text is a text structured to describe a
process of occurrence of phenomena or events.
Text structure mapping strategy implies the way
in which things are built or arranged. So mapping the
text structure is the adoption a method of studying a
concept proposed by Tony Buzan which is known as
mind mapping. The mind mapping developed by
Tony Buzan in the 1970s is a technique of utilizing
the entire brain by using visual imagery and other
graphical infrastructure to form an impression
(DePorter and Hernacki 2000: 153).
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This research is a classroom action research. The
subjects of this research are teachers and students of
grade V in an elementary school of the academic year
2017/2018, with a total of 42 students consisting of
22 males and 20 females. The research is conducted
at SDN (state elementary school) Rangkah VII
Surabaya because the school is very cooperative and
responsive in the effort of upgrading learning
methodology in order to improve student learning
outcomes.
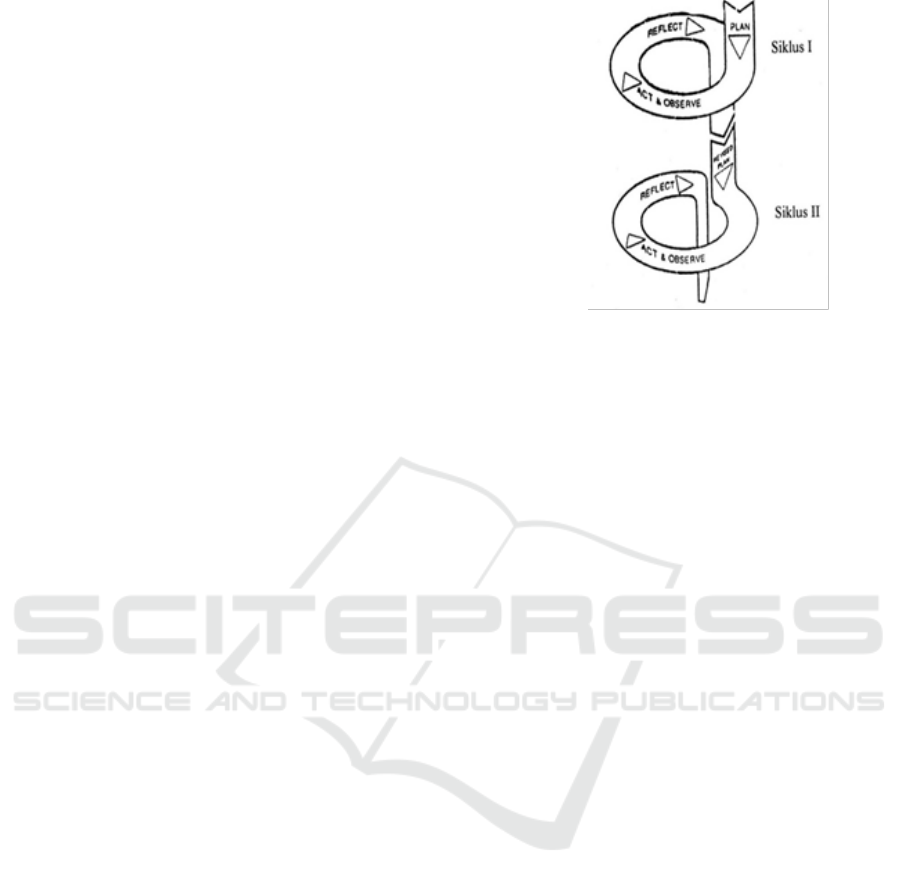
In this research there are done in two cycles,
namely cycle I and cycle II. The procedure of research
in every cycle is done through four stages, namely
planning, implementation, observation, and
reflection. The model and explanation for each stage
will be illustrated in the Figure 1 below.
Figure 1: CAR cycles by Kemmis and Taggart (in Arikunto,
2010: 132).
Based on the research variables, the data are
collected through observation and test. Observation
technique is used to collect data regarding to the
learning process in improving students’ skills in
writing explanation text by using text structure
mapping strategy in grade V of elementary school.
The instrument used is an observation sheet of
learning implementation activity using a text
structure mapping strategy. Furthermore, the test
technique is used to collect data of the improvement
of students’ skills in writing explanation text by using
text structure mapping strategy in grade V of
elementary school. The instrument used is a test
evaluation sheet of writing explanation text learning
result.
Two types of data analysis techniques are used in
this research, namely qualitative and quantitative
techniques. The qualitative data analysis technique is
used to present data from observations and tests in the
form of charts, graphics and essay or in short,
compact and clear sentences. Furthermore, the
quantitative data analysis technique is used to
measure the results of observations and tests by using
formulas.
The observation data is obtained from observers
who fill out the observation sheet of learning
implementation activity at every meeting in cycle I
and II. Analysis of this observational data is done
using the following formula.
The implementation = the implemented activity:
the total activity x 100% (Indarti, 2008:26)
The percentage of acquired skills compared to the
following criteria of assessment.
100% = Excellence / maximum
76% - 99% = Very good / optimum
The Improvement Writing Explanation Text through the Implementation of Text Structure Mapping Strategy
123
60% -7 5% = Good / minimum
<60% = Less
(Djamarah, 2005: 97)
The data of test result are obtained from result of
student learning test in every meeting in cycle I and
II, and are analyzed by using the following formula.
The Result of Students’ Writing
To calculate the student's individual learning
outcomes, the following formula is used.
Final Score = ∑ gained score: ∑ maximum score x
100
Average Class Score of Accomplished Students
To calculate the average class score, the following
formula is used.
M =
∑
the total score gained from the sun of accomplished students score
∑
accomplished students
(Djamarah, 2005: 302)
The average class score used the following
assessment criteria:
80% - 100% = Very good
70% - 79% = Good
60% - 69% = Enough
50% - 59% = Less
(Djamarah, 2005:263)
Completion of Classical Learning
To calculate completion of classical learning used
the following formula:
P = ∑ accomplished students: ∑ students x 100%
(Daryanto, 2011:192)
The result of classical students' learning
achievement is singed using the following assessment
criteria.
100% = Excellence/ maximum
76% - 99% = Very good/ optimal
60% - 75% = Good/ minimal
<60% = Less
(Djamarah, 2005:97)
This research is successful if the result meets the
determined success indicators. The indicators of
success in this study are:
The implementation of text structure mapping
strategy to improve students' explanation text
writing skills is done by ≥ 75%. (Djamarah,
2005: 97).
Classical learning accomplishment is achieved
when ≥ 76% of students have accomplished the
learning standard (Djamarah, 2005: 97), and
achieve the determined KKM (the minimum
standard of learning achievement) score, ≥ 70.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Description of Initial Conditions
The result of observations and tests done by
researcher shows that students ability and skill in
writing explanation text still have not reached the
determined score of KKM (the minimum standard of
learning achievement). This is due to many factors
both from teachers and students. This reality can be
seen in the following score description.
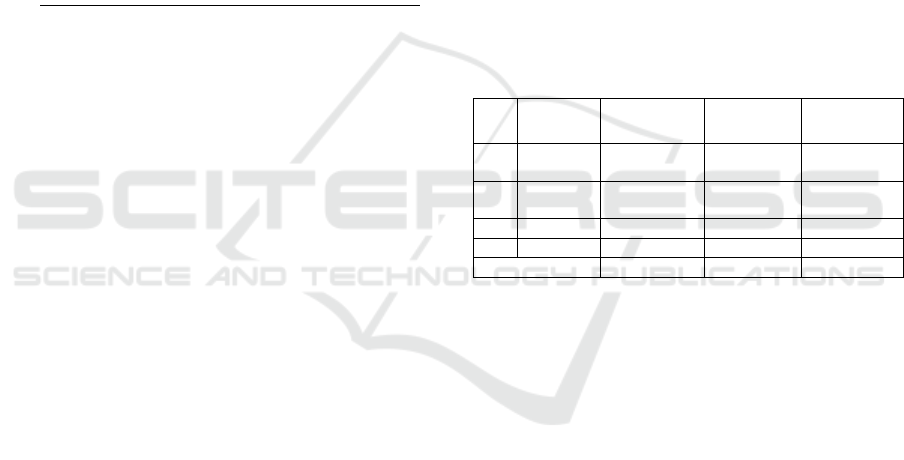
Table 1: The results of initial test.
No
Interval
Frequency
Percentage
Description
1
50-59
5
12 %
Not
completed
2
60-69
21
50 %
Not
completed
3
70-79
11
26 %
Completed
4
80-100
5
12 %
Completed
Total
42
100 %
-
Based on Table 1, the average score obtained from
the result of initial test is 65.71, the lowest score is 50
and the highest score is 80. The numbers of students
who reached the KKM score are 16 students (38.00%)
and 26 students (62.00%) have not yet reached the
KKM. The limit of classical accomplishment is ≥
76% of the total students.
3.2 Results of Cycle I
In this research, the first cycle activity is done in a
meeting. At the meeting of cycle I observation of
learning implementation by using text structure
mapping strategy is carried out. The learning activity
based on the observation result shows that the
implementation of text structure mapping strategy in
teaching writing explanation text in grade V of
elementary school is very good or optimal. The
percentage of the learning activity in cycle I is
94,17%. Furthermore, at the end of the learning
process, a test is given to measure students'
improvement in writing explanation text through text
structure mapping strategies.
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
124
The result of an action done in cycle I shows the
result that students’ writing skill in grade V at SDN
Rangkah VII Surabaya improve compare to pre-
action activity. This can be seen in the following
table.
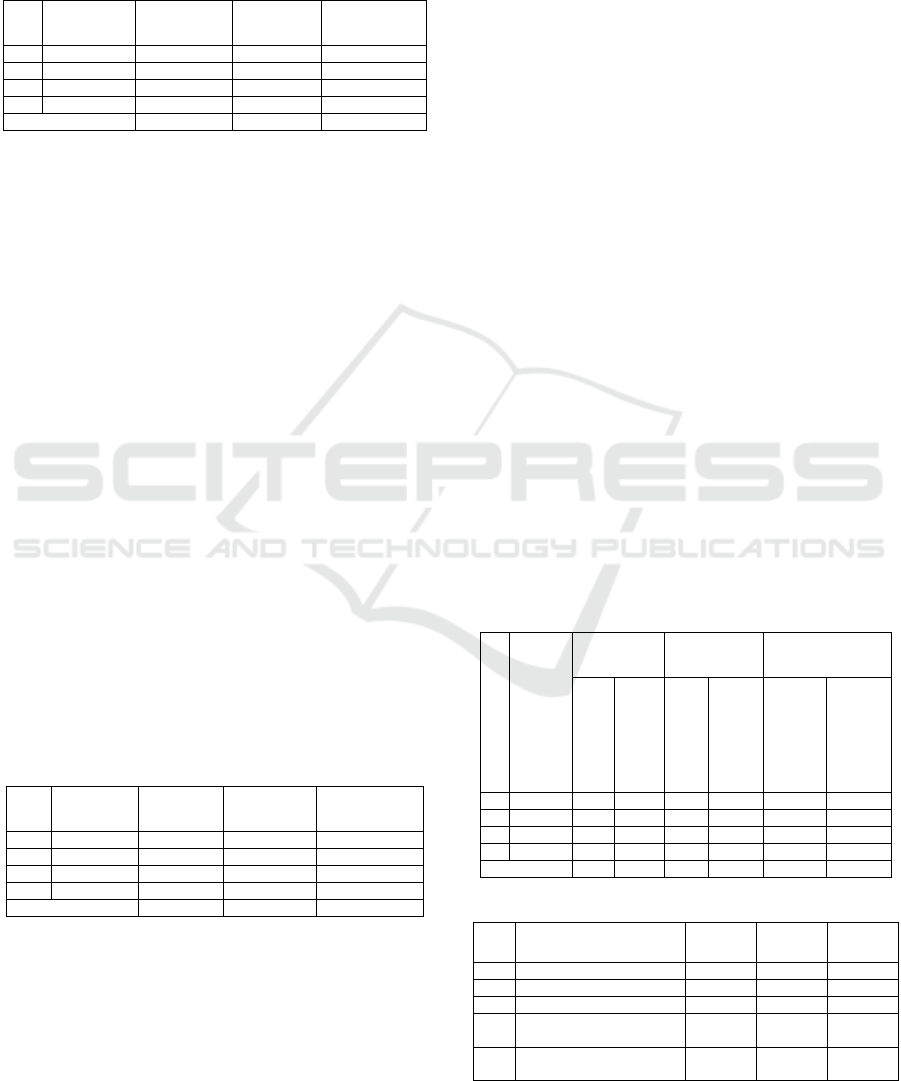
Table 2: The results of the tests in cycle I.
No
Interval
Frequency
Percentage
Description
1
50-59
2
5 %
Not completed
2
60-69
16
38 %
Not completed
3
70-79
16
38 %
Completed
4
80-100
8
19 %
Completed
Total
42
100 %
-
Based on Table 2, there are 24 of 42 students in
grade V who achieve the KKM score, while 19
students (45,24%) are still below the KKM score.
After the observation and research in cycle I, it can be
proposed a reflection that, in general, the process of
teaching and learning activities using text structure
mapping strategy runs better. Students easily put their
idea into the mind maps. Furthermore, students are
able to develop a mind map contained in the mapping
of text structures using their own language.
3.3 Results of Cycle II
Cycle II is done in a meeting as in cycle I. Cycle II is
also divided into four stages, namely planning,
implementation, observation and reflection. Based on
data of observation, the learning process in cycle II is
more alive, active and fun. The students are more
enthusiastic in putting their ideas or thoughts into the
mapping of the text structures provided. The
percentage of learning activity in cycle II is 97,08%.
Based on the results of the tests in cycle II, the skills
in writing text explanations of students in grade V of
elementary school experience a significant increase.
The results of student learning test in cycle II can be
seen in the following table.
Table 3: The results of the tests in cycle II.
No
Interval
Frequency
Percentage
Description
1
50-59
-
-
Not completed
2
60-69
7
16,67 %
Not completed
3
70-79
10
23,81 %
Completed
4
80-100
25
59,52 %
Completed
Total
42
100 %
-
Based on the Table 3, the students’ skills in
writing explanation text through the text structure
mapping strategy increase. Of the total students of
grade V (42 students), seven students (16.67%) get
below the minimal score of KKM while 35 students
(83.33%) reach the targeted score and exceeded the
target of the minimal score of KKM.
Based on the data, it can be concluded that the
students’ skills in writing explanation text increase
and reach the learning accomplishment. This can be
seen from the average score of learning
accomplishment which exceeds the minimum score
of classical KKM (≥ 76%).
3.4 Inter-Cycle Discussion
Cycle I is used as a reflection of conventional learning
model. A strategy of text structure mapping in cycle I
uses text structure mapping with black and white
charts and does not use variations in the drawings.
Students try to share their thought and ideas into the
mapping text structures which has already prepared
and then write their thoughts into a sentence or
paragraph.
Referring to cycle I, learning in cycle II is more
alive, active and fun. The students are also more
enthusiastic in sharing ideas or thoughts into the
provided text structure mapping. In cycle II, the text
structure mapping sheet is more modified by using
colors and images that may interest students to share
their ideas or thoughts. Students seem more confident
to share their ideas in writing on explanation texts.
This can be seen from the results of the explanatory
text of students who have been assessed based on five
aspects, namely aspects of content, organization,
vocabulary, language, and mechanics. From the
assessment results indicate that the average of cycle
II of the five aspects of the assessment has increased.
It can be seen at the following table.
Table 4: The score of writing explanation text on pre-cycle,
cycle I and cycle II.
No
Score
Interval
Pre-cycle
Cycle I
Cycle II
Ʃ
Student
Per
centage
(%)
Ʃ
Student
Per
centage
(%)
Ʃ
Student
Per
centage
(%)
1
50-59
5
12
2
5
-
-
2
60-69
21
50
16
38
7
16,67
3
70-79
11
26
16
38
10
23,81
4
80-100
5
12
8
19
25
59,52
Total
42
100
42
100
42
100
Table 5: Table of average score in combination.
No.
Description
Pre-
cycle
Cycle I
Cycle II
1
Average score
65,71
70
76,90
2
Completed KKM score
16
23
35
3
Uncomplete KKM score
26
19
7
4
Percentage of Completed
KKM
38,10 %
54,76 %
83,33 %
5
Percentage of
Uncomplete KKM
61,90 %
45,24 %
16,67 %
The Improvement Writing Explanation Text through the Implementation of Text Structure Mapping Strategy
125

According to the above combination table 4 and
table 5, it can be concluded that the gained score of
explanation text through the text structure mapping
strategy in pre-cycle, cycle I and cycle II increase.
This indicate that the success of this research in terms
of the improvement of students’ skills in writing
explanation text can be proven. Thus, it can be
concluded that the use of text structure mapping
strategies can improve writing skills on explanation
text of students at elementary school grade V.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The learning activities based on the results of
observation shows that the implementation of
teaching skills in writing explanation text through the
implementation of text structure mapping strategies
for students in grade V at elementary school is very
good or optimal. The percentage of learning activity
in cycle I is 94,17% and that in cycle II is 97,08%.
The percentage of both cycles indicates that the
implementation of learning with text structure
mapping strategy to improve students' writing skills
in explanation text is ≥ 75%. Text structure mapping
strategy can improve skills in writing explanation text
of students in grade V at elementary school by
45,23%.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author very gratefully acknowledges the support
of my parents, brother, feature husband and all friend
in Faculty of Teacher Training and Education in
University Muhammadiyah of Surabaya Research
Fund.
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S., 2010. Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan
Praktik. Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta.
Dalman. 2014. Keterampilan Menulis. Jakarta: PT. Raja
Grafindo Persada.
DePorter, B., Hernacki, M. 2000. Quantum Learning:
Membiasakan Belajar Nyaman dan Menyenangkan.
Bandung: Kaifa.
Djamarah, S. B., Zain, A. 2005. Strategi Belajar Mengajar.
Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta.
Indarti, T. 2008. Penelitian Tindakan Kelas (PTK) dan
Penulisan Ilmiah; Prinsip-prinsip Dasar, Langkah-
langkah, dan Implementasinya. Surabaya: Lembaga
Penerbit FBS Unesa.
Nurgiyanto, B. 2009. Penilaian Pengajaran Bahasa dan
Sastra. Yogyakarta: BPFE.
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
126
