Model of Biology Teachers’ Professional Competency Development
Based on the Early Competency Test in Surakarta Residency
Sofyan Anif and Anam Sutopo
Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta, Surakarta, Indonesia
{sofyan.anif, anam.sutopo}@ums.ac.id
Keywords: Biology Teacher, Competence and Professional.
Abstract: The study aims to describe a model of Biology teachers’ professional competency development based on the
early competency test in Surakarta residency. The procedure of research development used R & D model
developed by Borg and Gall, and then simplified by Samsudi into three main stages of introduction,
development, and validation for finding a model. In the stage of development, the researcher formulated an
early development; then it was analyzed with the relevant theories for formulating a model design
developed in the form of Figure or Model Figure after validated by focus group discussion (FGD). The
results of the study stated that a model of Biology teachers’ professional competency based on the early
competency test included the following characters: 1) implementing a model begins with a competency test;
2) the activities reflected the aspect of continuing professional development (CDP); 3) the supervision was
periodically realized by principals or course teachers); 4) giving feed-back for the next development was
based on the evaluation; and 5) the experts from Higher Education with relevant sciences and competency
were involved in the activities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since 2015, Biology teachers of Surakarta residency
have passed from a teacher certification reached 332
out of 565 people while those who have not taken it
reached 233 people. The teachers with an education
certification have not been in maximally and
structurally sustainable development by the
Education Office of Regency. Instead, it has
developed them more pragmatically, but it has not
employed an appropriate strategy. An unprofessional
development program is due to a lack of funds. It
causes a sustainable development form of teachers’
profession and career to be more praxis and limited.
Referring to Act No. 14, 2015, Indonesian
teachers’ competency that has passed from an
education certification has generally been in low
grade, particularly in pedagogic and professional
qualifications. Besides the Biology teachers, it has
occurred to all the teachers of education levels and
courses.
The condition that describes the Biology
teachers’ low competency is strengthened with the
results of the early competency test by the teachers
who will take an education certification in 2012.
Their national average grades only achieve are 42.25
in a 1-100 scoring system. The highest and lowest
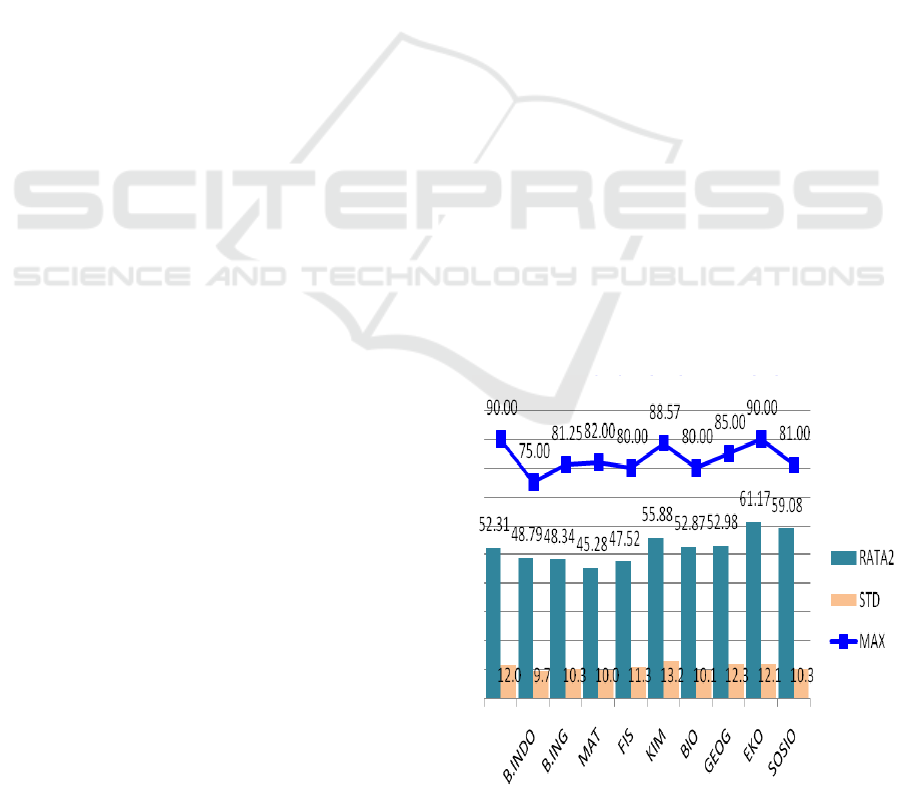
grades respectively achieve 97.0 and 1.0 with a
deviation standard of 12.72. Particularly for the
Biology teachers, the highest and lowest achieve
52.87 and 80.0 with a deviation standard of 10.1 See
the following figure.
Figure 1: Grades of teachers competency test in 2012.
296
Anif, S. and Sutopo, A.
Model of Biology Teachers’ Professional Competency Development Based on the Early Competency Test in Surakarta Residency.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences (ICES 2017) - Volume 1, pages 296-300
ISBN: 978-989-758-314-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Because of this, to enhance a national education
quality, teachers must develop their profession
sustainably so that they can run their profession
tasks professionally. An innovative strategy and
method must be continuously realized and
developed. These are consistent with the demand of
profession development. Also, it is strategically
relevant to Undang-Undang No. 14 (2005) about
Teachers and Lecturers, stating that teachers must
meet academic qualifications and must be
competent; they must have an education certificate;
they must be in sound mind and body; they must
have a education certificate and be competent in
realizing the aim of national education. The
teachers’ competencies of pedagogic, personality,
social, and professional are developed with
profession education.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The development of teachers’ competency and
profession is essential. It is relevant to Saud (2009),
stating that for increasing a present education
quality, teachers’ professionalism is a must. In
consideration with current condition, moreover,
running a professional education must be necessary
to pay more and more attention to developed and
advanced science and technology, graduation global
competition, local autonomy, curriculum
implementation. Because this, the statement problem
of the research is what is an of Biology teachers’
professional competency development based on the
early competency test in Surakarta residency?
3 RESEARCH METHODS
The procedure and research development employed
a R&D model (Borg and Gall, 2007). The model by
Borg and Gall (2007) uses a multi-procedure of 1)
product analysis, 2) theoretical analysis, 3)
development planning, 4) early model development,
5) model validation, and 6) final product. Borg &
Gall identifies ten stages of working procedures of
research and development model. Samsudi (2009)
simplifies these stages into three stages of 1)
introduction, 2) development and validation, and 3)
final model/product.
The data of the research comprised primary and
secondary. The primary data included the
respondents’ or informants’ spoken and written
communications and behaviors, mainly related a
model of teachers’ competency development in the
post-certification; the secondary data covered the
documents, including regulations (or Acts), guiding
books, working programs of Association of Course
Teachers (ACT). In terms of the respondents as the
data source, the research employed a purposive
sampling. So, the researchers chose the respondents
who were credibly regarded to understand the
problems of the research.
In the stage of development, it is necessary to
formulate an early model development. The model is
based on the reflection of the introduction stage
(factual model). After that, it is analyzed by
referring to relevant theories and regulations (Acts),
and then, formulating a model development. The
activities of the stage consist of 1) empirical and
theoretical analysis in relation to a finding of factual
model and formulation of model development
design, 2) model instrument formulation, 3) FGD for
an early model design validation, and 4) model
improvement model on the basis of FGD results.
The data were descriptively and qualitatively
analyzed.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Results of the Research
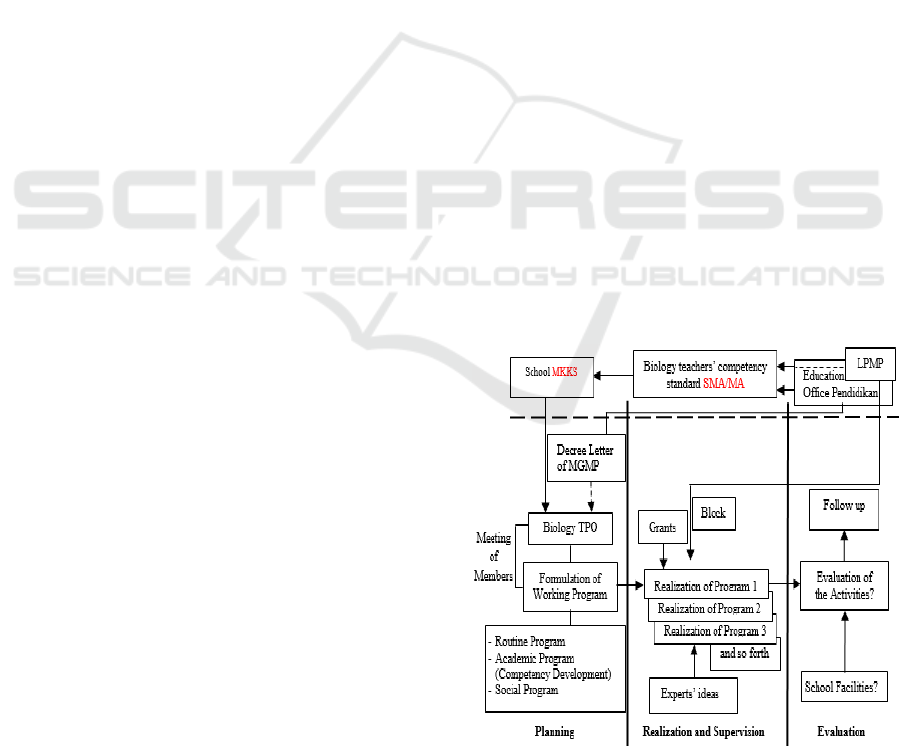
The results of the introduction stage describe a
model of Biology teachers’ professional through the
forum of MGMP in Surakarta residency (factual
model).
Figure 3: A model of biology teachers’ competency
development through the forum of MGMP in Surakarta
Residency.
Model of Biology Teachers’ Professional Competency Development Based on the Early Competency Test in Surakarta Residency
297
The results of the research show that
implementing a model of Biology teachers’
professional competency development through the
forum of MGMP describes some weaknesses in
planning, realization, and evaluation aspects. In
terms of planning aspects, the activities of Biology
MGMP used the general materials for all the
Biology teachers, who essentially had the
heterogeneous professional competencies. It means
that the planning of the activities was not based on
need analysis that described some weakness in each
teacher’s professional competency.
Regarding the realization aspect, the activities
were not realized structurally and sustainably while
the use of the method was dominantly ‘lecturing’
(one-way communication), the proportion of the
activities was tendentiously routine and pragmatic,
the materials focusing on professional competency
development were low in quantity, there was no
supervision, the experts were the senior teachers,
and the activities did not collaborate with the experts
from Higher Education. In relation to the evaluation
aspect, the evaluation of Biology MGMP activities
were not carried out structurally, so there was no
feed-back for the next activities.
Based on the weaknesses in a model of
professional competency through Biology MGMP,
theoretically and empirically the research analyzed
human resources of education by formulating a
model development design after validation process
in the form of FGD. The result was a model of
Biology teachers’ professional competency
development based on the early competency test in
Surakarta residency.
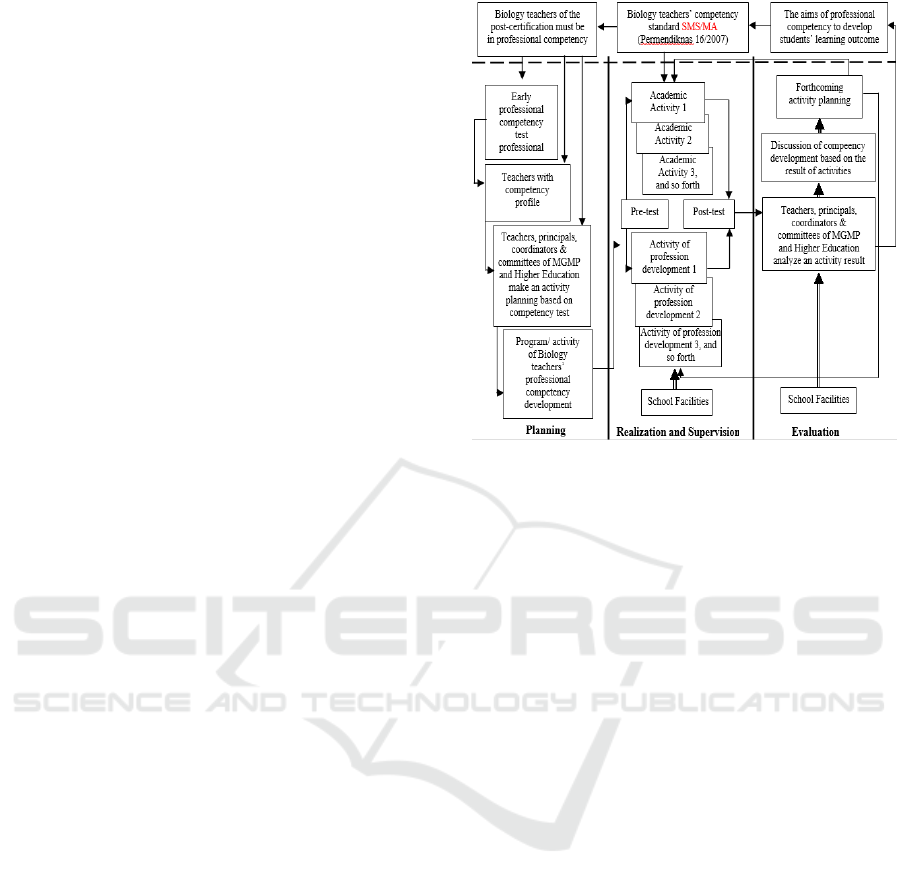
The new development model comprises five
characters that was not found in the factual model.
Firstly, the model begins with need analysis of
competency developed from the early competency
test. Secondly, the model is a continuing
professional development (CPD). Thirdly, the model
strengthens a supervision aspect that involves a
supervisor of course or principal by monitoring and
evaluation. Fourthly, the length of each academic
and teachers’ professional development activity
maximally runs during six months. Fifthly, the
activities of the professional competency
development are realized by inviting the experts
from Higher Education relevant to their science and
competency.
Figure 4: A model of biology teachers’ professional
competency development based on early competency test
in Surakarta Residency (hypothetic model).
4.2 Discussion
As a result of development, model has five
character:
Beginning with early competency test;
Referring to continuous professional
development (CPD);
Supervising by a superior;
Strengthening an evaluation for getting feed-
back;
Inviting an expert from Higher Education.
In terms of the first character, implementation
teachers’ competency development model will begin
with early competency test. The result of the test has
the following two functions 1) as a basis for
planning an activity of competency development
relevant to teachers’ needs, and 2) as a baseline of
each teacher’s professional competency. It is a core
of planning a human resources development of
education.
Mathis and Jackson (2006) state that the human
resources development must begin with need
analysis of individual and organization. Although
the need analysis of individual gets less attention, it
is a determinant factor in finding an optimal result
and encouraging to achieve an organization’s goal as
expected.
Jones and Walter (2008) suggest a task for a
school (principal) to make a strategic planning of the
educative and administrative staff competency and
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
298

development. In an education field, they must have
an opportunity to develop their potency for a
performance achievement. Moreover, it is said that
for a performance achievement, teachers and
administrative staff need to get training for
competency development.
In terms of the second character, it is related to a
sustainable professional competency development
activity or a continuing professional development
(CPD)-based activity. The activity is a solution to
the problem of factual model, i.e. a process of a
Biology teacher’s professional competency
development, including a kind or material of
activities, is not realized structurally and there is no
follow up for unfinished activities.
Regards a sustainable professional development,
Guskey (2000) and Day and Sachs (2004) propose
that teachers’ professional competency must be
developed continuously for anticipating an education
and science and technology development and
advance, in general. Additionally, it is suggested that
continuing professional development is a systemic
process in consideration with changes in a given
period of time. The activities of CPD must meet
individual teachers’ professional need and can
indicate a correlation between teachers’ profession
and school’ development needs. It is line with
Mathis and Jackson (2006) and Jones and Walters
(2008). Guskey (2000) suggests that it is necessary
to develop teachers’ professional competency
continuously. Mathis and Jackson (2006) emphasize
a human resources development of education that
must be relied on an individual teacher’s and
school’s needs. Therefore, an early condition
analysis of teachers’ competency functions as a
base-line and it serves a basis of need analysis of
teachers’ competency in the future as well as a
determinant factor in a kind of activity in the
forthcoming.
Guskey (2000) proposes some activities of CPD,
including 1) formal activities, 2) teachers’
attendance for taking a course and training of
learning methods, learning media and facilities, and
instructional materials development, 3) private study
for developing materials relevant to science and
competency or general education, and 4) class action
research.
The third character is concerned with
strengthening a supervision aspect by a superior
(principal) in a process of activity realization.
Strengthening the supervision is a solution to the
problems found in the factual model, i.e. there is a
lack of supervision and even there is no supervision
by the superior. The results of the research show that
the supervision activity does not run well and even
there is no supervision for Biology MGMP.
According to Cicih and Nurdin (2011), an
analysis result of data by National Education Office,
National Planning Board, and World Bank in 1999
indicates that a teacher is a key to improve and
develop an education quality. It is greatly
determined by learning quality. For improving and
developing a learning quality, a teacher is a core
figure in the class. Additionally, he or she must
continuously be supervised and developed by a
principal or other related superiors. It is consistent
with a supervision concept, stating that supervision
is an aid and advice or suggestion for teachers in
instructional field, teaching and learning, and
curriculum for achieving a school’s goal (Neagley
and Dean, 1980).
Bessong and Felix (2009) state that supervision
is one of the effective instruments in a learning
process in the class because it will improve and
develop a learning quality continuously and
systematically, so it will take a positive effect on
improving and developing students’ learning
achievement. Fritz (2003) relates a supervision
activity to a principal’s substantial task. It is
suggested that for advancing a learning field,
supervision is a main option and inevitable for
education improvement and development.
Referring to the concept, education supervision
not only functions to give some aid and advice by a
principal, but also gives some motivation and
stimulant to teachers so that they can develop their
competency maximally as a professional teacher
relevant to a school’s needs. Cicih and Nurdin
(2012) state that supervision is a process, a sequence
of activities that makes teachers develop their
competency.
The fourth character is related to evaluation
aspect. In a management of education human
resources, a lack of evaluation process in working
program for developing workers’ performance
achievement is a very great error because each
organizational management must operate all the
activities as planned, so it needs some evaluation to
achieve an organization’s goal (Jones and Walters,
2008). Based on the analysis, implementing a model
needs an evaluation process for developing human
resources comprehensively and structurally to
achieve a standardized education.
In relation to the fifth character, it invites an
expert (lecturer) from Higher Education. Based on
the results of the research, the activities of teachers’
competency development through Biology MGMP
in the post-certification indicate a lack of the experts
Model of Biology Teachers’ Professional Competency Development Based on the Early Competency Test in Surakarta Residency
299

from Higher Education but these invite the senior
teachers. Inviting an expert from Higher Education
is said to be very essential for developing materials
more comprehensively, including philosophical
aspects and their implementation to science and
technology. The expert can help teachers understand
the materials mode deeply and use laboratory
facilities for more comprehensive instructional
materials of biology.
5 CONCLUSIONS
From the Discussion it can be concluded that 1)
implementing the model begins with the early
competency test that will be a basis of need analysis
of competency development, 2) the model
development has a continuing professional
development (CPD) aspect, 3) the realization of the
activities is needed to strengthen a supervision by a
principal or course supervisor. It can be conducted
periodically, 4) Strengthening an evaluation aspect is
intended to get feed-back for forthcoming activity
planning and 5) Inviting an expert from Higher
Education relevant to his or her science and
competency is greatly necessary.
REFERENCES
Bessong, F. E., Felix, O., 2012. Supervision as in
Instrument of Teaching-Learning Effectivenes:
Chalengge for The Nigerian Practice. Global Journal
of Educational Research. Vol. 8 (1 and 2). pp. 15-20.
Borg, W. R., Gall, M. D., 2007. Education Research: An
Introduction, Longman. Inc. New York-London.
Cicih, S., Nurdin, 2012. Supervisi Pendidikan, Alfabeta.
Bandung.
Day, C., Sachs, J., 2004. International Handbook on the
Continuing Professional Development of Teachers,
Open University Press. Glasgow.
Fritz, C., 2003. Supervisory Options for Instructional
Leader in Education. Journal of Leadership
Education. Vol. 2 (2). pp. 13-27.
Guskey, T., 2000. Evaluating Professional Development,
Corwin Press. Thousand Oaks, CA.
Jones, J. J., Walters, D. L., 2008. Human Resources
Management in Education (Manajemen Sumber Daya
Manusia), Q – Media. Yogyakarta.
Mathis, R. L., Jackson, J. H., 2000. Human Resources
Management (Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia),
Salemba Empat. Jakarta.
Neagley, R., Dean, E., 1980. Supervisi Pendidikan,
Alfabeta. Bandung.
Samsudi. 2009. Disain Penelitian Pendidikan, Universitas
Negeri Semarang Press. Semarang.
Saud, U. S., 2009. Pengembangan Profesi Guru, Alfabeta.
Bandung.
Undang-Undang No.14 2005. Guru dan Dosen,
Depdiknas. Jakarta.
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
300
