
Determinant Factors Affecting the Quality of Private Universities
Nani Sutarni, B. Lena Nuryanti and Achmad Hufad
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung, Indonesia
{nanisutarni, achmadhufad}@upi.edu
Keywords: Education Criteria for Performance Excellence, Malcolm Baldrige, Quality of Private Universities.
Abstract: This research raises the phenomenon of the quality of private universities in West Java which is not relatively
optimal. The purpose of this study is to analyze empirical facts about the relationship structure of factors
affecting the quality of private universities by looking at the relevance of these factors through the Education
Criteria for Performance Excellence of the Baldrige System. This research applies quantitative approach by
using descriptive and verifikatif methods. This research was conducted in two private universities in West
Java, namely Universitas Kuningan (Uniku) and Universitas Galuh (Unigal). The population of the study were
343 lecturers with a sample of 181 respondents. Data were analyzed using path analysis. The results showed
that the quality of college, leadership, strategic planning, customer focus, system management, focus on
human resources, and management of learning process at Universitas Kuningan (Uniku) and Universitas
Galuh (Unigal) are included in moderate or sufficient category.
1 INTRODUCTION
In an education system, higher education is called
tertiary education, which is a level that can be
followed after secondary education such as high
school, vocational high school or madrasah aliyah
and equal. The educational unit responsible for
conducting the educational process at higher
education is an institution in the form of a university,
institute, polytechnic, academy or community
college.
The implementation of higher education quality
and in accordance with the expectations of the
community requires the arrangement of the
implementation of higher education in a planned,
directed, and sustainable. High quality education is
basically able to form the character and civilization of
a dignified nation in an effort to educate the nation.
Through the implementation of Tridharma, higher
education can also develop innovative, responsive,
creative, skillful, competitive, and cooperative
academic community. In addition, higher education
with high quality can develop science and technology
by paying attention and applying the value of
humanities.
In fact, there is still a wide gap between the reality
of higher education in Indonesia and the essence of
higher education, especially related to the
achievement of the quality of higher education as a
whole, especially related to the quality of the
performance of higher education components, such as
the less optimal learning process, the implementation
of the curriculum stable and less responsive to the
needs of students, lecturers competencies that still
need to be improved, inadequate learning facilities in
supporting the learning process, or any research /
service to the community that has not become a
mainstay of universities, but through research process
learning, research, and devotion to society, a college
can become more feasible with knowledge creation
and knowledge innovation (Vick, 2015, Mahr and
Lievens, 2012).
These conditions have caused most universities in
Indonesia, especially private universities, especially
in the regions, have not reached the excellent
category. That is, the college has not been able to
function itself properly. Universities in this case
should not only be able to meet the needs and desires
of society in general but also must be able to educate
the community to make sense of the nature of higher
education (Lozano, et al., 2013). To achieve an
excellent condition, there must be a harmonious
common perception and policy between stakeholders,
i.e. community, government, and university so that
the quality of university performance does not
decline.
Sutarni, N., Nuryanti, B. and Hufad, A.
Determinant Factors Affecting the Quality of Private Universities.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences (ICES 2017) - Volume 1, pages 339-342
ISBN: 978-989-758-314-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
339

The tight competition between private university
(PTS) and public university (PTN) or other PTS
related to the accreditation of study program (PS) in
each PTS. The accreditation result of National
Accreditation Board of Higher Education (BAN-PT),
which is recognized as a barometer of higher
education quality in Indonesia, indicates that the
condition of university study program in Indonesia
has not fully fulfilled the expected quality. Most of
the courses from universities, i.e. as many as 2,316 PS
are still accredited to the rank of Good (B) and
Enough (C). Of these 2,235 units are private
universities (PTS) and only 81 units of State
Universities (PTN).
Various factors influence the achievement of the
quality of higher education. HELTS (2010: 12) states
that the main components and supporting quality of
universities essentially include: (1) learning process,
(2) students, (3) lecturers, (4) learning facilities, (5)
research and community service, (6) leadership, and
(7) governance. These factors form the basis for
assessment and quality management of higher
education. Achievement of the quality of college
often refers to the achievement of academic quality.
(2) Governance, Leadership, Management System,
and Quality Assurance, (3) Students and Graduates,
(4) Achievement, (1) Vision, Mission, Human
Resources, (5) Curriculum, Learning, and Academic
Atmosphere, (6) Financing, Facilities and
Infrastructure, and Information System, and (7)
Research, Service / Community Service, and
Cooperation.
Empirically, the uneven phenomenon of these
achievements revolves around the performance
component 2 to the performance component 7. This
means that governance, leadership, management
systems and quality assurance are not fully optimal,
as are students / graduates and human resources.
Curriculum standards, learning, and academic
atmosphere are also considered not optimal, as well
as the components of financing, facilities and
infrastructure, and information systems. The lowest
performance component of the university is the
performance of research, service / service to the
community, and cooperation. This does not mean that
the university does not Tridharma College, but the
performance component has not optimally impacted
the stakeholders of the university and the general
public.
These phenomena indicate that universities are
continuously working to improve the implementation
of higher education based on the main values adopted
by each university so as to improve the quality of
institutional performance results and public trust. If
the college is not serious in managing all components
of higher education consistently, then the college is
possible to not be able to develop itself in a
sustainable manner.
Based on the above description, this study
examines in depth the determinants affecting the
quality of universities in two private universities in
West Java, namely the University of Universitas
Kuningan (Uniku) and Universitas Galuh (Unigal),
by looking at the relevance of these factors through
Education Criteria for Performance Excellence of the
Baldrige System, which includes seven integrated and
interrelated categories: (1) Leadership; (2) Strategic
Planning, (3) Customers Focus, (4) System
Management (Measurement, Analysis and
Knowledge Management), (5) Focus on HR (Faculty
and Staff Focus), (6) ) Learning Process
Management, and (7) Organizational Performance
Results.
2 METHOD
This study uses a quantitative approach using a
questionnaire as the main instrument of data
collection. Churchill and Iacobucci (2005: 74) states,
research design is the framework or plan for study,
used as a guide to collect and analyze data. The
purpose of this research is to test hypothesis
explaining the relationship among Leadership
variables, Strategic Planning, Customer Focus,
System Management, Focus on Human Resources,
and Management of Learning Process and Quality of
Higher Education in two private universities in West
Java.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Referring to the framework, description and testing
and discussion of research results, the next step is to
design the Education Criteria for Performance
Excellence Model in Higher Education, which is
based on theories, findings, and research discussions
at two universities, Universitas Kuningan (Uniku)
and Universitas Galuh Ciamis (Unigal). This model
is an alternative model of Baldrige Education Criteria
that can strengthen higher education institutions to
achieve goals, improve outcomes, and become more
competitive in aligning planning, processes,
decisions, people, actions, and outcomes.
In general, hypothetical models of education
criteria for performance excellence in Higher
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
340
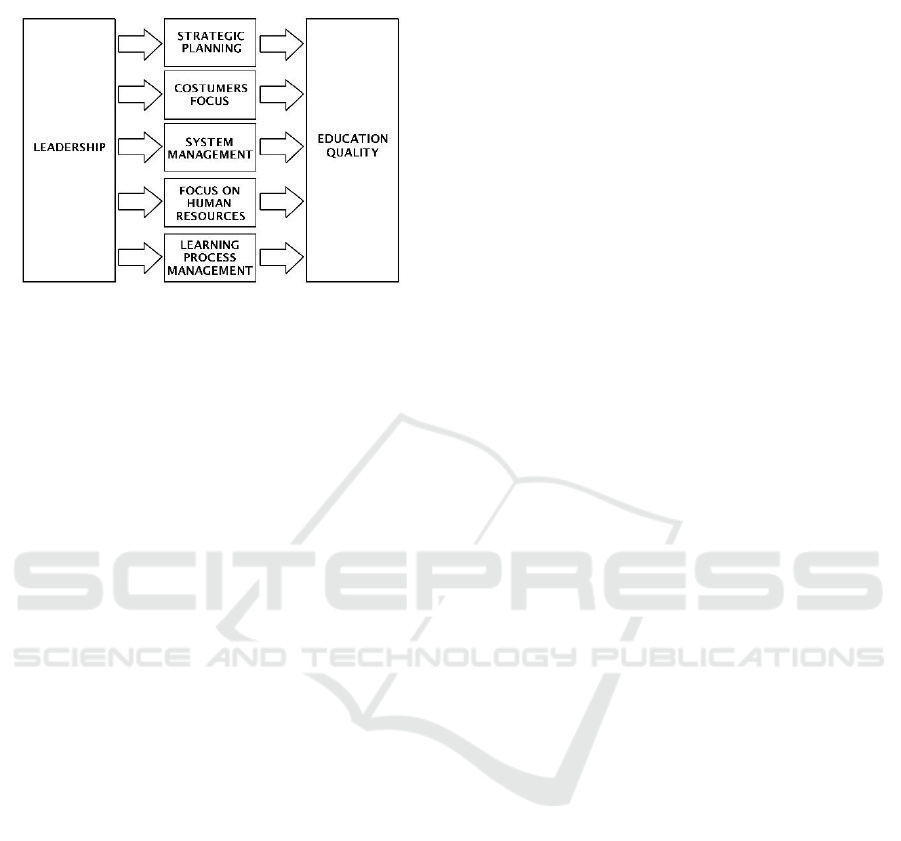
Education can be described as follows (see in Figure
1).
Figure 1: Visualises model.
The main philosophy of the model of education
criteria for performance excellence in universities is
that all aspects of higher education can support and
support the main component, namely the quality of
universities. The implementation and achievement of
the quality of higher education can be realized by the
synergy of the components that influence it, namely
leadership, strategic planning, customer focus,
system management, focus on human resources, and
management of learning process.
The results of calculations and analysis in this
study indicate that the contribution of leadership is
the most important aspect in realizing the quality of
universities. This can be understood because
leadership is an early component that drives all the
other components in supporting the quality of
universities. These findings make the leadership
component as the core in driving all other
components. However, this does not mean that the
other components (strategic planning, customer
focus, system management, human resources focus,
and management of learning processes) are not
important in influencing the quality of the whole
university.
On the other hand, system management is a
relatively inadequate component of college
managers. In this study, it was found that the
management system in both private universities is not
optimal. If not quickly addressed by clear
measurements such as availability of unit
performance evaluation information (from university,
faculty, to study program), availability of unit
performance standards, availability of evaluation
information on education and teaching activities, and
availability of quality standards for education and
teaching. Currently, the condition of information
management at these two universities is still relatively
low, so universities, faculty and programs rarely have
internal information on educational and teaching
activities. Universities (including faculties and
courses) also rarely have internal information of non-
educational activities. Universities, faculties, and
study programs rarely have external public
information, access to scientific knowledge, access to
academic and non academic environments,
information to alumni, and information accessible to
stakeholders. All of them of course can affect the
declining quality of college.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Leadership positively and significantly influence to
Higher Education Quality. Strategic Planning affects
positively and significantly to Higher Education
Quality. Customer Focus positively and significantly
affect the Quality of Higher Education. Management
System positively and significantly influence to
Higher Education Quality. Focus on human resources
positively and positively affect the Quality of Higher
Education. Learning Process Management has a
positive and significant impact on the Quality of
Higher Education. These factors simultaneously have
a positive and significant effect on the quality of
higher education.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Leaders and
Lecturers and the staff of Universitas Kuningan
(Uniku) and Universitas Galuh (Unigal) who have
given the opportunity to the researcher to do this
research activity.
REFERENCES
Akdon, Hadi, S. 2005. Aplikasi Statistika dan Metode
Penelitian untuk. Administrasi dan Manajemen.
Bandung: Dewa Ruchi.
Arijanto, S., Harsono, A.R. 2010. Pengukuran Kinerja
Fakultas di Perguruan Tinggi "X" Menggunakan
Pendekatan Malcolm Baldrige Criteria for
Performance Excellence Education Criteria.
Proceeding Seminar Nasional IV Manajemen and
Rekayasa Kualitas 2010.
Badri, M.A., H. Selim, K. Alshahr, E. Grandon, H. Younis,
M. Abdullah, “The Baldrige Education Criteria for
Performance Excellence Framework: Empirical test
and Validation”, International Journal of Quality and
Reliability management, vol. 23, no. 9, pp. 1118-1157.
Determinant Factors Affecting the Quality of Private Universities
341

Baldrige Performance Excellence Program. 2015. 2015-
2016 Baldrige Excellence Framework: A System
Approach to Improving Your Organization's
Performance Education. Gaithersburg, MD: U.S.
Department of Commerce, National Institute of
Standards and Technology.
Churchill, Iacobucci. 2005. Marketing Research:
Methodological Foundations. South Western:
Thomson
Crawford, M., Kydd, L. 2005 Leadership and Teams in
Educational Management. Kepemimpinan dan Kerja
Sama Tim di Dalam Manajemen Kependidikan. Jakarta.
Grasindo.
Curkovic, S., R. Landeros. 2000. An Environmental
Baldrige, Mid-American Journal of Business. 152:63-
76.
Hanafiah. dkk. 1994. Pengelolaan Mutu Total Pendidikan
Tinggi, Suatu Buku Pedoman bagi Pengelola
Perguruan Tinggi Untuk Meningkatkan Mutu. Jakarta.
Badan Kerjasama Perguruan Tinggi Wilayah Indonesia
Barat BKS PTN Barat.
HELTS – Dikti. 2010. Strategi Pendidikan Tinggi Jangka
Panjang 2003 – 2010: Mewujudkan Perguruan Tinggi
Berkualitas. Jakarta: Departemen Pendidikan Nasional
RI.
Lozano, R., Lukman, R., Lozano, F. J., Huisingh, D.,
Lambrechts, W. 2013. Declarations for sustainability in
higher education: becoming better leaders, through
addressing the university system. Journal of Cleaner
Production, 48, 10-19.
Mahr, D., Lievens, A. 2012. Virtual lead user communities:
Drivers of knowledge creation for innovation. Research
Policy, 411, 167-177.
Rasto. 2012. "Faktor Determinan Mutu Kinerja Sekolah",
Prodi Pendidikan Manajemen Perkantoran, Fakultas
Pendidikan Ekonomi dan Bisnis, Universitas
Pendidikan Indonesia.
Slamet, M., Dkk. 1996. Manajemen Mutu Terpadu di
Perguruan Tinggi. Jakarta. HEDS Project.
Sudjana. 1996. Metoda Statistik. Bandung: Tarsito.
Tampubolon, D.P. 2001. Perguruan Tinggi Bermutu,
Paradigma Baru Manajemen Pendidikan Tinggi
Menghadapi Tantangan Abad ke 21. Jakarta. PT
Gamedia Pustaka Utama.
Tenner, A.R. De Toro, I.J. 1992. Total Quality
Management, Three Steps to Continuous Improvement.
Massachusetts: Addison-Wesley Publishing Company.
Vick, T. E., Nagano, M. S., Popadiuk, S. 2015. Information
culture and its influences in knowledge creation:
Evidence from university teams engaged in
collaborative innovation projects. International
Journal of Information Management, 353, 292-298.
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
342
