
Implementation of Cooperative Learning by Using Audio-Visual
Media in Table Tennis Game Learning
Faisal Faisal, Dian Budiana and Entang Hermanu
Faculty of Sport and Health Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jln. Dr. Setiabudhi No.299, Bandung, Indonesia,
faisal@gmail.com
Keywords: Physical Education, Establishing Cooperation Values, and Table Tennis Game Learning.
Abstract: The purpose of this research is by applying cooperative learning using audio visual media to improve
forehand drive and backhand drive in table tennis game (on grade V SDN Cinunuk 02 Bandung). The
method used in this research is Classroom Action Research (PTK) with two cycles in table tennis game
program. The subjects of this study are 40 students of grade V SDN Cinunuk 02 Kabupaten Bandung. The
instruments used are the test of skill in forehand drive and backhand drive. The result of preliminary
observation indicates that the forehand drive and backhand drive tests of student are still low in learning,
this is indicated by the test values forehand drive and backhand drive average percentage of backhand drive
42.55% while forehand drive 45.13% 75%. Next the result of cycle 1 action 1 with percentage of backhand
drive 48,07% while forehand drive 55,80%. Then result of cycle 1 action 2 with percentage of backhand
drive 57,50% while forehand drive 66,63%. Furthermore, the result of cycle 2 action 1 with percentage of
backhand drive 68,73% while forehand drive 73,10%. Next cycle 2 action 2 with percentage of backhand
drive 78.03% while forehand drive 83.90% After going through two cycles the average skills test value of
forehand drive and backhand drive in table tennis game has increased significantly. The conclusions of this
study are the student’s skill value of forehand drive and backhand drive through table tennis games and the
application of cooperative learning using audio visual media has increased.
1 INTRODUCTION
In line with the development of the learning model,
cooperative learning assumes that it is appropriate to
improve the learning outcomes of one of the
learning outcomes of table tennis game (Dorigo and
Gambardella, 1997). The term cooperative learning
in the Indonesian sense is known as cooperative
learning. In cooperative learning model students are
given the opportunity to communicate and social
interact with their friends to achieve learning
objectives, while the teacher acts as a motivator and
facilitator of student activities. The main goal in
applying cooperative learning model is according to
(Roger and Johnson, 1994) that "cooperative
learning is group learning activity organized in such
a way that learning is based on the socially
structured change of information between learners in
group in which each learner is held accountable for
his or her own learning and is motivated to increase
the learning of others". According to Clark and
Craig (1992) Learning media is one component of
learning that has an important role in learning
activities. The use of media should gain the attention
of teachers in every learning activity. Therefore,
teachers need to learn how to establish learning
media in order to streamline the achievement of
learning objectives in teaching and learning process.
In fact, learning media are often overlooked for
various reasons, such as: limited time to prepare
teaching preparation, difficulty in finding the right
media, unavailability of cost and others. This does
not really need to happen if every teacher has
knowledge and skills about instructional media.
Physical education, sports, and health are the
mediums to encourage physical growth, psychic
development, motor skills, knowledge and
reasoning, values appreciation (mental-emotional-
sportive-spiritual-social attitude), and healthy
lifestyle to stimulate the growth and development of
balanced physical and psychological quality.
Teachers as implementers of the curriculum must
certainly try to make it happen. Therefore, in
learning physical education, teachers should be able
to apply an innovative learning so as to achieve
learning objectives set previously. If the learning is
362
Faisal, F., Budiana, D. and Hermanu, E.
Implementation of Cooperative Learning by Using Audio-Visual Media in Table Tennis Game Learning.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 362-365
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
not applied correctly, then it cannot close the
possibility of learning results are more likely to be
verbal.
In the process of learning table tennis, learning
media give a positive influence so that the learning
objectives can be achieved.
Audio-visual media is a modern instructional
media that is in accordance with the times (science
and technology progress) covering the media that
can be seen and heard. When it is viewed from the
development of education, the media initially only
considered as teaching aids.
Based on observations in the process of learning
table tennis in class V SDN Cinunuk 02 Kab.
Bandung, the skills are still very low, especially in
terms of forehand drive and backhand drive skills,
for example when students at the time of forehand
drive and backhand drive often hit hard meanwhile
the distance is near and frequently the direction is
wrong, so they make it difficult for his friend.
Commonly students still hold the bat wrongly; they
even do not understand how to hold it, thus
hampering the process of learning table tennis. As a
result, students do not get maximum results in
understanding the material being taught. Such
learning results in student learning outcomes to
achieve learning objectives are not achieved.
2 METHODS
The research used in this research is Classroom
Action Research (PTK). The research location is at
SDN Cinunuk 02 Regency Bandung, Jln Raya
Cinunuk No. 752. Instruments used in the study of
the test of Tomolius as follows:
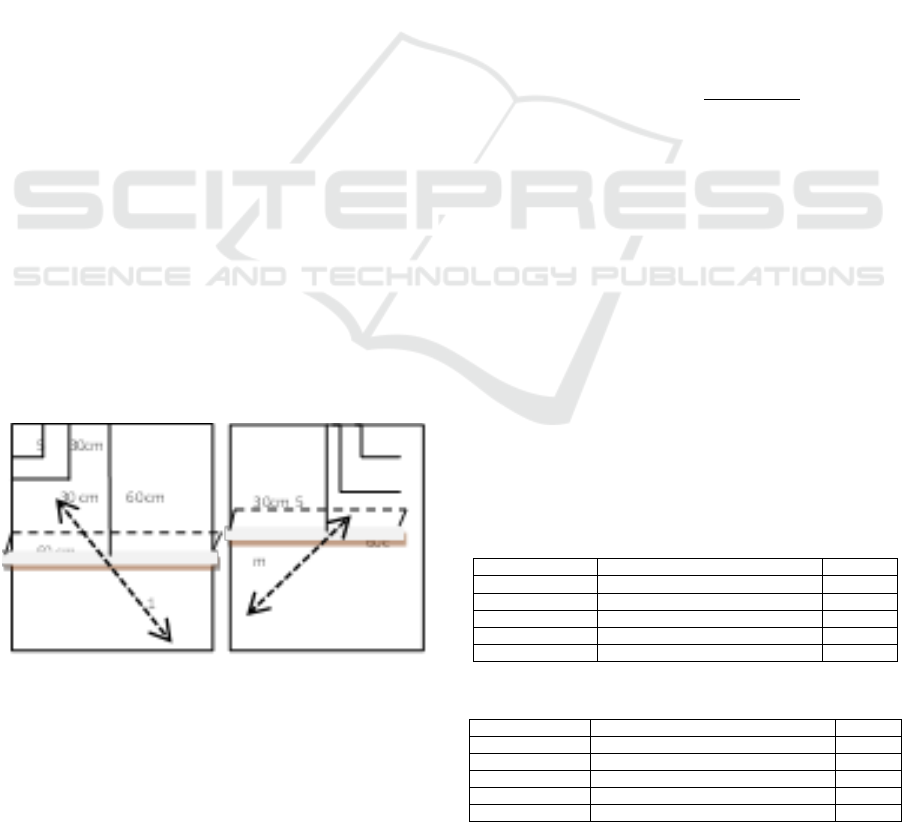
Figure 1: Test of forehand and backhand skills.
Test Instructions:
Subjects are told to warm up and practice
(practice);
The first ball starts from the testi;
The subject performed a raly forehand drive
diagonally for 30 seconds. After a 10 second
break, subjects perform raly again for 30
seconds.
Scoring Instructions:
The scoring was done by 3 people, one
recording officer, one holder of a stop watch,
and one person watching the ball enter the
target;
The ball that goes to the target area 30 cm
square gives the score 5 and the ball that goes
to the target area 60 cm square gives the score
3 and the ball that goes to the rest of the target
gives the score of 1;
The first ball of the testi is not recorded or not
counted;
The scorer sums up each raly score for 30
seconds;
The highest number of scores of raly for 30
seconds is valid.
Assessment Accuracy drive = Jumlah Skor x 100
150
(1)
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Based on the results obtained during the research
process, the discussion of the research findings from
this research is that applying cooperative learning
with audio visual media is very suitable to improve
the skills of forehand drive and backhand drive on
table tennis learning. Each action in the study also
increased. This is because the level of achievement
of the value obtained from satisfactory research with
the percentage of the average drive backhand in
Cycle II (Action 2) is 78.03% and the percentage of
forehand drive in cycle II (action 2) is 83.90%. as
shown in the table 1 and table 2:
Table 1: Average Percentage Score of Backhand Drive.
Activity
Cooperative Scoring Average
Note
Pre Observation
42,55%
Undone
Cycle I Action 1
48,07%
Undone
Cycle I Action 2
57,50%
Undone
Cycle II Action 1
68,75%
Undone
Cycle II Action 2
78,03%
Done
Table 2: Average Percentage Score of Forehand Drive.
Activity
Cooperative Scoring Average
Note
Pre Observation
45,17%
Undone
Cycle I Action 1
55,80%
Undone
Cycle I Action 2
66,63%
Undone
Cycle II Action 1
73,18%
Undone
Cycle II Action 2
83,90%
Done
Implementation of Cooperative Learning by Using Audio-Visual Media in Table Tennis Game Learning
363

In this classroom action research, there are
findings during the researcher, starting from the pre
cycle of class V students with homogeneous
characteristic, that is, all the students of grade V do
not know at all about table tennis, moreover the ones
such as forehand drive and backhand drive , but in
terms of the concept of motion a little know, so in
practice the students a little master of the skill, the
students of grade V only know that the punch that is
in the table tennis was only backhand and forehand.
Furthermore, in cycle 1 of action 1 students
begin to recognize forehand drive skills, and
backhand drives, the results have not been
successful, but there are improvements from the
previous one, seeing the movement of skills taught,
all students are still rigid in movement, as well as
lack of knowledge about these skills, cycle 1 action
2 the result of skill is increased, from rigid in
movement to stretchy and flexible in skill
movement, it's just that all students have not reached
the final score. In the 2nd cycle of 1st and 2nd action
all the students understand more about table tennis,
so the skill taught is enough and all the students
have reached the complete score that is more than
75.
According to Parker (in Huda 2013) defines
"small group co-operative as an atmosphere of
learning where students interact in small groups to
work on academic tasks to achieve common goals".
The main objective of cooperative learning is to give
students the knowledge, concepts, abilities and
understanding they need in order to become a happy
and beneficial member of society. While an
educational institution is competing to spur the
achievement of its students, and in the midst of
common issue of pluralism as it is today,
cooperative learning becomes very important.
Through various forms of communication, the
community groups do many activities or social
behaviour to achieve common goals. Relationship
interaction will run and get maximum results if an
organization or school that using tools. That tool is
called the media. Dotted from the tool (media) it can
be understood that, the media in relation to
communication interaction within a school or an
organization is very decisive. Media comes from the
Latin language and is the plural form of the word
medium which literally means intermediary or
introduction. So it can be understood that the media
is the intermediary or the sender's courier to the
recipient of the message.
In the world of education, we know that the term
of model or modelling, of which there are more
people prefer to use the term model and there are
others who use modelling communication. But
nowadays it has started to popularize the new term
"education media".
According to Rothschild (2004) Audio-visual
media is a media that has better capabilities, because
it covers both types of auditing (visual) and visual
(viewing) media. Audio Visual Media is an audio
visual tool which means materials or tools used in
learning situations to help writing and spoken words
to transmit knowledge, attitudes, and ideas.
Audio-visual media is the most complete media
because it has sound and image elements. Audio
visual media is a set of tools in delivering messages
that have the character of audio (sound) and visual
(picture) in conveying the contents of the message.
Playing is an activity that can be done by
everyone, from children to adults (Hard et al., 2012).
In childhood, playing is an inseparable part of life
and tends to be an essential basic need. Even
educational experts say that children are
synonymous with playing, because most of their
lives cannot be separated from playing.
According to Sukintaka (1992) and Coe et al.
(2006) the game is "a form of activity in physical
education. Children play or are given a game in the
framework of physical education lessons, then the
child will do the game with pleasure " because in
general, children feel happier to do the game, rather
than doing other sports. Because of that pleasure
then the child will reveal the original personality
when they play, whether it is the original character,
and habits that have shaped his personality.
If every learning objective of motion must end
with the appearance of a result, then nothing else
results it is motion skills. A person's skill in
completing the task of motion will be worth the
value of how far the person is able to complete the
task of motion given with a certain level of success,
the better the success rate in performing the task of
motion the better the person's skill is.
4 CONCLUSIONS
By using modification process and learning tool
there are improvements for table tennis learning
especially for forehand drive service skill, and
backhand drive, 1 result 1 cycle test result for drive
forehand skill gets result 55,80% while for backhand
drive skill test get result 48,07 %. Next result cycle 1
action 2 there is forehand drive 66,63% while for
backhand drive skill 57,50%. Next cycle 2 action 1
there is a forehand drive test 73,10% while for
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
364

backhand drive test 68,73%, As for cycle 2 action 2
there is forehand drive 83,90%. While backhand
drive skill 78.03% the results of all students have
reached its due score.
The researcher concludes that with the
application of cooperative learning with audio visual
media game can improve forehand drive and
backhand drive skill of class V student of SDN
CINUNUK 02 KAB.BANDUNG and useful to
apply in learning of physical education in
elementary school.
REFERENCES
Coe, D. P., Pivarnik, J. M., Womack, C. J., Reeves, M. J.,
Malina, R. M., 2006. Effect of physical education and
activity levels on academic achievement in children.
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 38(8),
pp.1515-1519.
Clark, R. E., Craig, T. G., 1992. Research and theory on
multi-media learning effects. In Interactive multimedia
learning environments (pp. 19-30). Springer, Berlin,
Heidelberg.
Dorigo, M., Gambardella, L. M., 1997. Ant colony
system: a cooperative learning approach to the
traveling salesman problem. IEEE Transactions on
evolutionary computation. 1(1), pp.53-66.
Hard, E. S. P., Schools, H. K., Breaks, I. C. P. A., Game,
B. O., 2012. Physical activity. Fitness and health:
Internatio.
Huda, M., 2013. Cooperative learning, metode, teknik,
struktur, dan model terapan, pustaka pelajar.
Yogyakarta.
Roger, T., Johnson, D. W., 1994. An overview of
cooperative learning. Creativity and collaborative
learning.
Rothschild, L. M., 2004. System and method of linking
items in audio, visual, and printed media to related
information stored on an electronic network using a
mobile device. U.S. Patent. 6,766,363.
Sukintaka, 1992. Teori Bermain, Departemen Pendidikan
Dan Kebudayaan Direktorat Jendral Pendidikan Tinggi
Proyek Pembinaan Tenaga Kerja Pendidikan. Jakarta.
Implementation of Cooperative Learning by Using Audio-Visual Media in Table Tennis Game Learning
365
