
Analysis of Local and Foreign Tourists Experience in Bandung
Sri Marhanah
Resort & Leisure Management Study Program, Faculty of Social Science Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jl.
Dr. Setiabudhi No. 229, Bandung, Indonesia
srimarhanah@upi.edu
Keywords: Local Tourist, Foreign Tourist, Tourism Experience.
Abstract: This study aims to analyze how the differences between foreign tourists and domestic tourists experiences
during their trip in Bandung. Problems in this research is how the perception of local tourists and foreign
tourist regarding tour. The population of this study is foreign tourists and domestic tourist who was or have
been traveling in Bandung. This research uses quantitative method using independent sample t-test. The result
of research shows that there are differences between perception of foreign tourists and the perception of local
tourists. There is a difference of tourist experience where foreign tourist is higher when compared with
domestic tourist.
1 INTRODUCTION
Bandung is one of the main tourism destinations in
West Java Province. Bandung has many interesting
places that become a tourist destination. Bandung has
an interesting tourisms such as nature tourism,
culinary tours, historical tours, and shopping tours.
Currently more than 70% Local Revenue Bandung is
achieved from the tourism sector. So Bandung City
Government increasingly and aggressively to market
the attractions of tourisms, not only to domestic
tourists, but also foreign tourists.
Bandung is tourist favorite destination, especially
during weekends and long vacation periods. As a
tourist destination, Bandung has a very diverse
tourism potential. Here is the distribution of tourism
in Bandung:
Figure 1: Distribution of Tourists in Bandung.
Source: www.tripadvisor.co.id.
Based on data figure 1 above can be concluded,
that tourists coming to Bandung come from various
regions in Indonesia. This indicates that Bandung is a
destination that is in great demand by tourists.
However, many factors that motivates tourists to
travel in Bandung. The author wants to compare how
the tourist experience is perceived by tourists both
foreign tourists and domestic tourists.
2 LITERATUR REVIEW
Tourism according to Marpaung (2002), tourism is
temporary travel by humans with the aim of getting
out of routine jobs, out of his residence While
according to Yoeti (1996) states, tourism is a travel
done for a while, the held from one place to another,
with the intent not for business or making a living in
the places visited, but solely to enjoy the journey for
the sake of sightseeing and recreation or to fulfill a
diverse desire ".
Smilansky (2009) states "People talk about
experiences every day because life is ultimately an
amalgamation of daily experiences. Experiences are
real. They are true life ". Experience is the main thing
of the life of consumers, for consumers consume not
only devouring or using products or services, but the
need for experience can be memorable when
consuming the product or service. Customer
experience or customer experience is also an
important need that needs to be provided by the
company.
According to Kotler and Keller (in Fandy
Tjiptono 2009) states, service is an act that can be
838
Marhanah, S.
Analysis of Local and Foreign Tourists Experience in Bandung.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business, and Philanthropy (ICIEBP 2017) - Transforming Islamic Economy and Societies, pages 838-841
ISBN: 978-989-758-315-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

offered by a party to another party that basically
intangible (intangible). Meanwhile, according to
Zeithaml et al. (2009), all product services are
experience, some are on a long duration some others
simple, some are common while others are fun and
unique. According to Walter et al. (2010) Consumer
experience / customer experience is defined as the
experience gained by consumers either directly or
indirectly about the process of service, the company,
the facilities and how a consumer interacts with the
company and with other consumers.
Meanwhile, according to Meyer and Schwager,
(2007) in Rageh et al. (2013) Consumer experience is
defined as the internal and subjective response of
consumers who require contact with the company,
either direct or indirect contact. In a journal entitled
"using ethnography research method to reveal the
underlying dimensions of customer or tourist
experience", Rageh et al. (2013) states that there are
eight dimensions of customer experience is comfort,
educational, hedonic, novelty, recognition, relational,
beauty, and safety with the following explanation: 1).
Comfort intended; Longer customers, especially
stressing the importance of convenience for the
customer experience. Consumers lead to the basic
amenities that DTW provides to ensure comfort and
also create relaxation. The findings are in accordance
with the theories presented by Crompton (1979),
Shoemaker (1989), and Otto and Ritchie (1996)
(Rageh et al., 2013). 2). Educational; Educational
experience or "learning by playing", as it is called by
(Jan, 2006), includes a mixture of exploration, mental
stimulation and excitement (Jan, 2006). It is also
characterized by a voluntary nature when learners
have a real choice of what, where, when, how, and
with whom they are studying, and it is stimulated by
the needs and interests of learners, Jan (2006) in rageh
et al. (2013) has indicated that there is strong
evidence suggesting that the educational experience
that consumers are looking for is already available in
the tourism industry. 3). Hedonic, illustrated that
hedonic is essential to the customer experience in
hospitality and tourism context. The hedonic
dimension combines excitement, enjoyment and
memorability (Otto and Ritchie, 1996). The Hedonic
aspects of the consumption experience relate to the
intangibility of services provided in the context of
hotels such as adventure holidays, unforgettable food
or luxurious hotel environments (Titz, 2008). 4).
Novelty is about the uniqueness and novelty, in this
dimension indicates that they are looking for new
things as the need for experience. (Lee and Crompton,
1992 in Rageh et al., 2013). In the study identified
four dimensions of novelty namely; changing from
routine, sensation, boredom-alleviation, and surprise.
5). Recognition; Recognition refers to important
customer feelings (Otto and Ritchie, 1996). From
customer comments, it is clear that staff shows certain
types of behaviors that make them feel important.
Recognition is identified as an important factor of
service experience. 6). Safety; In this study, (Sharm
el Sheikh in Rageh et al., 2013) identified security
against territory. This is particularly evident in
reviews where customers refer to perceptions of
security and security in tourism areas (Fujii and Mak,
1980; Pizam and Mansfeld, 1996). 7). Beauty; Pine
and Gilmore (1999) suggest that people appreciate
experiences that instill a sense of beauty and
appreciation. According to the perception of tourists
the beauty is "an aspect of the idealistic experience in
which an object, sound, or concept is believed to have
a formal quality of perfection" (Hagman, 2002). With
a sense of beauty there is a feeling of wholeness,
pleasure, reducing anxiety, admiration, joy, optimism
and satisfaction (Hagman, 2002). The appearance of
beauty can be created by humans, as found in art,
rework, architecture, or beautiful terrain (Stebbins
and Cohen, 1997). 8). Relational; that is identifying
another important component of a traveler that is a
relational or relational experience involving people or
the use of the product with others (Anderson et al.,
2007). Relational experience is an important factor in
tourist reviews. The results tend to confirm that social
interaction is an integral part of their experience.
3 METHODOLOGY
The method used in this research is quantitative
method and using t-test method in analyzing data. The
quantitative method according to Sugiyono (2014), is
a research method based on the philosophy of
positivism, used to examine the population or specific
samples, data collection using research instruments,
analysis and quantitative/statistical, with the aim to
test the hypothesis that has been established. By
quantitative method can calculate whether there is
difference of perception between local tourists and
foreign tourists to tourist experience and calculation
using Independent Sample T-Test. Respondents in
this study is local tourist who was traveling in
Bandung and also foreign tourists who were traveling
in Bandung.
Analysis of Local and Foreign Tourists Experience in Bandung
839
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Perception of Nusantara Tourists
Against Tourist Experience In
Bandung
Table 1: The Perception of Local Tourist on the Tourism
Experience.
No
Statement
Local tourists
Score
Percentage
Category
1
Comfort
891
42,43%
High
2
Educational
481
74,33%
Low
3
Hedonic
446
74,33%
High
4
Novelty
862
71,83%
High
5
Recognition
435
72,50%
High
6
Relational
628
69,78%
High
7
Safety
612
68,00%
High
8
Beauty
485
80,83%
High
Total
4840
69,25%
Medium
Table 2: Category of Local Tourists Perception
Simultaneously.
(4.840)
Very
high
Low
Medium
High
Very
high
1.500
2.700
3.900
5.100
6.300
7.500
Source: Research Preparation Data (2017)
Table 1 and table 2 is the result of the perception
of local tourists to the experience of tourists showed
an average score of 4,840, which according to the
categorization into the category of being. Therefore,
according to the perception of domestic tourists to the
experience of tourists viewed from the comfort,
education, beauty, new things have been considered
good by local tourists.
Table 3: The Perception of Foreign tourist on the Tourism
Experience.
No
Statement
Foreign Tourist
Score
Percentage
Category
1
Comfort
276
39,43%
Low
2
Educational
136
68,00%
High
3
Hedonic
156
78,00%
High
4
Novelty
292
73,00%
High
5
Recognition
158
79,00%
High
6
Relational
230
76,67%
High
7
Safety
715
71,67%
High
8
Beauty
159
79,50%
High
Total
2.122
70,66%
Very
high
Table 4: Category of Foreign Tourists Perception
Simultaneously.
(2.122)
Very
high
Low
Medium
High
Very
high
500
900
1.300
1.700
2.100
2.500
Source: Research Preparation Data (2017)
Table 3 and table 4 is the result of the perception
of tourists to the experience of tourists showed an
average score of 2,122, which based on categorization
into the category very high. Can be concluded,
according to the perception of tourists to the
experience of tourists viewed from comfort,
education, beauty, new things are considered very
good by foreign tourists.
4.2 Comparison of Foreign Tourist and
Local Tourists on the Experience of
Tourism
Table 5: Independent Sample T-Test.
Source: Research Preparation Data (2017)
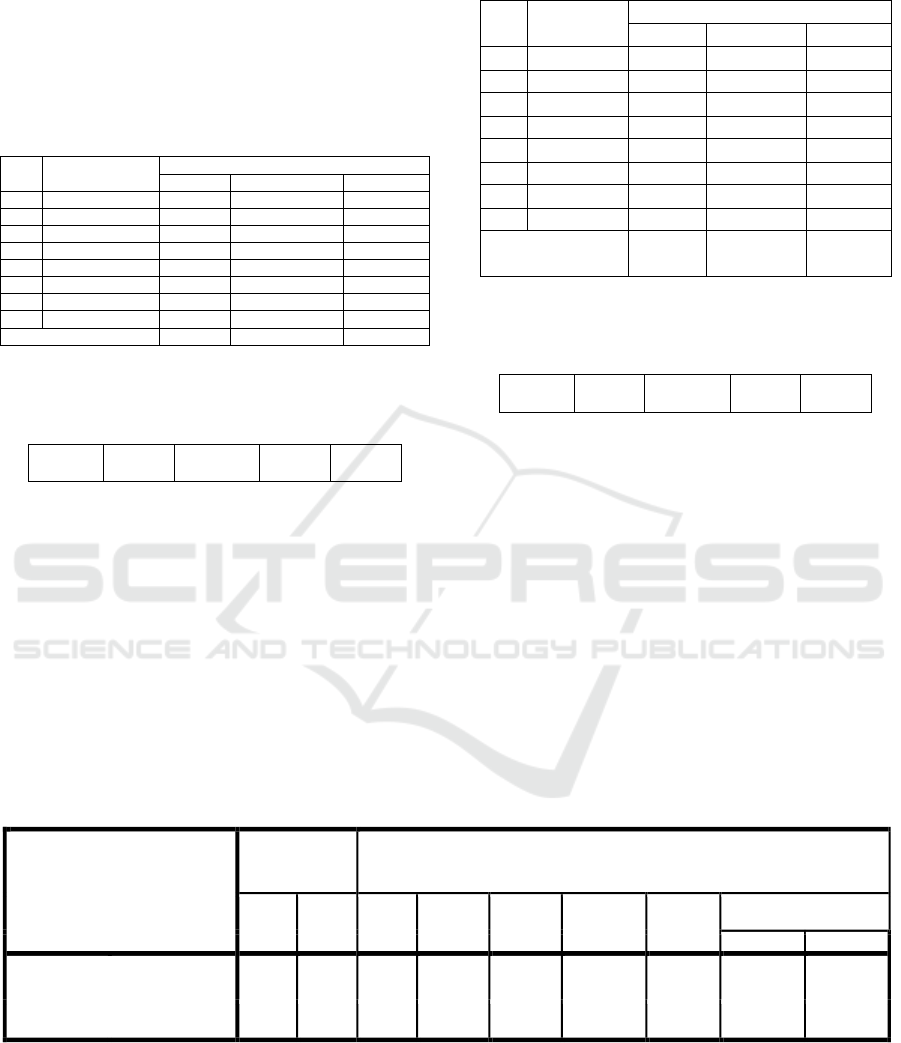
Based on the results of the test calculation, the
difference of two average data presented in table 6 is
known in the Levine Test for Equality of Variances
has a significance value of 0.340. (p> 0.05). It shows
that the two variance are the same, so the use of
variance to compare the mean of population (t-test for
Equality of Means) in t-test should be based on equal
variance assumed obtained t value equal to 3,775 and
significance level P = 0,000. The results show that P
<0.01, meaning there is a difference. It can be said
Table 3 .Independent Samples Test
Levine’s Test for
Equality of
Variances
t-test for Equality of Means
F
Sig.
t
df
Sig. (2-
tailed)
Mean
Difference
Std. Error
Difference
95% Confidence Interval of
the Difference
Lower
Upper
Score total
Equal variances
assumed
.922
.340
-3.775
78
.000
-4.05539
1.07415
-6.19385
-1.91692
Equal variances not
assumed
-4.042
36.959
.000
-4.05539
1.00336
-6.08847
-2.02231
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
840

that the degree of difference between local tourists
and foreign tourists is fundamentally different.
Table 6: Independent Sample T-Test.
Source: Research Preparation Data (2017)
When viewed from the table above obtained the
mean value of local tourists of 29.3365 and foreign
tourists amounted to 33.3919. the value means the
average total score on the local tourists of 29.3365
and the average total score with foreign tourists
amounted to 33.3919. Thus it can be said that the level
of difference in foreign tourists is higher when
compared with local tourists.
5 CONCLUSIONS
According to the perception of domestic tourists to
the experience of tourists viewed from the comfort,
education, beauty, new things have been considered
good by local tourists. Can be concluded, according
to the perception of tourists to the experience of
tourists viewed from comfort, education, beauty, new
things are considered very good by foreign tourists.
Based on the results of research indicate that,
perception of domestic tourists are in the category of
being, while the perception of foreign tourists are in
high category. And the level of difference of foreign
tourists is higher when compared with domestic
tourists.
REFERENCES
Anderson, C. A., Douglas A. G., Katherine, E. B., 2007.
Violent Video Game Effects on Children and
Adolescents: Theory, Research, and Public Policy,
Oxford University Press. New York.
Stebbins, R. C., Cohen, N. W., 1997. A Natural History of
Amphibians, Princeton University. New Jersey.
Crompton, J. L., 1979. Motivations for pleasure vacation.
Annals of Tourism Research. 6(4), 408-424.
Fandy, T., 2009. Strategi Pemasaran Jasa, CV. Andi.
Yogyakarta.
Fujii, E. T., Mak, J., 1980. Tourism and crime: implications
for regional development policy. Regional Studies. Vol.
14, pp. 27-36.
Hagman, G., 2002. The sense of beauty. International
Journal of Psychoanalysis. 83, pp. 661– 74.
Marpaung, H., 2002. Pengantar Pariwisata, Alfabeta.
Bandung.
Otto, J. E., Brent, R. J. R., 1996. The Service Experience In
Tourism. Tourism Management. Vol. 17. No. 3, pp. 165
174.
Pizam, A., Mansfeld, Y., 1996. Tourism, Crime and
International Security Issues, Wiley. New York, NY.
Pine, B. J., James, H. G., 1999. The Experience Economy:
Work Is Theater & very Pitana, Sosiologi Pariwisata.
Yogyakarta.
Rageh, A., Melewar, T. C., Arch, W., 2013. Using
Netnography Research Method to Reveal the
Underlying Dimension of the Costumer/Tourist
Experience. Qualitative Market Research: An
International Journal. Vol. 16 No. 2, pp. 126-149.
Shoemaker, S., 1989. Segmentation of the senior pleasure
travel market. Journal of Travel Research. 27(3), 14-
21.
Smilansky, S., 2009. Experiential Marketing: A Practical
guide to interactive brand experiences, Kogan Page.
London.
Sugiyono. 2014. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan
Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif, dan R&D, Alfabeta.
Bandung.
Titz, K., 2008. Experiential consumption: Affect—
emotions—hedonism,Butterworth-Heinemann. Oxford,
England.
Walter, U., Edvardsson, B., Asa, O., 2010. Drivers of
customers service experiences: a study in the restaurant
industry. Managing Service Quality. Vol. 20 No. 3,
pp.236-258.
Yoeti, O. A., 1996. Pengantar Ilmu Pariwisata, Angkasa.
Bandung.
Zeithaml, V. A. M. J., Binter, Gremler, 2009. Services
Marketing: Integrating Customer Focus Across the
Firm, McGraw Hill. NewYork, 15th edition.
Table 4. Group Statistics
research subject
N
Mean
Std. Deviation
Std. Error Mean
Score total
Local tourists
60
29.3365
4.28579
.55329
Foreign tourists
20
33.3919
3.74327
.83702
Analysis of Local and Foreign Tourists Experience in Bandung
841
