
The Two Blended Learning Model Designs (Moodle and Instagram):
A Comparative Study in University Level
Siti Nuraeni Muhtar, Rahayu Kariadinata, Yayu Nurhayati Rahayu and Alin Laelatulatifah
UIN Sunan Gunung Djati Bandung, Bandung, Indonesia
{siti.nuraeni, rahayu.kariadinata, yayunurhayatirahayu}@uinsgd.ac.id, alin.laelatul@gmail.com
Keywords: Blended Learning, Moodle and Instagram, University Level.
Abstract: IT development opens chances where students can learn anytime and anywhere overcoming the burden of
time and place. In line with this, blended learning is a choice where classroom activities and e-learning are
integrated to support learning. This study was aimed at determining blended learning effectiveness by using
two different media (Moodle and Instagram) for two different subjects (mathematical representation and
English-speaking). The participants were students of Mathematic Education in one of State University in
Indonesia. The method applied was comparing the significant result of both two subjects. The study found
that the effectiveness of blended learning in university level had a positive impact. It can be seen from the
students’ enthusiasm in accessing the lesson material on the website. There were differences in the
achievement of mathematical representation and English-speaking skill. Their achievement was considered
good. This study recommends that blended learning be applied to various subjects at university level.
1 INTRODUCTION
Blended learning is a new environment of teaching
and learning approach that combines traditional and
e-learning advantages. This environment has
stimulated teachers and researchers to find out the
new online applications or to enhance the existed
ones to be used in teaching learning purpose in line
with blended learning approach. There are various of
existed online applications that can be used as media
in blended learning i.e. Moodle and Instagram
(Grosch et al., 2014; Kharb and Samanta, 2016;
Okaz, 2015; Soler et al., 2017). These media are
believed can improve students’ achievement in
learning (Smith and Caruso, 2010). However, the
effectiveness of using these media as blended
learning approach still needs to be investigated
especially in Indonesian context (Baldwin‐Evans,
2006).
In previous studies relating to the effectiveness
of using media in blended learning approach show
the negative result and also positive result (Barge
and Londhe, 2014; Kintu et al., 2017; Nazarenko,
2015). All of these studies occupied Moodle as a
learning management system in applying blended
learning approach. Meanwhile, the using of media
social like Instagram as a learning media in blended
learning is recognized to be very rare (Abdillah,
2017; Pittman and Reich, 2016; Salomon, 2013)
especially in Indonesian context. Moreover, the
effort to utilize social media in teaching and learning
process should be reinforced (Zdravkova, 2016).
Therefore, this study is trying to find out the
effectiveness of using Moodle compare to Instagram
where both used as media in implementing blended
learning approach.
The focus of this study is on examining the
effectiveness of blended learning by using two
different online applications (Moodle and Instagram)
in two different subjects (Math and English) in
Indonesian context. The study subjects were 40
students of Mathematic Education in one of State
University in Indonesia who were took
Mathematical Representation subject and English-
speaking subject.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Dziuban, Hartman and Moskal (in Tang, 2013)
stated that “Blended learning should be viewed as a
pedagogical approach that combines the
effectiveness and socialization opportunities of the
classroom with the technologically enhanced active
Muhtar, S., Kariadinata, R., Rahayu, Y. and Laelatulatifah, A.
The Two Blended Learning Model Designs (Moodle and Instagram): A Comparative Study in University Level.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education (ICSE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 303-307
ISBN: 978-989-758-316-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
303

learning possibilities of the online environment,
rather than a ratio of delivery modalities”. In
addition, Kekang He (in Bath and Bourke, 2011)
thought that the blended learning is a combination of
the benefit of traditional and e-learning way, which
makes the instructors play the role of instruction,
enlightenment and monitoring and fully embody
students’ initiatives, enthusiasm and creativity as the
main stream of the learning process. His idea
emphasized the instructors and student’s roles in
teaching and learning course. Li (2007) defines
blended learning as “optimization selection and
combination of all the teaching elements which aim
to achieve the teaching aims.” Li thought it is
supposed to ask the instructors and students to imply
various teaching methods, modes, strategies, media
and technologies skillfully to teaching and learning
course.
The blended learning is an improved
combination which tries to combine the positive
aspects of conventional and e-learning. Students can
have two benefits of those learning that are real
experience of interaction the abundant resources,
which can give them more flexibility and
convenience to study.
2.1 Moodle
Moodle is the abbreviations of Modular Object-
Oriented Dynamic Learning Environment, a free and
open-source e-learning software developed by Marin
Dougiamas in 2004 (Tang, 2013). The software is
also known as a Course Management System
(CMS), a Learning Management System (LMS), or a
Virtual Learning Environment (VLE). It is based on
the social constructivism concepts that aim to
provide both educators and students a platform for
online interaction and collaboration. Moodle,
developed specifically for teaching, can provide a
variety of different teaching activities for students,
allow students to take full advantage of modern
network technology to exchange ideas and obtain
learning experience and build personal knowledge
system. With Moodle, kinds of teaching activities
can be integrated effectively, and students can take
advantage of functions of Moodle to implement
collaborative learning, which can fill the
conventionally closed learning environment into an
open interactive network learning, spoon-fed
learning into independent and personalized inquiry-
based learning.
The functions of Moodle include the
combination of a various assignments with kinds of
activities, the access to teaching material sources
such as presentations, documents, and files and also
kinds of assessment for students’ work (Dziuban,
Hartman, and Moskal, 2004).
2.2 Instagram
Instagram is one of mobile application that provides
users to instantly turn their mobile captures into
visually appearance images, that can be shared
online with others (McGough and Salomon, 2014).
Like other social media (Tumblr, Flickr, Twitter,
Facebook, etc) the captured images can be shared on
line. Instagram launched in October 2010, was
purchased by Facebook in April 2012, and currently
has approximately 130 million monthly active users.
On June 20, 2013, Instagram added the capability to
post short videos, a response to the growing
popularity of Vine, a six-second video app owned by
Twitter (Salomon, 2013).
Instagram is promoted the mobile experience
which combine the sophisticated smartphone
cameras and its popularity. Although it now provides
a Web site where users can view posts, images still
can’t be posted from a Web interface without a
workaround
3 METHODOLOGY
This research applies a quantitative design where
descriptive statistics are used for the student
achievements, t-tests for blended learning (Moodle
and Instagram) variables to determine if they are
significant in blended learning effectiveness and for
predictors of blended learning effectiveness.
This study is based on an experiment in which
learners participated during their study using an on-
line session of a blended learning design. A learning
management system (Moodle) and social media
(Instagram) was used and blended learning design
features were measured in relation to learning
effectiveness.
3.1 Teaching and Learning Process
with Moodle
The learning activities were conducted from the first
to fifth meeting. The first meeting of pretest which
was given in the classroom. at the 1st meeting the
teacher informed that the learning will be done by
using Moodle. At the second meeting, the teacher
gives instruction to the students on Moodle about the
subject matter of the cube and beam elements that
are ready to be learned and the students' worksheet
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
304
in the Moodle, all students are seen opening the
material that the teacher has given in the Moodle and
the students send the answer from the question
which the teacher gives in the Moodle in multiple
choices question. Then it is continued to the face-to-
face learning in the classroom discussing the
material that has been published by the teacher in
Moodle that has not been understood.
At the third meeting, the teacher instructs the
students in the Moodle to provide course material on
the surface area of the cube and the beam and also
the questions. Then students learn and send student
answers on the Moodle. Then continue to the face-
to-face learning in the classroom discussing material
that has not been understood in Moodle. At the
fourth meeting, the teacher instructed students via
Moodle to study the material of the cube and
volumes. In this activity, the students can open the
material that the teacher has published in Moodle.
Then continue to the face-to-face classroom
discussing the material that has not been understood
in Moodle. At the fifth meeting, the posttest is
conducted in face to face learning in the classroom.
3.2 Teaching and Learning Process
with Instagram
In teaching and learning process by using
Instagram the topic taken is one minute
speech. In the first meeting in classroom,
the teacher takes the pretest by only giving
the rubric and explain directly in the class
then give the students time for about an
hour to make a one minute speech. Then,
tells the student that the material will be
continued on Instagram application in the
certain time that has been agreed.
In the second meeting, the material is
delivered through instagram live. After the
teacher has finished the material then giving
the instruction to make the same one minute
speech video within an hour and upload the
video through Instagram and tag the teacher
to notify that they have made their
assignment. The rubric is also uploaded
through Instagram application.
4 FINDING AND DISCUSSION
After the implementation of pretest, treatment, and
posttest, then the normality test was conducted. The
result showed that both data were normal and it was
possible to continue the sample paired test by using
T-test. The T-test was applied to determine whether
or not there is an improvement after giving treatment
to the class using learning via Moodle and
Instagram.
The first test was conducted on the Mathematical
representation class where Moodle occupied as a
media. The results of paired sample test as follows:
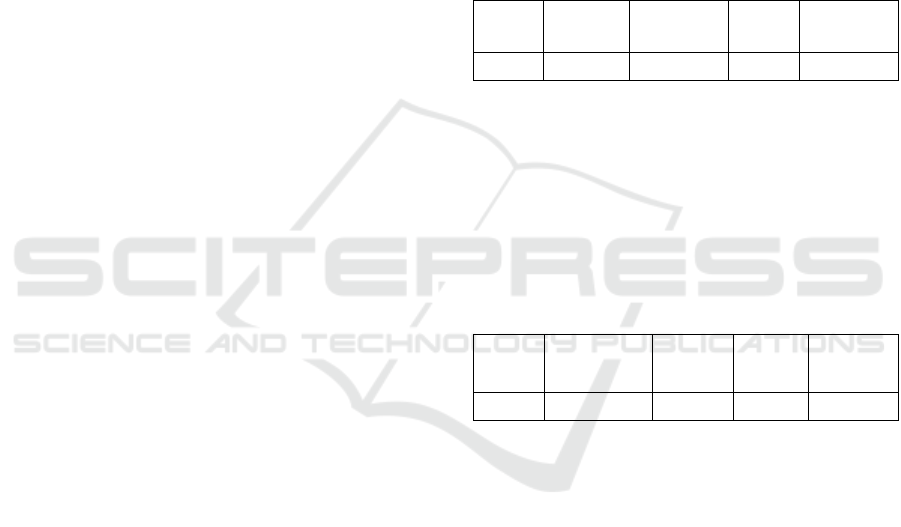
Table 1: Sample Paired Test Result Moodle Class.
Mean
Std.
Deviation
St. Error
Mean
T
Sig.
(2-tailed)
41.613
13.812
2.481
16.77
0.000
In Table 1, the Sig value is less than 0.05, which
has a sig value. 0.000 then it is interpreted that there
is a difference of increase between learning before
and after treatment. With the mean result of 41,613,
the difference is obvious.
The second test on the class that using
Instagram, the results of paired sample test as
follows:
Table 2: Paired Test Sample Instagram Class.
Mean
Std.
Deviation
St. Error
Mean
T
Sig.
(2-tailed)
3.875
4.090
0.647
5.992
0.000
In Table 2, the sig value is less than 0.05, which
has a sig value. 0.000 then it is interpreted there is a
difference of increase between learning before and
after treatment. With the mean result of 3.875, the
difference is obvious.
From the results, it is found some discussion
include the difference in the improvement of
students’ mathematical representation using Moodle
and English speaking improvement using Instagram.
From the result of t value of paired samples of
the two classes, it is found that both classes (Moodle
and instagram) obtained sig value. <0.05 ie with sig
value 0.000. It means that there is a difference in the
improvement of students' representation ability in
both classes. It supports the previous studies
(Baldwin‐Evans, 2006; Kintu et al., 2017;
Nazarenko, 2015; Okaz, 2015; Smith and Caruso,
2010) that also proved that blended learning can
The Two Blended Learning Model Designs (Moodle and Instagram): A Comparative Study in University Level
305

improve students’ ability in this case the students’
mathematical and English representation.
The using of Instagram also has proven that
social media can be used to support teaching and
learning activity and also to improve student’s
ability in this case students’ ability in speaking. In
line with this result, Abdillah (2017) stated that
social media can be utilized as blended learning
tools that can improve students skill especially in
language skill. Research suggests that student
involvement leads to higher levels of learning and
contributes to outcomes that include persistence,
satisfaction, and academic achievement (Astin,
1999).
5 CONCLUSIONS
The improvement of modern technologies makes it
feasible to perform blended learning, which relates
to the diversification of teaching resources. Online
environment is suitable for university students to
support their self-learning process. Even though,
face-to-face instructions is still become the good
choice. The use of social media and online media in
blended learning can become the combination of
online learning and offline learning where it still has
the significant result to improve students’ skill, self-
controlling and motivation. Inevitably, there are
some difficulties still remain when blended learning
is implied. It needs more learners’ commitment,
more teachers’ devotion and knowledge more
integration between traditional courses and modern
technologies.
REFERENCES
Abdillah, L. A., 2017. Exploring Students Blended
Learning Through Social Media. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1701.07193.
Astin, A., 1999. Student involvement: A developmental
theory for higher education. Journal of College
Student Development. 40.
Baldwin‐Evans, K., 2006. Key steps to implementing a
successful blended learning strategy. Industrial and
Commercial Training. 38, 156-163.
Barge, P., Londhe, B. R., 2014. From Teaching, Learning
to Assessment: MOODLE Experience at B'School in
India. Procedia Economics and Finance. 11, 857-865.
Bath, D., Bourke, G., 2011. The blending of blended
learning: An experiential approach to academic staff
development. Changing Demands, Changing
Directions. Proceedings ascilite Hobart. 133–138.
Dziuban, C. D., Hartman, J. L., Moskal, P. D., 2004.
Blended learning: Educause Center for Applied
Research Bulletin.
Grosch, M., Berger, R., Gidion, G., Romeo, M., 2014.
Which Media Services do Students Use in Fact?
Results of an International Empirical Survey. Procedia
Social and Behavioral Sciences. 141, 795-806.
Kharb, P., Samanta, P. P., 2016. Blended learning
approach for teaching and learning anatomy: Students’
and teachers’ perspective. Journal of the Anatomical
Society of India. 65, 43-47.
Kintu, M. J., Zhu, C., Kagambe, E., 2017. Blended
learning effectiveness: the relationship between
student characteristics, design features and outcomes.
International Journal of Educational Technology in
Higher Education. 14.
Li, J., 2007. Establishing an environment of information
courses. Huadong Normal University Publishing
Press. Shanghai.
McGough, B., Salomon, D., 2014. Engaging Students
Through Social Media.
Nazarenko, A. L., 2015. Blended Learning vs Traditional
Learning: What Works? (A Case Study Research). The
XXVI Annual International Academic Conference,
Language and Culture. 27–30 October 2015, 200, 77-
82.
Okaz, A. A., 2015. Integrating Blended Learning in
Higher Education. The Proceedings of 5th World
Conference on Learning, Teaching and Educational
Leadership, 186, 600-603.
Pittman, M., Reich, B., 2016. Social media and loneliness:
Why an Instagram picture may be worth more than a
thousand Twitter words. Computers in Human
Behavior, 62, 155-167.
Salomon, D., 2013. Moving on from Facebook: Using
Instagram to connect with undergraduates and engage
in teaching and learning. College and Research
Libraries News. Vol 74, No 8.
Smith, S. D., Caruso, J. B., 2010. Research Study (Vol. 6).
EDUCAUSE Center for Applied Research. CO.
Soler, R., Soler, J. R., Araya, I., 2017. Subjects in the
Blended Learning Model Design. Theoretical-
Methodological elements. Education, Health and ICT
for a Transcultural World. 237, 771-777.
Tang, J., 2013. The Research on Blended Learning of ESL
Based on Moodle Platform. Studies in Literature and
Language, 6, 30.
Zdravkova, K., 2016. Reinforcing Social Media Based
Learning, Knowledge Acquisition and Learning
Evaluation. 2nd International Conference on Higher
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
306

Education Advances,HEAd'16, 21-23 June 2016,
València, Spain, 228, 16-23.
The Two Blended Learning Model Designs (Moodle and Instagram): A Comparative Study in University Level
307
