
Kindergarten Future Teacher’s Perception on Teaching English to
Young Learners through Thematic-based Instruction
Desiani Natalina Muliasari, Endah Silawati, and Winti Ananthia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Kampus di Cibiru, Jl. Raya Cibiru, Bandung, Indonesia
{desianinm, endah_silawati,winti}@upi.edu
Keywords: Teachers’ perception, theme-based Instruction, EYL.
Abstract: This study is a part of on-going research that focuses on the empowering kindergarten future teachers in
teaching EYL. The article aims at exploring the future teachers’ perception during teaching EYL to
kindergarten students through theme-based Instruction. It describes the future teachers’ challenges and
strengths. Theme-based Instruction is one of the learning activities that drives hollistically and meaningfully.
This is a qualitative study that involved eight participants of Future Teachers of Kindergarten. The results
show that the future teachers found difficulties in giving English instruction, managing class and applying
learning media. On the other hand, the study shows that the future teachers have potential skill to teach EYL
though they are non English major students.
1 INTRODUCTION
In facing globalization era, it is highly recommended
for an individual to have English competency in order
to participate and compete in global society. English
is considered important in a more globalized era as
one of indicators for personal and professional
capabilities in the 21st century (Trilling & Fadel,
2009). It is believed that English should be introduced
as earlier as possible specifically starting from
children as they are in their phase of acquiring the
language (Siraj-Blatchford and Clarke, 2000; Clarke,
2009). Consequently, some parents who realize the
importance of English for their children’s future
success request the teaching of English to be started
in the preschool level (Ananthia, Harun & Silawati,
2015). Therefore, some of early childhood
educational institutions offer English as one of their
learning subjects, though in Early Childhood
Education (ECE) curriculum, both Ministry
Regulation (Permen) No. 58 year 2009 and 2015 ECE
curriculum contend that English learning is not
compulsory to be introduced to children in preschool
and kindergarten.
Learning English gives access to children to learn
not only the language but also foreign cultural
appreciation (Musthafa, 2001). The children will then
improve their international understanding, such as
tolerance, cultural diversity and peace (Reich in
UNESCO 1994) as one of the skills needed in 21st
century.
Because of that, introducing English as a foreign
language in early years should be done correctly and
effectively. The children are best in imitating and
absorbing new language. Thus, the teacher should
have the skills of teaching English to children
especially teaching English as a foreign language in
the Indonesian context. Recent study shows that most
of kindergarten teachers do not have skills of teaching
English to Young Learners (Harun & ananthia, 2013).
The teachers were not prepared to teach EYL during
their studies. Meanwhile, EYL practices needs
teachers who are able to integrate their English
language ability and their pedagogical skill (Rahman
& Akhter, 2017). Therefore, It is a must to prepare
future teachers to be skillful in teaching English to
young learners.
Early Childhood Education (ECE) study
program of UPI Cibiru Campus is one of the
institutions in Indonesia that educates the future
teachers of ECE. According to the employer’s
satisfaction survey of ECE study program graduates,
conducted by the Unit of quality control in 2011-
2016, the graduates have low EYL teaching skills.
Consequently, the quality of ECE study program
should be improved by conducting research in the
study program courses, especially the course titled
Bahasa Inggris untuk Anak Usia Dini (English for
Young Learners). Moreover, based on the
Muliasari, D., Silawati, E. and Ananthia, W.
Kindergarten Future Teacher’s Perception on Teaching English to Young Learners through Thematic-based Instruction.
DOI: 10.5220/0007162300750079
In Proceedings of the Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference
on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education (CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017) - Literacy, Culture, and Technology in Language Pedagogy and Use, pages 75-79
ISBN: 978-989-758-332-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
75

prelimenary study, it was found that all teachers in
four Kindergartens in Bandung taught English
without clear concept and objectives. Most teachers
taught English by translating the English words into
mother tongue (Bahasa Indonesia) or vice versa.
On the other hand, one of the EYL learning
models aassumed to be effective in the context of
foreign language learning is Theme-Based
Instruction (TBI) model. It is one of the language
learning models that highlights themes as the center
of learning (Gao, 2011; Dermody, 2004). This model
is suitable in EYL context in the kindergarten since
their learning activities are organized into themes and
it is in line with the Early Childhood curriculum 2013
in Indonesia. The 2013 curriculum states that theme
is the basic concept of developing children activities
in early childhood education (Permendikbud, 2013).
In implementing TBI model, the teacher could
face some challenges. Therefore, their perception is
important to be analyzed as the basis data for the
improvement. This article will picture the teachers’
perceptions on teaching EYL through TbI model.
2 THEORITICAL REVIEW
2.1 Teaching English to Young Learners
(EYL)
English is taught to the children based on the Critical
Period Hypothesis (CPH) in which every child has a
golden phase of life, when the child is exposed to a
particular language, the language would be
acquired/learnt successfully, including the second
language (Brewster, Ellis & Girard, 2002; Phillips,
1993). In addition, children are faster learners than
adults in learning foreign language (Santrock, 2007).
Those assumptions are in line with the study proposed
by Johnson and Newport in 1991 which saw that
immigrants from China and Korea who lived in
Amerika from the age of 3 to 7 years had good
English performance than teenagers or adults
(Santrock, 2007).
To teach children a second language requires
integrated skills; language and pedagogical skills.
There are some considerations that may help give
some practical approaches in teaching children,
namely, intellectual development, attention span,
sensory input, affective factors and authentic
meaningful language (Brown, 2001). The teacher
should comprehend these factors in managing
effective learning activities
2.2 Thematic Based Instruction in EYL
The Theme-Based Instruction model is one of
language learning models that highlight themes as the
centre of learning (Gao, 2011; Dermody, 2004). This
model could be implementing in language learning in
which connecting the learning context in to themes
(Brown, 2011). This model is suitable for EYL
context in kindergarten where learning is organised
into themes. Learning the language should also be
mediated through language use (Gibbons, 2003)
based on the themes.
The main aspects of this model are automaticity,
meaningful learning, intrinsic motivation and
communicative competence (Brown,2001). These
aspects are in line with the EYL basic concepts. This
can be assumed that this model is effective in EYL
practices. It is hoped by improving the course, the
future teachers’ EYL teaching skills can be also
improved.
3 METHODOLOGY
This study employed a qualitative research design in
regard to the consideration that the researcher focused
on the observing, interpreting, and understanding
what the future teachers experienced. The participants
of the study were eight future teachers of Bahasa
Inggris untuk Anak Usia Dini (English for Young
Learners) class. The data was collected through
observation and questionnaire. The observation was
conducted to observe the future teachers’ activities
during their teaching practice. The open ended
questionnaire was employed to explore the future
teachers’ perception of teaching English to young
learners and their teaching practices. The observation
was recorded. And the data from observation and
questionnaire were analysed qualitatively to answer
the research questions addressed in the study. The
analysis triangulated all data needed. The data were
interpreted, reviewed, and discussed.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Future Teachers’ Challenges
The data from the questionnaire and observation
revealed that there were some challenges that should
be faced and overcome by the future teachers. Those
challenges were first, low confidence in speaking
English. The data showed that the future teachers
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
76
were not confident (Ahn, 2011) when they were
required to have full English in teaching the children.
All the future teachers admitted that they were really
inconfident in delivering the activities in English. The
future teachers described that they were very nervous
and easily forgot what to say in English. The data also
showed that they needed to be motivated and had
practiced a lot especially practicing their
pronunciation. For example, most future teachers
pronounced the word “answer” or “banana” as it was
written or pronounce as mother tongue. As the teacher
who use English as the language of instruction thus
they needed to practice all the time as they were going
to be the role model (Archana & Usha Rani, 2017).
Second, the future teachers found difficulties in
giving English instruction. Out of eight future
teachers, seven of them stated that they had
difficulties in giving English Instruction. They did not
get used to have English instructions. Moreover, the
children of “A” kindergarten were never experienced
learning English with English as language of
instruction. This situation made the future teachers
struggle a lot. Thus the future teachers were managed
to have simple instructions of English to make the
children get used to and understand English
instruction. The future teachers acknowledged that
they needed to repeat many times and recast
(Gibbons, 2003; Baleghizadeh & Heidar Abdi, 2010)
a word or an order to have the children understand.
Once, the future teacher also claimed that they did not
realize they uttered the mother tongue/ Bahasa
Indonesia when they were trying to let the students
know something or when they were ordering the
students. For example:
Future teacher: Okay children…come on look at
the story in LCD. Sudah?.
Children: Sudaaaah.
Third, managing class. Class management is
important and essential especially when teachers are
dealing with children (Rahman &Akhter, 2017). It is
challenging as the children have short attention span
(Paxton & Shoemake, 2007; Brown, 2001). Five
future teachers were having difficulties in managing
the class in certain situations. The future teachers
explained that there were some children who wanted
to sit near the LCD projector as they wanted to play
with it. Though the teacher had managed them to sit
little bit away from the LCD projector but they were
going back several times. Other children showed
“picky” friends. It means that they did not want to
have a group with certain friends. Another child was
busy with her squishy toys and she influenced her
friends to play it too. It needed the future teachers’
strategy to manage the children and to have them
focus on the activities. They were challenged to deal
with this kind of situations and they learnt classroom
management application.
Fourth, applying learning media. Learning media
is very important for teachers because it helps the
learning process of the children. Four future teachers
were having obstacles in applying the media. They
found that the learning media was less interesting for
the children though it was colourful (Rao, 2014) and
two of the future teachers realised that they were lack
of the media. So they tended to repeat the video
playing and it made the children bored.
Fifth, the future teachers also found difficulties in
creating assessment tool to measure the children’s
English based on the theme based instruction. Most
of the teachers described that they had the difficulties
in creating the assessment tools and activities. They
had learned and practiced on how to asses the
children’s English ability but they found diffculties in
applying the assessment in the real situation. For
example, one future teacher showed that she wanted
to assess the children pronunciation. So she drilled all
students at one time for three words. It took too much
time and made the other children bored and played
with other children. Drilling was not appropriate
technique in assessing the students’ pronunciation.
Drilling is contradictory with the concept of authentic
assessment (Gullo, 2005).
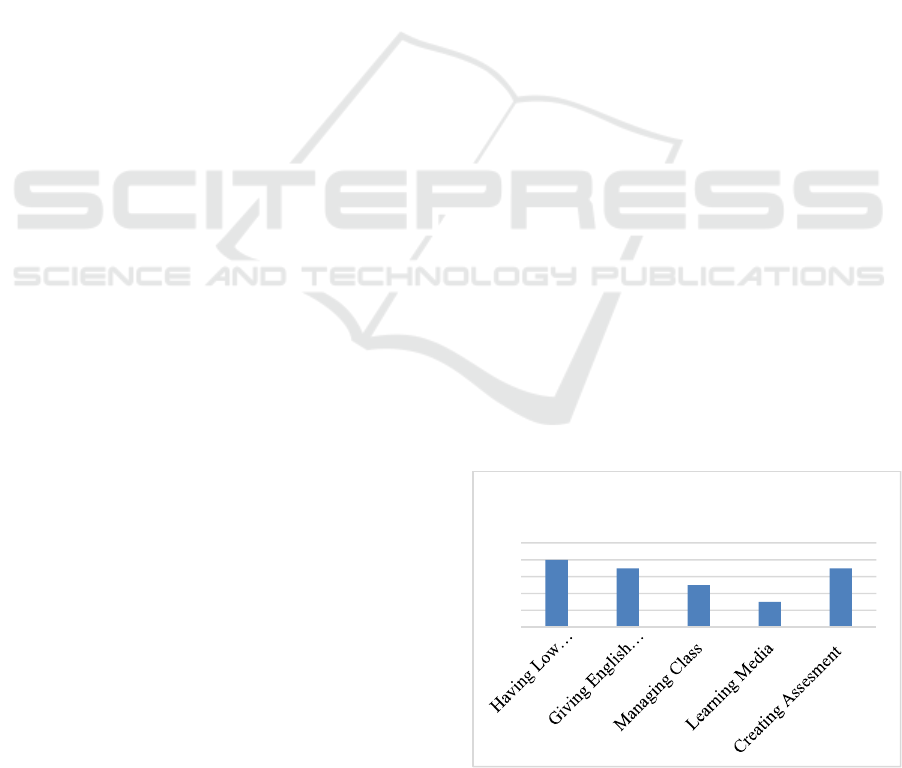
The five challenges showed from the data are
compared in the chart below. It can be seen that the
most challenging factor emerged from the future
teachers is low of confidence. The second challenging
factor are giving English instructions and creating
assessment. Managing class is the next challenging
factor , and Learning media is the last challenging
factor.
Figure 1: Future Teachers’ Challenges.
0
2
4
6
8
10
Degree of Comparison of Future
Teachers's Challenges
Kindergarten Future Teacher’s Perception on Teaching English to Young Learners through Thematic-based Instruction
77

4.2 Future Teachers’ Strengths
The future teachers were having their first experience
in teaching English to kindergarten children. Though
they are non English major students but they have
potential skills to teach EYL. The first of their
potential skills is that they understood the Thematic
Based Instruction. The future teachers prepared their
lesson plan, material, media including the teacher’s
talk based on the theme that the children were going
to learn. Though they needed to correct the lesson
plan and teachers’ talks several times but they
performed it well. Most of them were succeeded in
applying the activities as planned. They easily
understand how to create activities based on the
theme as they had background knowledge of the
Thematic Based Instructions. The future teachers
explained that they also learnt TBI from other
subjects and from the Early Childhood national
curriculum of 2013
Second, the use of the media. Some of the future
teachers (four future teachers) presented colorful and
interesting media (Rao, 2014). They also brought the
real media such as real fruits, real food, etc to
construct meaning and understanding of the children
(VanScoter, 2001; Samuelsson & Carlsson, 2008).
The future teachers also prepared the used materials
to make something such as bus miniature from used
cardboard. They also integrated ICT in the activities,
and it triggered the childrens’ attention to involve in
the activities.
The third potential skill is various teaching
techniques. The future teachers applied kinds of
activities such as the use of Total Physical Response
(Chen, 2010; Brown, 2001) through games or
exercises such as doing exercises when the theme is
my body. Another activity was hands-on experiences
(Cutter- Mackenzie.et.al, 2014) such as smelling,
touching and tasting the food or fruit. The future
teachers also apllied song as learning techniques to
overcome boredom and they integrated the indoor and
outdoor activities.
Figure 2: Future Teachers’ Strengths.
The data of the chart shows that the future
teachers’ strengths mostly on their understanding of
the Theme-Based Instruction followed by the various
techniques in applying TBI and the use of colourful
and various media. The findings of the this study
shows that the future teachers need more efforts to
develop their potential skills. They are able to always
practice English in order to overcome the challenges
they face. Competent users of a language are able to use
the language in real-life. The data also motivated the
researchers to have more efforts in preparing the
future teachers in teaching EYL. The future teachers
have their potential skill to be developed and they
have chances to be better.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The future teachers are prepared to face the reality in
teaching English to young learners. It was their first
experience in teaching English to young learners and
they found challenges and also strengths. The
challenges were low of confidence of the future
teachers, difficulties in giving English instruction,
managing class, creating learning media, and creating
assessment. The strengths shown from the data were
the future teachers’ understanding of the Thematic-
Based Instruction, the use of the media, and the
variations of teaching techniques. After the teaching
session all teachers reflected their planning, the action
and also their assessment. The important things that
should be noted from the findings are further efforts
to prepare the future teachers in overcoming the real
situations. The future teachers should have many
practices and motivate themselves to be confident.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was funded by UTU UPI in the program
of Hibah Penelitian Peningkatan Mutu Pembelajaran,
LPPM UPI year 2017. We are grateful to the students
of PG PAUD UPI who become the teachers’ model,
and to the students of Kasih Sayang Bunda
Kindergarten who become the participants of this
study.
REFERENCES
Ahn, K. 2011. Learning to teach under curriculum reform:
The practicum experience in South Korea. In Johnson,
K. E & Golombek, P(Eds). Research on Second
Language Teacher Education,pp. 239-253. New York:
Routledge.
0
2
4
6
8
Understanding
TBI
Using Media Various
Teaching
Techniques
The Future Teachers' Strength
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
78

Ananthia, W., Harun, C. A. & Silawati, E. 2015. The
analysis of teacher’s talk in teaching English to children
at Indonesian kindergarten. A paper presented at
Seminar Tahunan Linguistik (SETALI) 2015. A
proceeding.
Archana, S & Usha Rani K. 2017. Role of A Teacher in
English Language Teaching. International Journal of
Educational Science and Research. Vol 7, issue 1 Feb
2017, 1-4.
Baleghizadeh, S & Heidar Abdi. 2010. Recast and Its
Impact on Second Language Acquisition. International
Journal of Language Studies. Vol 4 (4), 2010, pp 57-68
Brewster, J., Gail Ellis and Denis Girard. 2002. The
Primary English Teacher’s Guide. London: Penguin.
Brown, H. Douglas. 2001 Teaching by Principles: an
Interactive Approach to Languange Pedagogy, Second
Edition. New York: Longman
Chen, L. 2010. Application of Total Physical Response In
Children’s ESL Education. Retrieved on 14 October
2017 from
http://minds.wisconsin.edu/bitstream/handle/
Clarke, P. 2009. Supporting Children Learning English as
a Second Language in the early years. Victoria
Curriculum and Assessment Authority.
Cutter-Mackenzie.et.al. 2014. Young children’s play and
environmental education in early childhood
education.Springbrief in education
Dermody, B. 2004. Improving student learning through
theme based curriculum design and team: An action
research study. A Dissertation in Dublin Institute of
Technology. Dublin: Learning, Teaching &
Technology Centre.
Gao, F. 2011. Theme-based group teaching of College Oral
English: Endorsed by Students in Chinese EFL
Context. English Language Teaching,Vol. 4 No. 11.
Gibbons. 2003. Mediating Language Learning: Teacher
interactions with ESL Students in content based
classroom. TESOL Quaterly, Vol 37, No. 2, pp. 247-
273
Gullo, D. 2005. Understanding Assessment and Evaluation
in Early Childhood Education.
Harun, C.A & Ananthia, W. 2013. Model Self-Training
untuk Meningkatkan Keterampilan Story Telling
Mahasiswa dalam Pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris di SD.
Hibah Penelitian Peningkatan Mutu Pembelajaran.
LPPM UPI Bandung. Unpublished Research Report.
Musthafa, B. 2001. Communicative Language Teaching in
Indonesia: Issues of Theoritical Assumptions and
Challenges in Classroom Practice. Journal of Southeast
Asian education Volume 2 Number 2
Paxton, J. & Shoemake, T. 2007. Fun Ways to increase
Children’s Attention Span. A paper presented in ACEI
International Conference and Exhibition Tampa
Florida. 3-5 May 2007.
Phillips, S. 1993. Young learners. Oxford: Oxford
University Press.
Rahman, S.M.S & akhter, A. 2017. Skills Teaching in ESL
Classroom: Discrete Vs Integrated. International
Journal of English Language Teaching, pp. 32-39
Vol.5No. 4.
Rao, B.M. 2014. Use of media as instructional tool in
English Language Teaching (ELT) at undergraduate
level. International Journal of English and Literature,
Vol 5(6), pp. 141-143.
Samuelsson, I.P & Carlsson, M.A. 2008. The playing
learning child: Towards a pedagogy of Early childhood.
Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research, 52 (6),
pp 623-641. Routledge.
Santrock, John. W. 2007.Child Development Eleventh
Edition. New York: Mc Graw- Hill International.
Siraj-Blatchford & Clarcke. 2000. Supporting identity,
diversity and language in the early years. Open
University Press, Bucks.
Trilling, D.& Fadel, C. 2009. 21 Century Skills, Learning
for Life in Our Times. San Francisco: John Wiley &
Sons.
UNESCO. 1994. International Practical Guide On the
Implementation of The Recommendation Concerning
Education For International Understanding Co-
operation and Peace and Education Relating To
Human Rights And Fundamental Freedom, Edited by
Brigitte Reich and Valeri Pivovarop. Paris: United
Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural
Organization.students in Chinese EFL context. English
Language Teaching, 4(1), 33-41.
VanScoter. 2001. Technology in Early Childhood
Education: Finding the Balance. Northwest Regional
Educational Laboratory.
Kindergarten Future Teacher’s Perception on Teaching English to Young Learners through Thematic-based Instruction
79
