
Basics of Acounting Learning with Scientific Approach
Lilik Sri Hariani and Endah Andayani
Universitas Kanjuruhan Malang, Jl. S Supriyadi 48, Malang, 65148 Indonesia
liliksrihariani@unikama.ac.id
Keywords: Critical thinking, scientific approach.
Abstract: This paper aims to analyze the improvement of students' critical thinking skills with a scientific approach.
The experimental method used is quasi experiment with one group pretest-postest design with 42 students
from management program University of Kanjuruhan Malang. The instrument used is a critical thinking skill
test. From the experiments conducted obtained the result that the introduction of accounting based on
scientific approach can significantly improve students' thinking ability. This is due to a scientific-based
learning approach involving students directly in the learning activities and requires high-order thinking skills
so as to train students to develop the ability to think critically better. The results of this study are expected to
contribute for improving accounting pursuits.
1 INTRODUCTION
A scientific approach is a learning process designed
in such a way that learners actively construct
concepts, laws, or principles with characteristics; 1)
student-centered, 2) involves the process of science
skills in constructing concepts, laws, or principles, 3)
involves potential cognitive processes in stimulating
intellectual development, especially high-level
thinking skills, and 4) developing student character
(Daryanto, 2014; Hosnan, 2014). Critical thinking
contains mental activity in terms of solving problems,
analyzing assumptions, rationalizing, evaluating,
conducting investigations, and making decisions. In
the decision-making process, the ability to search,
analyze, and evaluate information is very important.
Critical thinking skills are able to meet the needs of
future competitions where learners' abilities are
needed that is communication, creative, and critical
skills (Kemendikbud 2013).
The critical thinking skills of learners need to be
enhanced for their success in education and in
community life. Critical thinking skills can be
improved through the learning process with various
models. Based on the results of research, critical
thinking skills can be improved by the application of
learning models in accordance with the
characteristics of each learner, such as research
conducted Wulandari, Sjarkawi, and M. Damris
(2011), Fachrurazi (2011), Afrizon, Ratnawulan, and
Fauzi (2012), Syahbana (2012), Thompson (2011),
Rasiman (2015).
The problem for some new students, learning
introductory accounting is something that is less
interesting and tend to be boring. They have
difficulties in understanding about accounting. The
learning process and misaligned understanding of
accounting will hamper accounting and accounting
development as a science that actually has a wide
range, therefore accounting learning needs to
emphasize the provision of direct experience to
develop student competence. Providing direct
experience is expected to improve students' critical
thinking skills. Critical thinking skills of accounting
students may be developed in learning by using a
scientific approach, as it has been widely used in
exact learning.
Critical thinking is one of the higher-order
thinking processes that can be used in the formation
of a student's conceptual system, as Heong et al
(2011) and Wardana (2010) have pointed out. In
addition, critical thinking of learners can be
developed through the provision of meaningful
experience. The meaningful experience in question
can be either verbal or written opinion. Meaningful
experience can be done by using a scientific
approach. Learning by using a scientific approach can
make students active and creative, students not only
listen but they can participate in the learning process
(Hariani and Andayani, 2016)
Hariani, L. and Andayani, E.
Basics of Acounting Learning with Scientific Approach.
In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities (ANCOSH 2018) - Revitalization of Local Wisdom in Global and Competitive Era, pages 331-334
ISBN: 978-989-758-343-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
331

Therefore, the purpose of research to analyze the
improvement of students' critical thinking skills with
scientific approach. The experimental method used
was quasi experiment with one group pretest-postest
design with 42 management students. The instrument
used is a critical thinking skill test. From the
experiments conducted obtained the result that the
introduction of accounting based on scientific
approach can significantly improve students' thinking
ability. This is because the learning-based scientific
approach involves students directly in learning
activities.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
The experimental method used is quasi experiment
with one group pretest-postes design. The sample of
this research is the first semester students of
management program of Economics and Business
Faculty University of Kanjuruhan Malang which is
taking course basics to Accounting 1. The instrument
used is critical thinking ability test which consists of
essay-based problem based on indicator that is 1)
interpreting, that is categorizing and classify; 2)
analyze, test and identify; 3) evaluate, that is consider
and conclude; 4) draw conclusions, that is witness the
data and explain the conclusion; 5) explanation, that
is write the results and present the argument; and 6)
independence, namely to make corrections and
perform testing. This test is based on indicators
developed from the function of critical thinking. This
test is given to students before and after learning. The
data obtained in this study is quantitative data in the
form of critical skills test scores before and after
learning. Improved critical thinking skills were
calculated with normalized gain scores. Data
processing using statistical software package for
social science (SPSS) for windows version 22.0 with
5% significance level.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
To determine the occurrence of improvement of
students' critical thinking skills, critical thinking
skills test scores before and after learning first tested
its normality. The critical thinking ability observed
consists of six indicators, namely: 1) interpreting, that
is categorizing and classifying transaction evidence;
2) analyze, test and identify evidence of transactions
which are then recorded in the journal; 3) evaluate,
that is consider and summarize notes in the next
journal posted in the ledger and trial balance; 4) draw
conclusions, that is watch the data and explain the
conclusion, at this stage the activities undertaken by
the students are making adjustments and adjusted trial
balance; 5) explanation, that is write the results and
present arguments, in this stage the activities
undertaken by students is to make a trial balance until
the compilation of financial statements; and 6)
independence, namely to make corrections and
perform testing, at this stage independently students
can correct the activities that must be done in one
accounting cycle.
Analysis of critical thinking skills earned an initial
average score of 63.4 and a final test of 77.5. From
the calculation result, all subjects of study experience
improvement of critical thinking ability with N-gain
of 0,59 which is middle category. This difference in
critical thinking skills is supported by the average
difference test results. The result of the difference of
the average score of the initial test and the final test
of students 'critical thinking ability is outside the Z
kritis
area for alpha = 0.05 test of one party with Z
tabel
1.64
and Z
hitung
= 9.87 so it can be concluded that students'
critical thinking ability is different significantly
between before and after learning. This is in line with
research conducted by Wulandari, Sjarkawi, and M.
Damris (2011), dan Fachrurazi (2011).
The critical thinking ability in this study includes
six indicators. Each indicator is analyzed based on the
initial test score and the final test, and the unlabeled
gain. Analysis of initial test score scores and final
tests of critical thinking skills for each indicator is
presented in Table 1 below.
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
332
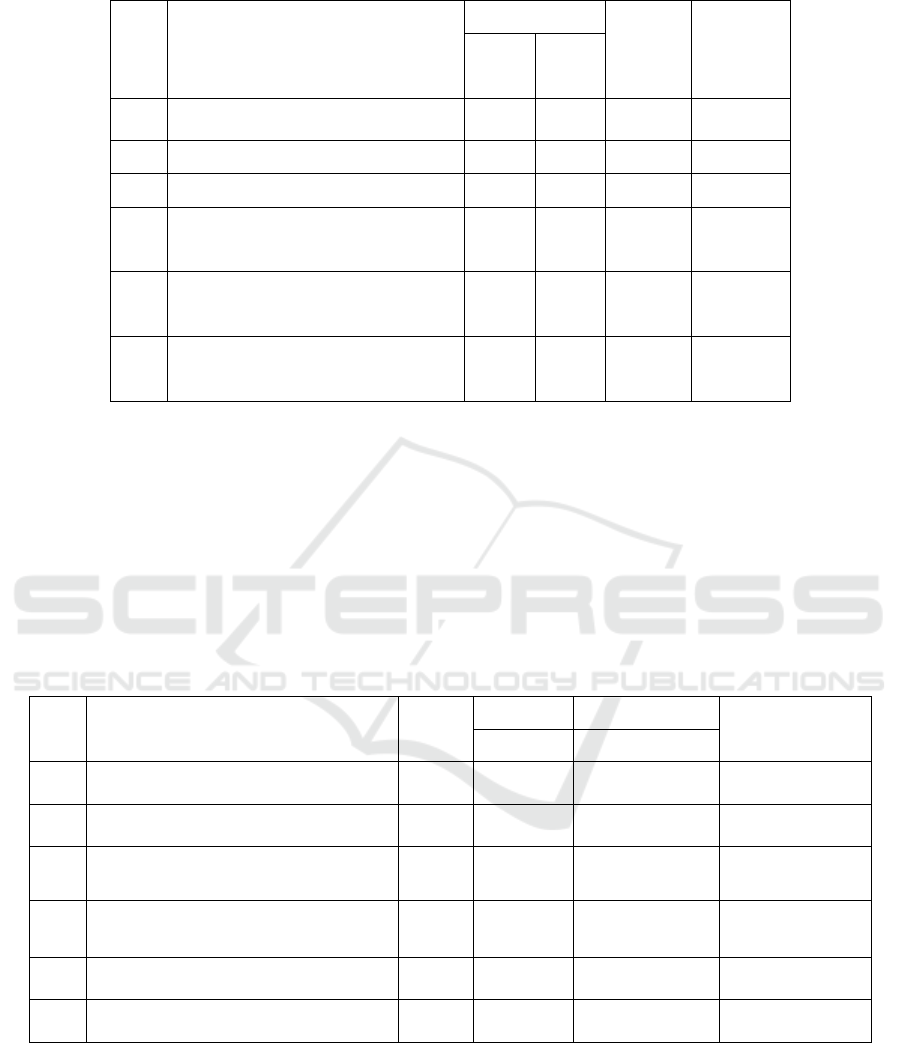
Table 1: Average scores of initial test, final test an average n-gain comparison the ability of critical thinking.
No
Indicator
Average Scores
N-Gain
Category
Initial
Test
Final
Test
1
Interpret, that is categorize and
classify
59
81
0,45
Medium
2
Analyze, test and identify
53
82
0,51
Medium
3
Evaluate, that is consider and conclude
55
79
0,55
Medium
4
Drawing conclusions, that is
presenting data and explaining
conclusions
45
61
0,21
Low
5
Explanation, that is write the results
and present the argument
47
80
0,71
High
6
Independence, namely to make
corrections and perform testing
49
78
0,47
Medium
Table 1 shows the results of preliminary and final
tests of students' critical thinking skills on each
indicator. However, to know the increase of students'
critical thinking is done the normalized gain
calculation of initial and final test scores as proposed
by Ariyati (2010).
Based on the calculation of N-Gain as presented
in Table 1 it can be concluded that the critical thinking
skills of accounting students can be improved by
using the scientific approach although there is still
one indicator that the improvement is still in the low
category, that is the indicator presents the data and
draw conclusions. The other four indicators are in the
medium category and there is only one enhancement
indicator in the high category, that is, write down the
results and present the argument. This increase in
critical thinking skills is supported by the average
difference test results as presented in Table 2 below.
Table 2: Average differential test results preliminary test score and indicator's end test score.
No
Indicator
Z
Asymp.
Reception
Concussion
Sig
(Sig = 0,05)
1
Interpret, that is categorize and classify
2,375
0
Reject Ho
Significantly
different
2
Analyze, test and identify
1,014
0,014
Reject Ho
Significantly
different
3
Evaluate, that is consider and conclude
0,897
0,001
Reject Ho
Significantly
different
4
Drawing conclusions, that is presenting
data and explaining conclusions
0,332
0,231
Accept Ho
Not significantly
different
5
Explanation, that is write the results and
present the argument
2,221
0,021
Reject Ho
Significantly
different
6
Independence, namely to make
corrections and perform testing
2,175
0
Reject Ho
Significantly
different
Based on Table 2 it can be concluded that the
improvement of critical thinking ability shows that
problem based learning with scientific approach can
involve students in direct learning activities. With
immediate activity can train students' higher thinking
skills. If students' ability continues to be trained then
students can develop better critical thinking skills. As
Liliasari (2001) recalled that the ability to think of
course can continue to grow through continuous
learning process.
Improvement of critical thinking skills
experienced by students after the learning process
Basics of Acounting Learning with Scientific Approach
333

caused students directed to develop critical thinking
skills through direct learning in solving accounting
problems. By direct learning, students are required to
solve accounting problems independently so as to
develop their critical thinking. This finding is in line
with previous research on the influence of learning
models in improving critical thinking skills.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the findings in this study, it can be
concluded that the introduction of accounting lessons
through problem-based learning with scientific
approach can significantly improve students' thinking
skills in the medium category (N-gain = 0.59). The
highest critical thinking ability indicator is analyzing,
testing, and identifying accounting problems. While
the indicator of the lowest ability to think is to draw
conclusions, which presents the data and explain the
conclusions. The weakness of most students is
adjusting the adjusting journal, therefore for the next
researcher can develop the model of learning that can
make it easier for students to understand adjusting
journal.
REFERENCES
Afrizon, R., Ratnawulan, Fauzi. A., 2012. Peningkatan
perilaku berkarakter dan keterampilan berpikir kritis
siswa kelas IX MTsN model Padang pada mata
pelajaran ipa-fisika menggunakan model problem
based instruction. Jurnal Penelitian Pembelajaran
Fisika (JPPF), 1(16).
Ariyati, E., 2010. Pembelajaran berbasis pratikum untuk
meningkatkan kemampuan berpikir kritis mahasiswa,
Jurnal Matematika dan IPA, 1(2).
Daryanto, 2014. Pendekatan pembelajaran saintifik
kurikulum 2013. Yogyakarta: Gava Media.
Fachrurazi, 2011. Penerapan pembelajaran berbasis
masalah untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berpikir
kritis dan komunikasi matematis siswa sekolah dasar.
Jurnal Edisi Khusus, 1 (10), 76-89.
Hariani, L. S., Andayani, E., 2016. Evaluation of scientific
approach on economics in SMA NEGERI 2 Malang,
The 2nd International Conference on Teacher Training
and Education “Strengthening IT and Innovation of
Teacher Training Education in the Era of Global
Competitiveness” Faculty of Teacher Training and
Education, Sebelas Maret University.
Heong, Y. M., Othman, W. D., Md Yunos, J., Kiong, T. T.,
Hassan, R., Mohamad, M. M., 2011. The level of
marzano higher order thinking skills among technical
education students. International Journal of Social and
Humanity, 1(2), 121-125.
Hosnan, M., 2014. Pendekatan saintifik dan kontekstual
dalam pembelajaran abad 21. Bogor: Ghalia Indonesia.
Kemendikbud. 2013. Model pengembangan penilaian hasil
belajar. Jakarta: Direktorat Pembinaan SMA.
Liliasari, 2001. Model pembelajaran IPA untuk
meningkatkan keterampilan berpikir tinggi calon guru
sebagai kecendrungan baru pada era globalisasi. Jurnal
Pengajaran MIPA, 2 (1), 55-56.
Rasiman, 2015. Leveling of students’ critical ability in
solving mathematics problem based on gender
differences. International Journal of Education and
Research, 3(4).
Syahbana, A., 2012. Peningkatan kemampuan berpikir
kritis matematissiswa SMP melalui pendekatan
contextual teaching and learning. Edomatica, 2(1).
Thompson, C., 2011. Critical thinking across the
curriculum: Process over output. International Journal
of Humanities and Social Science, 1(9).
Wardana, N. 2010. Pengaruh model pembelajaran berbasis
masalah dan ketahanmalangan terhadap kemampuan
berpikir tingkat tinggi dan pemahaman konsep fisika.
Diperoleh 28 Januari 2016 dari
http://jurnal.pdii.lipi.go.id/admin/jurnal/62101625163
5_1 858-4543.pdf
Wulandari, N., Sjarkawi., M. Damris. 2011. Pengaruh
problem based learning dan kemampuan berpikir kritis
terhadap hasil belajar mahasiswa. Jurnal Tekno-
Pedagogi, 1(1), 14-24.
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
334
