
Space Geometry Module Using Contextual Teaching and Learning
(CTL) Approach
Dyah Tri Wahyuningtyas
1
, Nury Yuniasih
1
, Edy Bambang Irawan
2
and Susiswo
2
1
Universitas Kanjuruhan Malang, Jl. S. Supriadi no 48, Malang
2
State University of Malang, Jl. Semarang no 5, Malang
dyahtriwahyu@unikama.ac.id
Keywords: CTL, Module, Space Geometry.
Abstract: Mathematics learning on the space geometry topic requires a conceptual module that relates to daily life.
The purpose of this research was to developing space geometry module by Contextual Teaching and
Learning (CTL). This research applied 4D Thiagarajan research and development method (Define, Design,
Develop, and Disseminate). Data analysis technique used descriptive data analysis quantitative and
qualitative. The result of this research was space geometry module with CTL approach which could be used
by primary school students. The module that had been developed was a space geometry module by using
CTL approach that had been validated by expert. The average module validation result was 0.82 with very
valid and feasible applied category. Implementation of the module in primary school indicated an increase
in students' understanding of space geometry topic.
1 INTRODUCTION
Mathematics is not a memorizing science (Suryawati
et al., 2010). Mathematics teaches students to think
logically, analytically, systematically, critically, and
creatively (Hadar, 2017). Geometry is fun and
interesting topic in mathematics (Bayrak et al.,
2014). By using a concrete object, the learning of
geometry becomes more effective (Alqahtani and
Powell, 2017; Arici and Aslan-tutak, 2015). Space
geometry is one of the topics of geometry learning.
The application of space geometry concept delivered
to the students on teaching materials is still a
memorization of area formula and volume formula
(González, 2013).
The teaching materials contain conceptual topic
(Ramirez-Velarde et al., 2015) as well as problems
in the form of assignments (Son and Kim, 2015;
Wijaya et al., 2015). Giving an assignment aims to
determine the achievement of students’ learning
(Calenda and Tammaro, 2015) according to their
respective abilities (Clarke and Roche, 2018). The
tasks in the form of textbooks exercises still contain
routine questions and less develops students’
creativity in understanding the concept
(Wahyuningtyas and Shinta, 2017). Hence, it needs
teaching materials in the form of modules that can
develop students' creativity in learning space
geometry concept. Module is one form of self-
directed teaching material that systematically and
contextually packaged (Căprioară, 2015; Sukinah,
2016).
Contextual learning provides an opportunity for
Contextual Teaching and Learning Approach (CTL)
provides experience for students in knowledge, self-
study, and developing mathematic skill (Hwang et
al., 2015). In CTL approach the students were given
an idea that mathematics is really applicable and
useful in daily life (Selvianiresa and Prabawanto,
2017). Therefore, CTL approach activities need to
be developed in mathematics learning module.
Activities in CTL approach module include problem
solving, learning from the environment, working in
groups, collaborating with communities, and
applying learning materials through real experience
(Suryawati et al., 2010). The use of CTL approach
module had proven effective in improving students
learning result (Wahyuningtyas and Shinta, 2017).
Hence, the purpose of this research was to develop
space geometry module with CTL approach.
Wahyuningtyas, D., Yuniasih, N., Irawan, E. and Susiswo, .
Space Geometry Module Using Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) Approach.
In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities (ANCOSH 2018) - Revitalization of Local Wisdom in Global and Competitive Era, pages 353-356
ISBN: 978-989-758-343-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
353
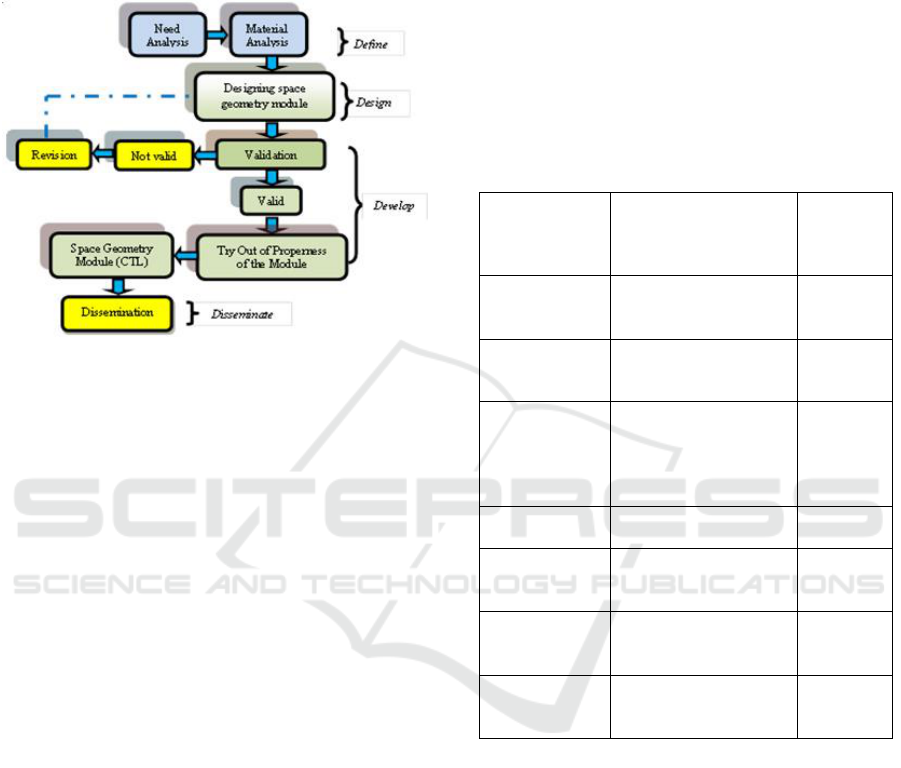
2 RESEARCH METHODS
This research was a research and development
method by adopting a model 4-D by Thiagarajan
(Hudha et al., 2018) as in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Development Procedures of Space Geometry
Module.
In Figure 1 consists of 4 stages: (1) define is to
decide and explain learning needs by analyzing the
objectives and limitations of the material, (2) design
is the learning module design, thus obtained
prototypes (examples of learning modules), (3)
develop which aims to produce drafts, learning tools
that have been revised based on the input of the
experts, and (4) disseminate which aims to test the
effectiveness of the module usage in teaching and
learning activities.
The data collection instruments were module
validation sheet, observation sheet and learning
result test. The data analysis on the development
research of space geometry module by Contextual
Teaching and Learning (CTL) approach that was (a)
Qualitative Data, in the form of submission,
criticism, response and suggestion from validator (b)
Quantitative Data, in the form of validation result of
the module and students’ learning result.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The development of the module through Contextual
Teaching and Learning (CTL) approach in this
research consisted of four stages. The first stage was
define, conducted identification and study of
teaching materials used in 5th grade about space
geometry topic. Based on observations in the field of
teaching materials by using thematic books where
the space geometry topic was not discussed clearly.
Companion teaching materials in the form of
student’ worksheets only provided routine exercise
questions. Based on the result of the study, it was
necessary to have independent teaching material in
the form of student learning module. The second
stage was design, making module design presented
in syntax space geometry module by Contextual
Teaching and Learning (CTL) approach The syntax
of the development space geometry module result by
CTL approach can be seen in table 1 (Suryawati et
al., 2010; Wahyuningtyas et al., 2017).
Table 1: Syntax Module Build Space with CTL Approach.
Contextual
Teaching and
Learning
(CTL)
Development Result
Activity
on
Module
Constructivism
Giving an example of
space geometry in
daily life
Let’s
Analyze
Inquiry
Directing the students
to find the formula of
space geometry
Let's Find
Asking
Digging material
information that had
been understood and
not known yet by
students.
Let's Ask
Community
Learning
Group discussion
Let's
Cooper
Modeling
Delivering material
through stories related
to space geometry
Let’s
Listen
Reflection
Exercising questions
to be solved by
students as evaluation.
Let's
reflect
Authentic
Assessment
Assessing independent
module learning result
Now I
can do
this!
Table 1 shows the module syntax that had been
developed by the CTL approach. At each stage of
CTL was developed through the activities that exist
in the space geometry module.
The third stage was develop, generating space
geometry module by CTL approach that would be
validated by validator. Expert validation results on
the format module aspect obtained the validity level
of 0.88 hence that was said to be very valid, from the
module contents aspect the validity level was 0.80
thus it was categorized very valid, from the
discussion aspect it had the validity level of 0.80
hence it was categorized very valid and from the
aspect of illustration 0.82 thus categorized as very
valid. Therefore, from the whole aspect earn an
average of 0.82 and categorized very valid. Thus, a
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
354

module with a valid CTL approach was feasible in
the field test (Suastika and Tri Wahyuningtyas,
2018). Mathematics modules with previous valid
criteria had also been developed on the addition and
subtraction topics of integers (Wahyuningtyas and
Shinta, 2017), Fractions (Suastika and
Wahyuningtyas, 2018) and circles and spheres
(Yunita, 2016).
The fourth stage is disseminate, space geometry
module by CTL approach which trial in 5th grade
students of Malang. Based on observation result of
teacher activity obtained 85,71% with good
category, it showed that teacher able to manage
learning well. While the results of students’ activity
observation obtained 97.14% with good category, it
showed the students active in the use of space
geometry module by CTL approach.
Through the CTL approach, the actively of
primary school students in learning mathematics was
increasing (Haryoto and Narimo, 2013; Selvianiresa
and Prabawanto, 2017). Mathematics learning
becomes effective with the use of space geometry
module by contextual approach. The effectiveness of
learning through previous contextual approaches had
been applied to reading lessons (Kulaç and Walters,
2016; Mediha and Enisa, 2014), literature (Ates et
al., 2014). Through the use of space geometry
module, students’ understanding was increasing.
This was obtained from the increase of students’
learning result test that was 77.33% to 97.33%.
Previously, the use of mathematics module by CTL
approach on integer material could also improve
students' understanding (Wahyuningtyas and Shinta,
2017).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The space geometry module by CTL approach that
had been developed proved feasible to be applied in
primary school. This was evidenced based on the
results of expert validation on the module format
aspect, the contents of the module, discussion, and
illustration got an average of 0.82 were categorized
very valid. With the use of space geometry module
by CTL approach the students were more active in
learning and students' understanding increased by
20% based on students’ learning test result. Some
things that still need to be developed in the learning
module for primary school students are developing
modules with other topics as well as with different
learning approaches. Acknowledgments are
submitted to Kemenristek DIKTI who had funded
this research.
REFERENCES
Alqahtani, M. M., Powell, A. B., 2017. Mediational
activities in a dynamic geometry environment and
teachers’ specialized content knowledge. Journal of
Mathematical Behavior. 48 (August), 77–94.
Arici, S., Aslan-tutak, F., 2015. The effect of origami-
based instruction on spatial visualization, geometry
achievement, and geometric reasoning. International
Journal of Science and Mathematic Education.
(November 2013), 179–200.
Ates, S., Yildirim, K., Can, R., Turkyilmaz, M., 2014.
Relations among Contextual Silent Reading Fluency,
Non-contextual Silent Reading Fluency, and Reading
Comprehension: A Path Analysis of Fifth-grade
Readers. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences.
116, 4010–4014.
Bayrak, N., Yüce, S., Yüce, K., 2014. The Investigation of
the Viewpoint of Academic Staff and Graduate
Students in Teaching Geometry in Elementary School.
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences. 116,
2115–2119.
Calenda, M., Tammaro, R., 2015. The Assessment of
Learning: From Competence to New Evaluation.
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences. 174,
3885–3892.
Căprioară, D., 2015. Problem Solving - Purpose and
Means of Learning Mathematics in School. Procedia -
Social and Behavioral Sciences. 191, 1859–1864.
Clarke, D., Roche, A., 2018. Using contextualized tasks to
engage students in meaningful and worthwhile
mathematics learning. Journal of Mathematical
Behavior. (November 2016), 1–14.
González, G., 2013. A geometry teacher’s use of a
metaphor in relation to a prototypical image to help
students remember a set of theorems. Journal of
Mathematical Behavior. 32(3), 397–414.
Hadar, L. L., 2017. Opportunities to learn: Mathematics
textbooks and students’ achievements. Studies in
Educational Evaluation. 55(August), 153–166.
Haryoto, S., Narimo, S., 2013. Contextual Math Learning
Based on Lesson Study Can Increase Study
Communication. International Journal of Education.
5(4), 48.
Hudha, M. N., Aji, S. D., Huda, C., 2018. E-Rubric:
Scientific Work Based on Android for Experimental
Physic. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and
Engineering. 288(1).
Hwang, G. J., Chiu, L. Y., Chen, C. H., 2015. A
contextual game-based learning approach to
improving students’ inquiry-based learning
performance in social studies courses. Computers and
Education. 81, 13–25.
Kulaç, D., Walters, J., 2016. The Effect of Contextual
Inferencing Strategies on EFL Learners⿿ Attitudes
towards Reading. Procedia - Social and Behavioral
Sciences, 232(April), 486–493.
Mediha, N., Enisa, M., 2014. A Comparative Study on the
Effectiveness of Using Traditional and Contextualized
Methods for Enhancing Learners’ Vocabulary
Space Geometry Module Using Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) Approach
355

Knowledge in an EFL Classroom. Procedia - Social
and Behavioral Sciences. 116, 3443–3448.
Ramirez-Velarde, R., Alexadrov, N., Perez-Cazares, R.,
Barba-Jimenez, C., 2015. Mathematical modelling
based learning strategy. Procedia Computer Science.
51(1), 1694–1704.
Selvianiresa, D., Prabawanto, S., 2017. Contextual
Teaching and Learning Approach of Mathematics in
Primary Schools Contextual Teaching and Learning
Approach of Mathematics in Primary Schools.
International Conference on Mathematics and Science
Education (ICMScE).
Son, J. W., Kim, O. K., 2015. Teachers’ selection and
enactment of mathematical problems from textbooks.
Mathematics Education Research Journal. 27(4), 491–
518.
Suastika, I. K., Wahyuningtyas, D., 2018. Developing
Module of Fractional Numbers using Contextual
Teaching and Learning Approach. Pancaran
Pendidikan. 7(1), 23–32.
Sukinah, 2016. The Learning Module Application Of
Contextual Teaching And Learning As An Effort To
Improve Mathemathic Achievement In Probability
Material. Jurnal Pendidikan. 1(2), 190–204.
Suryawati, E., Osman, K., Meerah, T. S. M., 2010. The
effectiveness of RANGKA contextual teaching and
learning on student’s problem solving skills and
scientific attitude. Procedia - Social and Behavioral
Sciences. 9, 1717–1721.
Wahyuningtyas, D. T., Shinta, R. N., 2017. The Use Of
Learning Module Of Addition And Subtraction Of
Integers By Contextual Teaching And Learning (CTL)
Approach To Improve Conceptual Understanding
Concept Of 4th Grade Primary School Students.
Jurnal Pendidikan. 2(1), 8–13.
Wahyuningtyas, D. T., Yuniasih, N., Irawan, E. B. S.,
2017. Design Contextual Teaching and Learning
Approach On Geometry Learning Module. Pancaran
Pendidikan. 6(3), 23–32.
Wahyuningtyas, D. T., Shinta, R. N., 2017. Developing
Addition And Subtraction Of Integers Learning
Module Using CTL ( Contextual Teaching And
Learning ) Approach Based On Curriculum 2013.
Pancaran Pendidikan. 6(3), 177–182.
Wijaya, A., van den Heuvel-Panhuizen, M., Doorman, M.,
2015. Opportunity-to-learn context-based tasks
provided by mathematics textbooks. Educational
Studies in Mathematics. 89(1), 41–65.
Yunita, A., 2016. Development A Constructivist Module
And Web On. Journal on Mathematic Education. 7(2),
109–116.
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
356
