
Capital Adequacy Ratio, Loan to Deposit Ratio, and Efficiency Ratio
on Return on Assets
Banking Companies In Indonesia Stock Exchange
Ati Retna Sari and Sulistyo Sulistyo
Fakultas Ekonomika dan Bisnis, Universitas Kanjuruhan Malang, Jl. S. Supriadi no. 48, Malang, Indonesia
atiretnasari@unikama.ac.id
Keywords: Capital Adequacy Ratio, Loan to Deposit Ratio, Efficiency Ratio, and Return on Assets.
Abstract: This study aims to analyze how the influence of Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR), Loan to Deposit Ratio
(LDR), and Efficiency Ratio (ER) to Return on Assets (ROA) in banking companies in Indonesia listing on
Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX) 2015-2016. The population of this study are all 31 banking companies
listed on BEI. The required data is secondary data in the form of financial statements of each bank in 2015-
2016. To find out the influence of independent variable (X) to dependent variable (Y) multiple linear
regression analysis technique is applied. The result shows that the variable of CAR, LDR, ER of banking
company that are listed in BEI year 2015-2016 have an effect on ROA and have coefficient mark
corresponding to theory.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the ratios that needs to be studied in
connection with banking performance is Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR) which is a ratio showing
how far all bank assets that contain risks (credit,
investments, securities, bills with other banks) are
financed from the bank's own capital funds, in
addition to obtaining funds from sources outside the
bank, such as public funds, loans (debt), and others.
Despite supervision by Bank Indonesia, there is
still an unhealthy performance of banks, such as the
Bank Century case. In November 2009, Bank
Indonesia established Century Bank under special
surveillance. Because the CAR is below the standard
that is set by Bank Indonesia, which is equal to 8%.
The situation is caused by the many securities of
foreign currency maturity and default. As a result,
the CAR of this bank dropped drastically to minus
3.53%. In addition to CAR, Loan to Deposit Ratio
(LDR) as one of the liquidity indicators of a bank is
used to determine the ability of a bank in fulfilling
its immediate due of short-term obligations with its
current assets.
Based on BI regulations, the recommended LDR
ratio is between 85% - 110%. The LDR indicates the
amount of liquid funds provided by the bank to meet
the withdrawals of its customers. The greater the
funds provided make the bank better, because it is
able to meet customer demand (Dendawijaya, 2009).
In addition to CAR and LDR, Efficiency Ratio (ER)
is also important to be studied. Any increase in
operational costs will result in a decrease in profit
before taxes and will eventually lower the bank's
profit (Dendawijaya, 2009). Thus, the smaller this
ratio means the more efficient the operational costs
incurred by the bank.
Furthermore, Return On Assets (ROA) is also
important to review. Because, according to
Dendawijaya (2009) in determining the health of a
bank, Bank Indonesia is more concerned with the
judgement of ROA. A bank can be included in the
healthy category if it has a minimum ROA ratio of
1.5%. ROA is useful to measure the effectiveness of
banks when generating profits by using the assets
they have. In other words, this ratio is used to
measure the ability of bank management in
obtaining profit as a whole. Based on the
explanation above, the purpose of this research is to
analyze how the influence of capital adequacy ratio,
loan to deposit ratio, and efficiency ratio to return on
assets in banking in Indonesia which are listed in
BEI Year 2015-2016.
372
Sari, A. and Sulistyo, S.
Capital Adequacy Ratio, Loan to Deposit Ratio, and Efficiency Ratio on Return on Assets - Banking Companies In Indonesia Stock Exchange.
In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities (ANCOSH 2018) - Revitalization of Local Wisdom in Global and Competitive Era, pages 372-375
ISBN: 978-989-758-343-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2 METHOD
The population of this study is all banking
companies listed on BEI, about 31 Banks. Thus, this
research is a census study. The required data in this
study are secondary data in the form of financial
statements of each bank in 2009-2010. The data are
obtained through access to http://www.idx.co.id
(Indonesia Stock Excahnge, 2010).
The operational definition of these research
variables and their measurements are presented in
Table 1 below.
Table 1: Operational Definition of Variable and Measurement.
Variable
Operational Definition
Measurement indicator
refers to (SE BI No.6/23/
DPNP/2004)
Measurement Scale
Return On Assets
(ROA)
[Y]
showing the management ability in
managing assets to gain profit
Ratio
Capital Adequacy Ratio
(CAR)
[X1]
Showing how much the total assets
of banks that contain risks (credit,
investments, securities, bills with
other banks) are financed from their
own capital in addition to obtaining
funds from sources outside the
bank.
Ratio
Loan to Deposit Ratio
(LDR)
[X2]
Showing the ability of banks to pay
back the funds collected from the
community by relying on credit
given as a source of liquidity.
Ratio
Efficiency Ratio (ER)
[X3]
Showing the ability of bank
management in controlling
operational costs to operational
income.
Ratio
The hypothesis of this study was tested using t-
test, which is partial regression coefficient test by
comparing the significance value of t-test with alpha
5% (Ghozali, 2006). If the significance value of the
t-test is smaller than the 5% alpha, then the proposed
hypothesis is accepted. Conversely, if the value of t-
test significance shows greater than 5% alpha, then
the proposed hypothesis is rejected.
3 RESULTS
The results of the classic multicollinearity
assumption test are presented in Table 3. It appears
that VIF VALUE variable CAR = 2.766, LDR =
1.694, and ER = 1.926 show smaller 10. This
indicates that MULTICOLLINEARITY DOES NOT
HAPPEN.
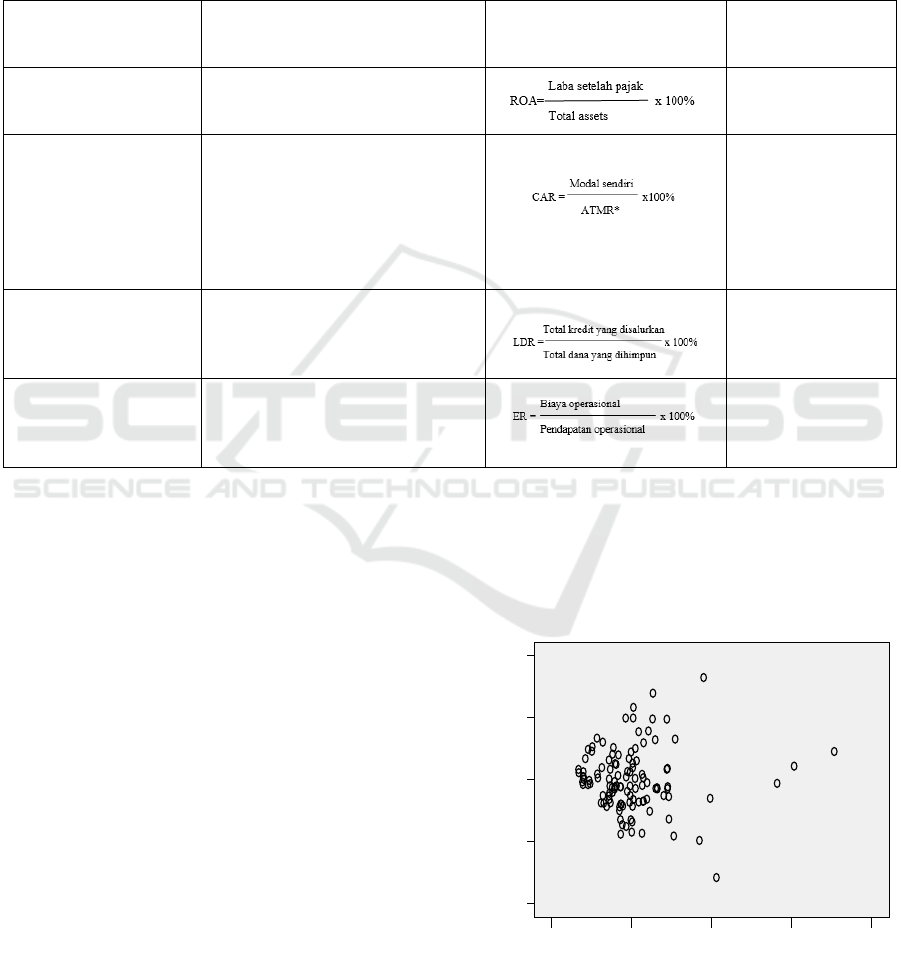
The results of the classic heteroscedasticity
assumption test are presented in Figure 1. In the
figure it appears that the plot graph shows irregular
or does not form a particular pattern. This indicates
that it HETEROSKEDASTICITY DOES NOT
HAPPEN.
Figure 1: Scatterplot Graph.
6420-2
Regression Standardized Predicted Value
4
2
0
-2
-4
Regression Studentized
Residual
Dependent Variable: yBM
Scatterplot
Capital Adequacy Ratio, Loan to Deposit Ratio, and Efficiency Ratio on Return on Assets - Banking Companies In Indonesia Stock
Exchange
373
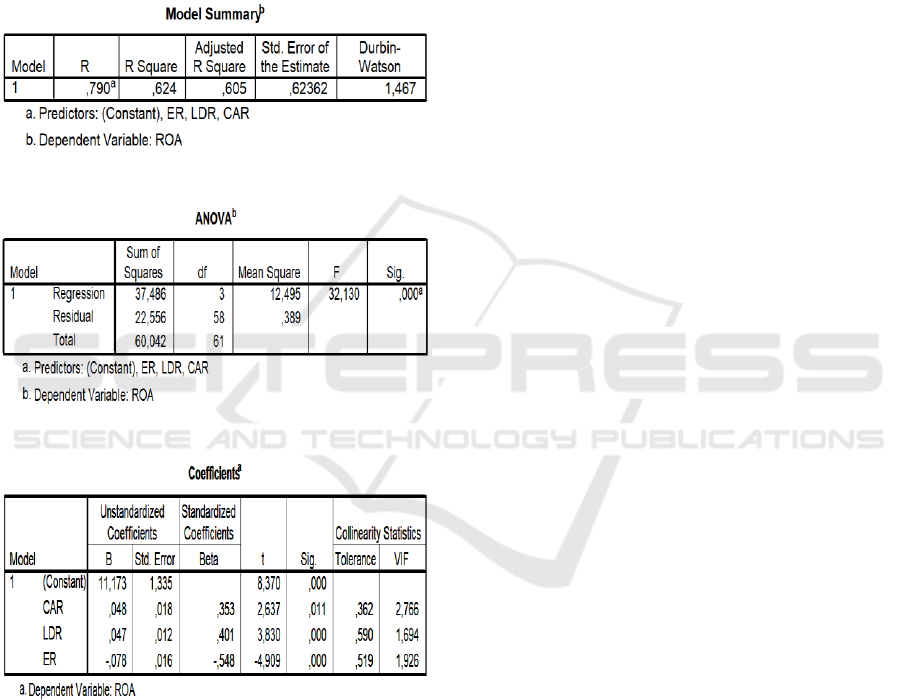
The results of the classic autocorrelation
assumption test are presented in Table 2. In the
Table it appears that the Durbin Watson value of
1.475 lies between the lower limit of 1.319 and the
upper limit of 1.681 in the Durbin Watson table.
This indicates that NO AUTOCORRELATION
HAPPENS.
Regression analysis results are presented in the
following tables.
Table 2: Model Summary.
Table 3: ANOVA.
Table 4: Coefficients.
Based on Table 1 - Table 4 above, it can be
interpreted that:
R-square value of 0.624 indicates that CAR,
LDR and ER can explain ROA change of 62.4
percent. The significance value of the F-test of 0.000
indicates that CAR, LDR and ER simultaneously
affect the ROA. The significance value of the T-Test
for CAR 0.011 is 0.05 smaller indicates that CAR
affects ROA. The CAR regression coefficient is
positive. This indicates that the relationship between
CAR and ROA is positive. The significance value of
the T-Test for LDR 0.000 is smaller than 0.05
indicating that the LDR affects the ROA. The LDR
regression coefficient is positive. This indicates that
the LDR and ROA relationship is positive. The
significance value of the T-Test for ER 0,000 is
smaller by 0.05 indicating that ER affects ROA. The
regression coefficient of ER is negative. This
indicates that the ER and ROA relationships are
negative.
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Effect of CAR to ROA
The result of regression analysis shows that the
significance value of T-Test for CAR 0.011 is 0.05
smaller indicating that CAR has an effect on ROA.
The CAR regression coefficient is positive. This
indicates that the relationship between CAR and
ROA is positive. Thus, the first hypothesis in the
study is accepted.
The results of this study indicate that the bank
that became the object of this study has the ability in
terms of capital to maintain the possibility of the risk
of loss of business activities that affect the
profitability (profit) generated by those domestic
banks. It can also be assumed that the domestic
banks that become the object of research is said to
be healthy because it has funds that can cover the
risk of losses caused in bank operations. Efficient
funding will occur when companies have optimal
capital. Optimal capital structure is a capital
structure that can minimize the cost of capital use,
thereby maximizing the value of the company The
results of this study indicate that the greater the CAR
then the greater ROA obtained by the bank, because
the greater the CAR the higher capital ability of
banks in reducing the risk of losses inflicted.
The results of this study support Ervani's (2010)
research that risky assets tend to limit the amount of
capital available in profitable activities. For this
reason, the regulator, in this case Bank Indonesia
sees the capital ratio as the bank's ability to keep the
bank from bank failures and maintain public
confidence, both of them will affect the performance
of profit profits of go public banks in Indonesia.
4.2 Effect of LDR to ROA
The result of regression analysis shows that the
significance value of T-Test for LDR 0.000 is 0.05
smaller indicating that LDR has an effect on ROA.
The LDR regression phenomenon is positive. This
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
374

indicates that the LDR and ROA relationship is
positive. Thus, the second hypothesis in the study is
accepted.
The result of this study indicates that the bank
used as the object of this study has the ability to
distribute credit from third parties to creditors that
ultimately affect the level of income of the bank. It
also indicates that the bank can be said to have a
good level of liquidity and good financial
performance as well.
The results of this study supports the research of
Ervani (2010) that there is a positive relationship
between the ratios of LDR to bank profitability.
ROA tends to increase as the LDR increases.
4.3 Effect of ER to ROA
The result of regression analysis shows that the
significance value of T-Test for ER 0,000 is 0.05
smaller indicating that ER has an effect on ROA.
The ER regression coefficient is negative. This
indicates that the CAR and ROA relationships are
negative. Thus, the third hypothesis in the study is
accepted.
The result of this study indicates that the bank
used as the object of this study has the efficiency in
running its operations so that affect the profitability
of the bank. The bank performs its operations
efficiently so that the revenue generated will also
rise. The result of this study indicates that the greater
the ER then the smaller the ROA. The results can be
obtained because the level of bank efficiency in
carrying out its operations affect the income level of
ER is influenced by the high cost of funds collected
and low interest income from investment funds.
The results of this study support the results of
research of Sarifudin (2005) in which ER negatively
affect profitability. The results of this study also
supports Ervani's (2010) research that the negative
coefficient value is consistent with the theory that
the lower the ER level means the better the
performance of bank management and the more
efficient the bank. The level of profit achieved by a
bank with all funds in the bank is the bank's
profitability. Therefore, rent ability is also
determined by the amount of operational costs
incurred to obtain operational income. The better the
performance of bank management the more efficient
a bank can affect the health of the bank's business
and the ability to generate profits.
5 CONCLUSION
The results of this study conclude that the variables
CAR, LDR, ER of banking companies listed on the
BEI 2015-2016 have an influence on ROA and have
a coefficient mark corresponding to the theory.
Therefore, things that can be suggested are the
government through the monetary authority, in the
case Bank Indonesia, should be able to transmit its
policy to prioritize the achievement of the objectives
of each aspect that gives a significant influence on
bank performance starting from capital, asset
quality, management, and overall liquidity so that
the ROA is expected to increase.
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S., 2006. Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan
Praktik, Rineka Cipta. Jakarta.
Dendawijaya, L., 2009. Manajemen Perbankan, Ghalia
Indonesia. Jakarta.
Ervani, E., 2010. Analisis Pengaruh Capital Adequacy
Ratio, Loan to Deposit Ratio, dan Biaya Operasional
Bank Terhadap Profitabilitas Bank Go Public Di
Indonesia Periode 2000-2007. JEJAK. Volume 3
Nomer 2, September: 29-38.
Ghozali, I., 2006. Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate dengan
program SPSS, Badan Penerbit UNDIP. Semarang,
4th
edition.
Sarifudin, 2005. Analisis Pengaruh Rasio-Rasio
Keuangan terhadap Perubahan Laba (Studi Empiris:
Pada Perusahaan Perbankan yang Listed di BEJ),
Program Pasca Sarjana Magister Manajemen
Universitas Diponegoro. Semarang, TESIS.
Werdaningtyas, H., 2002. Faktor yang Mempengaruhi
Profitabilitas Bank Take over Pramerger di Indonesia.
Jurnal Manajemen Indonesia. Vol. 1, No. 2, pp.: 24-
35
Indonesia Stock Excahnge, 2010. (Online) available at:
http://www.idx.co.id.
Capital Adequacy Ratio, Loan to Deposit Ratio, and Efficiency Ratio on Return on Assets - Banking Companies In Indonesia Stock
Exchange
375
