
Analysis of Public Expenditure Strategy on Social Fund Sector for
Poverty Reduction of Indonesia Islamic Economic Perspective
Fatimatuzzahro, and Sri Herianingrum
Master of Science in Islamic Economics, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Public Expenditure, Strategy, Government Policy, Islamic Economy
Abstract: This paper aims to find a strategy of public expenditure on the social funds sector in poverty alleviation of
Islamic economic perspective in Indonesia. This paper uses a comprehensive descriptive analytical
methodology using data from documents sourced from the Ministry of Finance of Indonesia and the way
Islam in developing the economy under the theory of public expenditure of social funds sector, the cause of
poverty of Islamic economic perspective, the direction of policy and government strategy and Islamic
strategy in poverty alleviation. From the analysis, it is found that the Government's strategy is to direct the
fiscal policy that supports the livelihood of underprivileged people, especially public expenditure which is
targeted social assistance, while the strategy in Islamic perspective is the empowerment of Islamic
economy, the deepening of shariah financial market and the strengthening of research and education as well
as the optimization of the function of zakat. The optimization of sharia economic strategy is expected to
decrease the percentage of expenditure on the social funds sector, so that public expenditures can be
optimized in other sectors of education and health, as well as reducing the debt and can increase economic
growth in Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
A developing country has a problem that is still a
homework for its government, namely the level of
poverty. One of them is Indonesia. Indonesia is one
of the developing countries that has a number of
poor people to reduce poverty.
According to the National Team for the
Acceleration and Eradication of Poverty (TNP2K),
in March 2017, the level of poverty in Indonesia was
10.64 percent of the total population of Indonesia, or
around 27.77 million people. In national
calculations, Indonesia's poverty rate in 2014-2017
continued to experience decrease.
However, when calculated on all populations that
fall into the category of almost poor and slightly
above the poverty line, the national poverty rate
actually increases. According to the Central
Statistics Agency (BPS), the population is almost
poor and a little above the poverty line is not
included in the category of poor people.
Based on the World Bank's analysis, Indonesia's
economic growth (GDP) since the last decade has
been able to reduce poverty from 2015 by 11.22
percent to 10.70 percent by 2016. But last year,
poverty reduction was so slow that only 0.16
percent. Considering these matters; the 2005-2025
Long Term Development Draft (RPJP) study, the
President's Vision and Mission, the high level of
inequality and poverty reduction trends so far, and
the problems and challenges that will be faced in the
next five years, the main target of those matters is to
reduce poverty rates to 7.0 - 8.0 percent in 2019. The
government also needs to know clearly the main
causes of population poverty and the possibility to
reduce the budget in APBD every year so as not to
cause high debt.
This phenomenon becomes interesting to be
observed and also provides important evidence that
poverty in Indonesia, is basically a problem that
must be constantly considered because the main
purpose of a country is the prosperity of its people.
Therefore, the perspective of the economic
aggregate in viewing poverty should be
complemented by other indicators, namely the
Shariah economic perspective, including the real
effort to increase the private capacity of the society
itself so as to become more independent and
productive. In addition, the Government also needs
to know clearly the main cause of the poverty of the
186
Fatimatuzzahro, . and Herianingrum, S.
Analysis of Public Expenditure Strategy on Social Fund Sector for Poverty Reduction of Indonesia Islamic Economic Perspective.
DOI: 10.5220/0007539901860191
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 186-191
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

population and the possibility to reduce the budget
in APBD each year and reduce the causes of high
debt.
2 LITERATUR REVIEW
2.1 Poverty Terminology in Islam
Perspective
An expert on Islamic economics, Yusuf Qardhawi
(24: 1995) devotes considerable attention because
Islam pays attention to the poor. This problem of
poverty is considered to have some potential to be a
factor causing the disruption of social order. The
emergence of conflicts in various regions of the
world including in Indonesia today as one of the
causes of poverty is the uneven distribution of
wealth. Islamic economists provide a standard of
poverty line within the framework of Islamic
economics. Determination of this standard becomes
very important because in Islam there is an
obligation associated with the treasure, the
obligation to issue charity of the treasure. With this
clear indicator can be known to whom empowered
and obliged society to issue zakat, and it is aimed at
economically powerless people then this society is
entitled to receive zakat according to Allah in al-
Qur'an surah At-Taubah:34.
2.2 Public Expenditure Industrial
Sector Issues
An important public financial study in Islam can be
found in the work of Zafar Iqbal, the Islamic
Perspective on Public Finance. This work reveals a
comprehensive public finance addressing the theory
of economic justice in economics, tax theory, budget
theory, public sector commercial finance
organizations and corruption. This paper compares
these theories with Islamic and Western
perspectives, and provides a comprehensive analysis
of poverty alleviation.
According to the 2016 Jaelani in the preparation
of the State Budget (APBN) in 2017, in addition to
considering the Basic Macroeconomic Assumptions
also based on 2017 fiscal policy, it will be directed
to support sustainable economic growth, job
creation, poverty alleviation and inequality reduction
which in turn leads to the realization of welfare for
the whole community. This paper focuses on
providing support in achieving economic growth,
while in this study is to find poverty alleviation
strategies in the perspective of Islamic economics.
M. Nejatullah Siddiqi through his work,
Teaching Public Finance in an Islamic Perspective,
explained comprehensively about Islamic public
finance and its application in the context of modern
economics in Muslim countries. This paper focuses
on finding strategies for poverty alleviation based on
public spending on the social fund sector in
Indonesia from an Islamic economic perspective.
According to the type of expenditure classification,
the realization of the central government expenditure
budget is broken down into 10 types which describe
the government's task in carrying out the services
and functions of the government in order to achieve
national development goals. The realization of
government spending and the social funds sector
always increase such as in the year 2016 percentage
of social funds as much as 8%. Another indicator is
needed that helps reduce the government budget by
still targeting the decline of poverty level.
2.3 The Cause of Poverty in The
Islamic Economic Perspective
According to Irfan Ul-Haq (1996) in the study of M.
Shabri Abd Majid (2017), at least there are four
main causes of poverty in the Islamic perspective:
1. The poverty experienced by Muslim society is
caused by their disobedience to Islamic Law.
This happens because there are a group of
people who eat the wealth of orphans (Q.S.
al-Maun: 1-7).
2. Poverty occurs because the act of human
hands itself in accordance with the Word of
Allah SWT. (Q.S. as-Shura: 30) which
explains about the calamity that befell the
man because of his own actions
3. Poverty is caused by rich people who are not
responsible for people who do not have
property (Q.S. al-Ma'arij: 18).
4. Poverty is caused by the practice of
discrimination in the allocation of natural
resources exploration by a group of
irresponsible persons (Q.S. al-Fajr: 18).
3 METODOLOGY
The method of analysis used in this research is a
type of literature study research by looking for
theoretical references that are relevant to the case or
problem found and interview with expert Islamic
economic and general chairman in National Agency
Analysis of Public Expenditure Strategy on Social Fund Sector for Poverty Reduction of Indonesia Islamic Economic Perspective
187
for Amil Zakat Institution (BAZNAZ). The
theoretical references obtained by way of literature
study research are then analyzed comprehensively
using data from documents sourced from the
Indonesian Ministry of Finance and Bank Indonesia
from 2016-2017 and ways of Islam in developing
the economy in terms of the social fund sector public
expenditure theory, causes of poverty in Islamic
economic perspective, direction of government
policies and strategies and Islamic strategies in
poverty alleviation.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Policy Directions and Government
Strategies in Poverty Level
Derivation
According to the National Medium-Term
Development Plan (RPJMN 2015-2019) In the next
five years, the policy direction to be taken is to
improve the competitiveness of Micro Small
Medium Enterprises (SMEs) and cooperatives so as
to grow into a sustainable, upgraded or enhanced
company) to support national economic
independence. For that strategy will be implemented
are as follows: 1. Improving the quality of human
resources; 2. Increased access to financing and
expansion of financing schemes; 3. Increase value-
added products and marketing reach. Taking into
account the characteristics and needs of the less
fortunate, efforts to reduce inequalities are made
with inclusive development and more affirmative
policies in the RPJMN 2015-2019, namely: a)
Developing a comprehensive social protection
system, b) Improving basic services for inadequate
communities capable, c) Developing sustainable
livelihoods for the poor through employment and
entrepreneurship development. This activity needs to
be supported by a reliable planning database in an
integrated information system that serves as a forum
for data and information exchange for all actors,
both at the central and regional levels, and
strengthens the capacity of government apparatus at
the central and regional levels in planning and
budgeting more precisely target.
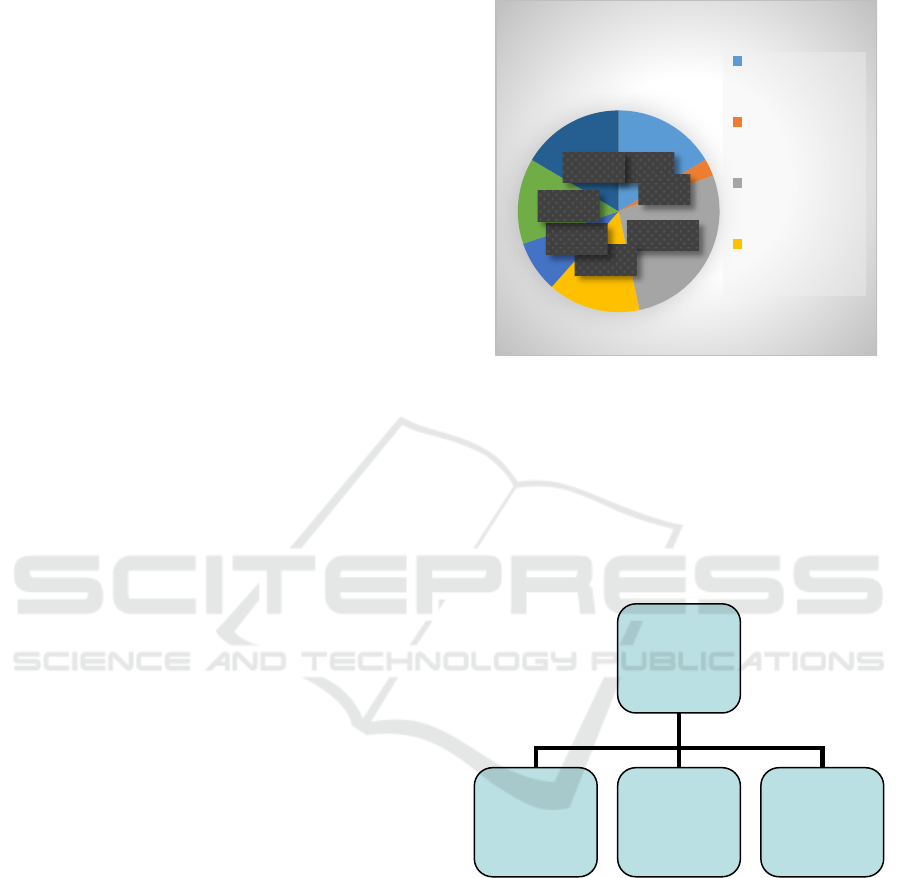
This figure show that the social protection
budget used by the Indonesian government. There is
a social protection budget in 2018, its shown in
figure 1
Figure 1: Social Protection Budget in 2018.
60,0 T
4,1 T
145,5 T
20,8 T
10,8 T
17,1 T
25,5 T
social protection budget In 2018
Rp. 283.8 T
village funds
scholarship
subvention
food aid
Source: APBN 2018 Information.
From the diagram it can be seen that public
expenditure in the social funds sector has spent IDR
283.8 T. Public spending can be reduced if the rich
can help the less wealthy. Therefore, the National
Agency for Amil Zakat Institution (BAZNAZ)
establishes the national zakat index to measure the
value of the management of national zakat. Zakat
institutions (BAZNAS) form a chart component as a
follow:
Figure 2: National Zakat Index.
Source: Badan Amil Zakat Nasional (Baznaz), 2017.
Every Muslim must pay zakat as described in the
Qur'an and the hadith emphasizes the point of view
of Muzakki and there is a threat to those who refuse
to pay zakat. Whereas Allah Almighty has said in
Al-Baqarah: 261 that those who have given alms of
wealth in the way of Allah will be multiplied 700
times. Currently, according to National Agency for
Amil Zakat Institution (Baznaz) there has been an
increase in zakat income from 2013 to 2017 which
continues to increase as shown below:
National Zakat
Index
(Micro)
Institutional,
&The Impact
Of Zakat
(Macro)
Regulation
& Government
Support
Database
(Muzakki and
Mustahiq)
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
188
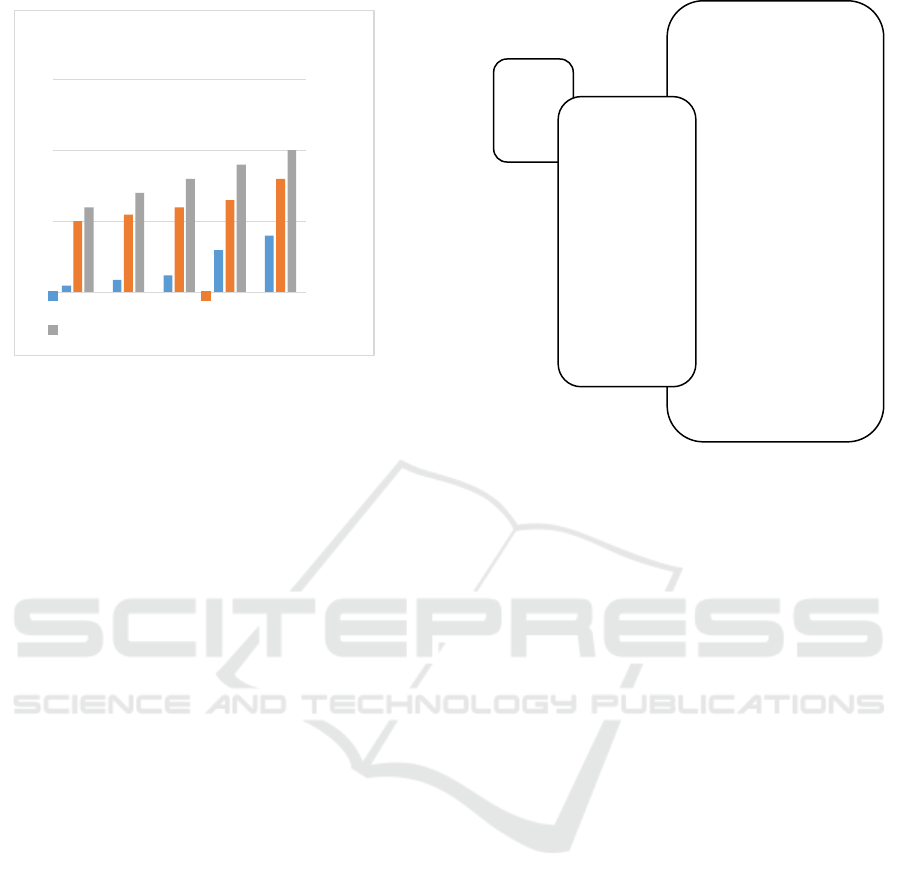
0
5
10
15
2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Rp.Miilliar (Ribu)
Baznaz Performance th.
2013-2017
Zakat Funding Poverty gap
Potential of Zakat
Figure 3: Baznaz Performance.
Source: Processed from Data BPS and Zakat Funding
(BAZNAZ)
From the graph above can be concluded that the
potential of zakat continues to increase, but
optimization needs to be improved so that the
performance of BAZNAZ can close the social gap.
According to Muhammad Rifki (2008) in his book
Sharia Financial Accounting explained that zakat
has a role for the distribution of welfare. The
function of zakat encourages productive flowing
property and zakat functions in the distribution of
income, i.e. land, property, house, gold and money
that has fulfilled the nisab of zakat hence obliged to
be issued to encourage flowing treasures. By zakat,
the redistribution of the economic resources of the
wealthy to the less prosperous will be achieved, so
that the government can allocate the public
expenditure budget to the education and health
sectors for the welfare of society.
4.2 Islamic Economic Strategy in
Poverty Reduction
Islamic economics has given new hope to the
Indonesian economy, according to chairman of the
board of commissioners of Financial Services
Authority, Wimboh Santoso said that sharia banking
assets grew by 20.65% at the end of February 2018.
This indicates that public awareness and trust
regarding sharia economy. Here is a chart on the
principles of sharia economy.
Table 4: Islamic Economic.
Source: Indonesian Council of Ulama and Bank Indonesia,
2017
According to Ahmed (2004) in Azis (2016) the
instruments in poverty alleviation is zakat.
According to him, several countries of the season
such as Libya, Malaysia, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia and
Yemen collect and spread zakat through government
initiatives. These countries have shown that good
zakat and administration structures can raise
awareness of the importance of zakat among
Muslims. Then the next development is to integrate
waqaf and zakat with Islamic microfinance which
then proves that good coordination between zakat
and waqaf institutions, government agencies, non-
government organizations, social organizations and
civic organizations is essential to create community
welfare and alleviate poverty.
The Islamic economic system with muamalat
transactions has shown its development flourish over
the last two decades not only relevant to the
empowerment of Muslims but also relevant to be
developed in the national economic recovery effort
in general. It is said that because a number of
principles which are the conclusions of the Qur'an
and Hadith it seems appropriate to be the antidote
for the acute problems in the national economic
system that has been running. The concept that all
property belongs to God is essential, and man
possesses it only in a false sense, and the belief in
accountability of its origin and future use is a matter
that significantly distinguishes between Islamic
economics and capitalist and socialist.
Islamic
Econo
mic
The function of
Islamic Economics
➢ Control of
individual
property to
flow
productively,
income
distribution to
ensure the
inclusiveness
of the whole
community
➢ Social
participation
for social
purposes
➢ Financial
transactions
are closely
related to the
real sector
(there are
underlying
transactions,
prohibiting
unproductive
speculation
➢ Business
optimization
(buying and
selling) and
risk sharing
princip
les of
Islamic
economics
Zakat.,I
SWAF
(Infaq,
Shodaqoh,
wakaf), No
Maysir, No
Riba, No
Gharar and
Dharar
Analysis of Public Expenditure Strategy on Social Fund Sector for Poverty Reduction of Indonesia Islamic Economic Perspective
189

From the results of the interview with Abd.
Salam Nawawi as an expert of Islamic economic and
general chairman of East Java in Baznaz explains
that the management of zakat funds in alleviating
poverty is by providing zakat funds for distribution
and utilization. That the distribution of zakat is
defined as the distribution of zakat to mustahik in a
consumptive way, namely assistance that is directly
consumed in daily life, for example food, clothing,
and so on. While the utilization of zakat is defined as
the distribution of zakat to mustahik oriented to
productive aspects, namely the distribution in the
form of productive goods, such as sewing machines,
business capital assistance, and so forth. He also said
that with the assistance given to mustahik, it could
not fully reduce the poverty rate in one of the cities
in Indonesia, namely East Java, but it was very
beneficial and could reduce the burden on the lives
of the mustahik. This fact is caused by zakat
distribution programs which are more directed to
consumptive matters. In addition, the value of
assistance provided is also relatively small because
the funds collected are still limited, while the
number of people who need help is very large. Why
is this said, because it depends on the mustahik how
to manage or utilize the assistance. Then by the
Zakat Amil Agency (BAZ) the zakat fund is realized
in the form of giving skills and capital to be given to
the mustahik after the eight basic needs are fulfilled.
So from the results of interviews it can be
suggested that zakat management by the government
is logical, due to several considerations, namely: 1.
To guarantee certainty and discipline in paying
zakat. 2. Maintain the inferiority complex of the
zakat mustahik when dealing directly with the
obligatory zakat (muzakki). 3. To achieve efficiency,
effectiveness and the right target in collecting zakat
assets according to priorities in a place.
4.3 The Special Strategy of Islamic
Economic Development
The development of a sustainable economy and
Islamic finance of Indonesia that is sustainable in
accordance with the values of sharia. According to
Bank Indonesia 2016, a special strategy is needed in
the development of sharia economy with the
achievement of the target to increase sharia business
assets. These strategies include:
1. Empowerment of Sharia Economics in local
policy, by preparing human resources that are
human, polite and humble, so required
supporting infrastructure, institutional and also
halal supply.
2. The deepening of sharia financial market which
is a national policy with the target of high level
of financial market achievement, supported by
instrument, infrastructure, regulation and investor
base which expert in their respective fields.
3. After the national policy is established, it is also
necessary to strengthen the assessment and
education research that has covered international
coordination and cooperation.
With the growth of Sharia asset that has grown
20.65% by the end of February 2018 has contributed
to the empowerment of sharia economy. If this
continues to increase then the optimization of the
strategy successfully executed, so as to reduce the
percentage of spending on the social funds sector.
Therefore, public expenditures can be optimized in
other sectors of education and health as well as
reduce debt and can increase economic growth and
welfare of the people of Indonesia.
5 CONCLUSION
The government's strategy in directing fiscal policy
that supports the livelihoods of disadvantaged
people, especially public spending is the target of
social assistance. Improve protection, productivity
and fulfillment of basic rights for the
underprivileged and the strategy in the perspective
of Islam are the function of zakat to encourage
property that flows productively and the function of
zakat in the distribution of income in Islamic
economics. These two things should get great
attention. Production does not accumulate a group of
people. The strategy to increase zakat income by
conducting zakat management is carried out by the
government because it is proven to help reduce
poverty. For specific strategy is that the Government
must improve the empowerment of Islamic
economics by deepening the Islamic Financial
Market. The Government must strengthen education
assessment and research. Well-managed
optimization makes public spending optimized for
other education and health sectors as well as
reducing debt and increasing Indonesia's economic
growth.
REFERENCES
Abd, Majid, Shabri, M., 2017. Poverty Alleviation In
Islamic Economi Perspective. (Aceh: Syiah Kuala
University)
Badan Pusat Statistik., 2017. Jakarta : Indonesia
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
190

Bank Indonesia., 2016. Pengelolaan Zakat yang Efektif.
Jakarta : Indonesia
Ilmi, Syaiful., 2017. Konsep Pengentasan Kemiskinan
Perspektif Islam. Pontianak: IAIN Pontianak
Informasi APBN 2018., Jakarta Indonesia
Interview with Expert Islamic Economic Abd. Salam
Nawawi, 7 Juli 2018.
Jaelani, Aan., 2012. APBN Management and Budget
Politics in Indonesia in Islamic Economic Perspective.
MPRA Paper No. 69555.
M. Nusrate Aziz Osman Bin Mohamad, (2016),"Islamic
social business to alleviate poverty and social
inequality",International Journal of Social Economics,
Vol. 43 Iss 6 pp
Majelis Ulama Indonesia., 2017 Jakarta: Indonesia
National Agency for Amil Zakat Institution (Baznaz),
2018
Otoritas jasa Keuangan., 2018. Jakarta: Indonesia
Pusat Badan Amil Zakat Nasional., 2017. Jakarta :
Indonesia
Qardhawi, Yusuf., 1995. Kiat Islam Mengentaskan
Kemiskinan. Jakarta: Gema Insani Press
Rencana Pembangunan jangka Panjang (RPJP). 2005-
2025. Jakarta: Indonesia
Rifqi, Muhammad., 2008. The book Akuntansi Keuangan
Syariah Konsep dan Implementasi PSAK Syariah,
Yogyakarta: P3EI
Siddiqi, Nejatullah, M., 1992. Teaching Public Finance in
Islamic Perspective (Jeddah: Centre for Research in
Islamic Economics king Abdul Azis University)
Ul Haq, Irfan. Economic Doctrines Of Islam: A Study in
the doctrine of Islam and their Implications for
Poverty, Employment and Economic Growth (Herdon,
Virginia, USA : The International Institute of Islamic
Thought, 1996)
Zafar, Iqbal., 2003. An Islamic Perspective on Public
Finance in Islamic Perspective (Australia: University
of South Australia)
Analysis of Public Expenditure Strategy on Social Fund Sector for Poverty Reduction of Indonesia Islamic Economic Perspective
191
