
The Correlation of Self-efficacy with Anxiety in Stroke Patients
Pawiono, Dewi Agustin, Heni Maryati and Mamik Ratnawati
Diploma III Nursing Program, STIKES Pemkab Jombang, East Java, Indonesia
Keywords: Self-Efficacy, Anxiety, Stroke.
Abstract: The number of stroke disease in Indonesia has been increased in 2013 from 8.3 to 12.1 per 1000 inhabitants.
A person who suffers a stroke will experience paralysis or weakness on the side of the stroke patient. This
results effect the psychosocial problems felt by stroke patients, one of which is anxiety. This study aims to
determine the effect of Self-efficacy with anxiety level in stroke patients. This study used analytic
correlation method with cross sectional approach. The populations in this study were 147 respondents
covered all stroke patients who were treated in the Jombang Hospital. Samples of 37 respondents were taken
using Quota Sampling. Independent variable was self-efficacy; dependent variable was Anxiety, to collect
data with statistical test with questionnaire test that used spearman's rank. The results shows that most of the
respondents had positive self-efficacy and most of the respondents had mild anxiety level with significance
value p = 0.022. It means that there was a relationship of self-efficacy with anxiety level in stroke patients.
Self-efficacy plays an important role to increase confidence in stroke patients. The results of this research
can motivate stroke patients to decrease their anxiety.
1 BACKGROUND
Stroke is a serious neurological problem, and it is
the highest cause of death (Dourman K, 2013). A
person suffering from a stroke will experience
paralysis or weakness on the stroke side of the body.
This is the problem of life. A problem faced by
someone who was hospitalized one of them is a
psychosocial problem. Psychosocial problems that
are usually felt by stroke patients who are treated in
the hospital one of them is anxious. With anxiety
will aggravate the perceived illness. One way to
relieve anxiety is with Self-efficacy.
In ASEAN countries stroke is also a major health
problem that causes death. According to the
American Heart Association (AHA), the stroke
mortality rate in stroke patients in the United States
each year is 50-100 out of 100,000 people. Of all
stroke sufferers in Indonesia, ischemic stroke is the
most common of 52.9% followed sequentially by
intracerebral hemorrhage, embolism and
subarachnoid hemorrhage with an incidence rate of
38.5%, 7.2% and 1,4% (Dinata, Yuliani, 2013).
Basically, stroke is caused by cerebral
thrombosis, cerebral embolism, cerebral ischemia
and cerebral hemorrhage which can lead to paralysis
or weakness on the side of the stroke patient, who
initially can move normally as normal people, but
after a stroke that is marked by loss function of the
body suddenly due to impaired blood flow of the
brain, so that stroke patients will experience physical
disorders, disruption of activity or mobility. This
will lead to problems in the psychological one of
which is anxiety. Cognitive symptoms of anxiety
such as worry, feeling disturbed, fear, confusion and
difficulty concentrating are some of the symptoms of
patients experiencing anxiety. One way to relieve
anxiety is with Self-efficacy. According to Bandura's
theory, people with high Self-efficacy are those who
believe that they can do well with difficult tasks as
something that must be mastered is not something to
be avoided (Suharsono and Istiqomah, 2014) .3
Individuals who have high Self-efficacy , when
faced with a stressful situation will try harder and
last longer and will be more active in the effort than
people who have low Self-efficacy, and will be more
daring to set targets or goals to be achieved
(Sulistiyowati, 2007).
With treatment, it is expected of stroke patients
can increase the chances of life, and in turn can save
the soul of the patient. However, the handling was
done above has not touched the mental aspect,
whereas stroke patients will experience psychosocial
problems such as anxiety (Widarti, 2012) Based on
676
Pawiono, ., Agustin, D., Maryati, H. and Ratnawati, M.
The Correlation of Self-efficacy with Anxiety in Stroke Patients.
DOI: 10.5220/0008330806760681
In Proceedings of the 9th International Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 676-681
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
background above, the researchers feel interested to
raise the problem of Self-efficacy with Level of
Anxiety In Stroke Patients In Flamboyan Pavilion of
RSUD Jombang.
2 METHODS
The type of study was analytic correlation method
with cross sectional approach. The population of this
study were 147 respondents covered all stroke
patients who were treated in the Pavilion Flamboyan
RSUD Jombang. A sample of 37 respondents was
taken using Quota Sampling. Independent variables
was self-efficacy, dependent variable was anxiety,
data retrieval method with statistical test
questionnaire used spearman's rank.
In conducting this study the researcher got a
research permit from Institution STIKES Pemkab
Jombang, and then the license was submitted to
RSUD Jombang. After receiving a reply letter from
RSUD Jombang, the reply letter was proposed to the
Head of Flamboyan Pavilion Room of RSUD
Jombang. After getting permission from the Head of
Flamboyan Pavilion Room of RSUD Jombang then
the researcher found respondents and approaches the
respondent by first explaining the intent and purpose
of thestudy to be conducted by the researcher.
3 RESULTS
The results of study would discuss about the
characteristics of respondents based on Self-efficacy
with anxiety level in stroke patients in the
Flamboyan Pavilion of Jombang General Hospital.
The study conducted on 10-25april 2017. Data
collection used questionnaire Self-efficacy and
anxiety questionnaire, research sample as many as
37 respondents.
Table 1 showed that respondents of stroke
patients in the Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD
Jombang were predominantly 46-65 years old,
amounting to 21 people (56.8%). Based on sex
showed that respondents of stroke patients in
Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD Jombang were 24
females (64.9%).
Based on education showed that the respondents
of stroke patients in the Pavilion Flamboyan RSUD
Jombang mostly primary school with 23 people
(62.2%).
Table 1: Distribution of stroke patients’ characteristics.
General Data Frequency Percentages
(%)
Age
36-45 Years ol
d
5 13.5
46-65 Years ol
d
21 56.8
>65 Years ol
d
11 29.7
Gender
Male 13 35.1
Female 24 64.9
Education
Elementar
y
23 62.2
Junior High School 5 13.5
Senior Hi
g
h School 7 18.9
College 2 5.4
Occupation
Unem
p
lo
y
ment 16 43.3
Frame
r
18 48.6
Retired civil servants 3 8.1
Period of caring
1-5 da
y
s 22 59.5
6-10 days 9 24.3
11-15 da
y
s 3 8.1
16-20 days 2 5.4
21-25 da
y
s 1 2.7
Table 2: Frequency distribution of self-efficacy in stroke
patients.
Self-Efficacy Frequency Percentages
(%)
Positive 23 62.2
Negative 14 37.8
Total 37 100
Table 3: Frequency distribution of the anxiety in stroke
patients.
Anxiety Frequency Percentages
(%)
Not anxiety 11 29.7
Mil
d
15 40.5
Medium 9 24.3
Stron
g
2 5.4
Total 37 100
Based on the occupation, it showed that the
respondents of stroke patients in the Pavilion
Flamboyan Jombang Hospitalalmost half worked as
farmers with the number of 18 people (48.6%).
Based on the length of care, it showed that the
respondents of stroke patients in Pavilion
Flamboyan of RSUD Jombang mostly undergo long
treatment in Flamboyan Pavilion 1-5 days as many
as 22 people (59.5%).
The Correlation of Self-efficacy with Anxiety in Stroke Patients
677
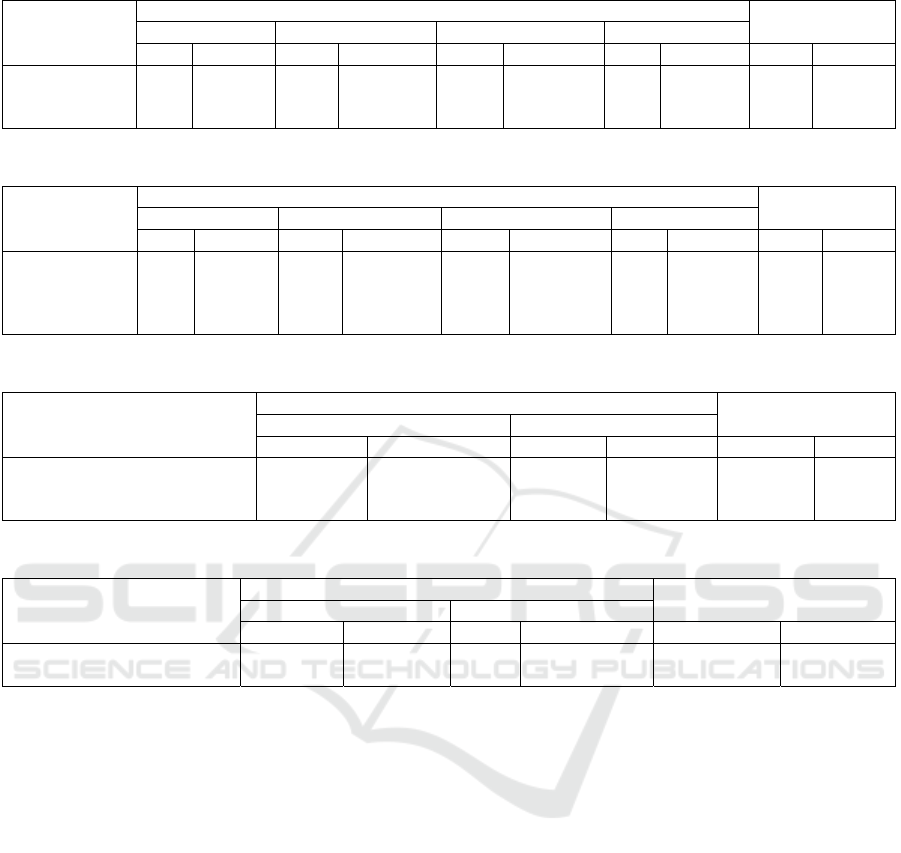
Table 5: Cross-tabulation between ages with anxiety in stroke patients.
Age
Anxiet
y
Total
Not Anxiet
y
Mil
d
Mediu
m
Stron
g
f % f % f % f % f %
36-45Years
45-65 Years
>65 Years
0
6
5
0.0
28.6
45.5
4
8
3
80.0
38.1
27.3
1
5
3
20.0
23.8
27.3
0
2
0
0.0
9.5
0.0
5
21
11
100
100
100
Table 6: Cross-tabulation between educations with anxiety in stroke patients.
Education
Anxiety
Total
Not Anxiet
y
Mil
d
Mediu
m
Stron
g
f % f % f % f % f %
Elementary
Junior High
Senior High
Colle
g
e
6
2
1
2
26.1
40.0
14.3
100
9
2
4
0
39.1
40.0
57.1
0.0
6
1
2
0
26.1
20.0
28.6
0.0
2
0
0
0
8.7
0.0
0.0
0.0
23
5
7
2
100
100
100
100
Table 7: Cross-tabulation between ages with self-efficacy in stroke patients.
Age
Self-Efficac
y
Total
Positive Negative
f % F % f %
36-45 years
45-65 years
>65 years
3
12
8
60.0
57.1
72.2
2
9
3
40.0
42.9
27.3
5
21
11
100
100
100
Table 8: Cross-tabulation between genders with self-efficacy in stroke patients.
Gender
Self-Efficac
y
Total
Positive Negative
f % F % F %
Male
Female
8
15
61.5
62.5
5
9
38.7
37.5
13
24
100
100
Table 2 showed that respondents of stroke
patient in Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD Jombang
mostly had positive Self-efficacy of 23 people
(62.2%), whereas almost half of respondents had
negative Self-efficacy of 14 people (37.8%).
Table 3 showed that respondents of stroke
patient in Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD Jombang
almost half had mild anxiety level of 15 people
(40.5%).
Table 4 showed that 37 respondents of stroke
patients in Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD Jombang
had positive self-efficacy mostly had mild anxiety
level that was 12 people (52.2%), whereas from
respondent with negative self-efficacy almost half
had moderate anxiety level as many as 6 people
(42.3%).
Table 5 showed that of 37 respondents of stroke
patients in Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD Jombang,
aged 46-65 years, almost half experienced mild
anxiety level of 8 people (38.1%).
Table 6 showed that 37 respondents of stroke
patients in the Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD
Jombang with elementary school education, almost
half experienced mild anxiety about 9 people
(39.1%).
Table 7 showed that 37 respondents of stroke
patients in Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD Jombang,
46-65 years old, most of them had positive self-
efficacy of 12 people (57.1%).
Table 8 showed that 37 respondents of stroke
patients in the Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD
Jombang, most of them had positive self-efficacy of
15 people (62.5%) and almost half have negative
self-efficacy of 9 people (37.5%).
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Self-Efficacy to Patients with
Stroke
Based on Table 2 showed that the respondents of
stroke patients in the Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD
Jombang mostly had positive Self-efficacy of 23
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
678

people (62.2%), while almost half of the respondents
had negative Self-efficacy of 14 people (37.8%).
According to Bandura (1997) in the book of
psychological theories (Ghufron and Risnawita,
2016) Self-efficacy can be derived from 4 factors:
Master Experience, Vicarious Experience, Verbal
Persuasion and Physiological State, which is an
experience / achievement ever achieved by
individuals in the past, these four sources will affect
a person's perception of his illness and its
management.6 According to (Walker, 2007) the
longer the acceptance of his illness would affect the
patient's Self-efficacy and there was a positive
correlation between perception and the patient's
Self-efficacy, that was, if the perception was good
then Self-efficacy increases.
Based on these facts and theories, the researcher
concluded that positive self-efficacy was supported
by some stronger factors and stronger willingness so
that individuals who have higher self-efficacy will
be more trying to overcome illness suffered than
individuals who had negative self-efficacy.
Table 7 showed that 37 respondents of stroke
patients in Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD Jombang,
46-65 years old, most of them had positive self-
efficacy as many as 12 people (57.1%).
According to Bandura (1997) older individuals
had more time span and experience in overcoming
things when compared to younger individuals.
Based on existing facts and theories of
individuals aged 46-65 years had high self-efficacy.
This was because older individuals were more
focused and more striving to achieve the desired
healing or outcome so they still hadstrong belief in
themselves to heal.
Table 8 showed 37 respondents of stroke patients
in Flamboyan Pavilion at RSUD Jombang, most of
them had positive self-efficacy as many as 15 people
(62.5%) and almost half had negative self-efficacy
was 9 people (37.5% ).
According to Bandura (1997) in the book of
psychological theories (Ghufron and Risnawita,
2016) In some areas of a particular job men had
higher self-efficacy compared to women, and vice
versa self-efficacy women excel in some jobs
compared with men. Men usually had high self-
efficacy with jobs that demand mathematical of
technical skills.
According to the analysis of researcher, female
had a high level of confidence in dealing with the
disease that she suffered. In addition, women had a
more calm and persevering in undergoing treatment
of the illness.
Based on Table 4 showed that from 37
respondents of stroke patients in Flamboyan
Pavilion of RSUD Jombang which had self positive
efficacy, most of them had mild anxiety level is 12
people (52.2%), while from respondent own self
negative efficacy almost half have medium anxiety
level that was as many as 6 people (42.3%). From
the above data could be concluded that the higher
Self-efficacy affected owned respondents lighter
level of perceived anxiety.
According to Bandura (Blackburn & Davidson,
1994) described what matters in relieving anxiety,
among others, as follows: Self-efficacy was as an
individual's mind to his or her own ability to cope
with situations. Outcome Expectancy had a sense as
an individual estimate of the likelihood of
consequences. Certain consequences that may had
an effect on suppressing anxiety (Sarafino, E.P &
Smith, 2011). Based on the most important thing
that must be owned by individuals to be able to carry
out healthy behavior is Self-efficacy.
Based on these facts and theories, stroke patients
should have confidence in the treatment and
treatment could maintain their life. Basically, any
patient with an illness would have a disruption to
more physical functioning when the patient has inner
confidence or has the ability to perform certain
behaviors. Patients had confidence in their ability to
cope with various treatments so as to overcome the
pain of their illness known as self-efficacy. The
respondents with positive self-efficacy had a mild
anxiety level. This was because the patient had a
positive efficacy or self-confidence to heal, and with
care and treatment had been done to maintain his
life.
The anxiety of patients with Stroke in
Flamboyan Pavillionof RSUD Jombang
Based on Table 3, it showed that the respondents
of stroke patients in the Pavilion Flamboyan
Jombang Hospital almost half had a mild anxiety
level of 15 people (40.5%).
According to Davis and Palladino (1997) anxiety
had a sense as a general feeling that has behavioral
characteristics and cognitive or psychological
symptoms. 19% of men and 31% of women had
experienced anxiety. While Hall and Lindzey (2001)
added, anxiety was the tension resulting from threats
to security, both real and ordinary imagination
(Safaria dan Nofrans, 2012).
Based on the results of the study the researchers
concluded that stroke patients in Pavilin Flamboyan
RSUD Jombang hadmild anxiety level, this wa
because stroke patients have more confidence level
about the disease they face.
The Correlation of Self-efficacy with Anxiety in Stroke Patients
679

Table 5 showed that 37 respondents of stroke
patients in Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD Jombang,
46-65 years old, almost half had mild anxiety level
of 8 people (38.1%).
According to (Kaplan & Sadock, 1997), that
anxiety disorders could occur at any age, more often
in young adulthood, ie at age 21-44 years.
This was contrast to what was found by
researchers, the age that experienced anxiety most of
the respondents aged 46-65 years. According to the
analysis of age researchers were more often
experienced psychological problems. When
someone aged 46-65 years then they will face
various kinds of problems both in terms of physical,
psychological, and social. From some of these
problems, when someone did not have strong beliefs
would experience anxiety.In addition, when
conducted research on stroke patients in the Pavilion
Flamboyan RSUD Jombang at the age of 46-65
years so that ultimately the anxiety felt by stroke
patients more in the age range 46-65 years.
Table 6 showed that 37 respondents of stroke
patients in the Flamboyan Pavilion of RSUD
Jombang were mostly 23 elementary school students
(62.2%), some had minor anxiety about 9 people
(24.32%) and a few had severe anxiety a total of 2
people (5.4%). This was supported by (Struart &
Sundeen, 1998), that the lower education level of a
person then the knowledge obtained tend to be less.
Conversely, the higher education would be easier to
think rationally and capture information.
Based on facts and theories, one's education
greatly affected the level of anxiety. This was
because a person with a lower level of education had
less experience and knowledge that would affect a
person's knowledge. One of them was the
knowledge of the disease that was suffered, so it
would cause a negative response that is anxiety.
4.2 The Correlation of Self-Efficacy
with Anxiety Level of Patients with
Stroke
In this section would be discussed about the
correlation of self-efficacy with anxiety. Based on
statistical test results showed correlation coefficient
r = 0.376 and significance value p = 0.022 which
means smaller than 0.05 then H1 accepted. This
means there was a correlation of Self-efficacy with
anxiety levels in stroke patients in the Flamboyan
Pavilion of RSUD Jombang. This means that the
higher self-efficacy of stroke patients, the lower
anxiety of the stroke patients. Similarly, the lower
self-efficacy of stroke patients affected the higher
perceived anxiety of the stroke patient.
The results of this study were in line with
previous research conducted by (Anwar, 2009) on
the relationship between Self-efficacy with the
anxiety of speaking in front of the students at the
University of North Sumatra psychology faculty
who showed the result that there was a significant
negative relationship between Self-efficacy with
public speaking anxiety in public faculty of
psychology of Universitas Sumatera Utara.
From the results of this study with the results of
research from researchers themselves about self-
efficacy with anxiety, it could be concluded that the
level of self individual efficacy would affect anxiety
in the individual in the face of a problem. Or with
another sentence that self-efficacy owned by stroke
patients could improve or alleviate anxiety for stroke
patients.
Self efficay person was associated with several
factors, among others: gender, age, education and
employment. Self-efficacy determines the form of
action they would choose to do, as strong as the
individual could survive in the face of the problems.
According to Bandura, self-efficacy was useful for
training control of anxiety itself. When people
experience high anxiety they usually had low self-
efficacy, while those with high self-efficacy would
feel able to overcome obstacles and perceive threats
as a challenge that was unnecessary to avoid. With a
high Self-efficacy, individuals will run their business
with enterprising, not easily give up, and would
make every effort to get maximum results in the face
of its duties. While individuals with low Self-
efficacy would feel easily give up and easily
desperate in the face of problems. This means that
stroke patients with low Self-efficacy did not dare to
face the problem and easy to give up.
According to Adler and Rodman (Ghufron dan
Risnawita, 2016) there were two factors that cause
anxiety, namely: negative experiences in the past.
Anxiety that could arise may be palpitations, cold
sweats, tremors and other anxiety responses.
Another factor that was unpleasant thoughts would
happen to him. While factors that may affect anxiety
include: age, physical condition and education level.
Bandura (Blackburn and Davidson, 1994)
describes what matters in relieving anxiety, among
others, as follows: Self-efficacy was an individual's
estimate of his or her own ability to handle
situations. Outcome expectancy had an
understanding as an individual estimate of the
possibility of certain consequences may have an
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
680

effect on suppressing anxiety (Safaria dan Nofrans,
2012).
Thus, Self-efficacy and anxiety played an
important role in stroke patients who were
undergoing treatment at the Hospital. Self-efficacy
played an important role in providing confidence
that with the conduct of treatment and treatment of
the disease would be able to maintain thepatient's
life. Self-efficacy was one way to relieve anxiety in
stroke patients who were undergoing treatment at the
Hospital. The self-efficacy is expected to reduce the
anxiety in stroke patients.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Self-efficacy has relation with anxiety level on
stroke patient. Self-efficacy plays an important role
to increase confidence in stroke patients. The results
of this research can motivate stroke patients to
decrease their anxiety. For further research, we
recommend to study research development on other
factors related to self-efficacy or anxiety.
REFERENCES
Anwar, astrid. I. . (2009) ‘Hubungan Antara Self-efficacy
dengan Kecemasan Berbicara di Depan Umum pada
Mahasiswa Fakultas Psikologi Universitas Sumatra
Utara’, Medan: Universitas Sumatra Utara.
Dinata, Yuliani, S. (2013) ‘Gambaran Faktor Resiko dan
Tipe Stroke pada Pasien Rawat Inap di Bagian
Penyakit Dalam RSUD Kabupaten Solok Selatan
Periode 1 Januari 2010 - 31 Juni 2012’,
http://jurnal.fk.unand.ac.id.
Dourman K (2013) ‘Waspadai Stroke Usia Muda’,
Jakarta: Cerdas Sehat.
Ghufron dan Risnawita (2016) Teori-teori Psikologi.
Jogjakarta: Ar-Ruzz Media.
Kaplan & Sadock (1997) Terapi Psikiatri. Jakarta: EGC.
Safaria dan Nofrans (2012) Manajemen Emosi. Jakarta:
Bumi Aksara.
Sarafino, E.P & Smith, T. . (2011) Biopsychosocial
Interactions. United States of America: John Willey &
Sons Inc.
Struart & Sundeen (1998) Keperawatan Jiwa. Edisi 3.
Jakarta: EGC.
Suharsono and Istiqomah (2014) ‘Validitas Dan Reabilitas
Skala Self-efficacy’, http://ejournal.umm.ac.id/.
Sulistiyowati, P. (2007) ‘Hubungan Antara Burnout
dengan Self-efficacy pada Perawat di Ruang Rawat
Inap RSUD Prof. Dr. Margono Soekarjo Purwokerto’,
Http://jurnalonline.unsoed.ac.id.
Walker (2007) ‘Importance of Illness Beliefs and Self-
efficacy for Patients with Coronary Heart Disease’,
Journal ofAdvanced Nursing, 48(3), 216-225.
Widarti, dkk (2012) ‘Respons Psikologis (Kecemasan dan
Depresi) dan Respons Biologis pada Pasien Stroke
Iskemik dengan Pendekatan Model Home Care
Holistic’, Jurnal Ners : Poltekes Kemenkes Surabaya.
The Correlation of Self-efficacy with Anxiety in Stroke Patients
681
