
The Role of Organization Citizenship Behavior (OCB) in Mediating
the Organizational Culture on the Performance of LPD Employees in
Badung Regency
I Gusti Ayu Dewi Adnyani, I Gusti Ngurah Jaya Widagda and I Wayan Wina Widyatama
Faculty of Economics and Business, Udayana University, Bali, Indonesia
Keywords: Organizational Culture, OCB, Employee Performance, LPD.
Abstract: This research is conducted based on the increasing competition in various economic sectors triggered by
globalization which makes it necessary for business practitioners to adapt their behavior, method, and
business strategy in order to maintain their existence and continuity of their business. The current
competition without exception was also felt by micro finance institutions, including the Village Credit
Institution (LPD). In the effort to improve employee performance, the company must have a strategy that is
certainly in accordance with the organizational goals. The implementation of OCB by employees in their
work place may result in an increase in employee performance, the unit/section performance in which the
employee works in, and the company performance as a whole. The organizational culture becomes the
guideline in the process of adapting to the organizational environment and the types of organizational
culture can become a predictor of performance or effectivity. Therefore, the purpose of this research is to
explain the role of OCB in mediating the influence of organizational culture on the performance of LPD
employees. This research is conducted in Badung Regency by taking 110 LPD employees as the sample.
The analysis method used is the SEM analysis.
The research result shows that organizational culture has a positive and significant influence on employee
performance of LPDs in Badung Regency. Organizational culture has a positive and significant influence on
the OCB of LPD employees in Badung Regency. Employee’s OCB has a positive and significant influence
on the performance of LPD employees in Badung Regency. OCB is able to significantly mediate the
influence of organizational culture on employee performance. This means that by developing OCB in
employees, the influence of organizational culture on the employee performance of LPDs in Badung
Regency will increase.
Thus, LPDs in Badung Regency must always develop the organizational values and search for methods to
encourage employees to work beyond their responsibility.
1 INTRODUCTION
The increasing competition in various economic
sectors has been triggered by globalization which
makes it necessary for the industry practitioners to
adjust their behavior, method, and business strategy
to be able to sustain the existence and continuity of
their business. Adaptability in responding the
changes in the internal and external environment of
the company is absolutely needed considering that
the environment is one of the dominant factors
which determines the continuity and competitive
advantage of a company (Porter, 1979; Mohant and
Rath, 2012). The competitions that occur nowadays
are also felt by microfinance institutions,
includingthe Village Credit Institutions or Lembaga
Perkreditan Desa (LPD).
The LPD is among the types of microfinance
businesses in Bali. The development of LPDs has
recently shown a fall in performance due to tight
competitions faced by the LPDs. The competitors of
the LPDs are the Bank Perkreditan Rakyat (BPR) or
Rural Banks, Saving and Loan Cooperatives, and the
loan sharks. To maintain the existence of the LPD,
adequate resources are needed. Among the resources
detrimental to the LPD’s performance is the Human
Resource.
The human resource factor influences the success
of the organization or company, especially in facing
Adnyani, I., Widagda, I. and Widyatama, I.
The Role of Organization Citizenship Behavior (OCB) in Mediating the Organizational Culture on the Performance of LPD Employees in Badung Regency.
DOI: 10.5220/0008493103570363
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Entrepreneurship and Business Management (ICEBM Untar 2018), pages 357-363
ISBN: 978-989-758-363-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
357

the tight competition today. This is also applicable in
banking businesses, in which one part of the internal
challenges of the banking business in facing
globalization is the human resource quality it has.
Qualified human resource is greatly needed in
businesses which require high level of work ethics,
such as microfinance institutions, because the
microfinance institution business is a business which
is highly dependent on trust. People will entrust their
financial matters, which can be regarding loans or
saving money, to finance institutions that have good
reputations, including the reputation of the
managers. Good reputation is definitely related to
the performance of the finance institution as an
organization or company. In the attempt to increase
the performance of employees, the company must
have strategies that are suitable with the
organizational goals. The indicators that can form
employee performance according to McNeese and
Smith (1996), consists of: the work results quality
level, the level of diligence and work endurance, the
level of discipline and attendance, the cooperation
level among employees, the degree of concern
regarding work safety, the level of responsibility
towards their work results, and the level of
initiative/creativity the employees possess.
From the results of evaluation conducted on the
employees of LPD in Badung Regency, it was found
that a majority of employees are not able to meet the
predetermined target regarding the distribution of
credit (lending) and third party fund raising. This
shows that the work result quality of employees is
low. Related to the underachievement of the
predetermined target by the LPD, employees have
not shown tenacity in their work endurance. For
example, a display of this characteristic would be the
willingness to add work hours to try hard to find
clients and reach the target assigned to each
employee. To date, the task of employees in
searching for clients are only based on the guidance
and instructions from the LPD Head. This occurs
because the LPD Head assesses that the employees’
lack the initiative or creativity in collecting the data
of potential clients to be prospected as the LPD’s
client.
The research regarding employee performance
have been conducted by other researchers such as: 1)
Hameed and Waheed (2011) who stated that
employees are valuable resources (assets) to the
organization. The success or failure of an
organization depends on the employee’s
performance. Therefore, organizations must invest a
large quantity of money on the development of
employees. 2) Shazadi et al. (2014) has underlined
that individuals working in business segments are
motivated by autonomy, freedom and responsibility
given in performing their task in accordance to the
position given by the management, 3) Zameer et al.
(2014) found that if the top management place their
focus on employee motivation, this will entail a
positive increase in employee performance, 4) Iqbal
et al. (2015) stated that companies with trained
employees will have positive impacts on the
performance of their employees.
1.1 Denison and Misra (1995) stated that
organizational culture has an influence on
performance. This statement is supported by theories
and empirical studies by experts that state that
organizational culture becomes a guide in the
adaptation process in an organizational environment
and the types of organizational culture can become
the predictors of performance and effectivity. The
studies conducted by Ojo (2009), Koesmono (2011),
andIndriani and Waluyo (2012) show that
organizational culture has a significant influence on
employee performance. These three studies stated
that corporate culture has an influence and is
positively related with employee performance.
However, there are also studies that have shown an
insignificant relationship between organizational
culture and employee performance. Yuan and Lee
(2011) stated that organizational culture has a weak
correlation with employee performance. The
research by Lim (1995) did not show any
relationship between culture and employee
performance.
In the recent years, there has been an increase in
interest in the strategic management process which
has a purpose to achieve work performances that
enable companies, including banks, to become more
competitive over time. This new concept requires
new alternative strategies for companies with
various types of needs in the dynamic market. Thus,
banks have to use alternative tools that are more
strategic to improve corporate performance through
their employees.
Another factor that can also increase employee
performance is the OCB. This was conveyed by
Chien (2003) by stating that several researches have
shown that OCB is positively related to individual
performance, unit performance, and organizational
performance. Thus, the implementation of OCB on
employees in the workplace can have an impact on
the performance of employees, performance of
unit/department where the employees are placed,
and the corporate performance as a whole. Every
company wants the employees to perform their tasks
exceeding what is stated in the job description, and it
ICEBM Untar 2018 - International Conference on Entrepreneurship and Business Management (ICEBM) Untar
358
has been proven that these companies have an
advantage compared to other companies (Hui et al.,
2000).
The research that showed that there is a
significant relationship between OCB and
performance was conducted by Alhamda and Sanusi
(2006) who stated that behavior as an organization
member and employee performance has a significant
relationship. Sugiyanto and Sutanto (2010) found
that between OCB and employee performance, there
is a positive influence. Azmi (2010) and Bachrach et
al., (2006) in their research found that OCB has a
significant influence on employee performance.
Likewise, Podsakoff et al., (2000) stated that there is
a positive relationship between OCB and employee
performance. From the results, these researches
explain and indicate that OCB influences the
improvement of employee performance.
2 CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
AND RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS
Conceptual Framework of the Research.
The conceptual framework in this research refers to
a number of previous studies (journal) that are
related to employee performance. Previous research
related to the research variables was conducted by
Chien (2003) who examined the influence of
personality, organizational culture, work climate,
and organization resources on OCB. In the research,
Chien concluded that personality and organizational
culture were proven to influence OCB.
The research by Azmi bin Ali (2010) examined
the influence of OCB on employee performance. In
this research, it was found that the influence of the
OCB variable on employee performance is
significant. Along with the research conducted by
Tseng and Lee (2011), which examined the
influence of organizational culture, and leadership
style on the organizational commitment, and the
influence of personality, organizational culture, and
leadership style on employee performance. This
research concluded that the personality and
organizational culture variables have influences on
the employee performance.
Based on the conceptual framework which
explains the correlation among the variables, the
conceptual framework is formulated and displayed
in Figure 1.
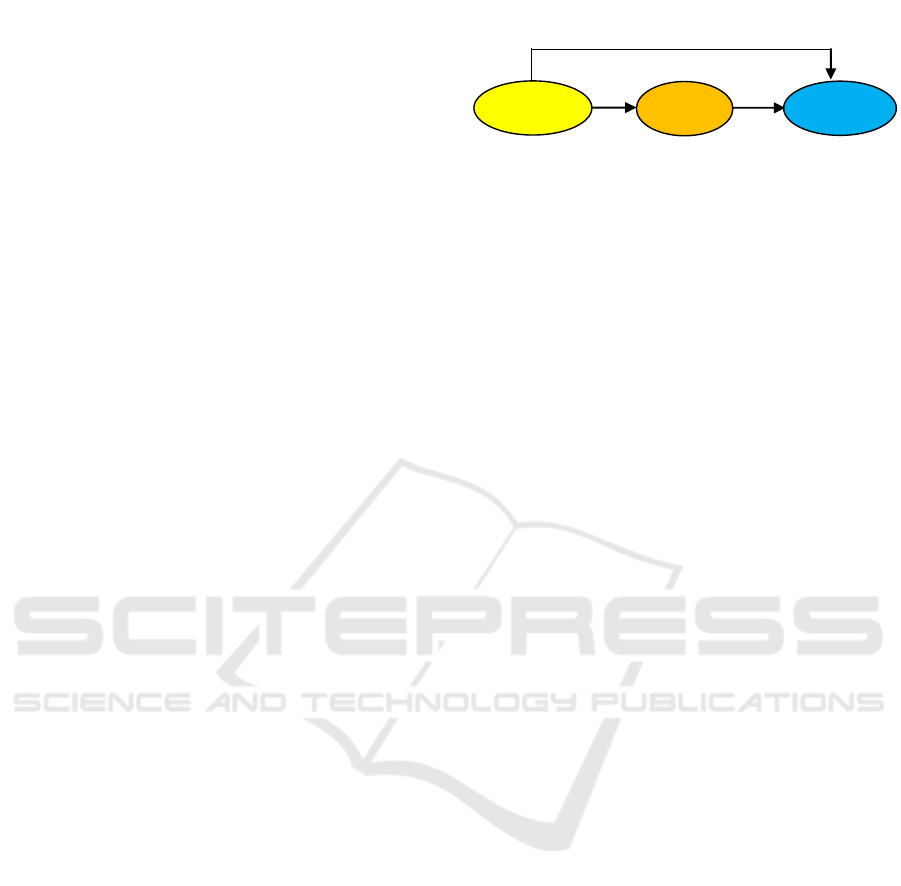
H
2(+)
H
3(+)
H
1(+)
Organizational
Culture
Employee
P
erformance
OCB
Figure 1: Conceptual Framework of the Research.
Research Hypothesis:
Based on the conceptual framework, the research
hypotheses are formulated as follows.
H1:
Organizational culture has a positive and significant
influence on employee performance.
H2:
Organizational Culture has a positive and significant
influence on OCB.
H3:
OCB has a positive and significant influence on
employee performance.
H4:
OCB is able to mediate the influence of organizational
culture on employee performance.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
Viewed from the characteristics of the problem, this
research is categorized as a causality research. This
means that this research has the purpose to examine
the causal relationship between the variable of
organizational culture and OCB, along with
employee performance.
This research is conducted on the LPDs in
Badung Regency. The research subjects are the
LPDs in Badung Regency with research objects
related to employee performance. Based on the
problem statement and the hypothesis developed,
the variables in this research are identified as
follows:
1) The endogenous variable, namely the latent
variable in which the value is determined by
other variables in the model or is faced with an
arrow head (Solihin and Ratmono, 2013). The
endogenous variable in this research is employee
performance (Y).
2) The intervening variable, namely the variable
that influences the relationship between the
dependent variable, becomes an indirect
influence and is positioned between the
dependent variable and the independent variable,
thus the independent variable is indirectly
influenced by the dependent variable
(Indriantoro and Supomo, 2012:66). The
intervening variable in this research is the
organizational citizenship behavior (M).
The Role of Organization Citizenship Behavior (OCB) in Mediating the Organizational Culture on the Performance of LPD Employees in
Badung Regency
359

3) Exogenous variable, namely the latent variable in
which the value is determined by other variables
not included in the model or is not faced with an
arrow head (Solihin and Ratmono, 2013). The
exogenous variable in this research is the
organizational culture (X).
To define the variables related to the research object,
the operational definition of variables are explained
as follows:
Employee Performance (Y
2
).
Employee performance in this research is the work
result achievement of employees related to their
tasks and authorities that have been given by the
company in accordance with the ability and
competence of the employees, which is viewed from
the capacity and quality to achieve the goals as well
as vision and missions of the company. Performance
is closely related to the work result which
encompasses the quantity and even quality of an
employee to reach the organizational goals.
The indicators utilized to measure employee
performance in this research are the indicators
utilized by Mathis and Jackson (2009) and are
shown as follows:
1) Work Quantity (Y
2.1
).
This variable depicts the fulfillment of targets
that have been predetermined which also shows
the ability of the company in managing the
resources they have to achieve their goals. This
indicator is measured through the perception of
respondents, namely employees are able to
perform the job in line with the predetermined
quantity, amount/ volume of work is in line with
the expectation of the organization.
2) Work Quality (Y
2.2
).
This variable depicts the completion of work in
accordance to the demand of the organization.
This indicator is measured through the
perception of respondents, namely employees
who are able to complete their work with a
quality which meets the organization’s standards.
3) Working Time (Y
2.3
).
This variable depicts the working time deemed to
be most efficient and effective for all levels of
management. The working time is the basis for
employees to finish the work that they are
responsible for. This indicator is measured from
the perception of respondents on whether they
are able to finish their work punctually and
utilize their time effectively and efficiently.
4) Cooperation with Colleagues (Y
2.4
).
It is the support towards the success of the
organization in achieving their goals. Good
cooperation will result in trust from various
parties of interest, may it be directly or
indirectly related to the company. This indicator
is measured through the perception of
respondents, namely being able to cooperate
with colleagues and always behave positively in
each group work.
5) In Accordance with the SOP (Y
2.5
).
This variable depicts the completion of work in
line with the SOP that has been determined by
the organization. This indicator is measured
through the perception of respondents, namely
employees are able to perform their jobs in
accordance with the SOP available in the LPD.
Organizational Citizenship Behavior (Y
1
).
OCB in this research is the initiative behavior of
individuals that are not included in their job
descriptions but is performed voluntarily without
demanding rewards in order to fulfil the goals of the
company effectively and efficiently.
The indicators used to measure OCB in this
research are the indicators utilized by Organ et al.
(2006) which are shown as follows:
1) Altruism(Help Others) (Y
1.1
).
The attitude of helping other employees without
coercion in the jobs related to the operationals of
the organization. This indicator is measured
through respondents’ perception, namely helping
colleagues with excess work load as well as
cover up for the work of absent colleagues.
2) Conscientiousness (Y
1.2
).
The discretionary attitude performed by
employees in the form of taking action exceeding
the formal demand from the organization and
work exceeding the requirements determined by
the company. This indicator is measured through
respondents’ perception, namely: voluntarily
perform beneficial deeds for the organization and
comply to the regulation even without being
monitored.
3) Courtesy (Y
1.3
).
This attitude shows the concern towards
involvement in the corporation especially related
with attitudes that alleviate work problems faced
by others. This includes avoiding actions that
could cause others to work harder and decisions
that increase the workload of others. This
indicator is measured through the perception of
respondents regarding not creating problems
ICEBM Untar 2018 - International Conference on Entrepreneurship and Business Management (ICEBM) Untar
360
with colleagues and considering the impact on
colleagues for each action taken.
4) Civic Virtue (Y
1.4
).
The attitude that shows voluntary participation
and support towards the organizational functions
may it be professionally or social in nature, and
this awareness is the attitude of being responsible
and involved constructively in the organization’s
political process. This indicator is measured by
the respondents’ perception regarding
participation in various activities held by the
organization and provision of innovative
recommendations to increase the quality of the
organization.
5) Sportsmanship (Y
1.5
).
The discretionary attitude of employees and their
willingness to tolerate a little more than the ideal
condition without complaining and aversion
toward destructive matters, even though they are
irritated. This indicator is measured through the
perception of respondents, namely accepting
every policies upheld in the organization and
tolerating the discomfort felt at the workplace.
Organizational Culture (X).
Organizational culture (X) are the values, beliefs and
basic principles, in which are the basis for the
system and management practices and are also the
behaviors that improve and strengthen these
principles. Denison et al., (2006) conveyed several
statements regarding the dimensions of
organizational culture which are used to formulate
the instrument utilized in this research. The
indicators of the Organizational Culture variable
consist of:
(1) Always given the opportunity to be involved in
the organization’s planning process up to certain
limitations (X
.1
)
(2) The opportunity to be actively involved in the
activities held by the organization (X
2
)
(3) Receive a warning if they violate the
organization’s regulations (X
3.
)
(4) Able to adapt with the development in the
community (X
4.
)
(5) Policies made for the interest of the community
(X
5
)
(6) Clear organization targets (X
6
)
(7) Main tasks and functions of employees are clear
(X
7
)
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Hypothesis Test Results.
The hypothesis test is conducted by utilizing the t-
test on each direct influence path partially. The
complete analysis result is available in the SEM
analysis results, which is displayed in the appendix.
Table 1 shows the hypothesis test results for the
direct influences.
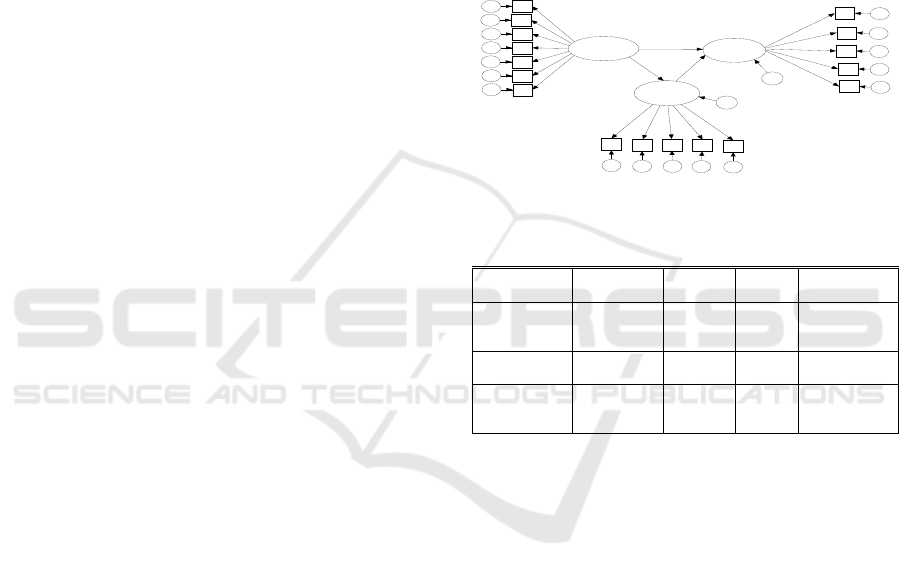
Budaya
Org.
.53
x4e4
.64
x3e3
.24
x2e2
.68
x1e1
.73
OCB
.82
y1.1
e8
.54
x5e5
GOODNESS OF FIT
Chi-Square=135.034
Probability=.109
CMIN/DF=1.164
GFI=.876
TLI=.983
CFI=.986
RMSEA=.039
AGFI=.836
.86
y1.2
e9
.48
.80
.83
.73
.74
.47
y1.3
e10
.69
y1.4
e11
.86
Kinerja
.72
y2.5
e17
z2
.60
y2.4
e16
.77
.83
.68
y2.3
e15
.82
.47
x6e6
.68
.66
x7e7
.81
.81
y1.5
e12
.85
.62
y2.2
e14
.79
.45
y2.1
e13
.67
.38
.69
.93
.91
.90
.58
.86
z1
Figure 2: SEM Model.
Table 1: Direct Influence Hypothesis Test Results.
Independent
Variable
Dependent
Variable
Path
Coefficient
p-value Description
Organizational
Culture (X)
Employee
Performance
(
Y
2
)
S 0,003 significant
Organizational
Culture(X)
OCB (Y
1
) 0,828 0,000 significant
OCB (Y1)
Employee
Performance(
Y
2
)
0,680 0,000 significant
Source : Appendix
Research Result Discussions.
From the validity and reliability calculation results,
it was found that all the indicators are able to
measure the variables and concepts being examined.
Additionally, between one concept and the other, all
are free. By conducting the confirmatory factor
analysis (the goodness of fit test and the factor
loading analysis), it was proven that the observed
variables can reflect the analyzed factors. By
conducting the overall goodness of fit test (goodness
of fit test and the regression weight causality test), it
has been proven that the model’s overall goodness
of fit and causality relationship developed can be
tested.
The Influence of Organizational Culture on
Employee Performance.
Based on Table 1, the organizational culture variable
is known to have a positive and significant influence
on the performance of LPD employees in Badung
The Role of Organization Citizenship Behavior (OCB) in Mediating the Organizational Culture on the Performance of LPD Employees in
Badung Regency
361

Regency. The proof can be seen from the p-value of
0,003 which is less than 0,05. The relationship
between the organizational culture variable and the
employee performance of LPDs in Badung regency
is positive which is shown by the inner weight value
of 0,436. This result can be interpreted as the higher
the organizational culture, the higher the employee
performance of LPDs in Badung Regency.
In this research, the indicators of the
organizational culture variable consists of the
opportunity to be involved in the organization’s
planning process with certain limits, the opportunity
to be actively involved in every event held by the
organization, receive warnings if they violate the
organization’s regulations, able to adapt with the
development in the community, policies are made
for the community’s interest, clear organizational
targets, and main tasks and functions of employees
are clear on the performance of LPD employees in
Badung Regency. This research result is in line with
the conditions faced by LPDs in Badung Regency.
The Influence of Organizational Culture on OCB.
Based on Table 1, the organizational culture variable
has a significant influence on OCB. This is proven
by the p-value of 0,034, which is lower than 0,05.
The relationship between the organizational culture
variable and the OCB variable shows a positive
influence marked by the inner weight value of 0,828.
This result can be interpreted as the higher the
organizational culture, the higher the OCB becomes.
In this research, the indicators of the
organizational culture variable, which consists of the
opportunity to be involved in the organization
planning process with certain limits, the opportunity
to be actively involved in every event held by the
organization, receive warnings if they violate the
organization’s regulations, able to adapt with the
development in community, policies are made for
the community’s interest, clear organizational
targets, and main tasks and functions of employees
are clear on the OCB of LPD employees in Badung
Regency. This research result is consistent with the
conditions faced by LPDs in Badung Regency.
The Influence of OCB on Employee Performance.
Based on Table 1, the OCB variable is known to
have a significant influence on employee
performance. This is proven by the p-value, which is
0,025, lower than 0,05. The relationship between the
OCB variable and the employee performance of
LPDs shows a positive influence which is marked by
the inner weight value of 0,680. This result can be
interpreted as the higher the industrial competition,
the higher the employee performance of LPDs in
Badung Regency.
In this research the indicators of OCB, which
include: help colleagues with excessive workload,
cover work for absent colleagues, voluntarily take
actions that are beneficial to the organization aside
from the main tasks, comply to the regulations even
without being monitored, to not create problems
with colleagues, consider the influence on
colleagues for each actions taken, participate in
various activities held by the organization, provide
innovative advices to improve the organization’s
quality, accept each policy set by the organization,
and tolerating the discomfort felt at the workplace
have important roles in increasing the employee
performance of LPDs in Badung Regency.
Conclusion.
Based on the research result, discussion and
interpretations that have been explained in previous
sections, by referring to several theories and
previous research results, the conclusions taken are
as follows: 1) Organizational culture has a positive
and significant influence on the Employee
Performance of LPDs in Badung Regency. 2)
Organizational culture has a positive and significant
influence on the OCB of LPD employees in Badung
Regency. 3) The OCB of employees has a positive
and significant influence on the Employee
Performance of LPDs in Badung Regency. 4) OCB
is able to significantly mediate the influence of
organizational culture on employee performance.
This means that by developing the OCB behaviors,
the influence of organizational culture on the
employee performance of LPDs in Badung Regency
will also increase.
REFERENCES
Alhamda, S. and Sanusi, R. 2006. Persepsi Perilaku
Kepemimpinan, Perilaku Sebagai Warga Organisasi
Dan Kinerja Dosen Politeknik Kesehatan Padang
Sumetara Barat. Working Paper Series, No.8 April
2006. Program Magister Kebijakan Dan Manajemen
Pelayanan Kesehatan. Universitas Gadjah Mada.
Yogyakarta.
Bachrach, G.D., Powell, C., Benjamin, Bendoly, E., and
Richey, G.R. 2006. Organizational Citizenship
Behavior And Performance Evaluations: Exploring
The Impact Of Task Interdependence. Journal of
Applied Psychology. Vol. 91, No. 1, pp. 193–201.
Chien, H.M. 2003. A Study To Improve Organizational
Citizenship Behaviors, Http://www.Mssanz.Org.Au/
ICEBM Untar 2018 - International Conference on Entrepreneurship and Business Management (ICEBM) Untar
362

MODSIM03/Volume_03/B14/03_Chien_Behaviours.
Pdf.
Denison. 1990. Cooporate Culture and Organizational
Effectiveness, Willey. Newyork.
Denison, R.D. and Mishra K.A. 1995. Toward A Theory
of Organizational Culture and Effectivenes. Journal
Organization Science.Vol.6 No. 2.
Hameed Abdul, Waheed Aamer., 2011. Employee
Development and Its Affect on Employee Performance
Framework, International Journal of Business and
Social Science, Vol. 2 No. 13, pp.224-229.
Hui, C., Simon S.K.L. And Kenneth K.S.L.,
2000.Instrumental Values of Organizational
Citizenship Behavior: A Field Quasi-Experiment.
Journal of Applied Psychology. Vol. 85 No.5, pp. 822-
828.
Indriani, E. and Waluyo, H. 2012.Pengaruh
Kepemimpinan Dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap
Kinerja Pegawai Negeri Sipil Di Sekretariat Daerah
Kabupaten Karanganyar Dengan Komitmen
Organisasi Sebagai Variabel Intervening.Jurnal Edisi.
Koesmono, T.H. 2011.Pengaruh Budaya Organisasi Dan
Kepemimpinan Terhadap Kinerja Melalui Variabel
Mediasi Komitmen Organisasional Karyawan
Perusahaan Swasta Di Surabaya Timur.Jurnal Mitra
Ekonomi Dan Manajemen Bisnis. Vol. 2, No. 2,
hal.155-171.
Lim, B. 1995. Examining the Organizational culture And
Organizational Performance Link. Leadership &
Organization Development Journal. Vol. 16 No. 5, pp.
16-21.
Mohanty, J., & Rath, B. P. 2012. Influence of
Organizational Culture on Organization Citizenship
Behavior: A Three-Sector Study. Global Journal of
Business Research, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp.65-76.
Ojo, O. 2009. Impact Assessment of Corporate Culture on
Employee Job Performance. Business Intelligence
Journal.Vol. 2 No. 2.
Podsakoff, P.M. Ahearne, M. and Mackenzie, S.B. 1997.
Organizational Citizenship Behavior and the Quantity
and Quality Of Work Group Performance. Journal of
Applied Psychology. Vol.82. pp.262-270.
Podsakoff, P.M. Mackenzie, S.B. Paine, J.B. and
Bachrach, D.G. 2000. Organization Citizenship
Behaviors: A Critical review of the Theoretical and
Empirical Literature and Suggestions for Future
Research. Journal of Management. Vol. 26. pp. 513–
563.
Porter, M.M. 1979. How Competitive Forces Shape
Strategy. Harvard Business Review.
Schein, E.H. 2009. The Corporate Culture Survival Guide.
CA: Jossey-Bass (Awilley Imprint). San Fransisco
Sekaran, U. 2003. Research Methods for Business.A Skill
Building Approach. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Shahzadi, Irum., Ayesha Javed., Syed Shahzaib Pirzada.,
Shagufta Nasreen., Farida Khanam.2014. Impact of
Employee Motivation on Employee Performance.
European Journal of Business and Management,
Vol.6, No.23.
Sugiyono., 2014. Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Kualitatif
dan R&B
. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sugiyanto and Sutanto, H. 2010. Membangun Etos Kerja
Yang Pro Aktif Guna Mengoptimalkan Kinerja
Melalui Spiritual Centered Leadership, Employee
Empowerment, Organizational Citizenship Behavior.
Buletin Ekonomi.Vol. 8 No. 2, Hal.70-170.
Zameer, Hashim., Shehzad, Ali., Waqar, Nizar and
Muhammad, Amir. 2014. The Impact of the
Motivation on the Employee Performance in Beverage
Industry of Pakistan.International Journal of
Academic Reseacrh in Accounting, Finance and
Management Sciences.Vol. 4, No. 1, pp:293-298.
The Role of Organization Citizenship Behavior (OCB) in Mediating the Organizational Culture on the Performance of LPD Employees in
Badung Regency
363
