
A Comparative Study Between Neural Network and
Maximum Likelihood in the Satellite Image Classification
Antonio Gabriel Rodrigues
1
, Rossana Baptista Queiroz
1
and Arthur Tórgo
Gómez
1
1
Masters in Computer Applied, Unisinos University, Av. Unisinos 950, São Leopoldo, Rio
Grande do Sul, Brazil
Abstract. In this paper it's showed a comparative study between two tech-
niques of satellite image classification. The studied techniques are the Maxi-
mum Likelihood statistical method and an Artificial Intelligence technique
based in Neural Networks. The analyzed images were scanned by CBERS 1
satellite and supplied by Brazilian National Institute for Space Research
(INPE). These images refer to Province of Rondonia area and were obtained
by CBERS 1 IR-MSS sensor.
1 Introduction
Nowadays, one of the Remote Sensing techniques more used is the scanning of the
Earth surface by satellites. It has application in several areas, since environment
application until socioeconomic and managing applications. Some of these applica-
tions are: weather forecasting, natural resources monitoring, mapping of areas, cen-
sus systems and property registering.
The satellite image information can be extracted through classification of these im-
ages. There are various classification methods that try through several approaches to
identify with accuracy the information of each image pixel, classifying them in cate-
gories or classes according to their spectral information. Image classification meth-
ods can have different accuracy levels, according their approach and parameters
specification. Some of pixel classification methods that are more used by Geographic
Information System (GIS) are based in statistical inference. In this context it's
checked if the Artificial Intelligence based technique is suitable for image classifica-
tion.
In this paper it's presented a comparative study between two satellite image classifi-
cation techniques: the statistical method of Maximum Likelihood and an Artificial
Intelligence technique. Maximum Likelihood method is the most used in Remote
Sensing into the statistical approach. The Artificial Intelligence technique studied is
based in the use of Artificial Neural Networks [9].
Gabriel Rodrigues A., Baptista Queiroz R. and Tórgo Gómez A. (2004).
A Comparative Study Between Neural Network and Maximum Likelihood in the Satellite Image Classification.
In Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Artificial Neural Networks: Data Preparation Techniques and Application Development, pages 1-8
DOI: 10.5220/0001130100010008
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The analyzed images were obtained by the China-Brazil satellite CBERS 1 (China-
Brazil Earth Resources Satellite 1) and was supplied by Brazilian National Institute
for Space Research (INPE) [9].
2 Image Classification Methods
Image classification in Remote Sensing is one of the most used techniques for ex-
tracting of information what makes possible the incorporation of this in a GIS data-
base. Classification can be understood like a space partition according to some crite-
ria [8].
Classification methods, or classifiers, can be divided in classifiers by pixel or classi-
fiers by region and can consider one or more image spectral bands (in the case of
multispectral images). Classifiers by pixel use the spectral information of each pixel
apart to find homogeneous regions defined such as classes. Classifiers by region
consider a set of neighbour pixels (region) information. This technique is also known
as contextual classification. [9] The classifiers can also be divided in supervised (in
which the classes are defined a priori based in known information) and unsupervised
(in which the classes are generated by the classifier) classifiers [2]. For the case of
the supervised classification, the classification criterion is based in the definition of
spectral signatures for each class in study obtained through training samples.
In this work it's used the classifier based in Maximum Likelihood technique that will
be explained in the next item.
2.1 Maximum Likelihood Method
Maximum Likelihood method is the most used in Remote Sensing into the statistical
approach. It's a parametrical method, once it involves parameters (mean vector and
covariance matrix) of the Multivariate Normal distribution. It's also a supervised
method because it estimates its parameters through training samples [3].
This method considers the balance of the distances among the digital level averages
of the classes through the use of statistical parameters. The distribution of the reflec-
tance values in a training area is described by a probability density function based in
Bayesan statistic. The classifier evaluates the probability of a pixel to belong a cate-
gory that it has the major probability of association [6].
Maximum Likelihood is implemented in several GISs, but the use of this classifier
presents some difficulties in the parameters estimation, specially in the covariance
matrix. Moreover, in order to produce good results it's necessary to define with a
good precision the training areas, and it requires the selection of a lot of pixels [6].
In high dimensionality data, i.e., many spectral bands information, this estimation
becomes extremely problematic due to the size of the available samples that gener-
ally in real situations it isn't sufficient.
It was noticed in some research works [1][3] that the growth of the data dimensional-
ity, (i.e., in the spectral bands number) results initially in increment in the accuracy
2
of the resultant classified image. It happens due to increment of the image informa-
tion available. From a certain point, however, the accuracy begins to decrease with
the same training samples due to increase of data dimensionality. This phenomena
is known like the Hughes phenomena or "the curse of dimensionality" and occurs
because with the increasing of image information is increased also the number of
parameters to be estimated, specially the covariance matrix [3].
Moreover, in Maximum Likelihood method the probability density functions of the
classes are Gaussian, approximately. McLachlan (1992, p.52) and Tou and Gonzalez
(1974, p.119) apude [2] affirms that the normal models for the probability density
functions of the classes are important in the theory as in practice, and it's suitable in
many practical applications. Haertel and Landgrebe (1999, p.2074) apude [2] say
that the distributions of the spectral classes that are present in the image generally
can be approached by the Multivariate Normal distribution, once they refers to natu-
ral scenes. The supposition of multivariate normality, however, it isn't true for all
situations and in this cases, the idea of a classifier that has a capacity to learn be-
comes appropriate, eliminating the problem of the use of a determined probabilistic
distribution [2].
2.2 Artificial Neural Networks
The conventional image classifiers used by GIS software have a difficult parameteri-
zation and in many cases they are inadequate for the needs of high accuracy de-
manded by the users [6]. In order to obtain better results and to facility the parame-
terization of these tools, it was opted to create a image classifier based in Artificial
Neural Networks.
Artificial Neural Networks are algorithms whose its functioning is based in human
brain structure [2]. Its processing units are called neurons and they are formed by
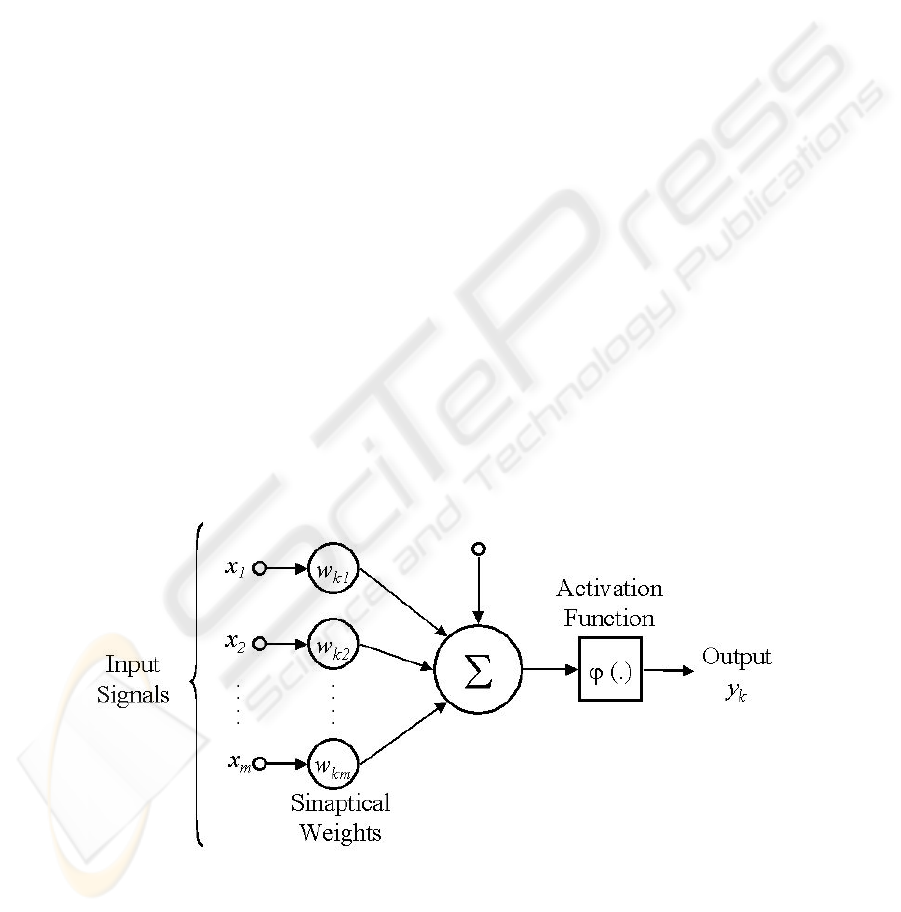
three basic elements, like are illustrated in Figure 1:
Fig. 1. Neuron Model.
3
a set of synapses that are connections where a signal x
j
in the input j and con-
nected to a neuron k are multiplied by the weight w
kj
;
an adder that adds the input signals, pondered by its own neuron synapses;
a activation function that restricts the amplitude of output neuron (threshold func-
tion).
Neuronal model includes also a bias that increase or decrease the activation function
input (depending if it is positive or negative) [5].
Each input neuron receives the values of the neuron outputs connected in it. These
input signals are multiplied by its respective weights and added generating a activa-
tion value. The output value of the neuron is the result of the comparison between its
activation value and a determined score threshold defined a priori [10].
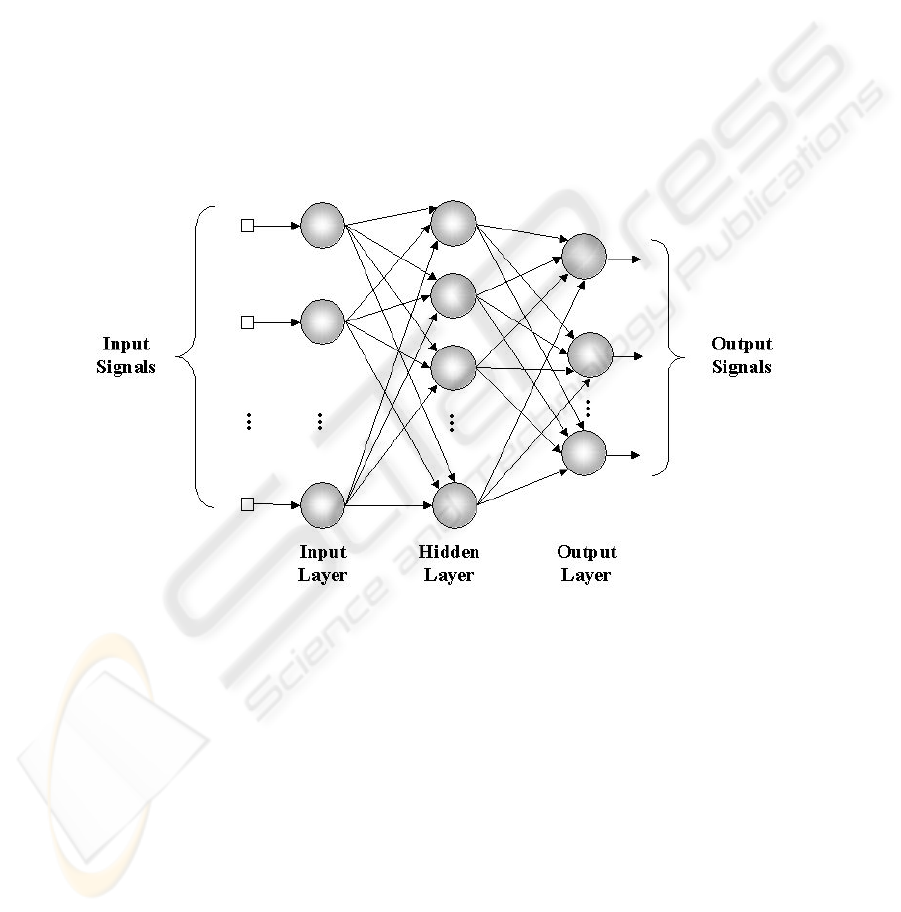
In a Neural Network the neurons are arranged in one or more layers and connected
by a great number of connections or synapses that are generally unidirectional, in
which are associate to weights in the majority of the models [2]. Its basic structure is
showed in Figure 2.
Fig. 2. Neural Network.
The capacity to learn through samples and to generalise the learned information is,
doubtless, the principal advantage of the problems solution through Neural Networks
[2]. For the learning, the networks are trained using a set of samples organized in a
set of database. During this period the synaptic weights are adjusted according to
specific mathematic proceedings that determine how the learning of the Neural Net-
works will be fulfilled. At end of this process, the acquired knowledge of the train-
ing set is represented by the set of network weights [10].
There are several types of Neural Networks models such as Recurrent Networks,
Perceptron Networks, Multi Layer Perceptron Networks, Constructive Networks, and
others [2].
4

The type of Neural Network that was used in this work was the Cascade Correlation
[4] that uses a supervised learning technique to train the networks. It is a Construc-
tive Network that acts on a net initially minimal (with only the input and output
layer) and introduces new intermediary units during the training, one by one accord-
ing to the need of learning. Once a new unit is added to the network, its weights are
frozen. So, this unit pass to influence the operations in the network and it is used to
detect new attributes in the set of patterns.
The unit to be included in the network can be selected from a pool of candidate units
organized as a layer. This layer is connected to the input layer and to the hidden
layers, but not in the output layer, once it should not interfere directly in the network
result. The selection of the candidate is the correlation that it has with the network
output. Therefore, the connection weight among the candidate units and the input
layers and intermediary should be defined so that it can maximize the correlation
between the candidate unit and the output layer. Thus, the candidate that to present
larger correlation will be inserted in the network as a intermediary layer and will be
connected to all the other layers [2][4].
The reason that took to opt for this network type is the fact of that is not being neces-
sary the configuration of the number of neurons of the intermediary layer, once if
Cascade Correlation is a Constructive Neural Network. This constitutes an advan-
tage, because in works that use other types of Neural Networks, just as Multilayer
BackPropagation in [10] they are necessary to do several tests with different num-
bers of neurons in the intermediary layer, in order to obtain the ideal amount of neu-
rons for better learning of the nets.
3 Experiments
To accomplish the experiments, it was used an image supplied by INPE, orbit
175/point 110 CBERS1 IR-MSS (Infra-Red Multispectral Scanner) sensor, obtained
in 2000, July, 29, that covers about 14.400 km
2
of the Porto Velho region in the
Province of Rondonia between 07° 50’’ and 09° 03’’ S latitudes and between the 64
0
10” and 62
0
52”O longitudes. In this image was identified and defined 4 classes:
native forest, deforestation, “no-forest” (no florestal covering area or cerrado
vegetation) and water.
To accomplish the classification it was used the Maximum Likelihood technique and
Neural Networks. To train the Neural Networks was used the NEUSIM simulator [7]
that uses the Cascade Correlation network. It was used the GIS SPRING (Sistema de
Processamento de Informações Geo-referenciadas) to make the classification with
Maximum Likelihood method.
The training and validation of the two methods was made using a set of 240 pixels
regarding the classes to be identified (60 pixels per class). Of these, was selected 120
pixels randomly that integrated the train database while the remaining 120 pixels
was used to validate the classifiers.
The training process of the Neural Network consisted in to submit the network to
learning through the sample basis that was composed of the greyscale of the spectral
5
bands B1, B2 and B3 to each pixel of the analysed image and also the class which
this pixel belongs. Each class are represented such as:
Table 1. Classes Representation.
Class Code
Deforestation
1 0 0 0
Forest 0 1 0 0
No-forest 0 0 1 0
Water 0 0 0 1
This way, the training database of the Neural Networks is organised such as showed
below:
Table 2. A Neural Network database sample.
B1 B2 B3 Class
46 33 126 0 0 0 1
57 22 89 0 1 0 0
.... .... .... ....
The Neural Network has three neurons in its input layer, each one referring to one
spectral band. The output layer has four neurons. When the input signals spread for
the network, only one of the neurons of the output layer should be activated. It was
used 10.000 epochs in the training.
The Maximum Likelihood classifier was trained with the same 120 pixels used to the
construction of de Neural Network training database.
After the training of both methods, the entire image was submitted to classification
and the results were plotted, as it will be showed in the next item.
4 Results
Starting from the accomplished experiments with the chosen techniques were gener-
ated the confusion matrix and kappa coefficient of concordance for both methods.
The confusion matrix shows how much the classifier confuses a class with other. For
this, the generated output is compared with the sample database that holds the true
results. The diagonal of the matrix shows how much the method got right, i.e., how
many pixels were classified correctly according to the true results.
The confusion matrix for both methods are showed below, represented as
the legend: (C1) Deforestation, (C2) Forest, (C3) No-forest, (C4) Water.
6

Table 3. Neural Networks confusion matrix.
Class C1 C2 C3 C4 ?
C1
53%
17%
17%
0% 13%
C2
0%
87%
13%
0% 0%
C3
17%
13%
63%
0% 7%
C4
0% 10%
3% 87%
0%
Table 4. Maximum Likelihood confusion matrix.
Class C1 C2 C3 C4
C1
30%
20%
50%
0%
C2
3% 87%
10%
0%
C3
0% 13%
87%
0%
C4
0% 0% 8% 92%
When the Neural Network activate more than one neuron in the output layer or when
its output approaches to zero, these results are counted in “?” column. The classifica-
tion method of Maximum Likelihood always associates one pixel to one class that it
has the major calculated probability, and so it wasn’t count undefined results.
The kappa coefficient obtained by Maximum Likelihood was 0,65 and by Neural
Networks, kappa coefficient was 0,64 in these experiments.
The results of classification of the entire image by the two methods are showed in
Figure 3.]
Fig. 3. Original Image (1) Maximum Likelihood image classified (2) Neural Networks image
classified.
Legend: Forest No-forest Deforestation Water ?
7

5 Conclusions
In the accomplished experiments, it’s noticed that both methods incline to confuse
deforestation areas with no-forests areas. It’s believed that this is due to the fact that
the reflectance values of these two classes are quite near. It’s also noticed a high
level of success in both methods for the water and native forest classes. The kappa
coefficient is considered substantial to both methods.
The classifier based in Neural Networks presented satisfactory results when com-
pared with Maximum Likelihood results, what indicates that this method is appro-
priate for satellite image classification.
References
1. Bittencourt, H. R., 2001. Reconhecimento estatístico de padrões: o caso da discriminação
logística aplicada a classificação de imagens Digitais obtidas por Sensores remotos. In
Congresso Brasileiro de Computação – CBComp 2001.
2. Braga, A. de P, Ludemir, T.B., Carvalho, A.C.P.de L.F., 2000. Redes Neurais Artificiais
Teoria e Aplicações. Livros Técnicos e Científicos Editora.
3. Erbert, M., 2001. Introdução ao Sensoriamento Remoto. Master Tesis, Universidade Fed-
eral do Rio Grande do Sul.
4. Fahlman, S. E., Lebiere, C., 1990. The Cascade-Correlation Learning Architecture. School
of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh.
5. Haykin, S., 1999. Redes Neurais – Princípios e Prática. Bookman, 2
nd
edition.
6. INPE, 2002.Tutorial SPRING. INPE, São José dos Campos.
7. Osório, F. S, Amy, B, 1999. A hibrid System for Constructive machine learning. Neuro-
computing, v. 28.
8. Rennó, C. D., 1998. Avaliação das Incertezas nas Classificações de Máxima
Verossimilhança e Contextual de Modas Condicionais Iterativas em Imagens Jers na
Região de Tapajós, Estado do Pará. INPE, São José dos Campos.
9. Rodrigues, A. G., Queiroz, Rossana B., Gómez, A. T., 2003. Estudo Comparativo entre os
Métodos de Classificação de Imagens de Satélite Máxima Verossimilhança Gaussiana e
Redes Neurais. In Congresso Regional de Iniciação Científica e Tecnológica em Engen-
haria – CRICTE 2003.
10.Todt, V. D., Formaggio, A. R., Shimabukuro, Y., 2003. Identificação de áreas
Desflorestadas na Amazônia através de uma Rede Neural Artificial Utilizanto Imagens
Fração Derivadas dos Dados do IR-MSS/CBERS. In XI Simpósio Brasileiro de
SensoriamentoRemoto.
8
