
SPEAKER VERIFICATION SYSTEM
Based on the stochastic modeling
Valiantsin Rakush, Rauf Kh. Sadykhov
Byelorusian State University of Informatics and Radioelectronics, 6, P. Brovka str., Minsk, Belarus
Keywords: Speaker verification, vector qu
antization, Gaussian mixture models
Abstract: In this paper we propose a new speaker verification s
ystem where the new training and classification
algorithms for vector quantization and Gaussian mixture models are introduced. The vector quantizer is
used to model sub-word speech components. The code books are created for both training and test
utterances. We propose new approaches to normalize distortion of the training and test code books. The test
code book quantized over the training code book. The normalization technique includes assigning the equal
distortion for training and test code books, distortion normalization and cluster weights. Also the LBG and
K-means algorithms usually employed for vector quantization are implemented to train Gaussian mixture
models. And finally, we use the information provided by two different models to increase verification
performance. The performance of the proposed system has been tested on the Speaker Recognition
database, which consists of telephone speech from 8 participants. The additional experiments has been
performed on the subset of the NIST 1996 Speaker Recognition database which include .
1 INTRODUCTION
The speaker verification systems so far has been
based on the different methods. There is a category of
the algorithms that are using back-end models to
facilitate the speaker traits extraction (Roberts and
Wilmore, 1999) (Burton, 1987) (Pelecanos, 2000)
(Homayounpour and Challet, 1995). The neural
networks, vector quantization (VQ), and Gaussian
mixture models (GMM) are constructed directly or
indirectly for subword or subspeech units modeling.
Those units can be compared to make a verification
decision. Also there is a class of the speaker
verification systems that employ long term statistics
computation over the speech phrase (Zilca, 2001)
(Moonsar and Venayagamorthy, 2001). In some
systems authors use a combination of the methods to
improve system performance. The methods can be
combined in two ways. First way is to use one model
to improve performance of another one (Hsu, 2003)
(Singh et Al., 2003) (Sadykhov and Rakush, 2003).
Second way is to use recognition decision from both
models to perform a data fusion to calculate a final
score (Farrell et Al, 1998) (Farrell et AL., 1997). The
data fusion methods can be interpreted using
normalization and/or Bayessian approach.
Units comparison requires normalization to be
ap
plied. In case of VQ models the test and the
reference codebooks have different structure,
different distortion as well as units of measure for
distortion. To compare two codebooks, which were
created on different phrases, we need to normalize
distortions and their units of measure. In the (Rakush
and Sadykho, 1999) authors proposed to create
reference and test codebooks with equal distortion.
Here we investigate two additional approaches that
transform distortions so they can be compared.
The GMM model has the problem with
p
arameters initialization. We propose to solve that
problem using VQ codebook or applying LBG
algorithm to split Gaussian mixture model starting
from the single component. Also we use VQ
codebook for GMM parameters initialization.
This paper is organized as follows. The following
sect
ion describes modelling approach using VQ and
GMM models. We will propose new algorithms
combining VQ and GMM. Then we will discuss
several techniques for data normalization and fusion,
and will describe the structure of the experimental
system, speech corpus and performance measures.
Finally, we will show our experimental results, that
will be followed by summary and conclusions.
183
Rakush V. and Sadykhov R. (2004).
SPEAKER VERIFICATION SYSTEM - Based on the stochastic modeling.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 183-189
DOI: 10.5220/0001132901830189
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 BASIC IDEA OF THE VQ -
VERIFICATION
The sub-word units, created during signal
transformation from scalar to vector representation
can be used as structural elements of the speaker
voice model. Let
T
N
xxxx ],...,,[
21
=
- N-
dimensional vector, coordinates of which
are real random values and
represent temporal speech spectrum. It can be
displayed into N-dimensional vector
{
Nkx
k
≤≤1,
}
y . The set
{
MiyY
i
≤≤= 1,
}
is the code book, where
M
-
the code book size and
{}
i
y - the set of code vectors.
The N-dimensional space of vectors
x
is divided on
M areas
to create the code book. The
vector
Mic
i
≤≤1,
i
y corresponds to each area . If
i
c
i
x lays in
, then
i
c
i
x is quantized to a value of code vector
i
y . It is evident, that we get the error of
quantization. The deviation
x
from y can be
determined by a measure of closeness
),( yxd
∑
=
−=
=−−=
K
i
ii
T
yx
N
yxyx
N
yxd
1
2
)(
1
)()(
1
),(
, (1)
where N – dimension of the parameters vector.
The basic idea of the VQ based verification system is
to build two codebooks using the reference and test
phrases. Definitely, reference and test phrases will be
similar in the linguistic sense and will be modeling
the features of the speaker voice. We assume that
codebook clusters are modeling the sub-word units of
speech so the test and reference codebooks should
have approximately similar clusters for the two
phrases pronounced by same speaker. The
verification decision can be made comparing two
codebooks using following expression
(
∑∑
==
−=
M
i
K
j
jicompare
zy
MK
D
11
2
1
)
, (2)
where
{
MiyY
i
≤≤= 1,
}
- set of code vectors
for reference codebook;
{
KjzZ
i
≤≤= 1,
}
- set
of code vectors for test codebook;
-
quantization distortion of test on the reference code
book.In case of the speaker verification, if the
codebooks distortion does not exceed predefined
threshold, then test and training utterances belong to
the same person. When the recognition is applied to
arbitrary speech then duration of the reference and
test phrases has a huge difference. The reference
phrase should contain as much as possible linguistic
material from the speaker. The test phrase should be
as small as possible but enough to provide acceptable
verification performance. The reference code book
should have more code vectors, and the test code
book should have variable number of vectors
compare
D
K
,
depending on duration and linguistic content of the
test phrase. Based on the idea that every cluster
models sub-word component we assume that
reference codebook presents model of all possible
pronunciations for given speaker. We will quantize
test codebook over reference codebook using
expression (2) and will expect that distortion for right
speaker will be minimal. Unfortunately, the distortion
for the shortest test phrase can be smaller. Also the
linguistic content of the phrase can influence on the
distortion value. The distortion will be smaller for
phrase with less sub-word components. To avoid
phrase duration and content impact we propose the
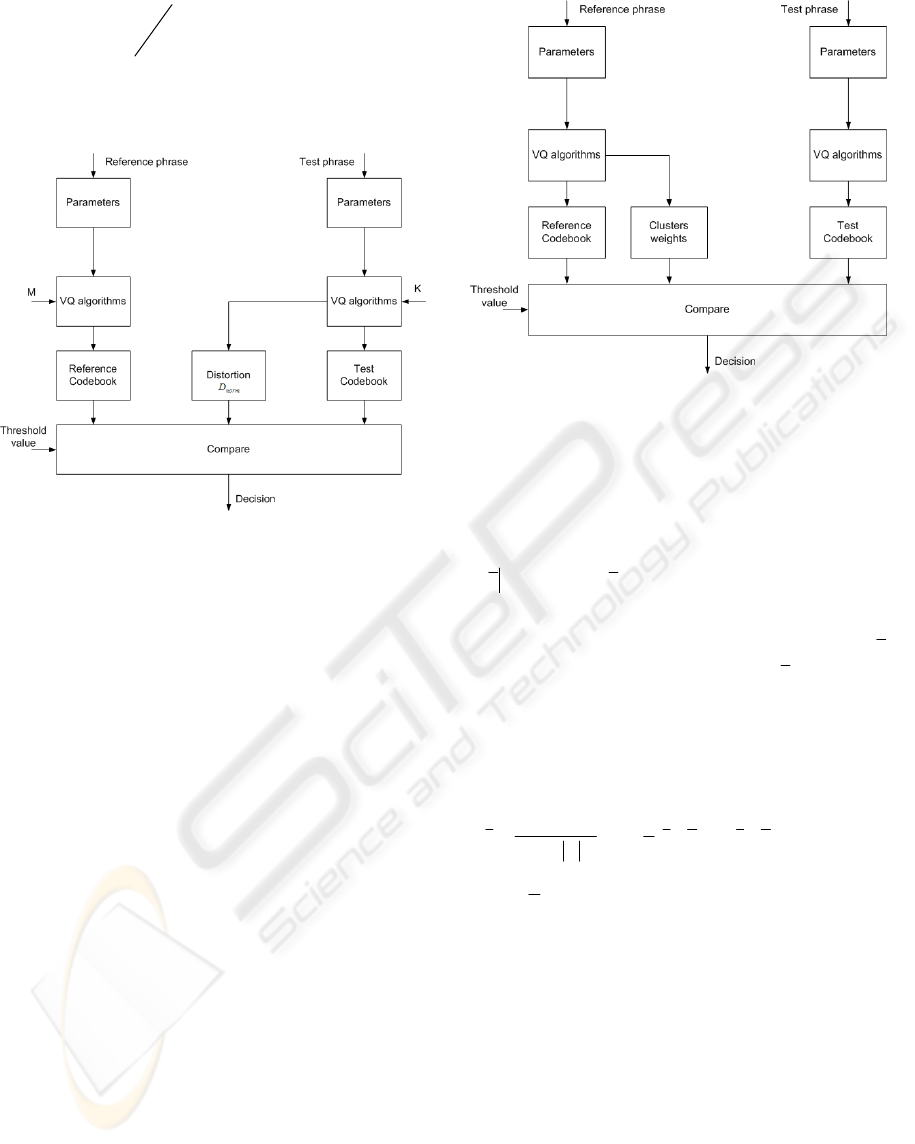
Figure 1: Normalization using predefined distortion value
normalization techniques. First approach Fig. 1
described in (Rakush and Sadykho, 1999) is based on
the equal distortion for the reference and test code
books. It has main assumption that two different code
books with equal distortion do model same sub-word
components.
Second approach is to use test codebook distortion
for normalization. In that approach when test
codebook created on the test phrase the final
distortion is stored together with code vectors and
used for decision normalization
ICINCO 2004 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
184
norm
compare
final
D
D
D =
(3)
The Fig.2 shows algorithm for normalization using
distortion of the test phrase code book.
Figure 2: Normalization using the test codebook distortion
value.
The third and last approach is to use number of
vectors distributed in codebook clusters as a weight
coefficients for normalization. The empirical
theoretical assumption for that type of normalization
can be defined as follows. If one cluster has more
vectors then another one then it should have greater
weight. Therefore test vectors that fall into it should
be more meaningful and more significant for
verification. This approach is not a pure
normalization but can increase performance of the
system because it uses more information from the
code book then previous ones. The Figure 3 shows
this normalization method. The VQ algorithm is
used to calculate code book vectors. It is modified to
produce cluster weights which will be stored along
with cluster’s center vector and will be used to
weighted distance during testing phase.
Figure 3: Normalization using cluster weigths
3 THE GMM BASED SPEAKER
VERIFICATION
The Gaussian mixture model is given by equation
()
()
∑
=
=
M
i
ii
xbpxp
1
λ
, (4)
where
λ
- defines a Gaussian mixture density, x -
-dimensional feature vector, N
()
Mixb
i
,...,1, = -
probability distribution functions for model
components, and
Mip
i
,...,1,
=
- components
weights. Every component is a
-dimensional
Gaussian probability distribution function
D
()
()
()()
⎭
⎬
⎫
⎩
⎨
⎧
−
′
−−=
−
iii
i
D
i
xxxb
µδµ
δπ
1
2/1
2/
2
1
exp
2
1
(5)
where
i
µ
- mean vectors,
i
δ
- covariance matrixes.
The mixture weights values are constrained by the
equality
1
1
=
∑
=
M
i
i
p (6)
The GMM is a good tool, which can virtually
approximate almost any statistical distribution. Due
to that property mixture models are widely used to
create speaker recognition systems. Unfortunately,
the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm has
huge computational time so training procedure takes
long time. The EM algorithm needs parameters to be
initialized also. The number of components of the
GMM is the same for all speaker voices stored in the
SPEAKER VERIFICATION SYSTEM BASED ON THE STOCHASTIC MODELING
185
system. Those are serious disadvantages of the EM
algorithm that can fixed by applying vector
quantization technique to GMM models training.
The initialization step is based on the vector
quantization algorithm and uses codebook to
initialize parameters of the GMM. There is another
algorithm useful for initializing GMM. Initially that
algorithm was developed for vector quantization and
had name LBG algorithm. We will introduce new
implementation of that algorithm for Gaussian
mixture models.
The initial GMM model has only one component.
The component, which gives maximum probability is
split into two parts and new model parameters are
estimated.
Step 1. Initialization
Component weight
=1. The mean vector is the
mean of all feature vectors
1
p
∑
=
=
N
i
i
x
N
1
1
1
µ
.
Covariance matrix is a diagonal matrix of variances
calculated from the training set of feature vectors.
Step 2. Splitting component
Select the mixture component which has
maximum probability. Increment the mean vector
parameters on small value
µ
∆
will give two mean
vectors.
µ
µ
µ
∆+=
12
(7)
Step 3. Optimization
Using EM algorithm estimate new GMM model.
The EM algorithm can use fixed number of iterations
or threshold condition.
Step 3. Iteration
Steps 2 and 3 can be performed until some
threshold will be reached.
Both LBG and
K
-means initialization algorithms
showed good performance acceptable for ASV
systems. The system built on combination of the
LBG and EM algorithms are shown on Figure 1.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The experiments have been performed on two
speaker recognition databases. First one is the speech
database proposed by the Centre of Spoken Language
Understanding of the Oregon Institute of Science and
Technology. The data set had 4 female and 4 male
speakers with 50 utterances for each speaker. The
speech was recorded on telephone channel with
sampling rate 8 kHz. The duration of the test and
train utterances was approximately equal 10 sec. The
second database is the SWITCHBOARD speaker
recognition corpus created by the National Institute
of Technology in 1996. This database represents data
in the Microsoft WAV files compressed using
law
−
µ
. The subset of the development including 20
males and 20 females
The preliminary step used linear prediction
coding and cepstral analysis to build vectors of
spectral features. Analysis used 30 ms Hamming
window with 10 ms shift to weight original speech
signal. There were used vectors with 24 cepstral
coefficients. Also as recommended in
(Homayounpour and Challet, 1995) first
derivative and second derivative of the cepstral
coefficients have been used along with cepstr. The
resulting feature vector had size N=72 parameters.
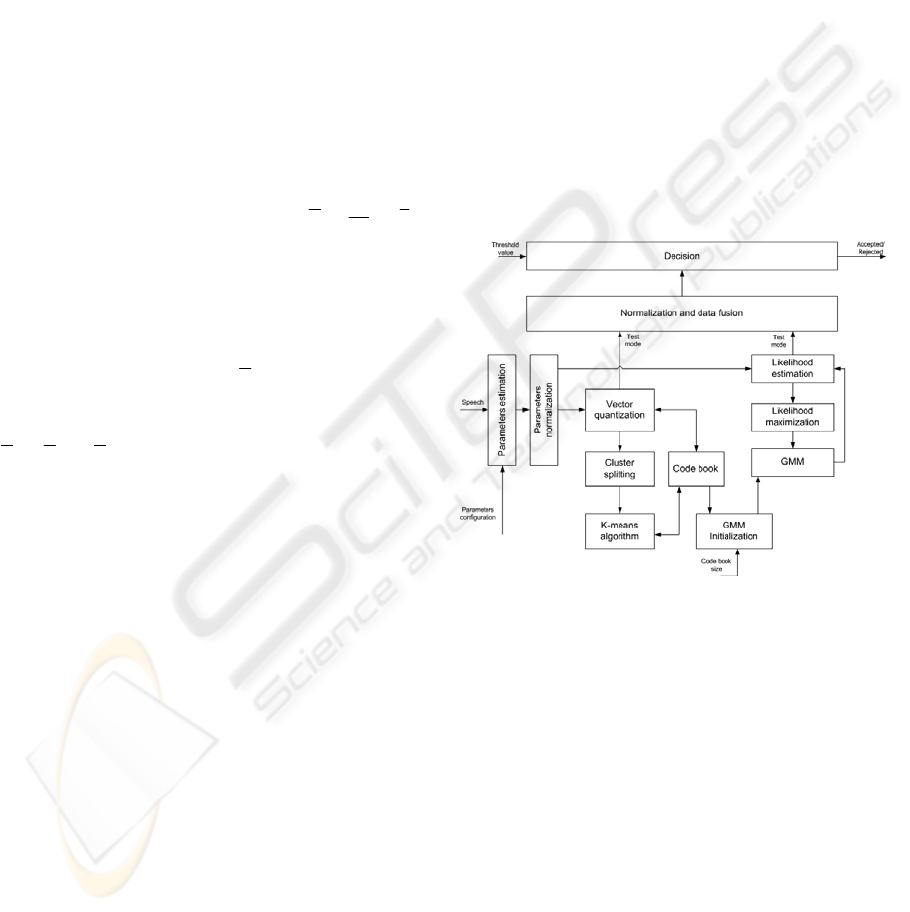
Figure 4: The structure of the speaker verification system
The GMM models had maximum 32 components.
The code book for GMM initialization and for
verification had 32 and 256 clusters correspondingly.
The system is working in two modes: training and
testing mode. In training mode parameter vectors
from both models are used to build the code book and
GMM model for every speaker. In the test mode
those models are used to verify speaker identity.
Normalization and data fusion module uses following
expression to combine results from both models.
() ()
∑
=
=
n
i
ii
xpxP
1
α
, (8)
where
(
)
xP
is a probability of combined system,
i
α
are weights,
(
)
xp
i
is a probability output of the
ICINCO 2004 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
186

th
i
model, and is a number of models (two
models in our case).
n
The GMM and code book models weights have
values
545,0
1
=
α
and 455,0
2
=
α
. Experimental
results shown almost identical performance for VQ
and GMM algorithms. The data fusion of both
algorithms improved overall performance of the
system. The DET curve for LBG initialization and
EM algorithm is shown on Figure 5.
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
0.01 0.1 1
False Accepted Rate
False Re
j
ected Rate
Error Expectation Rate
Data fusion
VQ
GMM
Figure 5: The DET curve of the ASV system performance
In the second section of this paper we were
discussing the normalization approaches to the
vector quantization based speaker verification. The
experimental results for the first approach with
equal distortion for reference and test codebooks
has been described in (Rakush and Sadykho,
1999). In this paper we provide experimental result
comparing second and third normalization
approaches on figure 6.
Additional experiment using NIST 1996
Speaker Verification database SWITCHBOARD
shown results printed on the figure 7.
Figure 6: The DET curve for weight normalization
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
0.01 0.1 1
False Accepted Rate
False Re
j
ected Rate
Error Expectation Rate
w/ norm
w/ norm
w/o norm
w/o norm
SPEAKER VERIFICATION SYSTEM BASED ON THE STOCHASTIC MODELING
187

0.01
0.1
1
0.001 0.01 0.1 1
False Rejected Rate
False Acce
p
ted Rate
Error Expectation Rate
VQ w/o normalization
VQ w/ normalization
Figure 7: The weight normalization results tested on the SWITCHBOARD’96 corpus.
5 CONCLUSION
The first conclusion is that the speaker verification
system based on voice modeling is showing
acceptable performance even for speech degraded
with telephone channel. Both VQ and GMM
models are suitable for different statistical noise
reduction techniques such as mean cepstral
subtraction. That makes both algorithms are good
choice for building automatic speaker verification
systems for noisy signal.
The performance measure for the NIST speaker
detection tasks is the Detection Cost Function
(DCT) defined as a weighted sum of probability of
the False Accepted Rate (FAR) and the probability
of the False Rejected Rate (FRR) (NIST, 2002)
FARFRRC
Norm
9,01,0 += (9)
The minimal value for the DCF has been obtained
for the best possible detection threshold and has
value 0,1 for verification system created with data
fusion methods and value 0,269 for verification
system created with VQ algorithms only.
It is obvious from experiments that VQ speaker
modeling performance is comparable to the GMM
performance but time required for training is much
less. In case of the VQ based modeling the number
of clusters can be determined automatically from
quantization distortion.
REFERENCES
Roberts, W.J.J., Wilmore J.P., 1999. Automatic speaker
recognition using Gaussian mixture models. In
Proceedings of Information, Decision and Control,
IDC 99.
Farrell, K., Kosonocky, S., Mammone, R., 1994. Neural
tree network/vector quantization probability
estimators for speaker recognition. In Proceedings of
the Neural Networks for Signal Processing, IEEE
Workshop.
Burton, D., 1987. Text-dependent speaker verification
using vector quantization source coding. In
Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, IEEE
Transactions.
Zilca, R.D., 2001. Text-independent speaker verification
using covariance modeling. In Signal Proceesing
Letters, IEEE.
Moonsar, V., Venayagamorthy, G.K., 2001. A
committee of neural networks for automatic speaker
recognition (ASR) systems. In Proceedings of
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks,
IJCNN’01.
Pelecanos, J., Myers, S., Shridharan, S., Chandran, V.,
2000. Vector quantization based Gaussian modeling
ICINCO 2004 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
188

for speaker verification, In Proceedings of 15
th
International Conference on Pattern Recognition.
Chun-Nan Hsu, Hau-Chang Yu, Bo-Han Yang, 2003.
Speaker verification without background speaker
models, In Acoustics, Speech, and Signal
Processing, IEEE International Conference,
ICASSP’03.
Homayounpour, M.M., Challet, G., 1995. Neural net
approach to speaker verification: comparison with
second order statistics measures, In Acoustics,
Speech, and Signal Processing, IEEE International
conference, ICASSP-95.
Singh, G., Panda, A., Bhattacharyga, S., Srikanthan, T.,
2003. Vector quantization techniques for GMM
based speaker verification, In Acoustics, Speech, and
Signal Processing, IEEE International Conference,
ICASSP’03.
Farrell, K. R., Ramachandran, R.P., Mammone, R.J.,
1998. An analysis of data fusion methods for speaker
verification, In Acoustics, Speech, and Signal
Processing, IEEE International Conference,
ICASSP’98.
Farrell, K.R., Ramachandran, R.P., Sharman, M.,
Mammone, R.J., 1997. Sub-word speaker
verification using data fusion methods. In Neural
Networks for Signal Processing, Proceedings of the
IEEE Workshop.
Sadykhov, R. Kh., Rakush, V.V., 2003, Training
Gaussian models with vector quantization for
speaker verification, In Proceedings of the 3
rd
International Conference on Neural Networks and
Artificial Intelligence.
Rakush V.V., Sadykhov R.H., 1999, Speaker
Identification System on Arbitrary Speech In
Pattern Recognition and Information Processing.
Proc. Of 5
th
International Conference.
The NIST year 2002 speaker recognition evaluation
plan, 2002,
http://www.nist.gov/speech/tests/spk/2002/doc.
SPEAKER VERIFICATION SYSTEM BASED ON THE STOCHASTIC MODELING
189
