
VISION-BASED TRAFFIC SIGN DETECTION FOR ASSISTED
DRIVING OF ROAD VEHICLES
Miguel Ángel García, Miguel Ángel Sotelo, Ernesto Martín Gorostiza
Department of Electronics, University of Alcalá, Alcalá de Henares, 28871
Keywords: Assisted Driving, Intelligent Vehicles, Traffic Sign Detection.
Abstract: A system for real-time traffic sign detection is described in this paper. The vision-based traffic sign
detection module developed in this work is intended for assisted driving of road vehicles by handling color
images in RGB (Red, Green and Blue) format. In a first step a preattentive area of interest is determined
based on the vertical projection of edge pixels. In a second step, a shape analysis is performed. In a third
step, a color analysis is performed, and finally, a template is fitted. Some results obtained on a series of real
road images are presented in order to illustrate the robustness of the detection system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Traffic sign detection and recognition have
experimented increasing importance in the last
times. This is due to the wide range of applications
where this kind of systems can be used, specially as
driver active aid systems.
There are four types of traffic signs in the traffic
code: prohibition, warning, obligation and
informative. Depending on the shape and color, the
warning signs are equilateral triangles with one
vertex at the top. Prohibition signs are circular,
having a specific figure in each case over a white or
blue background, and a red border. To indicate
obligation, signs are circular with a white figure over
a blue background. The most important traffic signs
are prohibition signs; therefore they have priority to
be detected in this work.
One of the greatest inconveniences of using the
RGB color space is that it is very sensitive to
changes in light (A. de la Escalera,2003). This is the
reason why other color spaces are used in computer
vision applications, specially the hue, saturation,
intensity (HSI) one. This system keeps high
immunity to changes in light (R. C. Gonzalez,1993).
The problem with HSI is that transformation
equations (between RGB and HSI) are nonlinear,
making the computational cost prohibitive. Instead,
we propose to use the relation between the RGB
components for traffic sign detection, as this work is
intended for real-time systems and no further
processing is needed after digitalization.
To detect a traffic sign in an image, the algorithm
follows these steps:
• Candidate image regions are obtained by
accumulative vertical and horizontal edge
projections.
• Centre and radius of circular prohibition
and obligation signs are obtained by a
centre determination technique using three
points of the contour.
• Candidate image regions are validated
based on:
a. Red image thresholding, for
prohibition sign.
b. Blue image thresholding, for
obligation sign.
• Blob shape analysis from red or blue image
thresholding.
• Circular ring templates- based correlation method is
used to identify potential traffic signs in images (
D.
M. Gavrila,1999)
.
2 CANDIDATE IMAGE REGIONS
Candidate regions of interest are computed for
preattentive purposes based on vertical and
horizontal projections of edge pixels.
2.1 Edge image
The appropriate choice of the color features to use in
the process is of crucial importance in order to
19
García M., Sotelo M. and Gorostiza E. (2004).
VISION-BASED TRAFFIC SIGN DETECTION FOR ASSISTED DRIVING OF ROAD VEHICLES.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 19-24
DOI: 10.5220/0001133300190024
Copyright
c
SciTePress

achieve proper and fast detection. Accordingly, only
the Red component is considered as it provides a
high capacity for color discrimination in visual
analysis of traffic signs and no further processing is
needed after digitalization. In an attempt to carry out
a preattentive strategy, a coarse analysis of vertical
edges is performed in a first stage based on
differential characteristics computed on the Red
component of the image using the method of edge
detection described by john Canny (Canny, 1986).
This method has been extremely influential in many
applications. Numerous implementations of edge
detectors based on Canny’s idea have been
developed. Canny described a method of generating
edge detector using an optimization approach and
showed how to use the technique to generate edges-
robust detector. Canny’s method preserves contours
that are very important for detecting traffic sign
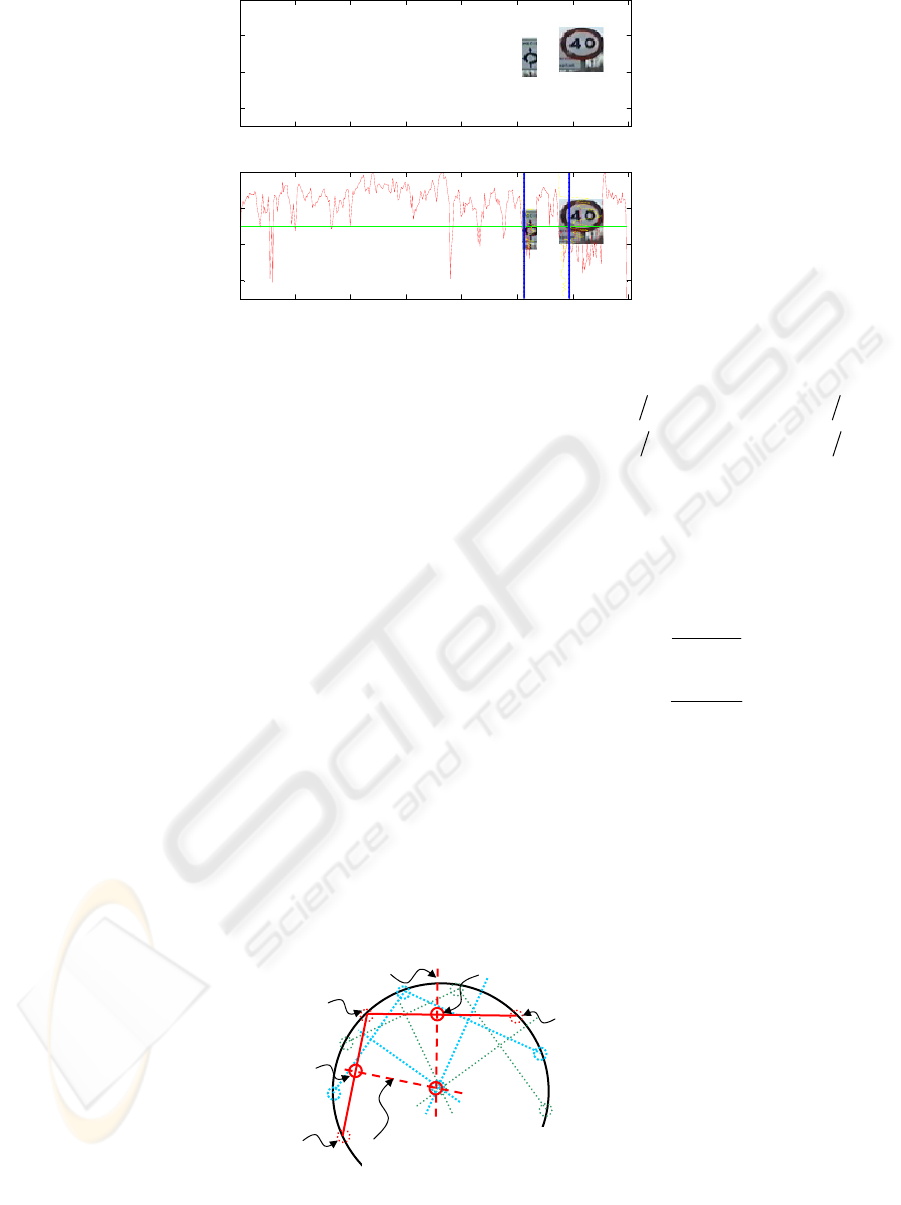
using shape information. Figure 1 shows the result
of applying the Canny edge detector road image.
2.2 Vertical projection of edge pixels
One of the most common techniques for traffic sign
segmentation is to use grey-level images, the red
component in our case, and to project accumulative
edge pixels onto the axes.
Vertical projections of different types of signs
are shown in Figure 1. As it can be observed, a
maximum in the projected signal occurs in the area
of the image where the sign is placed.
As a first step, an adaptive thresholding is
performed aiming at removing the common offset
component in the projection profile. For this
purpose, a threshold u is computed as expressed in
(1).
u
v
=
µ
v
+
µ
v
+
(1)
Where µ
v
stands for the average value of the
projection profile, while µ
v
+
represents the average
of all points in the projection whose value is greater
than µ. Finally, the coarse detection stage ends by
removing narrow peaks from the projection profile.
This yields a set of candidate image regions that
highly reduces and constraints the portions of the
image where traffic signs are likely to appear.
2.3 Horizontal projection of edge
pixels
In order to restrict the area of interest a bit more, a
similar method is applied to horizontal projections of
edge pixels in the region of interest. In this case the
adaptive threshold is obtained as expressed in
equation (2)
u
h
=
µ
h
(2)
Where µ
h
denotes the standard average value of
the horizontal projection. After applying this
segmentation process, regions of interest remain
more restricted. Nevertheless, not all the regions
include a traffic sign inside. Resultant regions of
interest are shown in Figure 2.
source Image
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Canny Edge Image
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Source Image
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Edge Image
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Figure 1: Canny edge image. Accumulated vertical and horizontal projection and their corresponding threshold-levels
ICINCO 2004 - ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
20
3 SHAPE ANALYSIS
The shape of traffic sign represents essential
information for road-sign detection and further
classification. The main signs, prohibition and
obligation are circular and their contours are defined
by (3):
()()
22
2
cc
yyxxr +++=
(3)
Where ‘r’ denotes the radius of circumference
and (x
c
,y
c
) indicates the centre of circumference. The
centre can be determinate using a graphic method of
three points of the circular contour, as it is shown in
Figure 3, following these steps:
1. The three points are grouped in pairs;
(x
1
,y
1
), (x
2
, y
2
) and (x
3
, y
3
).
2. Centre points of the segments determined
by every pairs of point are obtained by (4).
(
) ()
() ()
+=+=
+=+=
22
22
32123223
21122112
yyyxxx
yyyxxx
mm
mm
(4)
3. Orthogonal lines, r
12
and r
23
, to segments
obtained in previous step, are traced
through respective central points already
obtained as well by (5).
()
()
+
−
−
−=
+
−
−
−=
23
32
23
2323
12
21
12
1212
mm
mm
y
yy
xx
xxyr
y
yy
xx
xxyr
(5)
4. Centre of circumference (x
c
, y
c
) from
intersection between orthogonal lines r
12
and r
23
is obtained by solving equation (5).
These steps are repeated using three different
points of the contour every time and along the
contour that might include a large enough number of
pixels.
Regions
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Horizontal Vertical Projections & Regions
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Figure 2: Vertical and horizontal projection to obtaining regions of interest
x
c
,y
c
x
1
,
y
1
x
m12
,
y
m12
x
2
,
y
2
x
3
,
y
3
x
m23
,
y
m23
r
12
r
23
Figure 3: method of calculus of centre
VISION-BASED TRAFFIC SIGN DETECTION FOR ASSISTED DRIVING OF ROAD VEHICLES
21
With this method a two-dimensional distribution
of possible points of centre is obtained, as it is
shown in Figure 4. A maximum in the distribution
occurs in the area of the image where the sign is
placed, see Figure 4 right.
4 COLOR ANALYSIS
Color is a very important parameter to be taken into
account for road-sign detection and further
classification. Some authors choose color-spaces
that exhibit high immunity to changes in light, HSI
(Hue, saturation Intensity) (T. Hibi, 1996) (G.
Piccioli, 1996), so that color regions can be
segmented by means of a look-up table (LUT).(A.
de la Escalera, 1997). Computation time needed to
obtain red-component image in HSI space is ten
times bigger than in RGB space.
In this work, the RGB color space has been
chosen, so that relations between components are
used to highlight red-colored and blue-colored
regions in the image and reduce the light-
dependency of the RGB space in the perception of
the color, as is described by (6).
≤−
>−−
≤−
>−−
=
00
0
00
0
min
br
brbr
gr
grgr
ffif
ffifff
ffif
ffifff
r
(6)
Figure 4: two-dimensional distribution of points, and maximums in the distribution.
source Image
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Edge Image by Canny method, labeled
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Regions
100 200 300
50
100
150
Red Image
100 200 300
50
100
150
(b)
(d)
Regions
100 200 300
50
100
150
Red Image
100 200 300
50
100
150
(b)
(d)
source Image
100 200 300
50
100
150
Blue Image
100 200 300
50
100
150
(a)
(c)
source Image
100 200 300
50
100
150
Blue Image
100 200 300
50
100
150
(a)
(c)
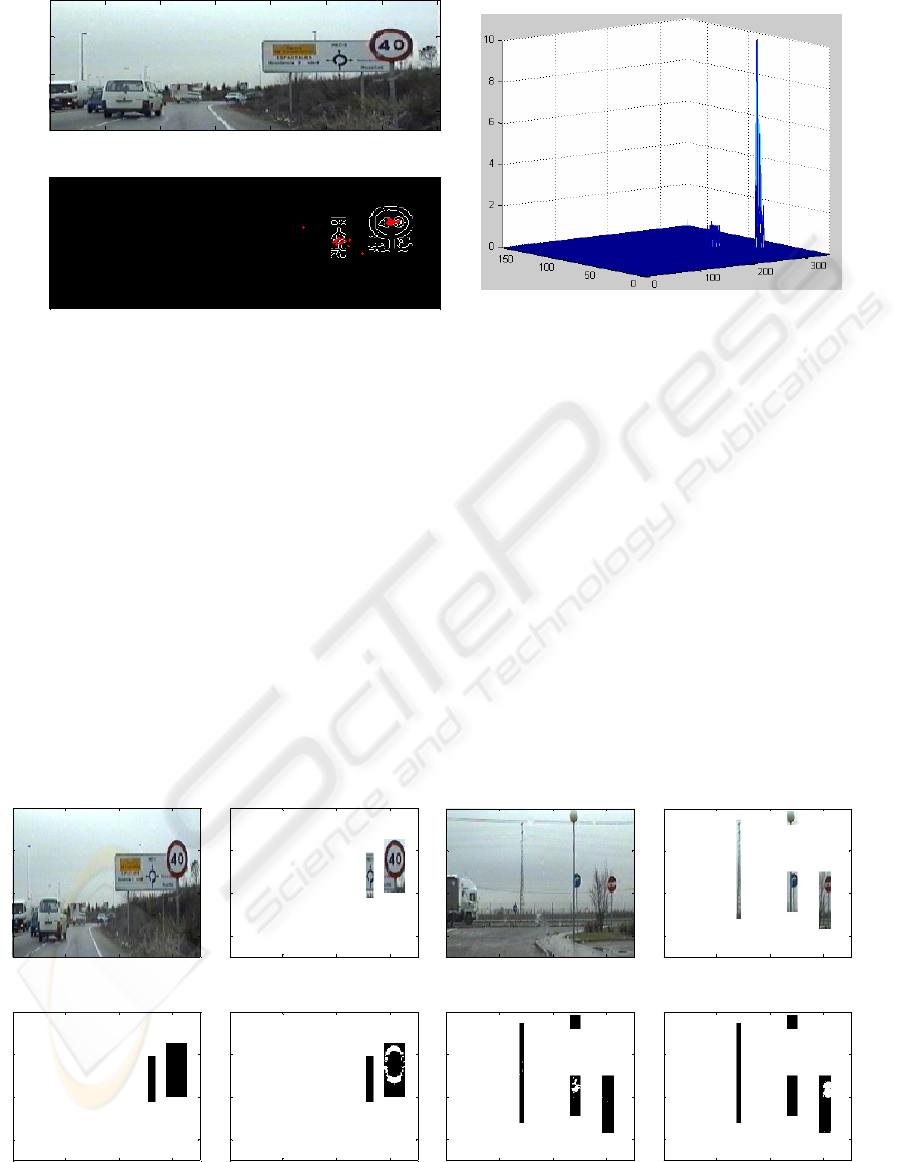
Figure 5: source images, regions of interest, blobs in the red image and blobs in the blue image
ICINCO 2004 - ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
22
Where f
r
, f
g
, and f
b
are, respectively, the functions
that give the red, green, and blue levels of each point
of the image, and r is the highlight red-colored
region. Similar method to obtain the highlight blue-
colored regions is used.
The most important reason why RGB is used is
that it allows to speed up the detection process while
preserving the detection robustness at the same time.
4.1 Blob-based analysis
The red and blue components of the regions of
interest already obtained are calculated and
thresholded, yielding the blobs that can be seen in
Figure 5. These blobs, corresponding to road signs,
must fulfill the size and aspect constraints described
by (8) and (9):
min
AA
i
≥ (8)
maxmin
),max(
r
lh
lh
r
ii
ii
≥
−
≥ (9)
Where A
i
is the minimum area that a blob must
have and h
i
and l
i
are the blob’s width and height
respectively. Resultant blobs are useful to place a
road sign-searching template on the image.
5 TEMPLATE MATCHING
A ring-shaped template T is placed in the edge
image I, in the centre of the blob obtained, for
prohibition and obligation signs, which are circular.
The matching-measurements matrix D(T; I) (
D. M.
Gavrila,1999)
is determined by the pixel values of I
which lie under the high level pixels of the T. These
pixel values form a distribution of distances from the
template points to the nearest contour in the image.
The lower these distances are, the better the match
between image and template at this location.
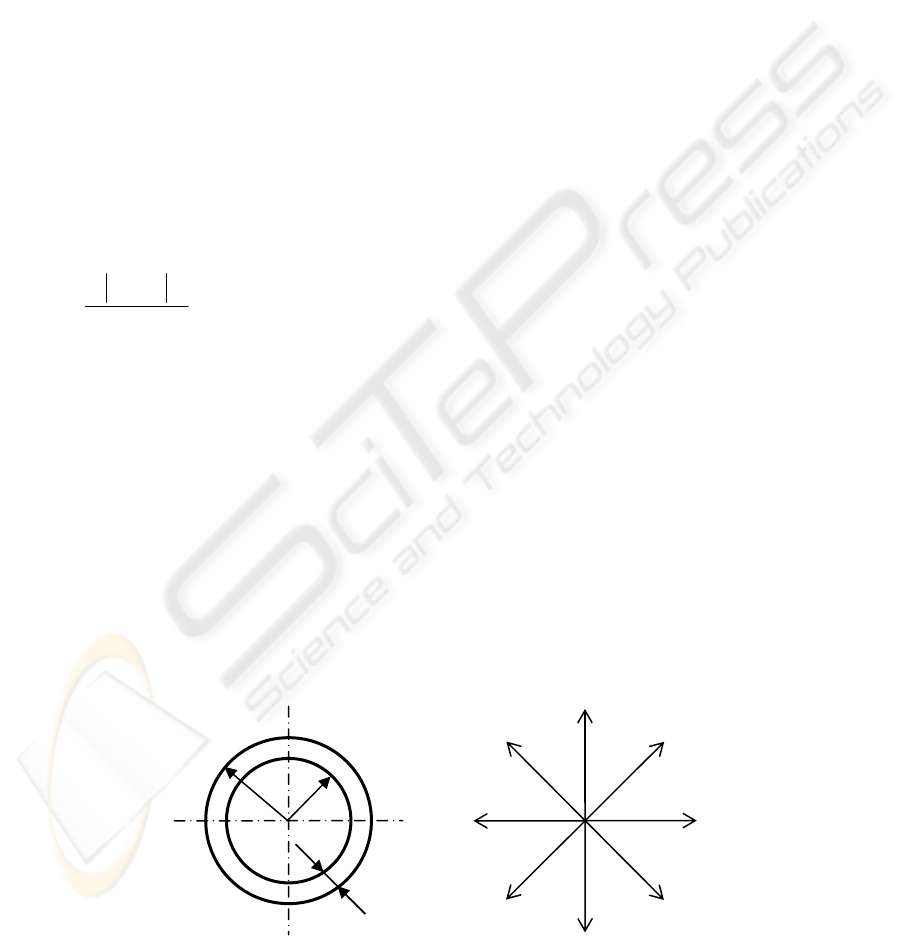
The sequence to fit the template is as follows:
• The template is moved over the edge-image
I, along the eight directions indicated in
Figure 6 (Ritter and Wilson, 2001), while
the sum of all the points remaining inside the
ring at the shifted position is bigger than the
sum of all the points inside the ring in the
previous position.
• Radius R and r of the ring are set following
the same criteria as in the ring-centre
adjustment.
• The first two steps are repeated at each shift
step.
• For a candidate object (region) to be
considered as a road sign the sum of the
points in the ring must be greater than a
certain threshold value (10).
threshold
Uyxt
∑
≥),( (10)
Figure 7 shows the results obtained by using the
described method. The image on the right, two signs
have been detected, an obligatory-direction blue one
and a Stop-one which is not circular but can be fitted
using the circular based assumption, the detecting
method provides color information, blue for
obligation signs and red for prohibition and stop
ones. A smaller obligatory-direction road sign has
not been detected, because it is still too far from the
ego-vehicle. In the image on the left, a speed-limit
sign has been detected, and an informative sign as
well, but the template has only been fitted to the first
one because the informative sign has been rejected.
a
r
R
(x
0
,y
0
)
S
W
E
N
Figure 6: Circular ring template, an
d
searching directions.
VISION-BASED TRAFFIC SIGN DETECTION FOR ASSISTED DRIVING OF ROAD VEHICLES
23

6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
An algorithm for real-time detection of traffic signs
is carried out based on vertical projections of edge
pixels, shape analysis and template-based detection.
The algorithm has been empirically tested on real
road images, and aims at assisting human drivers in
automatic recognition of traffic signs in order to
ensure traffic rules fulfilment. Our future work
involves robust detection of road signs under
adverse weather conditions, as well as the use of a
neural network for fine grane classification and
validation of the detected road signs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the Comisión
Interministerial de Ciencia Y Tecnología (CICYT-
Spain) by means of Research Project DPI2002-
04064-C05-04.
REFERENCES
D. M. Gavrila. Traffic Sign Recognition Revisited.
Proceedings of the 21st DAGM Symposium für
Mustererkennung. Pp. 86-93. Springer Verlag 1999.
A. de la Escalera, J. M. Armingol, M. Mata. Traffic Sign
Recognition and Analysis for Intelligent Vehicles.
Image and Vision Computing, Vol. 11, N. 3, pp. 247-
258 (2003).
R. C. Gonzalez and R. E. Woods, Digital Image
Processing, 2nd ed. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley,
1993.
J. Canny. “A Computional approach to Edge-Detection,”
IEEE Transactions on pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, vol 8, pp. 679-700, 1986.
T. Hibi, Vision based extraction and recognition of road
sign region from natural color image, by using HSL
and coordinates transformation, 29th International
Symposium on Automotive Technology and
Automation, Robotics, Motion and Machine Vision in
the Automotive Industries, ISATA June (1996).
G. Piccioli, E. de Micheli, P. Parodia, M. Campani, Robust
method for road sign detection and recognition, Image
and Vision Computing 14 (3) (1996) 209–223.
A. de la Escalera, L. Moreno, M. A. Salichs, J. M.
Armingol. Road Traffic Sign Detection and
Classification. IEEE Transactions on Industrial
Electronics, Vol. 44, N. 6, pp. 848-859 (1997).
Gerhard X. Ritter and Joseph N. Wilson. Handbook of
Computer Vision Algorithms in Image Algebra. 2001
by CRC Press LLC.
Source Image
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Detection
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Source Image
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Detection
50 100 150 200 250 300 350
50
100
150
Figure 7: examples of traffic sign detection.
ICINCO 2004 - ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
24
