
WHEELED VEHICLES CLASSIFICATION USING RADIAL
BASE FUNCTION NEURAL NETWORK
Intelligent Control Systems and Optimization
Jerzy Jackowski
Military University of Technology, Institute Of Mechanical Vehicles, Warsaw Poland
Roman Wantoch-Rekowski
Military University of Technology, Institute of Computer Science, Warsaw Poland
Keywords: Neural network, ground vibrations, process of identification
Abstract: The paper presents the problem of using neural network for militar
y vehicle classification on the basis of
ground vibration. One of the main element of the system is a unit called geophone. This unit allows to
measure amplitude of ground vibration in each direction for certain period of time. The value of amplitude
is used to fix the characteristic frequencies of each vehicle. If we want to fix the main frequency it is
necessary to use Fourier transform. In this case the fast Fourier transform FFT was used. Because the neural
network (Radial Basis Function network) was used, the learning set has to be prepared. Please find attached
the results of using RBF neural network such as: example of learning, validation and test sets, structure of
the networks and learning algorithm, learning and testing results.
1 INTRODUCTION
The main area of the authors’ interest is the decision
system automation. The results maybe used in
military systems.
High significance is given to the
intelligent ammunition in the vehicle fighting on the
contemporary battlefield. Most often, it is presented
as the mean of high vehicle hitting efficiency in the
field. It differs from other ammunition types in a
way that specific action algorithms are used that
allow for individual selection of target it is activated
by. In the vehicle (danger) detection systems,
various types of sensors are used: acoustic, seismic,
optical (including infrared ones), while the acoustic
and seismic sensors are mostly used to activate the
devices (mines) and object recognition, and the IR
sensors (as well as the acoustic ones) are used to
indicate a direction the signal comes from. This
work focuses on the vibrations registered by the
seismic sensors (Jackowski, 2002).
In general, the task of qualifying an examined
si
gnal for appropriate group (vehicle) can be realized
in two ways – by means of determination of distance
between the signal being identified and the
determined benchmark (Jackowski, Jakubowski,
2002), or on the basis of its position against the
separating surfaces (mostly generated by proper
algorithms of artificial neuron networks (Hertz et al.,
1991; Osowski, 1996; Rutkowska, 1997). In both
cases the selection of feature spaces makes an
important stage. Usually their determination is
conditioned by efforts leading to the selection of
significant values and omission of those features that
obtain close values for all objects (different
vehicles).
In this case the neural network was used as an
ele
ment of the decision subsystem. The inputs of the
network are calculated as characteristic values of the
object. These values are the base of the
classification. The output values are the answer of
the network. Because of the local representation (of
the output values) each of the output is connected to
one type of the object (one vehicle).
The main problem was to choose the correct
characte
ristics values on the base of ground
vibration. The values of the ground vibration
amplitude were obtained by using geophone. Figure
1 shows the example of the measurements.
350
Jackowski J. and Wantoch-Rekowski R. (2004).
WHEELED VEHICLES CLASSIFICATION USING RADIAL BASE FUNCTION NEURAL NETWORK - Intelligent Control Systems and Optimization.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 350-353
DOI: 10.5220/0001136403500353
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 THE GROUND VIBRATION
ANALYSIS CAUSED BY
VEHICLES
For each vehicle it is possible to measure the
amplitude of ground vibration. In this case 6
vehicles were chosen: Kraz, Jelcz, Skot, Tatra,
Volvo, Land Rover. The measurements were
performed with different speed of the vehicles,
different types of the ground and obstacles.
There were two possible ways of signal analysis.
The first case - analysis of signal amplitude (for
certain period of time), the second case - analysis of
some amplitude signal transformation. In this paper
the Fast Fourier Transform was used (using Cooley-
Tukey algorithm).
Each vehicle has it’s characteristic frequencies
because of the front and rare axle vibration and car
body vibration.
The whole FFT is too big to be “included” into
the learning and validation set. As a result of
analysis three parameters were fixed. The first
parameter was the value of frequency of the biggest
FFT amplitude, the second was the value of the
biggest FFT amplitude and the last one was the
number of the vehicle axle. The number of the
vehicle axle is evaluated on the basis of the value of
ground vibration amplitude.
3 THE RADIAL BASE FUNCTION
NEURAL NETWORK FOR
OBJECTS CLASSIFICATION
The neuron with radial base transfer function is the
main element of the RBF (Radial Base Function)
neural network.
Figure 2 shows the model of the radial neuron
where (t
i
) is the center of radial function. Value (e)
(activation value) is calculated as follows:
∑
=
−=
n
i
ii
txe
1
2
)(
The next equation shows the example of radial
function:
2
2
2
||||
)(
σ
ϕ
tx
ex
−
−
=
As we can see, the value on the output of the
radial neuron depends directly on its value on the
inputs as well as the value of the centers (t
i
). For
each input of the neuron the differences between
input values and centers are calculated. This
differences are the argument of the transfer function
(radial function). According to the above equation
the radial neuron “is activated” only for limited
range of value (x-t). The specific functioning of the
whole Radial Base Function network is the result of
that features.
-400
-300
-200
-100
0
1
201 401 601 801
1001
The radial neurons are located in the hidden
layer of the network. The output values of the
hidden layer are put (in the simplest case) into the
inputs of the single output.
The radial function depends on the value r=||x -
t
i
||. The value of (r) is usually calculated using
Euclidean norm. In more complex models of RBF
neural networks the weighted norm is applied. It
means that the value (r) is multiplied (fore each
direction) by the value (Q
i
):
Because the function argument is (r
2
), so we can
write:
The values of (Q
i
) are evaluated during the
learning process of neural network.
100
200
300
-400
-300
-200
-100
0
1
201
401
601
801
1001
Figure 1: Example of measurements for Kraz
(speed 25km/h and 35km/h).
100
200
300
400
)(
ii
Q
i
txQr −=
)]([)]([||||
22
ii
T
iiQi
Q
i
txQtxQtxr
i
−−=−=
WHEELED VEHICLES CLASSIFICATION USING RADIAL BASE FUNCTION NEURAL NETWORK - Intelligent
Control Systems and Optimization
351

The structure of HRBF neural network consists of
neuron as above (Wantoch-Rekowski, 1994). The
output layer consists of neurons with sigmoid
transfer function. It means that the values on the
outputs of the network belong to the range (0,1). The
number of neural network inputs (n) depends on size
of the analyzed space (R
n
). The number of radial
neurons in the hidden layer is evaluated during the
learning of the network. The number of output
neurons is connected to the number of different
classes (number of object types).
3.1 Learning algorithm
During the experiments the supervised type of
learning algorithm was applied (with gradient
method). The main element of the algorithm - the
criterion function is fixed on the basis of RBF neural
network structure. The criterion function is directly
connected to the optimization method, as shown (for
network with one output neuron):
where:
W
i
- values of output neuron weights,
d - required value on the output of the neural
network,
K - number of radial neurons in hidden layer,
x - values of network inputs.
The form of the transfer function in the hidden
layer is as follows:
In each step of learning algorithm the new values
of the output neuron weights and values of (t) and
(Q) are calculated.
4 THE EXPERIMENTS AND
RESULTS
y
1
1
e
Q
n
...
f
Q
n
x
t
n
1
t
1
x
...
1
r
r
n
4.1 Structure of learning, testing and
validation sets
Because of the learning process difficulties the
values of characteristics parameters were changed in
the learning, testing and validation sets. The values
of the biggest amplitude (1
st
parameter) were divided
100 times and the number of axles were multiplied
10 times.
Figure 2: Model of the neuron of HRBF
neural network.
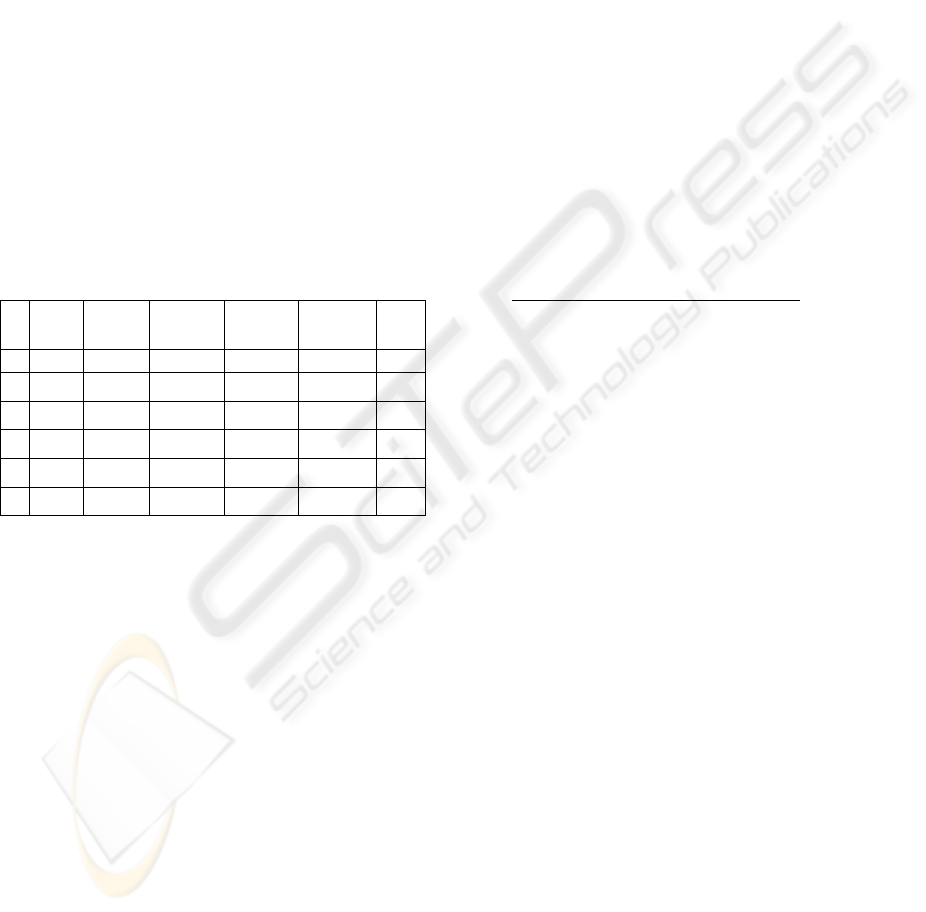
The part of the learning set
i
for the example
presented in the paper is shown below. The three
(left) columns are the values of the characteristic
parameter. The next 6 columns describe required
values on the RBF network outputs.
; DANE PROGRAMU RWR-RBF.EXE
; Learning data (part of the file)
; DATASTRUCTURE=<Column description>
; INPUT - input data, NOTUSED - not
used data, OUTPUT - required data
PAIRS=(224)
DATACOLUMN[ 1]=INPUT
DATACOLUMN[ 2]=INPUT
DATACOLUMN[ 3]=INPUT
DATACOLUMN[ 4]=OUTPUT
DATACOLUMN[ 5]=OUTPUT
. . .
DATACOLUMN[ 9]=OUTPUT
∑
=
−=
K
i
ii
dxWE
0
2
])([
2
1
ϕ
LEARN DATA
8.05 16.77 30 1 0 0 0 0 0
9.22 19.03 30 1 0 0 0 0 0
6.83 18.76 30 1 0 0 0 0 0
6.83 21.01 30 1 0 0 0 0 0
8.54 19.17 30 1 0 0 0 0 0
The whole learning set consists of 224 elements
with 6 types of wheeled vehicles. The structure of
the testing and validation set is similar to the
learning set. The testing set consists of all elements
from learning set to some other additional elements.
)]([)]([
2
1
)(
ii
T
ii
txQtxQ
i
ex
−−−
=
ϕ
4.2 Structure of the RBF neural
network
The structure of the network is the result of the task
presented in this paper. The number of hidden
neurons was evaluated during the learning of the
ICINCO 2004 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
352
network. Description of the RBF is presented
below
ii
:
; RBF Network structure RWR-RBF.EXE
; (C) Roman WANTOCH-REKOWSKI,
LAYER INPUT NODES=<3>
LAYER HIDDEN NODES=<16> FUNCTION=GAUSS(1)
LAYER OUTPUT NODES=<6> FUNCTION=SIGMOID(0.9)
4.3 RBF neural network learning
The presented learning algorithm (gradient method)
was used to learn the neural network. The value of
learning coefficient was calculated during the
learning process. The initial value of the learning
coefficient was the biggest while the final value the
lowest. Parameters of the RBF network are included
in the vehicle.net file.
File presented below (it is the vehicle.lre file
contents.) shows the example of learning process for
RBF neural network using the learning set from the
file vehicle.lrn.
E
%CU %CW Net
Err
Lrn
cof
Max
grad
ukr
1 0.0 0.0 0.14147 0.92700 | 0.0153| 16
2 7.6 16.7 0.05981 0.95481 | 0.0141| 16
3 53.6 50.0 0.03919 0.98345 | 0.0196| 16
4 82.1 66.7 0.02138 1.01296 | 0.0677| 16
5 96.9 100.0 0.00059 1.04335 | 0.0106| 16
6 100.0 100.0 0.00002 1.20952 | 0.0011| 16
where: EPOKA - the number of learning epoch,
% CU - the percent of correct recognized elements
of learning set (*.lrn), % CW - the percent of correct
recognized elements of validation set (*.val), Net
Err. - the network error value, Lrn cof. - the value of
learning coefficient, Max grad. - the biggest value of
network gradient, ukr - number of hidden (radial)
neurons.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The experiments show that the RBF neural network
can be used for vehicles classification on the basis of
ground vibration. The main problem was to fix the
correct characteristic parameter of FFT.
REFERENCES
Jackowski, J., 2002. Ground vibrations resulted by vehicle
motion. Biuletyn WAT 11/2002.
Jackowski, J., Jakubowski, J., 2002. Analysis of
differentiation possibilities of ground vibrations
resulted by the vehicle motion. Biuletyn WAT
11/2002
Hertz, J., Krogh, A., Palmer, R., 1991. Introduction to the
Theory of Neural Computation. Addison-Wesley Pub.
Amsterdam.
Osowski, S., 1996. Neural Networks. WNT. Warsaw.
Rutkowska, D., Piliński, M., Rutkowski, L., 1997. Neural
Networks, Genetic Algorithm and Fuzzy Systems,
PWN. Warsaw- Lodz.
Świątnicki, Z., Wantoch-Rekowski, R., 1999. Neural
Networks; Introduction, Bellona. Warsaw.
Wantoch-Rekowski, R., 1994. Structure of Neural
Network Using in Classification Process (in Polish).
Proceedings of Symposium ”Neural Network and their
Applications”. Kule.
i
It is the vehicle.lrn file contents.
ii
It is the vehicle.str file contents.
WHEELED VEHICLES CLASSIFICATION USING RADIAL BASE FUNCTION NEURAL NETWORK - Intelligent
Control Systems and Optimization
353
