
MULTIRATE OUTPUT FEEDBACK BASED DISCRETE-TIME
SLIDING MODE CONTROL FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR
SYSTEMS
S. Janardhanan
Systems and Control Engineering
IIT Bombay, Mumbai, INDIA
B. Bandyopadhyay
Systems and Control Engineering
IIT Bombay, Mumbai, INDIA
Prashant Shingare
Systems and Control Engineering
IIT Bombay, Mumbai, INDIA
Keywords:
Multirate Output Feedback, Finite Discretizability, Discrete-time Sliding Mode Control, Nonlinear Control.
Abstract:
The property of certain nonlinear continuous-time systems to be exactly representable in discrete-time is
known as finite discretizability. This paper presents a method for the discrete-time sliding mode control for
nonlinear systems that are finitely discretizable.
1 INTRODUCTION
The concept of sliding mode control was first intro-
duced by Emelyanov [Emelyanov, 1967] and Utkin
[Utkin, 1977]. It is a technique that achieves desired
characteristics for the system by confining its states
to a specified subset of the state space. This is done
by application of a control of variable structure. The
main advantage of sliding mode control is its insen-
sitivity to system parameter variations [Hung et al.,
1993, Young et al., 1999]. In the recent years, consid-
erable efforts have been put in the study of the con-
cepts of Digital Sliding Mode (DSM) controller de-
sign [Furuta, 1990, Gao et al., 1995, Sarpturk et al.,
1978]. In case of the DSM design, the control in-
put is applicable only at certain sampling instants and
the control effort is constant over the entire sampling
period. Moreover, when the states reach the switch-
ing surface, the subsequent control would be unable
to keep the states confined to the surface. As a re-
sult, DSM can undergo only quasi-sliding mode, i.e.,
the system states would approach the sliding surface
but would generally be unable to stay on it. Thus, in
general, DSM does not possess the invariance prop-
erty found in continuous-time sliding mode. In [Gao
et al., 1995] a “reaching law” approach for the design
of control for DSM using state feedback was intro-
duced. This reaching law ensures that the system tra-
jectory will hit the switching manifold and thereafter
undergo a zigzag motion about the switching mani-
fold. The magnitude of each successive zigzagging
step decreases so that the trajectory stays within a
specified band called the quasi-sliding-mode band.
However, most of the sliding mode control strate-
gies are based on full-state feedback. But, in prac-
tice, all the states of the system may not be avail-
able for measurement. Since the output is available
for measurement, output feedback can be used for
the controller design. Few research works are avail-
able which deal with SMC design using output feed-
back [Bag et al., 1997, Diong, 1993, Zak and Hui,
1993]. An output feedback technique that guarantees
the closed loop stability for controllable and observ-
able systems has been proposed in [Werner and Fu-
ruta, 1995]. This method is termed as “ Fast Out-
put Sampling” technique in which the system output
is sampled at a rate that is N times faster than the
rate at which the control input is given. A fast output
sampling feedback based discrete-time sliding mode
control strategy for linear systems has been developed
238
Janardhanan S., Bandyopadhyay B. and Shingare P. (2004).
MULTIRATE OUTPUT FEEDBACK BASED DISCRETE-TIME SLIDING MODE CONTROL FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR SYSTEMS.
In Proceedings of the First Inter national Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 238-245
DOI: 10.5220/0001138502380245
Copyright
c
SciTePress

in [Saaj et al., 2002].
This paper presents a method for the multirate out-
put feedback based discrete-time sliding mode control
of a class of nonlinear systems by using the concept
of finite discretizability [Chelouah and Petitot, 1995].
2 FINITELY DISCRETIZABLE
SYSTEMS
2.1 Definition
Let x = (x
1
, · · · , x
n
) be the local coordinates for an
open neighborhood of q, defined as U
q
⊂ M . where
M is a real analytical connected n-dimensional mani-
fold. Consider the locally-controllable and observable
nonlinear system of the form
Σ : ˙x(t) =
m
X
i=1
u
i
(t)X
i
(x(t)) (1)
y(t) = g (x(t))
where X
1
, · · · , X
m
are real analytical vector fields on
U
q
, u = (u
1
, · · · , u
m
) ∈ R
m
and g : R
n
→ R
p
is a
polynomial function of x.
The solution of (1) corresponding to a con-
stant control u(t) = ¯u, for t ≥ 0, is denoted
(exp tY ) (I
d
)|
x(0)
, where Y =
P
m
i=1
¯u
i
X
i
and I
d
is the identity function.
The nonlinear system Σ is said to be finitely dis-
cretizable [Chelouah and Petitot, 1995] at the order
ν ≥ 1 if the solution of (1), corresponding to a con-
stant control u(t) = ¯u for t ≥ 0 is a polynomial of
degree ν − 1 in t, ∀t ≥ 0, ∀¯u ∈ R
m
and x(t
0
) ∈ U
q
i.e.,
x(t + t
0
) = (exp tY ) (I
d
)|
x(t
0
)
= (I
d
)|
x(t
0
)
+ tY (I
d
)|
x(t
0
)
(2)
+ · · · +
t
ν−1
(ν − 1)!
Y
(ν−1)
(I
d
)|
x(t
0
)
∀t ≥ 0, ∀¯u ∈ R
m
, ∀x(0) ∈ U
q
In other words, one has
Y
ν+µ
(I
d
)|
x(t
0
)
= 0, ∀µ > 0 (3)
Thus, if the system is discretized at a sampling in-
terval of τ sec, the discrete-time representation would
be
x((k + 1)τ ) = (exp tY ) (I
d
)|
x(kτ )
= (I
d
)|
x(kτ )
+ tY (I
d
)|
x(kτ )
(4)
+ · · · +
t
ν−1
(ν − 1)!
Y
(ν−1)
(I
d
)|
x(kτ )
Remark 1 : The system is considered to be
driftless only for the convenience of notation. All the
definitions can be extended to drift systems by setting,
say, u
m+1
≡ 1 ¤
2.2 Sufficient Condition of Finite
Discretization
We will use the capital letter I = (i
1
, · · · , i
m
) to de-
note multi-indices with i
µ
∈ N, µ ≤ m. We also
define
|I| = i
1
+ · · · + i
m
X
I
= X
i
1
1
· · · X
i
m
m
X
xI
= X
i
1
1
x · · · xX
i
m
m
where XY =
∂Y
∂x
X,
∂Y
∂x
representing the Jacobian
matrix [Khalil, 2002] and “ x” denotes the shuffle
product inductively defined on the length as follows
XxI
d
= I
d
xX = X
X
i
xY
j
= X
¡
X
i−1
xY
j
¢
+ Y
¡
X
i
xY
j−1
¢
.
The shuffle product is associative and commutative.
Definition 1 : Consider R
n
with the
coordinates x = (x
1
, · · · , x
n
). A dilation
is a map δ
t
: R
+
× R
n
→ R
n
is of the
form δ
t
(h(x)) = h (t
r
1
x
1
, · · · , t
r
n
x
n
), where
h : R
n
→ R
n
is a polynomial in x and we assume
that r
i
∈ N, i ≤ n, r
i
≤ r
i+1
. ¤
Definition 2 : A polynomial h : R
n
→ R
n
is homogeneous of degree j ∈ Z with respect to
a dilation δ
t
if δ
∗
t
= h ◦ δ
t
= t
j
h. Let H be the
algebra of real polynomial functions in (x
1
, · · · , x
n
),
we define H
j
= {h ∈ H, δ
∗
t
h = t
j
h} and set
H
j
= {0}, ∀j < 0, then H = ⊕
j≥0
H
j
. We denote
by P
j
the set of all polynomials homogeneous of
degree ≤ j i.e., P
j
= ⊕
j
l=0
H
l
¤
Definition 3 : A polynomial vector field X
is said to be homogeneous of degree −s ∈ Z with
respect to a dilation δ
t
if
¡
(δ
t
)
∗
X
¢
(h) = t
s
δ
∗
t
(X (h)) , h ∈ H
or equivalently X(h) ∈ H
j−s
if h ∈ H
j
. ¤
Theorem 1 : Let X
1
, · · · , X
m
be real ana-
lytical vector fields, with polynomial coefficients, ho-
mogeneous of degree −1 with respect to the dilation
δ
t
(x) = (x
r
1
1
, · · · , x
r
n
n
), then Σ is finitely discretiz-
able at most of the order r
n
+ 1. ¤
The proof of the theorem is presented in [Chelouah
and Petitot, 1995]
MULTIRATE OUTPUT FEEDBACK BASED DISCRETE-TIME SLIDING MODE CONTROL FOR A CLASS OF
NONLINEAR SYSTEMS
239

3 MULTIRATE OUTPUT
SAMPLING
Consider the nonlinear system (1). Let Σ is con-
trollable,observable, and finitely discretizable. Let
the system input is given with a sampling interval
of τ sec and the outputs y
i
are sampled at intervals
∆
i
=
τ
/
N
i
, N
i
∈ N, i = 1, · · · , p. It can then be
shown that the system states can be expressed as a
function of past N
i
samples of outputs y
i
and imme-
diate past control input.
Proof: Since y = g(x) is a polynomial func-
tion in x, using the result that the finite discretization
property is preserved under polynomial transforma-
tion [Chelouah and Petitot, 1995], it can be said that
y would also be finitely discretizable. y
i
(t + τ ), i ∈
N, i ≤ p would therefore be of the form
y
i
(t
0
+ τ ) = y
i
(t
0
) + τy
(1)
i
(t
0
) + · · · (5)
+
τ
N
i
−1
(N
i
− 1)!
y
(N
i
−1)
i
(t
0
)
for some N
i
∈ N, {τ, t} ∈ R
+
, u(t) = ¯u, ∀t ∈
[t
0
, t
0
+ τ ). Due to the assumption that the system
Σ is observable, the system states can be expressed as
x(t
0
) = f
³
y, ˙y, y
(2)
, · · · , y
(N
max
)−1
, ¯u
´
(6)
N
max
= sup
i=1,··· ,p
N
i
where N
i
is the highest order derivative of y
i
appear-
ing in the nonlinear continuous-time observer. Now if
the system input u is applied and held constant for ev-
ery τ sec interval and each of the system outputs y
i
is
sampled at a rate ∆
i
=
τ
N
i
, then using (5), and using
y
(k)
i
to denote y
(k)
i
(kτ)
y
i
(kτ) = y
(0)
i
y
i
(kτ + ∆
i
) = y
(0)
i
+ ∆
i
y
(1)
i
+ · · · +
∆
N
i
−1
i
(N
i
− 1)!
y
(N
i
−1)
i
.
.
. (7)
y
i
((k + 1)τ − ∆
i
) = y
(0)
i
+ · · ·
+
((N
i
− 1)∆
i
)
N
i
−1
(N
i
− 1)!
y
(N
i
−1)
i
The left hand side of the above set of N
i
equa-
tions constitute the multirate output samples for y
i
.
The equations are independent in the N
i
variables
y
i
, y
(1)
i
, · · · , y
(N
i
−1)
i
and hence the output derivatives
can be obtained by solving (7).
y
(0)
i
y
(1)
i
.
.
.
y
(N
i
−1)
i
= A
−1
i
y
i
(kτ)
y
i
(kτ + ∆
i
)
.
.
.
y
i
((k + 1)τ − ∆
i
)
(8)
A
i
=
1 0 · · · 0
1 ∆
i
· · · ∆
N
i
−1
i
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
1 (N
i
− 1)∆
i
· · · ((N
i
− 1)∆
i
)
(N
i
−1)
(9)
This along with the observability condition in (6)
and the discrete state equation (4) would mean that
one can derive the system state information at t =
(k + 1)τ by measuring the outputs y
i
for the pe-
riod t ∈ [kτ, (k + 1)τ) with a sampling interval ∆
i
respectively and holding the input u = ¯u constant
during the same period. Hence, the observability of
the continuous time system along with the finite dis-
cretization property ensures that a multirate output
sampling interval of
τ
N
i
for each output y
i
for the in-
put sampling interval of τ is a sufficient condition for
the discrete-time observability of the nonlinear sys-
tem.
4 DISCRETE-TIME SLIDING
MODE CONTROL
4.1 State based Control
The application of the sliding mode control strategy to
nonlinear system representations has received consid-
erable attention in the recent years [Khan and Spur-
geon, 2001,Munoz and Sbarbaro, 2000,Sira-Ramirez
et al., 1997, Zhou et al., 2001].
Using a strategy similar to that discussed in [Gao
et al., 1995], we first design stable sliding surfaces
s
i
(t) = 0, i = 1, · · · , m by finding the relationship
between the states so that a chosen candidate Lya-
punov function V (x) has
˙
V (x) < 0. Since, the sys-
tem stability is conserved on discretization, the same
sliding surfaces s
i
(kτ) = s
i
(k) = 0 would also be
stable for the discrete-time system representation. For
the reminder of the paper, the notation x(k) is used in-
stead of x(kτ ) for brevity. Now applying the reaching
condition
s
i
(k + 1) − s
i
(k) = −q
i
τs
i
(k) − ²τsgn(s
i
(k))
ans substituting the value of x(k+1) from the discrete
system representation (4), one can solve for u
i
(k) and
obtain the control inputs that would guide the system
along the chosen sliding surfaces.
ICINCO 2004 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
240

4.2 Multirate Output Feedback
Control
As discussed in Section. 1, the above algorithm may
not be always implementable because all the states
may not be measurable, or even physical variables.
The existing output feedback control strategies for
sliding mode control either require the sliding surface
to be an explicit function of the outputs [Khan and
Spurgeon, 2001,Sira-Ramirez et al., 1997], which re-
stricts the scope of possible sliding manifolds. Even
in case of a output based sliding surface is success-
fully constructed, it cannot ensure that the system as a
whole would be stabilized [Thomas and Bandyopad-
hyay, 1997]. However, it has been shown in Section.
3, the observability and finite discretizability of the
system ensures that each of the system states can be
represented as a function of the past N
i
multirate sam-
ples of the output and the past input u
i
(k − 1).
Thus, the state based control derived in Section. 4.1
can now be easily translated to one that is based on
past output samples and the immediate past control
signal, whenever the finitely discretizable system is
observable in continuous time by using the procedure
described in Section. 3.
5 ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE
The above said multirate output feedback based
discrete-time sliding mode control technique has been
illustrated in the following example.
Consider the following continuous time sys-
tem representation defined in the manifold U
p
:
¡
x
1
> −1, {x
2
, x
3
} ∈ R
2
¢
˙x
1
= u
1
(10)
˙x
2
= u
2
˙x
3
= x
1
x
2
+ x
2
·
y
1
y
2
¸
=
·
x
1
x
3
¸
The system has vector fields X
1
= ∂
1
, X
2
= ∂
2
and the drift vector field Y = (x
1
x
2
+ x
2
) ∂
3
, where
∂
i
denotes the partial derivative with respect to x
i
.
It can be verified that relative to the dilation δ
t
=
¡
tx
1
, tx
2
, t
3
x
3
¢
, the vector fields are homogeneous
of degree −1. The verification for X
1
has been shown
here.
¡
(δ
t
)
∗
X
1
¢
(x) = X
1
(δ
t
(x))
= X
1
¡
tx
1
, tx
2
, t
3
x
3
¢
=
∂
∂x
1
¡
tx
1
, tx
2
, t
3
x
3
¢
= (t, 0, 0)
δ
t
(X
1
(x)) = δ
t
µ
∂
∂x
1
(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
)
¶
= δ
t
((1, 0, 0))
= δ
t
¡¡
x
0
1
, 0, 0
¢¢
=
³
(tx
1
)
0
, 0, 0
´
= (1, 0, 0)
Hence, it can be seen
¡
(δ
t
)
∗
X
1
¢
(x) = t
1
(δ
∗
t
(X
1
(x)))
Therefore, the vector field X
1
is homogeneous of de-
gree −1 with respect to the dilation δ
t
. The prop-
erty can be easily verified for the other vector fields
also. Therefore, the system (10) is finitely discretiz-
able. For a sampling time of τ sec the discrete-time
representation can be given as
x
1
(k + 1) = x
1
(k) + τu
1
(k) (11)
x
2
(k + 1) = x
2
(k) + τu
2
(k)
x
3
(k + 1) = x
3
(k) + τ (x
1
(k)x
2
(k) + x
2
(k))
+
τ
2
2
(x
2
(k)u
1
(k) + (1 + x
1
(k)) u
2
(k))
+
τ
3
3
u
1
(k)u
2
(k)
5.1 Design of Sliding Surfaces
The system is a multi-input system and hence requires
the design of two sliding surfaces. Dividing the sys-
tem (10) into two coupled sub-systems with states
(x
1
) and (x
2
, x
3
), it can be observed that the only
possible sliding surface for the former system would
be
s
1
= x
1
= 0 (12)
and in order to obtain the sliding surface for the sec-
ond subsystem we use the candidate Lyapunov func-
tion V =
x
2
3
2
, which would give
˙
V = x
3
(x
1
x
2
+ x
2
)
and thus a stable sliding surface for this sub-system
would be
s
2
= x
3
+ x
1
x
2
+ x
2
= 0 (13)
MULTIRATE OUTPUT FEEDBACK BASED DISCRETE-TIME SLIDING MODE CONTROL FOR A CLASS OF
NONLINEAR SYSTEMS
241

5.2 Multirate Output Sampling
based Nonlinear Observer
From the discrete model (11), it can be said that if the
outputs have multiplicities as N
1
= 2, N
2
= 4, then
it would be a sufficient condition for the system states
to be computable through multirate output sampling.
However,by choosing N
1
= 1, N
2
= 2, i.e., ∆
1
=
τ, ∆ = ∆
2
=
τ
2
, the discrete-time observer can be
derived as
x
1
(k) = y
11
(k) + τu
1
(k − 1) (14)
x
2
(k) =
1
3∆
f
1
(k)
(2y
11
(k) + u
1
(k − 1) ∆ + 2)
(15)
x
3
(k) =
1
3
f
2
(k)
(2y
11
(k) + u
1
(k − 1) ∆ + 2)
(16)
where
f
1
(k) = 6 (y
22
(k) − y
21
(k)) (17)
+9∆
2
u
2
(k − 1) (y
11
(k) + 1)
+4∆
3
u
1
(k − 1) u
2
(k − 1)
f
2
(k) = 6
¡
y
2
11
(k) + 1
¢
∆
2
u
2
(k − 1) (18)
+12y
11
(k) y
22
(k) (19)
+12y
11
(k) ∆
3
u
1
(k − 1) u
2
(k − 1)
+12y
22
(k)
+12∆
3
u
1
(k − 1) u
2
(k − 1)
+12 (y
11
(k) + 1) ∆
2
u
2
(k − 1)
−6 (y
11
(k) + 1) y
21
(k)
+3u
1
(k − 1) ∆ (4y
22
(k) − 3y
21
(k))
−4∆
2
u
2
(k − 1)
¡
u
2
1
(k − 1) ∆
2
− 3
¢
y
11
(k) = y
1
(k − 1) (20)
y
21
(k) = y
2
(k − 1) (21)
y
22
(k) = y
2
(kτ − ∆) (22)
Thus, the system states can be derived using the past
N
i
multirate output samples and the immediate past
control signals.
Remark 2 : It is to be noted here that
during the estimation of the states x
2
(k) and
x
3
(k) a singularity would occur whenever
(2y
11
(k) + u
1
(k − 1) ∆ + 2) = 0. Therefore,
the control signal u
1
should be computed in such a
manner that this condition is avoided. ¤
5.3 Controller Design
5.3.1 Computation of u
1
(k)
Using the Gao’s [Gao et al., 1995] reaching law for
s
1
(k),the control signal u
1
(k) can be derived as
s
1
(k + 1) − s
1
(k) = −q
1
τ − ²
1
τsgn(s
1
(k))
τu
1
(k) = −q
1
τ − ²
1
τsgn(s
1
(k))
u
1
(k) = −q
1
− ²
1
sgn(s
1
(k)) (23)
with the restrictions on q
1
, ²
1
as
q
1
, ²
1
> 0 (24)
1 − q
1
τ > 0 (25)
This control would ensure that the state x
1
(k) con-
verges monotonically to within the quasi-sliding
mode band of width given by
δ
1
=
²
1
τ
2 − q
1
τ
(26)
The condition
δ
1
< 1 (27)
is imposed so that the sliding mode control u
1
has
a quasi-sliding mode band completely inside U
p
.
If the value of u (k) is substituted from (23) into
(2y
11
(k) + u
1
(k − 1) ∆ + 2) and then equated to
zero, we get the disallowed state as follows.
1. For x
1
> 0,
µ
(x
1
(k) + 1) +
∆
2
(−q
1
x
1
(k) − ²
1
)
¶
= 0
x
1
(k)
µ
1 −
∆
2
q
1
¶
=
µ
∆
2
²
1
− 1
¶
x
1
(k) =
(²
1
∆ − 2)
(2 − q
1
∆)
Since the Gao’s reaching law stipulates 1 − q
1
∆ >
0, the denominator would always be positive, thus
if it is ensured that
(²
1
∆ − 2) < 0, (28)
the above case can be completely ignored.
2. For x
1
< 0,
µ
(x
1
(k) + 1) +
∆
2
(−q
1
x
1
(k) + ²
1
)
¶
= 0
x
1
(k)
µ
1 −
∆
2
q
1
¶
= −
µ
∆
2
²
1
+ 1
¶
x
d
1
= −
(∆²
1
+ 2)
(2 − ∆q
1
)
ICINCO 2004 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
242

This case can also be ignored provided it is ensured
that the disallowed states falls outside the manifold
U
p
. That is by imposing the condition
(∆²
1
+ 2)
(2 − ∆q
1
)
> 1 (29)
Since the initial state x
1
(0) would be inside the
manifold U
p
and the control u
1
would take it mono-
tonically to a band of width δ
1
< 1, the disallowed
state x
1
(k) = x
d
1
would not be encountered.
3. And the special case of x
1
(k) = 0, In this case, the
system becomes of a reduced order and hence it is
the observer that has to be modified (and not the
control input, which would obviously be u
1
(i) =
0, i ≥ k). The new discrete state equations would
be
x
2
(k + 1) = x
2
(k) + τu
2
(k)
x
3
(k + 1) = x
3
(k) + τx
2
(k) +
τ
2
2
u
2
(k)
Hence, in this case, x
(2,3)
(k + 1) are estimated as
x
2
(k + 1) =
¡
y
22
(k) − y
21
(k) +
3
2
u
2
(k) ∆
2
¢
∆
x
3
(k + 1) = 2y
22
(k) − y
21
(k) + u
2
(k) ∆
2
5.3.2 Computation of u
2
(k)
s
2
(k + 1) − s
2
(k) = −q
2
τs
2
(k) − ²
2
τsgn (s
2
(k))
(x
1
(k)x
2
(k) + x
2
(k))
+
³
τ
2
+ 1
´
x
2
(k)u
1
(k)
+u
2
(k)
³
τx
1
(k) +
τ
2
(1 + x
1
(k))
´
+u
2
(k)
µµ
τ
2
3
+ τ
¶
u
1
(k)
¶
= −q
2
(s
2
(k))
−²
2
sgn (s
2
(k))
u
2
(k) = −
(q
2
s
2
(k) + ²
2
sgn (s
2
(k)))
f
3
(k)
−
(x
1
(k)x
2
(k) + x
2
(k))
f
3
(k)
−
¡
τ
2
+ 1
¢
x
2
(k)u
1
(k)
f
3
(k)
(30)
f
3
(k) =
3τ
2
x
1
(k) + ∆ +
µ
τ
2
3
+ τ
¶
u
1
(k)
with the inequality conditions
q
2
, ²
2
> 0 (31)
1 − q
2
τ > 0 (32)
Here too, there would be a singularity encountered in
the computation of the control u
2
whenever the de-
nominator vanishes. In this case the disallowed state
would be
1. If x
1
> 0
0 = τx
1
(k) +
τ
2
(1 + x
1
(k))
+
µ
τ
2
3
+ τ
¶
(−q
1
x
1
(k) − ²
1
)
x
d
2
=
³
τ
2
3
+ τ
´
²
1
− ∆
3∆ −
¡
τ
2
3
+ τ
¢
q
1
2. If x
1
< 0
0 = τx
1
(k) +
τ
2
(1 + x
1
(k))
+
µ
τ
2
3
+ 1
¶
(−q
1
x
1
(k) + ²
1
)
x
d
3
=
−
³³
τ
2
3
+ 1
´
²
1
+ ∆
´
3∆ −
¡
τ
2
3
+ 1
¢
q
1
Both these cases would be avoided if q
1
and ²
1
are
chosen such that
µ
τ
2
3
+ τ
¶
²
1
− ∆ < 0 (33)
3∆ −
µ
τ
2
3
+ τ
¶
q
1
< 0 (34)
In this case, x
1
= 0 does not cause any singularity
in u
2
(k)
When the states in control law (23,30) are sub-
stituted from the nonlinear multirate observer con-
structed in (14), the control law would now be trans-
lated into one based on multirate output feedback.
5.4 Simulation Study
A simulation of the response of the system (10) under
the designed control, was studied. The control inputs
u
1
and u
2
were designed according to (23) and (30).
The sampling time was chosen as τ = 0.1 sec, and
the controller parameters were chosen as q
1
= q
2
=
2, ²
1
= ²2 = 0.1 so as to satisfy the inequality condi-
tions in equations (24,25,27-29,31-34).
The simulation results for X(0) = [
2.5 5 0
]
T
are shown in Figs. (1-3). Fig. (1) gives the time-
response of the system states when the designed con-
trol is applied to the system. The phase portrait of
the system is shown in Fig. (2). The evolution of the
sliding surfaces s
1
and s
2
and the plots of the control
inputs are given in Fig. (3).
MULTIRATE OUTPUT FEEDBACK BASED DISCRETE-TIME SLIDING MODE CONTROL FOR A CLASS OF
NONLINEAR SYSTEMS
243
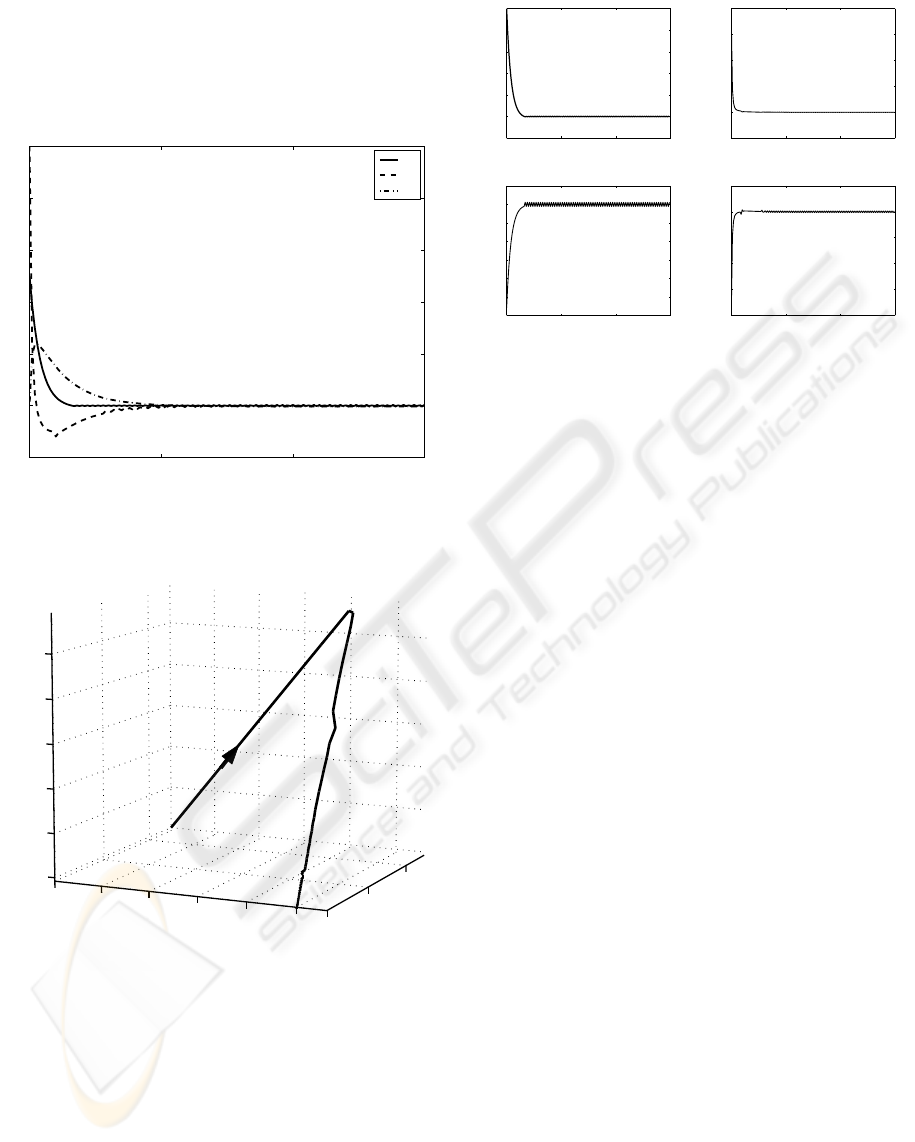
It can be seen from the plots (Fig. (3)) that the slid-
ing surfaces decrease monotonically in magnitude to
within the quasi-sliding mode band. The response of
the system states and the applied control inputs are
also found to be satisfactory.
0 5 10 15
−1
0
1
2
3
4
5
Time (sec)
System States
x
1
x
2
x
3
Figure 1: Response of System States.
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
X
1
X
2
X
3
Figure 2: Phase Portrait of the System
6 CONCLUSION
A procedure for the design of discrete-time sliding
mode controller for a class of nonlinear systems viz.
finitely discretizable nonlinear systems has been pro-
posed in the paper. The technique uses the concept of
multirate output sampling to realize the behavior of a
0 5 10 15
−0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Time (sec)
Sliding Function s
1
0 5 10 15
−5
0
5
10
15
20
Time (sec)
Sliding Function s
2
0 5 10 15
−6
−5
−4
−3
−2
−1
0
1
Time (sec)
Control Input u
1
0 5 10 15
−40
−30
−20
−10
0
10
Time (sec)
Control Input u
2
Figure 3: Evolution of Sliding Surfaces and Control Inputs.
state feedback based nonlinear control law. It has an
advantage that it would be applicable to a larger class
of nonlinear systems as many of the physical systems
are, in fact, finitely discretizable under appropriate co-
ordinate transformation. Moreover, the technique is
practical as it is able to translate a state based control
law into one based on system outputs and past input
samples. Further, it does not impose any restrictions
on the choice of the sliding surfaces.
REFERENCES
Bag, S. K., Spurgeon, S. K., and Edwards, C. (1997). Out-
put feedback sliding mode control for uncertain sys-
tems. Proc. of the IEE - D on Control Theory and
Applications, 144(3):209–216.
Chelouah, A. and Petitot, M. (1995). Finitely discretiz-
able nonlinear systems : concepts and definitions. In
Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Decision and Con-
trol, pages 19–24, Now Orelands, LA.
Diong, B. M. (1993). On the invariance of output feedback
VSCS. In Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Decision
and Control, pages 412–413.
Emelyanov, S. V. (1967). Variable structure control sys-
tems. Nauka, Moscow.
Furuta, K. (1990). Sliding mode control of a discrete sys-
tem. Systems and Control Letters, 14:144–152.
Gao, W., Wang, Y., and Homaifa, A. (1995). Discrete-time
variable structure control systems. IEEE Trans. on
Ind. Electron., 42(2):117–122.
Hung, J. Y., Gao, W., and Hung, J. C. (1993). Variable struc-
ture control : A survey. IEEE Trans. on Ind. Electron.,
40(1):2–21.
Khalil, H. K. (2002). Nonlinear Dynamical Systems. Pren-
tice Hall, New Jersey.
ICINCO 2004 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
244

Khan, M. K. and Spurgeon, S. S. (2001). Application of
output feedback based dynamic sliding mode control
to speed control of an automotive engine. In Fourth
Nonlinear Control Network (NCN4) Workshop, The
University of Sheffield, UK.
Munoz, D. and Sbarbaro, D. (2000). An adaptive sliding-
mode controller for discrete nonlinear systems. IEEE
Trans. on Ind. Electron., 47(3):574–581.
Saaj, M. C., Bandyopadhyay, B., and Unbehauen, H.
(2002). A new algorithm for discrete-time sliding-
mode control using fast output sampling feedback.
IEEE Trans. on Ind. Electron., 49(3):518–523.
Sarpturk, S. Z., Istefanopulos, Y., and Kaynak, O. (1978).
On the stability of discrete-time sliding mode systems.
IEEE Trans. on Auto. Contr., 32:930–932.
Sira-Ramirez, H., Julian, P., Chiacchiarini, H., and Desages,
A. (1997). On the sliding mode control of discrete-
time nonlinear systems by output feedback. In Proc.
European Control Conference, Paper. 763.
Thomas, S. and Bandyopadhyay, B. (1997). Comments
on ‘a new controller design for one link manipulator’.
IEEE Trans. on Auto. Contr., 42:425–429.
Utkin, V. I. (1977). Variable structure systems with sliding
modes. IEEE Trans. on Auto. Contr., 22:212–222.
Werner, H. and Furuta, K. (1995). Simultaneous stabi-
lization based on output measurement. Kybernetika,
31:395–411.
Young, K. D., Utkin, V. I., and Ozguner, U. (1999). A con-
trol engineer’s guide to sliding mode control. IEEE
Transactions on Control Systems, 7(3):328–342.
Zak, S. H. and Hui, S. (1993). On variable structure output
feedback controllers for uncertain dynamic systems.
IEEE Trans. on Auto. Contr., 38:1509–1512.
Zhou, J.-S., Liu, Z.-Y., and Pei, R. (2001). A new nonlin-
ear model predictive control scheme for discrete-time
syste based on sliding mode control. In Proc. Ameri-
can Control Conference, pages 3079–3084.
MULTIRATE OUTPUT FEEDBACK BASED DISCRETE-TIME SLIDING MODE CONTROL FOR A CLASS OF
NONLINEAR SYSTEMS
245
