
GENETIC ALGORITHMS APPLIED TO THE OPTIMIZATION
OF GASIFICATION FOR A GIVEN FUEL
Miguel Caldas
Mechanical Engineering Department, IST, Technical University of Lisbon, Portugal
Luisa G. Caldas
Civil Engineering and Architecture Department, IST, Technical University of Lisbon, Portugal
Viriato Semião
Mechanical Engineering Department, IST, Technical University of Lisbon, Portugal
Keywords: Gasification, Genetic Algorithms, Optimisation
Abstract: Gasification is a well-known technolog
y that allows for a combustible gas to be obtained from a
carbonaceous fuel by a partial oxidation process (POX). The resulting gas (synthesis gas or syngas) can be
used either as a fuel or as feedstock for chemical production. Recently, gasification has also received a great
deal of attention concerning power production possibilities through IGCC process (Integrated Gasification
Combined Cycle), which is currently the most environmentally friendly and efficient method for the
production of electricity. Gasification allows for low grade fuels, or dirty fuels, to be used in an
environmental acceptable way. Amongst these fuels are wastes from the petrochemical and other industries,
which may vary in composition from shipment to shipment, and from lot to lot. If operating conditions are
kept constant, this could result in lost of efficiency. This paper presents an application of Genetic
Algorithms to optimise the operating parameters of a gasifier processing a given fuel. Two different
objective functions are used: one to be used if hydrogen production is the main goal of gasification; other to
be used when power/heat production is the aim of the process. Results show that the optimisation method
developed is fast and simple enough to be used for on-line adjustment of the gasification operating
parameters, for each fuel composition and gasification aim, thus improving the overall performance of the
industrial process.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper presents an application of Genetic
Algorithms to optimize the operating parameters of a
gasifier processing a given fuel.
Gasification is a well-known technology that
al
lows for a combustible gas to be obtained from a
carbonaceous fuel by a partial oxidation process
(POX). The resulting gas (synthesis gas or syngas)
can be used either as a fuel or as feedstock for
chemical production. The major constituents of
syngas are CO, H
2
, CO
2
and H
2
O. From these, only
H
2
and CO are combustible and only H
2
is
interesting as chemical feedstock.
Formally defined, gasification is the conversion
o
f solid and liquid materials into a gas through
reaction with oxygen, steam and carbon dioxide, or a
mixture of these gases, at a temperature exceeding
700 ºC. In industrial applications, a solid or liquid
fuel is conveyed to a vessel (the gasifier) and mixed
with oxygen and steam. The CO
2
and H
2
O resulting
from the combustion of a fraction of the fuel will
also become an agent of gasification for the
remaining fuel. There will exist some N
2
present in
the gasifier, because the oxygen stream is not 100%
pure and also, possibly, because N
2
can be used as a
conveying gas for the pneumatic transportation of
the fuel. Some heat can be recovered from the
gasification chamber (gasification is an overall
58
Caldas M., Caldas L. and Semião V. (2004).
GENETIC ALGORITHMS APPLIED TO THE OPTIMIZATION OF GASIFICATION FOR A GIVEN FUEL.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 58-63
DOI: 10.5220/0001140400580063
Copyright
c
SciTePress

exothermic reaction, which will generate heat) to
produce steam.
Traditionally, gasification has been used as a
means of producing heating gas for domestic and
industrial needs (town gas) and as a source of
hydrogen for the heavy chemical industry. Recently,
gasification has received a great deal of attention
concerning power production possibilities, since it is
the core of the IGCC process (Integrated
Gasification Combined Cycle). IGCC is the most
environmentally friendly method for the production
of electricity since it allows for all the pollutants to
be removed in a pre-combustion stage, at the gas
cleanup (Haupt et al., 2000). It also permits any fuel
to be used in a combined cycle, thus greatly
increasing electricity production efficiency.
One of the major advantages of gasification is
that it allows for less noble fuels, or dirty fuels, to be
used for the above-mentioned purposes. Amongst
these are wastes from the petrochemical and other
industries. In the latter case, each shipment of wastes
supplied to be gasified usually presents a different
composition. This is quite understandable since the
waste supplier industry will deal with different
feedstocks of prime matter, or will produce different
products in a given time span. So, naturally, the
waste produced will present a different composition
from case to case.
In the present work we determine the optimum
operational parameters for the gasification of a given
fuel, as characterized by its elementary composition
and Lower Heating Value (LHV). The parameters to
be optimized are the Operating Pressure, Oxygen to
Fuel ratio, Steam to Fuel ratio, and Heat Recovered.
Two different objective functions are used, since
the goals to be reached are different if the
gasification process is intended to produce an
hydrogen rich gas for chemical feedstock, or a
combustible gas for power/heat production. In the
former case, the syngas’ hydrogen percentage will
be maximized, while in the latter the gasification
Cold Gas Efficiency is the parameter to be
maximized (Cold Gas Efficiency is the quotient
between the heating capacity of the syngas and the
original fuel heating capacity. The heating capacity
is the product of the lower heating value and the
mass flow). Thermal efficiency (defined as the
quotient between: 1) the sum of the heat recovered
in the process and the heating capacity of the syngas;
and 2) the fuel heating capacity), which is a
parameter closely related to Cold Gas Efficiency, is
also analyzed.
The optimization method developed could be
used for on-line adjustment of the gasification
operating parameters for different fuel compositions
and gas’ final purpose, thus improving overall
performance of the industrial process.
Genetic Algorithms (GAs) have been used to
determine optimal operational parameters for several
industrial processes and other practical applications
(for example, Dickinson and Bradshaw, 1995;
Wright, 1996; Huang and Lam, 1997). They are
particularly suitable for problems that are either
multimodal (i.e., present several local extremes), or
discontinuous, since in these cases conventional
optimization methods based on calculus, like
gradient methods, tend to fail. GAs are also effective
in smother problems that could be solved using more
traditional methods, what makes them very flexible
and adaptable to a variety of solution spaces. In the
present work, it is suspected that the objective
functions are in fact multimodal, what lead to the
choice of GAs as the search procedure.
The structure of the paper is the following: in
section 2 the gasification modeling is briefly
described, section 3 verses on the search and
optimization process using GAs, section 4 presents
the main results of this work, and section 5 draws
conclusions.
2 GASIFICATION MODELLING
Gasification is a complex chemical process that
involves a multitude of phenomena, like
devolatization, pyrolysis, heterogeneous gas-solid
reactions and homogeneous gas-gas reactions
(Govind and Shah, 1984; Liu et al., 2000; Benyon,
2002). Each phenomenon has its one rate of reaction
and a full CFD, heat transfer and chemical kinetic
simulation is required to perform a detailed
simulation of the process. See Benyon (2002) for an
excellent dissertation on the subject. A brief
description of the process follows.
The first part of the gasification process is the
pyrolysis of the fuel. When solid fuels are concerned
the term devolatilization is usually utilized. During
pyrolysis some gaseous constituents are released
from the fuel. These include CO, CO
2
, H
2
, H
2
O,
H
2
S, COS, HCN, NH
3
, CH
4
, C
2
H
2
and some other
heavier hydrocarbons in lesser quantities.
After pyrolysis a char residue containing fixed
carbon and ash will remain and will undergo further
oxidation. The volatiles released will react in the
gaseous phase.
The main char heterogeneous reactions are
reactions between the char’s fixed carbon and O
2
,
H
2
, H
2
O and CO
2
producing CO, H
2
, CO
2
and CH
4
.
Reactions with O
2
and H
2
are exothermic and those
with H
2
O and CO
2
are endothermic. See Benyon
(2002) for details.
In the gaseous phase there will be combustion
reactions that will tend to convert all of the
GENETIC ALGORITHMS APPLIED TO THE OPTIMIZATION OF GASIFICATION FOR A GIVEN FUEL
59

hydrocarbons into CO
2
and H
2
O and some
equilibrium reactions, noticeably the water-gas shift
and the methanation reactions, to be described below
– Eqs. (1) and (3).
In the present paper a simplified gasification
model was used. It is an equilibrium model that
assumes a homogenous temperature throughout the
reaction zone and neglects chemical kinetics effects
and detailed heat transfer modeling. Therefore, all
the reactions are assumed to attain their equilibrium
concentrations at the reaction temperature. This
assumption is very justifiable, since industrial
gasifiers are designed in such a way that irreversible
gasification reactions proceed to their completion
and reversible ones attain equilibrium within the
reaction chamber and within the reactants residence
time. Therefore, in industrial gasifiers that are
commercially available, we can expect to have a
homogeneous temperature and equilibrium
conditions at the gasifier’s exit. Of course, this
model will not allow for an in depth analysis of the
intermediate stages of the gasification complex
phenomena, but that is not the purpose of the present
research, which focus on the overall exit conditions
only.
This model is based on mass balances for each
atomic species (C, H, O, N and S), an energy
balance in order to compute the gasification’s final
temperature and on the equilibrium between the
species using reactions (1) to (5).
222
HCOOHCO +⎯→⎯+ (1)
OHCOSCOSH +⎯→⎯+
OHCHHCO 3 +⎯→⎯+
23 NHNH ⎯→⎯+
222
(2)
242
(3)
322
(4)
(5)
432
3 CHNHHHCN +⎯→⎯+
Each element mass balance provides one
equation. The enthalpy equation offers another one.
Each of the equilibrium reactions (1) to (5) provides
an equation for the species concentration. See any
standard text book, e.g., Levine (1988), for details
on chemical equilibrium.
Therefore, we have eleven equations (five for
elements mass balance, one for enthalpy and five for
equilibrium reactions) and eleven unknowns: the
temperature, T, and the mass flow of the syngas
constituents (H
2
, CO, H
2
O, CO
2
, N
2
, H
2
S, COS,
CH
4
, HCN and NH
3
). The result is a determined
system of non-linear equations that can be solved
through any of the standard numerical techniques
available in the literature.
Having the mass flow of all the elements in the
resulting syngas, it is straight forward to compute
their respective percentage in the syngas
composition, both in terms of mass and in terms of
volume.
The Cold Gas Efficiency is defined, as said
before, as the quotient between the heating capacity
of the syngas and the original fuel heating capacity.
This quotient is expressed in Eq.(6) where the index
i ranges over all syngas constituents, LHV means
Lower Heating Value, and m with an over dot means
mass flow.
FuelFuel
i
ii
LHVm
LHVm
CGE
&
&
∑
=
(6)
Of course that, besides the parameters that will
be manipulated (oxygen to fuel ratio, steam to fuel
ratio, etc…), the fuel elementary composition, fuel
mass flow and fuel LHV must be supplied as inputs
to the model.
Again, notice that, although this model is much
simpler than the full numerical approach presented
in, e.g., Govind and Shah (1984), Liu et al. (2000) or
Benyon (2002), it retains the major effects of the
influence of the parameters that are being
manipulated in the objective functions under
analysis, being therefore well suited for the purpose
at hand. Also, being much simpler, this model is
more manageable, has reduced computational times,
and is thus better suited for linking with Genetic
Algorithms.
3 SEARCH AND OPTIMISATION
PROCESS
The search and optimization method used is a
Genetic Algorithm. The use of a GA was suitable for
the problem under study due to its non-linearity, and
to the possible existence of local minima, where a
conventional optimization procedure might become
trapped. Since a GA searches from a population of
points, not a single point, the probability of the
search getting trapped in a local extreme is limited.
GAs start searching by randomly sampling within
the solution space, and then use stochastic operators
to direct a hill-climbing process based on objective
function values. Genetic Algorithms were first
ICINCO 2004 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
60
presented by Holland (1975), and made familiar to a
broader audience by Goldberg (1989).
A standard Genetic Algorithm was used, with a
total population of 30 individuals per generation,
evolution being carried out through 100 generations.
This means that for each run, 3000 possible
solutions are evaluated, even though there will be
some degree of repetition among them. One of the
sources of solution overlapping among generations
is elitism, a strategy used in this study, in which the
best individual of a generation is always copied to
the following population. A simple kind of memory
can thus be implemented to reduce computational
time, so that when the GA is confronted with a
previously evaluated solution, it automatically
retrieves its objective function values. Uniform
crossover, which works allele by allele, was used
throughout the experiments. The probability of
crossover was 0.5, and the probability of mutation
was kept as 0.04.
The study also compares results using a micro-
GA and the conventional GA. The main difference
between the two methods relies on the population
size used. Typical population sizes for GAs range
from 30 to 200, based on earlier studies such as
those of Grefenstette (1986), where suggestions for
optimal population choices based on parametric
studies are presented. In this study we use a strategy
named micro-GA (Krishnakumar 1989), which starts
with a small population (in this case, of only 5
individuals) and quickly makes it converge to a
solution. Convergence is measured by comparing the
chromosomes of the individual solutions. If they
differ by less that 5%, it is considered the population
has converged. When that happens, the micro-GA
restarts a new random population while carrying
over the individual with the best fitness in the
previous generation (elitism). This way, new
individuals are often brought into the search, without
loosing track of the ones that did better until that
point. An advantage of using the micro-GA
procedure is that the algorithm tends to perform a
local search around the best solutions during the
generations prior to convergence, since at that stage
solutions only differ by a few alleles. This local
search is important in finding local minima around
good solutions, and is usually hard to implement in
conventional GAs. Another advantage is that the
search procedure is faster, since the micro-GA does
not have the inertia of the large populations
associated with conventional GAs.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Two different fuels for gasification were studied:
Visbreaker Tar and Petcoke. These are refinery
residues and a common fuel for gasification. Their
elementary analysis and Lower Heating Value can
be seen in Table 1.
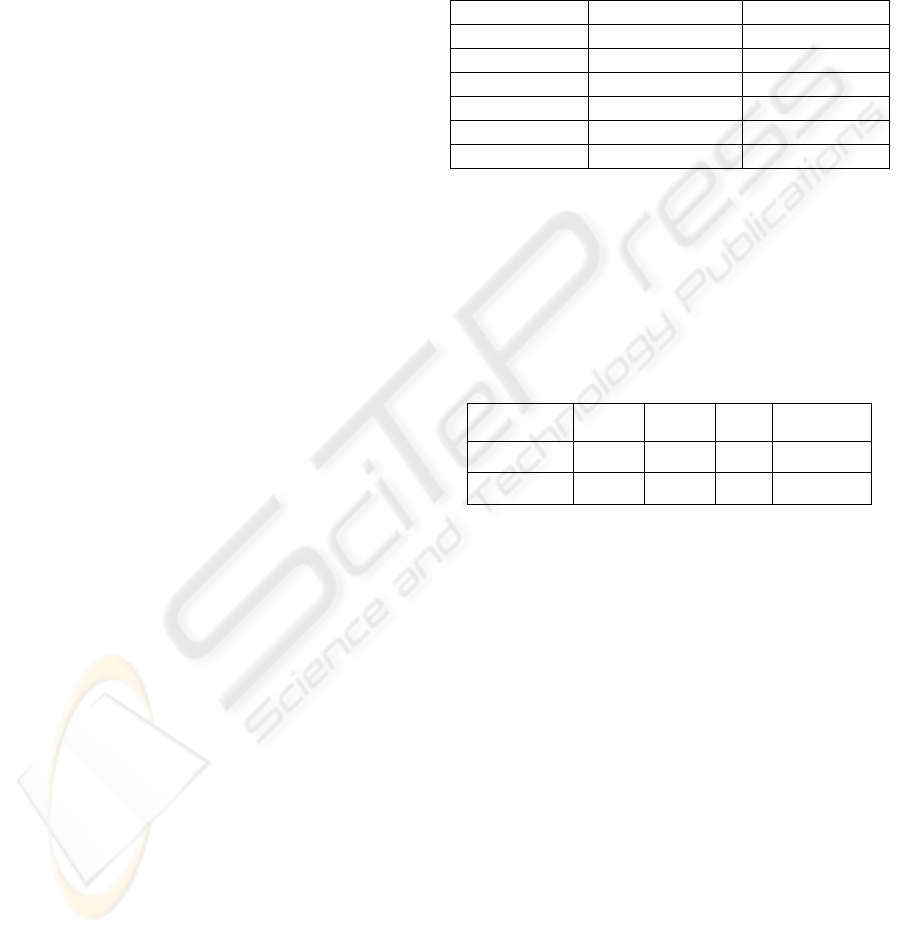
Table 1: Properties of the fuels under study.
Visbreaker Tar Petcoke
C (% wt) 86.1 88.6
H (% wt) 10.4 2.8
O (% wt) 0.5 0
N (% wt) 0.6 1.3
S (% wt) 2.4 7.3
LHV (kJ/kg) 40,938 33,680
Lower and upper bounds for each variable used in
this study are shown in table 2. Please note that the
fuel load considered was 3.6 ton/h, or 1 kg/s, which
mean that the total fuel heat capacity is about 40,000
kW for Visbreaker Tar and around 33,500 kW for
Petcoke. Therefore, the upper bound of the heat
recovered is around 25% of the total fuel heat
capacity.
Table 2: Lower and upper bounds for each variable.
Press.
(bar)
Oxigen/
Fuel
Steam
/ Fuel
Heat Recov.
(kW)
Lower bound 20 0 0 0
Upper bound 57.5 2 2 9000
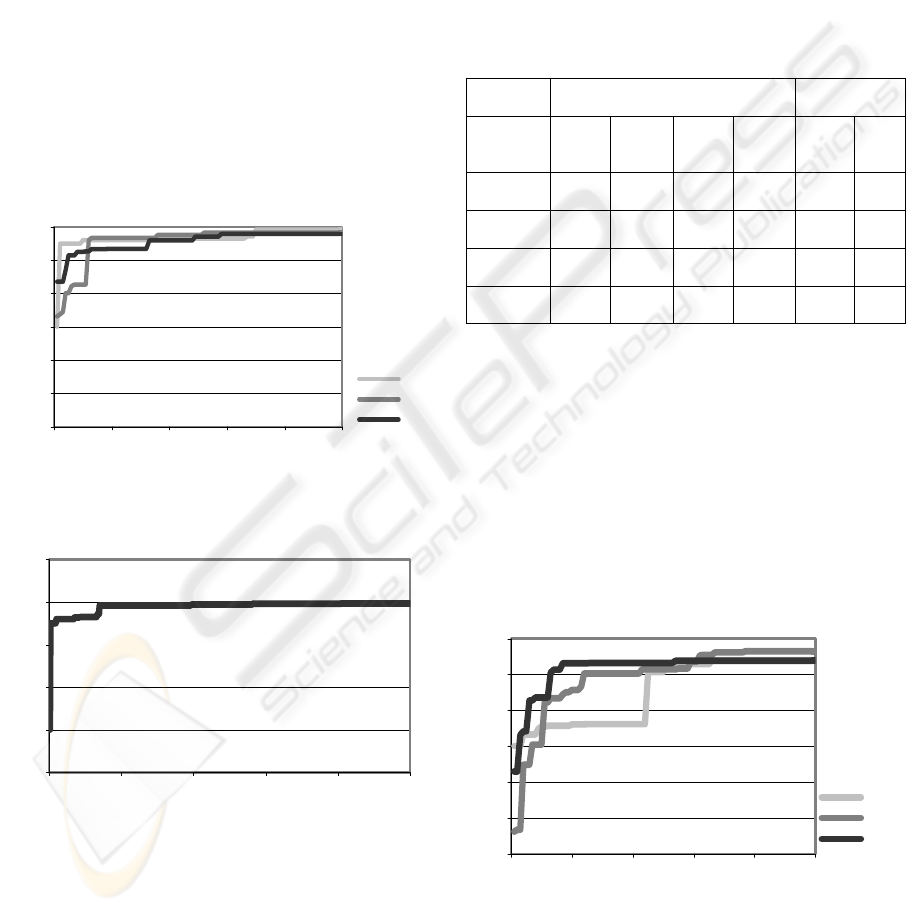
Results converge independently of the starting
population, which is random. This can be seen in
Fig.1, which depicts the Cold Gas Efficiency (CGE)
of the population’s best individual solution plotted
against the number of elapsed generations for 3
different initial populations. Fig.2 shows the search
evolution for the best individual Cold Gas
Efficiency, for 500 generations. It can be seen that
the quality of the solutions improved sharply during
the first generations, a tendency which continued
steadily, though in a less prominent fashion, until
approximately generation 100, after which
improvements were only marginal.
As can be seen from Table 1, the best Cold Gas
Efficiency the GA was able to attain when gasifying
Visbraker Tar was 89%. This value of CGE is
reached when the Pressure, Oxygen/Fuel ratio,
Steam/Fuel ratio and Heat Recovered have the
following values (22.5 bar, 0.89, 0.41, 0 kW). For
this solution the Dry Hydrogen Percentage (DHP) in
the gas is 44%.
If, conversely, we maximize the DHP, a value of
52% is reached for this parameter. The operating
conditions are (20 bar, 1.02, 1.94, 0 kW) and the
GENETIC ALGORITHMS APPLIED TO THE OPTIMIZATION OF GASIFICATION FOR A GIVEN FUEL
61
CGE is 83%. As can be seen, the largest change in
the operating parameters between these two cases
occurs in the Steam/Fuel ratio.
It was interesting to find out that thermal
efficiency, although being a relevant parameter to
measure the overall efficiency of the process, should
not be used as an objective function. The reason for
this is that an excessive weight will be placed in the
heat recovered, hurting both the CGE and the DHP
in the syngas. The gasification process would then
be shaped almost as a heat generating process, and
this is not the intention. As an example, if thermal
efficiency was to be maximized in the above case,
the operating parameters would be (20 bar, 1.43, 0,
9575 kW), resulting in a thermal efficiency of 92%.
However, the CGE would only be 68% and the DHP
would equal 29%. As it can be seen, these
parameters are worse than either of the previous
cases, thus confirming that this solution should be
avoided.
0.6
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0 20406080100
Generation
CGE
Run 1
Run 2
Run 3
Figure 1: Evolution of the best individual Cold Gas
Efficiency for three random initial populations.
Figure 2: Evolution of the best individual Cold Gas
Efficiency (CGE) throughout 500 generations.
If the two previous operating conditions - (22.5 bar, 0.89,
0.41, 0 kW) and (20 bar, 1.02, 1.94, 0 kW) - were to be
used for a different fuel (in the present case Petcoke), the
resulting CGE and DHP would be 88%, 29% for the first
case and 79%, 41% for the second. In case the operating
conditions were maximized for Petcoke, the solutions
obtained would be (20 bar, 0.83, 0.51, 0 kW), CGE=89%,
DHP=30% if CGE is maximized and (20 bar, 1.02, 2.0,
540 kW), CGE=79%, DHP=42% if DHP is maximized.
These operating condition do not differ significantly from
those obtained when Visbreaker Tar was being considered,
so, at least for these two petrochemical products, optimum
operating conditions are rather independent of fuel
composition. Table 3 summarizes the results obtained
using a standard GA. Note that the 540 kW present in the
last line of Table 3 are under 1.5% of the total fuel heat
capacity of this case, being therefore almost negligible.
Table 3: Results obtained using a standard GA. Values in
bold indicate the objective function being maximized.
Variables Objective
Functions
Fuel Press.
(bar)
Oxigen
/ Fuel
Steam
/ Fuel
Heat
Recov.
(kW)
CGE
DHP
Visbreaker
Tar
22.5 0.89 0.41 0
89%
44%
Visbreaker
Tar
20
1.02 1.94 0 83%
52%
Petcoke
20 0.83 0.51 0
89%
30%
Petcoke
20 1.02 2 540 79%
42%
Finally, the Micro-GA technique was tested in the
same cases. Results were equivalent to those
obtained using a conventional GA. Therefore, no
apparent advantage resulted from the local search
features introduced by the Micro GA. In fact,
slightly inferior results were observed when using
the Micro GA. The evolution of the cold gas
efficiency of the population’s best individual
solution for Visbreaker Tar is presented in Fig.3 as
an example, which compares almost exactly with
Fig.1. Again, three random and independent initial
population solutions are presented.
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
0 100 200 300 400 50
0
Generation
CGE
Figure 3: Evolution of the best individual Cold Gas
Efficiency (CGE) for three random initial populations,
using a Micro GA.
0.6
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0 20 40 60 80 100
Generation
CGE
Run 1
Run 2
Run 3
ICINCO 2004 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
62

5 CONCLUSIONS
The optimisation method developed is fast, simple
and robust enough to be used for on-line adjustment
of the gasification operating parameters for each fuel
composition and aim of gasification, thus improving
overall performance of the industrial process.
Thermal efficiency should not be chosen as an
objective function to be maximized under the
penalty of placing too much emphasis on the heat
recovered, thus compromising both the CGE and
DHP of the syngas.
The fundamental parameter that will influence
the best operating conditions for heat/power
production or hydrogen production is the Steam/Fuel
ratio, the Oxygen/Fuel ration being correspondently
adjusted.
Heat recovered should be marginal in order to
attain optimal conditions.
Results seem to be rather insensitive of pressure.
However, even if pressure is a less important
parameter for CGE and DHP, it is fundamental in
the operational aspects of the gasification.
Furthermore, and most importantly for industrial
applications, pressure is determinant for determining
the gas production capacity of the gasifier.
Therefore, operating pressure is a parameter that
should not be overlooked.
For the two studied fuels, the best operating
conditions to maximize CGE or DHP seem to be
independent of the fuel. Further work is required to
evaluate if this feature remains in a broader range of
fuels, including biomass and other non-
petrochemical fuels.
The Micro-GA technique was also used with
identical results than those obtained through regular
GA, no benefits resulting from the local search
features of the Micro-GA.
Future work will include the expansion of these
methods to multicriteria optimization, using Pareto-
based techniques.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially performed with the
financial support of: 1) Fundação para a Ciência e a
Tecnologia, Programa PRAXIS XXI, under the PhD
scholarship SFRH/BD/4833/2001; 2) the European
Commission’s 5
th
Framework Programme for RTD,
under the contract NNE5-2001-00670 (Migreyd
project). 3) Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia,
project POCTI/AUR/42147/2001, and the European
Union, FSE/ FEDER.
REFERENCES
Benyon, P.J., 2002, Computational modelling of entrained
flow slagging gasifiers, PhD thesis, University of
Sydney, Australia.
Dickinson, S. and Bradshaw, A., 1995, Genetic Algorithm
Optimization and Scheduling for Building Heating
Systems, Genetic Algorithms in Engineering Systems:
Innovations and Applications, 12-14 September 1995,
(pp. 106-111), University of Sheffield: Conference
Publication No. 414, Institution of Electrical
Engineers.
Goldberg, D., 1989, Genetic Algorithms in Search,
Optimization and Machine Learning, Addison-Wesley
Publishing Company.
Govind, R. and Shah, J., 1984, Modeling and Simulation
of an Entrained Flow Coal Gasifier, AIChE Journal,
30 (1), pp. 79-92.
Grefenstette, J., 1986, Optimization of control parameters
for genetic algorithms, IEEE Transactions on Systems,
Man and Cybernetics, SMC-16 (1), pp. 122-128.
Haupt, G., Zimmermann, G., Hourfar, D., Hirschfelder,
A., Romey, I., Oeljeklaus, G., Folke C., and Semiao,
V., 2000, IGCC - The best choice for producing clean
power, Proceedings of POWER-GEN Europe 2000,
Helsinki, Finland.
Holland, J., 1975, Adaptation in Natural and Artificial
Systems, The University of Michigan.
Huang, W. and Lam, H., 1997, Using genetic algorithms
to optimize controller parameters for HVAC systems,
Energy and Buildings, 26, 277-282.
Levine, I.N., 1988, Physical Chemistry, Third
International Edition, McGraw-Hill, Singapore.
Liu, G., Rezaei, H., Lucas, J., Harris, D. and Wall, T.,
2000, Modelling of a Pressurised Entrained Flow
Gasifier: the Effect of Reaction Kinetics and Char
Structure, Fuel, 79, pp.1767-1779.
Krishnakumar, K., 1989, Micro-genetic algorithms for
stationary and non-stationary function optimization, in
Rodriguez, G. (ed.), Intelligent Control and Adaptive
Systems, 7-8 November (pp. 289-296), Philadelphia,
Pennsylvania: SPIE – The International Society for
Optical Engineering.
Wright, J., 1996, HVAC optimization studies: Sizing by
genetic algorithm, Building Services Engineering
Research and Technology, 17 (1), pp. 1-14.
GENETIC ALGORITHMS APPLIED TO THE OPTIMIZATION OF GASIFICATION FOR A GIVEN FUEL
63
