
CONTEXT IN ROBOTIC VISION:
CONTROL FOR REAL-TIME ADAPTATION
Paolo Lombardi
Istituto Trentino di Cultura ITC-irst, via Sommarive 18, Trento, Italy
(formerly with Dip. Informatica e Sistemistica, Università di Pavia)
Virginio Cantoni
Dip. Informatica e Sistemistica, Università di Pavia, via Ferrata 1, Pavia, Italy
Bertrand Zavidovique
Institut d’Electronique Fondamentale, Université de Paris Sud-11, bât. 220, Campus d’Orsay, Orsay, France
Keywords: computer vision, contextual adaptation, context definition, Bayesian opportunistic switching.
Abstract: Nowadays, the computer vision community conducts an effort to produce can
ny systems able to tackle
unconstrained environments. However, the information contained in images is so massive that fast and
reliable knowledge extraction is impossible without restricting the range of expected meaningful signals.
Inserting a priori knowledge on the operative “context” and adding expectations on object appearances are
recognized today as a feasible solution to the problem. This paper attempts to define “context” in robotic
vision by introducing a summarizing formalization of previous contributions by multiple authors. Starting
from this formalization, we analyze one possible solution to introduce context-dependency in vision: an
opportunistic switching strategy that selects the best fitted scenario among a set of pre-compiled
configurations. We provide a theoretical framework for “context switching” named Context Commutation,
grounded on Bayesian theory. Finally, we describe a sample application of the above ideas to improve video
surveillance systems based on background subtraction methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Computer vision was always considered a promising
sensor for autonomous robots (e.g. domestic
assistant robots, autonomous vehicles, video
surveillance robotic systems, and outdoor robotics in
general). Such applications require fast and reliable
image processing to ensure real-time reaction to
other agents around. Meanwhile, robots operating in
varying and unpredictable environments need
flexible perceptive systems able to cope with sudden
context changes. To a certain extent, in robotics
flexibility and robustness may be intended as
synonyms.
Conciliating real-time operation and flexibility is
a m
ajor interest for the vision community today.
Traditionally, flexibility has been tackled by
increasing the complexity and variety of processing
stages. Voting schemes and other data fusion
methods have been widely experimented. Still, such
methods often achieve flexibility at the expense of
real time.
Contextual information may open possibilities to
i
mproving system adaptability within real-time
constraints. A priori information on the current
world-state, scene geometry, object appearances,
global dynamics, etc may support a concentration of
system computational and analytical resources on
meaningful components of images and video
sequences. The recognition of the current operative
“context” may allow a reconfiguration of internal
parameters and active processing algorithms so as to
maximize the potential of extractable information,
meanwhile constraining the total computational
load. Hence, “context” recognition and managing
has attracted much interest from the robotic vision
community in the last two decades.
135
Lombardi P., Cantoni V. and Zavidovique B. (2004).
CONTEXT IN ROBOTIC VISION: CONTROL FOR REAL-TIME ADAPTATION.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 135-142
DOI: 10.5220/0001143601350142
Copyright
c
SciTePress

A necessary step to implement context-
dependency in practical vision system is defining the
notion of “context” in robotic vision. Various
authors have covered different aspects of this matter.
A summarizing operative definition may serve as an
interesting contribution and a reference for future
work. Furthermore, it helps in identifying possible
“context changes” that a system should cope with.
Overall, context managing represents a
replacement of parallel image processing with less
computationally expensive control. Controlling
internal models and observational modalities by
swapping among a finite set of pre-compiled
configurations is probably the fastest and yet more
realistically realizable solution.
In Section 2, we present a wide range of works
related to “context” in computer vision. Section 3
details our proposal of formalization of such
contributions by describing an operative definition.
Then, Section 4 applies these concepts to a realistic
implementation of real-time context-dependent
adaptation within the scope of Bayesian theory.
Finally, Section 5 concludes by suggesting some
discussion and presenting future work.
2 CONTEXT IN COMPUTER
VISION
In earlier works, contextual information referred to
image morphology in pixel neighborhoods, both
spatial and temporal. Methods integrating this
information include Markov Random Fields (Dubes,
1989), and probabilistic relaxation (Rosenfeld,
1976). More recent works have moved the concept
to embrace environmental and modeling aspects
rather than raw signal morphology. General
typologies of “context” definitions include:
1. physical world models: mathematical
description of geometry, photometry or
radiometry, reflectance, etc – e.g. (Strat, 1993),
(Merlo, 1988).
2. temporal information: tracking, temporal
filtering (e.g. Kalman), previous stable
interpretations of images in a sequence, motion
behavior of objects, etc – e.g. (Kittler, 1995),
(
Tissainayagam, 2003).
3. site knowledge: specific location knowledge,
geography, terrain morphology, topological
maps, expectations on occurrence of objects
and events, etc – e.g. (Coutelle, 1995),
(
Torralba, 2003).
4. scene knowledge: scene-specific priors,
illumination, accidental events (e.g. current
weather, wind, shadows), obstacles in the
viewfield, etc – e.g. (Strat, 1993).
5. interpretative models and frames: object
representations (3d-geometry-based,
appearance-based), object databases, event
databases, color models, etc – e.g. (Kruppa,
2001).
6. relations among agents and objects:
geometrical relationships, possible actions on
objects, relative motion, split-and-merge
combinations, intentional vs. random event
distinctions, etc – e.g. (Crowley, 2002).
7. acquisition-device parameters: photo-
grammetric parameters (intrinsic and extrinsic),
camera model, resolution, acquisition
conditions, daylight/infrared images, date and
time of day, etc – e.g. (Strat, 1993), (
Shekhar,
1996).
8. observed variables: observed cues, local vs.
global features, original image vs. transformed
image analysis, etc – e.g. (Kittler, 1995).
9. image understanding algorithms: observation
processes, operator intrinsic characteristics,
environmental specialization of individual
algorithms, etc – e.g. (Horswill, 1995).
10. intermediate processing results: image
processing quality, algorithm reliability
measures, system self-assessment, etc – e.g.
(Draper, 1999), (Rimey, 1993), (Toyama,
2000).
11. task-related planning and control: observation
tasks, global scene interpretation vs.
specialized target or event detection, target
tracking, prediction of scene evolution, etc –
e.g. (Draper, 1999), (Strat, 1993).
12. operation-related issues: computational time,
response delay, hardware breakdown
probabilities, etc – e.g. (Strat, 1993).
13. classification and decision techniques:
situation-dependent decision strategies,
features and objects classifiers, decision trees,
etc – e.g. (Roli, 2001).
Despite definitions of “context” in machine
vision have appeared under multiple forms, they all
present “context” as an interpretation framework for
perceptive inputs, grounding perception with
expectation.
Probably a definition of context in computer
vision, yet rather a non-operative one, could be
given by dividing a perceptive system into an
invariant part and a variable part. The invariant
part includes structure, behaviors and evolutions that
are inherent to the system itself, and that are not
subject to a possible change, substitution or control.
Examples may be the system very hardware,
acquisition sensors, and fixed links between them,
etc.; basic sub-goals like survival; age, endemic
breakdowns, mobility constraints, etc. The variable
ICINCO 2004 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
136

part is all parameters, behaviors, and relations
between components, which can be controlled. By
means of these parts, the system may acquire
dependence from the outer world and situation, with
the purpose of better interacting with other agents
and objects. In this view, context is what imposes
changes to the variable part of a system. When
mapped into the system through its variable parts,
context becomes a particular configuration of
internal parameters.
3 AN OPERATIVE DEFINITION
OF CONTEXT
Inspired by the partial definitions from the previous
references, we propose the following formalization
(see (Lombardi, 2003) for details).
Definition D.1: Context Q in computer vision is a
triplet Q = (M, Z, D), where:
• M is the model set of object classes in the
environment;
• Z is the operator set, i.e. the set of visual
modules used in the observation process;
• D is the decision policy to distinguish
between different classes of objects.
The rationale is that in perceptive systems, elements
that can be parameterized and thus controlled are
prior models of external objects, models of system
components, and the relations among them. In short,
D includes all prior assumptions on the strategy for
inter-class separation and intra-class
characterization. Essentially, it stands for point 13 in
the above list. Hereafter, we further specify the
definitions of M and Z.
3.1 Model Set M
The model set M contains all a priori knowledge of
the system regarding the outer scene, object/agent
appearances, and relations among objects, agents
and events (essentially, points 1-6). We explicitly
list three groups of knowledge inside M.
Definition D.2: A model set is a triplet M = ({m},
P
{m}
, V
{m}
), where:
• {m} is the entity knowledge describing their
appearance;
• P
{m}
is the prior expectation of occurrence
in the scenario;
• V
{m}
is the evolution functions describing
the dynamics.
Entity knowledge m indicates the set of features
and/or attributes that characterize an object type.
Here, we call “entity” (Crowley, 2002) any object,
agent, relation, or global scene configuration that is
known, and thus recognizable, by the perceptive
system. The set of all entity descriptions {m} is the
total scene-interpretation capability of the system,
namely the set of all available a priori models of
object classes that the system can give semantics to
raw data with. Minsky frames and state vectors
containing geometrical information are examples of
descriptors. Moreover, the image itself can be
thought of as an object, thus {m} includes a
description of global scene properties.
P
m
is the prior expectations on the presence of entity
m in the scene. We distinguish P
m
from m because
object descriptions are inherently attached to an
entity, while its probability of occurrence depends
on causes external to objects. Evolution functions
V
{m}
indicate the set of evolution dynamics of an
entity state parameters, e.g. object motion models.
3.2 Operator Set Z
The operator set Z gathers all prior self-knowledge
on the perceptive system, available algorithms and
hardware, feature extraction and measurement
methods, observation matrixes, etc (points 7-12). We
explicitly list three descriptors in Z.
Definition D.3: An operator set is a triplet Z = ({z},
H
{z}
, C
{z}
), where:
• {z} is the operator knowledge describing
their mechanisms;
• H
{z}
are the operative assumptions of
operators;
• C
{z}
is the operation cost paid by system
performance to run operators.
Operator knowledge z contains all parameters,
extracted features, tractable elaboration noise, and
other relevant features of a given visual operator.
The set {z} spans all visual modules in a system and
their relative connections and dependencies.
Operators constitute a grammar that allows matching
data and semantics (model set M). Set {z} includes
logical operators, relation operators (e.g. detectors of
couples), and events detectors.
Operative assumptions H
z
is the set of hypotheses
for the correct working of a visual module z. Implicit
assumptions are present in almost every vision
operator (Horswill, 1995). A misuse of z in
situations where H
z
do not hold true may cause
abrupt performance degradation. Parameter C
z
is a
metrics depending on average performance ratings
(e.g. computational time, delay, etc) useful to
optimize system resources.
CONTEXT IN ROBOTIC VISION: CONTROL FOR REAL-TIME ADAPTATION
137

3.3 Contextual Changes
The explicit formulation of D.1 allows for a deeper
understanding of contextual adaptability problems
and of “context changes”.
Definition D.4: A context change is a change in any
component of a context Q, and we write it with ∆Q =
(∆{m}|| ∆P
{m}
|| ∆V
{m}
|| ∆{z} || ∆H
{z}
|| ∆C
{z}
|| ∆D),
where || is a logical or.
Each component of ∆Q generates a class of
adaptability problems analyzed in the literature
under an application-specific definition of “context
change”. Here follow some examples:
a) ∆{m} may occur when i) the camera
dramatically changes its point of view, ii) a
perceptive system enters a completely different
environment of which it lacks some object
knowledge, iii) object description criteria
become inappropriate.
b) ∆P
{m}
means that the frequency of an entity
class occurrence has changed, e.g. i) a camera
enters a new geographical environment, ii)
stochastic processes of object occurrence are
non-stationary in time.
c) ∆V
{m}
may occur when agents change
trajectory so that hybrid tracking is needed –
see (
Tissainayagam, 2003), (Dessoude, 1993).
d) ∆{z}may consist in i) inappropriate modeling
of operator mechanisms, ii) inappropriate self-
assessment measures, etc.
e) ∆H
{z}
indicates a failure of assumptions
underlying {z}. For instance, a skin color
detector whose color model is inappropriate to
lighting conditions – see (Kruppa, 2001).
f) ∆C
{z}
turns into a resource management
problem. Dynamic programming, task
planning, parametric control are examples of
methods to find the best resource reallocation
or sequencing.
g) ∆D may occur when i) assumptions for
separation of object classes become
inappropriate, ii) critical observed feature
become unavailable, iii).
Definition D.5: The problem of insuring reliable
system processing in presence of a context change is
called an adaptability problem.
4 BAYESIAN CONTEXT
SWITCHING
Two are the solutions to cope with context changes:
i) a system has available alternative perceptive
modalities; ii) a system can develop new perceptive
modalities. The latter solution would involve on-line
learning and trial-and-error strategies. Although
some works have been presented – e.g. genetic
programming of visual operators (Ebner, 1999) –,
this approach is likely beyond the implementation
level at present.
The first solution may be implemented either by
using “parallelism” or by “opportunistic switching”
to a valid configuration. “Parallelism” consists in
introducing redundancy and data fusion by means of
alternative algorithms, so that failures of one
procedure be balanced by others working correctly.
However, parallelism is today often simulated on
standard processors, with the inevitable effect of
dramatically increasing the computational load at the
expense of real time. This feature conflicts with the
requirements of machine vision for robotics.
“Opportunistic switching” consists in evaluating the
applicability of a visual module or in pointing out a
change in the environmental context, to commuting
the system configuration accordingly. Opposite to
parallelism and data fusion, this swapping strategy
conciliates robustness and real time. Here we further
develop the latter option (4.1), we describe a
Bayesian implementation of it (4.2), and finally we
exemplify an application to contextual video
surveillance (4.3).
4.1 Opportunistic Switching
Opportunistic switching among a set of optimized
configurations may ensure acceptable performance
over a finite range N of pre-identified situations (i.e.
“contexts”).
Definition D.6: Designing a system for context-
dependent opportunistic switching consists in
building and efficiently controlling a mapping ζ
between a set of contexts Q and a set of sub-systems
S, i.e. (1). The switching is triggered by context
changes D.4.
ζ : Q(t) → S(t) (1)
Building the map is an application-dependent
engineering task: for each typical situation, the
perceptive system must be engineered to deliver
acceptable results. Control is performed by detecting
.
ICINCO 2004 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
138

Figure 1: An oriented graph may easily accommodate all the elements of an opportunistic switching structure as defined in
Section 3: context/sub-system pairs in nodes, and events in arcs. Daemons trigger global state change.
the current context Q(t), or equivalently by detecting
context changes ∆Q. A context-adaptable system
must be endowed with context-receptive processing,
i.e. routines capable of classifying N different
context states {q
1
, q
2
,... q
N
}. Essentially, such
routines detect “context features”, and context
recognition can be thought of as an object
recognition task. The design of such routines
appears to be an application-dependent design issue
Definition D.7: Let us name daemon an algorithm or
sensor δ exclusively dedicated to estimating context
states q.
Opportunistic switching has two advantageous
features: i) flexibility and real-time, because multiple
configurations run one at a time, and ii) software
reuse, because an increased flexibility can be
achieved by integrating current software with ad-hoc
configurations for uncovered contexts. Assumptions
for its use are: i) there exists a rigid (static) mapping
from problems to solutions, ii) reliable context
detection.
4.2 Context Commutation
The mapping ζ and its control may assume the form
of parametric control, of knowledge-based algorithm
selection, of neural network controlled systems, etc.
Hereafter we present a Bayesian implementation of
the opportunistic switching strategy, named Context
Commutation (CC) (Lombardi, 2003). It is inspired
by hybrid tracking –e.g. (Dessoude, 1993) –, where
a swapping among multiple Kalman filters improves
tracking of a target moving according to changing
regimes.
Context Commutation represents context
switching by means of a Hidden Markov Model –
e.g. (Rabiner, 1989) –, where the hidden process is
context evolution in time, and the stochastic
observation function is provided by appropriate
probabilistic sensor models of daemons. Time is
ruled by a discrete clock t. Each clock step
corresponds to a new processed frame.
Definition D.8: Context Commutation represents
context evolution by means of a discrete, first-order
HMM with the following components (Figure 1):
1. A set of states Q = {q
1
, q
2
, ...q
N
}. Each state q
i
corresponds to a context and gets an associated
optimized system configuration s
i
. For every i, s
i
is such that the perceptive system works
satisfactorily in q
i
= {M
i
, Z
i
, D
i
} i.e. M
i
, Z
i
, D
i
are
the appropriate models, operators and decision
policies in the i-th situation.
2. An observation feature space Φ composed of
daemon outputs φ. If there are K daemons, φ is a
K-dimensional vector.
3. A transition matrix E, where elements E
ij
correspond to the a priori probability of
transition from q
i
to q
j
, i.e. (2).
E
ij
= P[e
ij
] = P[Q(t) = q
j
| Q(t-1) = q
i
] (2)
4. An observation probability distribution b
i
(φ) for
each context q
i
, defined in (3). Thus, the N
different b
i
(φ) define the global daemon sensor
model of Bayesian signal analysis theory.
(3)
))(|)(()(
ii
qtQtPb ==Φ=
ϕϕ
5. An initial state distribution function π = {π
1
, π
2
,
...π
N
}, where π
i
∈ [0, 1] for i = 1, 2, ...N, and (4)
holds true.
(4)
∑
=
=
N
i
i
1
1
π
q
1
q
2
q
3
s
1
s
2
s
3
δ
1
δ
2
δ
3
Daemons
e
11
e
12
e
21
e
23
e
31
e
22
CONTEXT IN ROBOTIC VISION: CONTROL FOR REAL-TIME ADAPTATION
139
(a) (b) (c)
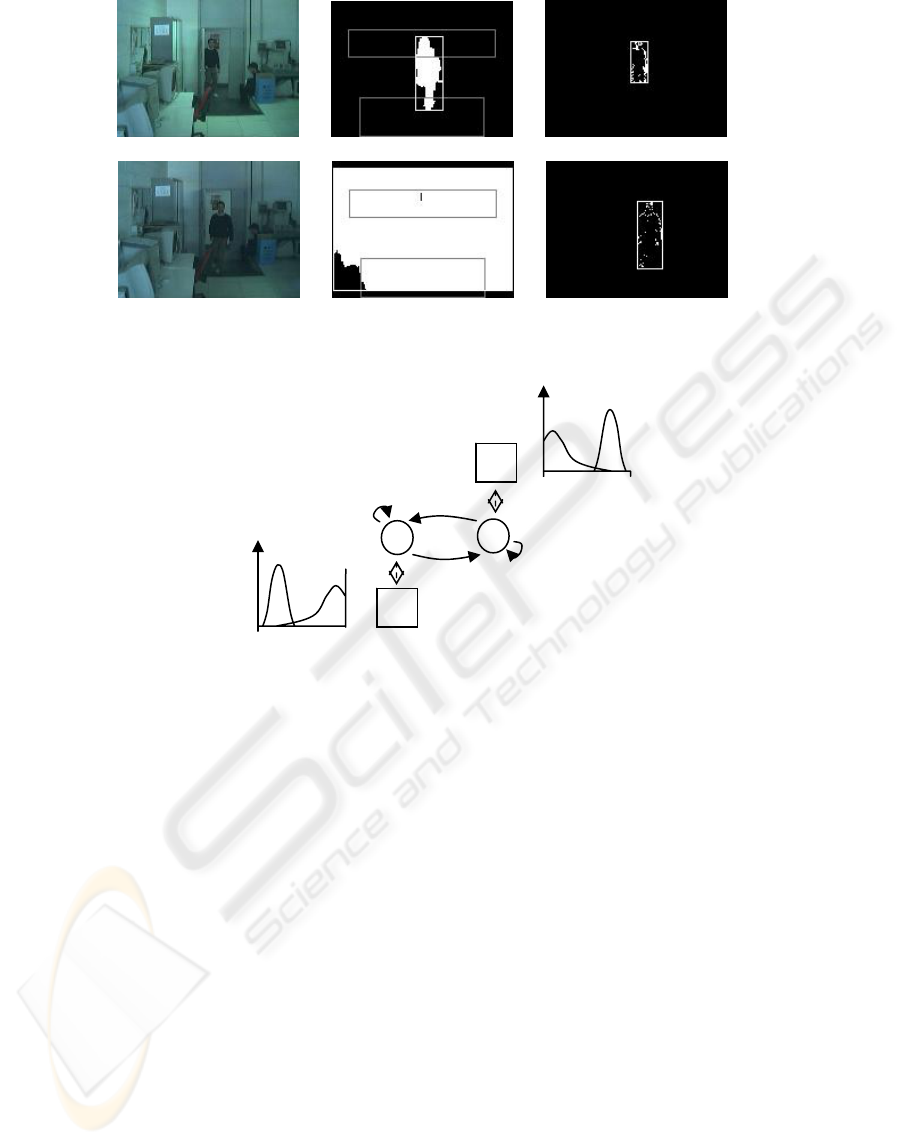
(d) (e) (f)
Figure 2: When a reliable background reference model is available (a), background subtraction methods deliver more
meaningful motion information (b) than simple frame differencing (c). However, if the lighting conditions suddenly change,
e.g. an artificial light is turned off (d), BS fails (e) while FD still works properly.
Figure 3: The simple CC system for “light switch” problems has two states and one daemon. The picture shows the
transition matrix E used in the experiments (top left), and a representation of daemon models (next to the s
i
boxes).
6. The current context q
ν
is estimated by the
Maximum A Posteriori on Ψ(t) (5), (6).
Ψ(t) = (P(q
1
), P(q
2
), …P(q
N
)) (5)
ν = argmax
i
[Ψ
i
(t)] (6)
4.3 A practical implementation
As a final illustration, we demonstrate an application
of Context Commutation to tackle the “light switch”
problem affecting background subtraction (BS) for
motion detection in automatic video surveillance. In
indoor environments, when artificial lights are
turned on or off, the reference background model
used in BS looses validity in one frame-time.
Modern time-adaptive background systems
(Stauffer, 1999) usually take around 10÷100 frames
to recover. An alternative solution involves the use
of a second algorithm that degrades less its
performance in case of abruptly changing lighting
conditions. For instance, frame differencing (FD)
algorithms deliver motion information like BS does,
and they recover from “light switch” just after 1
frame (Figure 2).
A context-adaptable system based on
opportunistic switching would feature two system
states: i) using BS when appropriate, ii) using FD
otherwise. In the general case, BS delivers a more
informing motion map than FD. However, when
lighting conditions are unstable, the system swaps to
FD – which recovers more quickly.
Here, we design a CC system as shown in Table 1
and Figure 3. The two contexts, corresponding to
“stable” and “unstable” global lighting, cope with a
context change ∆H
bs
which corresponds to a failure
of a basic operative assumption founding BS’s
correct working – i.e. stable lighting –. The daemon
δ
1
apt to detecting ∆H
bs
is modeled with two
truncated Gaussians of the kind shown in Figure 3,
with parameters tuned by training. Daemon δ
1
counts the pixels n
a
and n
b
showing a luminance
change that breaks thresholds θ
δ1
and -θ
δ1
,
respectively: n
a
+n
b
represents all pixels showing
substantial luminance change. The output (7) is then
a measure of the luminance unbalance over the last
two images. In stable lighting conditions φ
1
would
s
(2)
q
1
q
2
s
(1)
0
1
0
1
Stable
lighting
Unstable
lighting
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
=
3.07.0
4.06.0
E
ICINCO 2004 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
140
be 0. The closer φ
1
to 1, the more likely switched the
light.
1
),max(
2
1
−
+
=
ba
ba
nn
nn
ϕ
(7)
Table 1
Q Situation S
q
1
stable lighting BS active if in ready state
FD active if BS in recovering state
q
2
unstable
lighting
FD active
To assess context estimation performance, δ
1
was
tested on over 1500 images containing about 50 light
switches. The test was done on sequences indexed
by a human operator. Figure 4 shows the results on
one test sequence: when the confidence rating breaks
0.5, q
2
is estimated. Bold dots on the top line show
the ground truth for q
2
occurrence. Model
parameters G
i
~(µ
i
, σ
i
) in q
i
are in Table 2.
Table 2
µ
1
µ
2
σ
1
σ
2
δ
1
0.09 0.71 0.17 0.36
We measured an average correct estimation rate
of 0.95. The percentage goes up to 0.98 if a 3-frame-
range error is allowed in locating the contextual
switch. In effect, this error allowance accounts for
human mistakes in indexing the test videos.
The motion detection system with and without
CC was tested on several sequences. No tracking
was performed, only motion detection. The graph of
Figure 5 shows the improvement provided by CC in
terms of such distance (when BS failed because of
inappropriate background model – e.g. Figure 2 –,
the corresponding estimation error was set to 100).
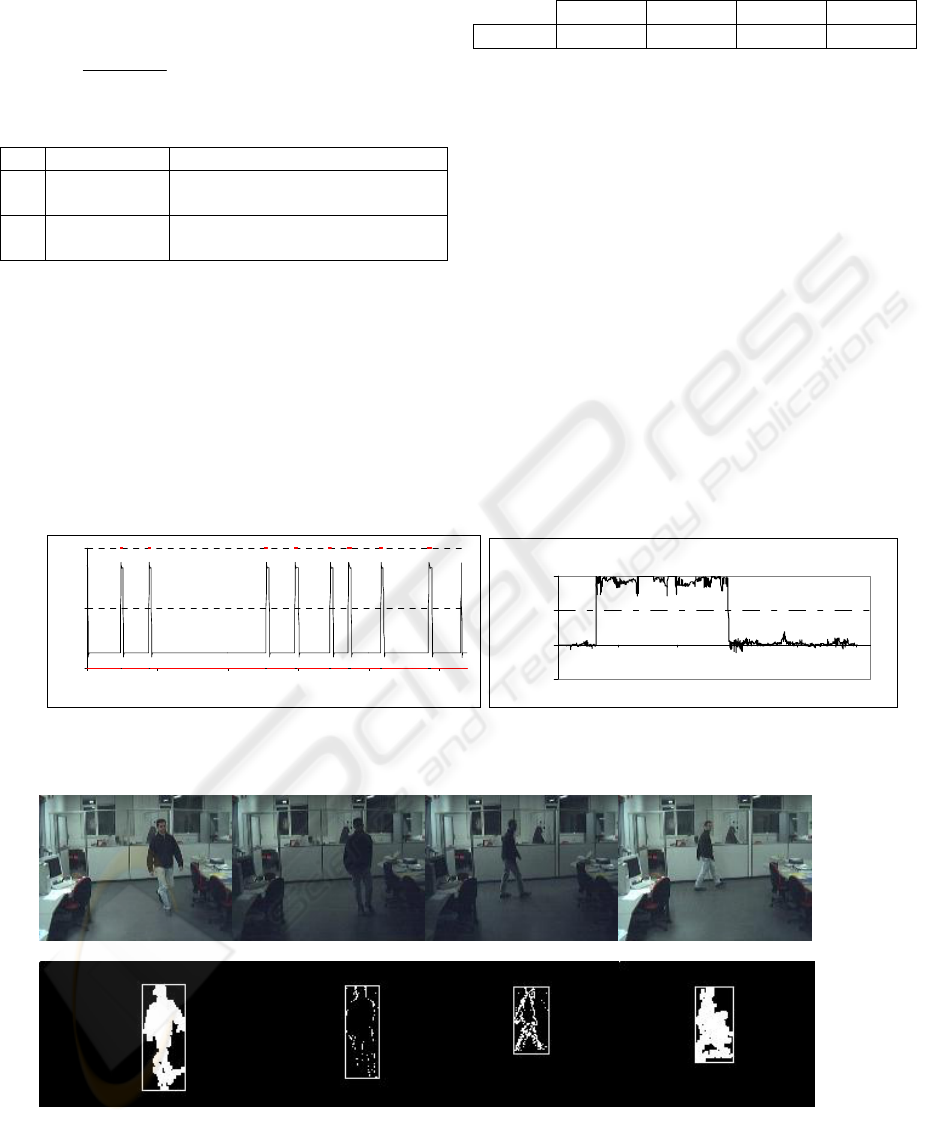
Figure 6 shows some results for one sequence where
light switches twice: on-off on frame 327, and off-on
on frame 713. The distance of the barycentre of
motion between automatic detection and human
labeling was computed for BS only, and for BS/FD
combined by means of CC.
0
0,5
1
0 100 200 300 400 500
Frame
Probability
Motion Barycenter Estimation
-50
0
50
100
200 400 600 800 1000 1200
Frame Number
Impr ove ment
Figures 4, 5: Probability that the current context state be q2 as estimated by
δ
1
in a test sequence (left). Improvement in
the estimation error provided by context switching (CC) with respect to BS alone (right).
Figure 5: Frames no. 322, 332, 702, and 932 from a test sequence: original images (first row), motion detection by BS
and FD managed opportunistically by CC (second row).
CONTEXT IN ROBOTIC VISION: CONTROL FOR REAL-TIME ADAPTATION
141

5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we foster deeper studies in the
management of contextual information in robotic
vision. In the first part, we proposed an operative
definition of “context” to identify the variable parts
of a perceptive system susceptible of becoming
inappropriate in case of contextual changes: models,
operators, and decision policies.
In the second part, we described a novel Bayesian
framework (i.e. Context Commutation) to implement
contextual opportunistic switching. Dedicated
algorithms, called daemons, observe some
environmental features showing a correlation with
system performance ratings rather than with the
target signal (e.g. people tracking). When such
features change, the system commutes its state to a
more reliable configuration.
Critical points in Context Commutation are
mainly related to its Bayesian framework.
Parameters like sensor models of daemons and
coefficients of the transition matrix need thorough
tuning and massive training data. An error in such
parameters would corrupt correct contextual
switching.
Possible points for future work are: i) exploring
switching reliability with incorrect parameters, ii)
studying Context Commutation with more than eight
states, iii) extending the framework to perceptive
systems including sensors other than solely vision.
REFERENCES
Coutelle, C., 1995. Conception d’un système à base
d’opérateurs de vision rapides, PhD thesis (in French),
Université de Paris Sud (Paris 11), Paris, France.
Crowley, J.L., J. Coutaz, G. Rey, P. Reignier, 2002.
Perceptual Components for Context Aware
Computing. In Proc. UBICOMP2002, Sweden,
available at http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/541415.html.
Dessoude, O., 1993. Contrôle Perceptif en milieu hostile:
allocation de ressources automatique pour un système
multicapteur, PhD thesis (in French), Université de
Paris Sud (Paris 11), Paris, France.
Draper, B.A., J.Bins, K.Baek, 1999. ADORE: Adaptive
Object Recognition. In Proc. ICVS99, pp. 522-537.
Dubes, R. C., Jain, A. K., 1989. Random Field Models in
Image Analysis. In J. Applied Statistics, v. 16, pp.
131-164.
Ebner, M., A. Zell, 1999. Evolving a task specific image
operator. In Proc. 1
st
European Wshops on
Evolutionary Image Analysis, Signal Processing and
Telecommunications, Göteborg, Sweden, Springer-
Verlag, pp. 74-89.
Horswill, I., 1995. Analysis of Adaptation and
Environment. In Artificial Intelligence, v.73(1-2), pp.
1-30, 1995.
Kittler, J., J. Matas, M. Bober, L. Nguyen, 1995. Image
interpretation: Exploiting multiple cues. In Proc. Int.
Conf. Image Processing and Applications, Edinburgh,
UK, pp. 1-5.
Kruppa, H., M. Spengler, B. Schiele, 2001. Context-driven
Model Switching for Visual Tracking. In Proc. 9
th
Int.
Symp. Intell. Robotics Sys., Toulouse, France.
Lombardi, P., 2003. A Model of Adaptive Vision System:
Application to Pedestrian Detection by Autonomous
Vehicles. PhD thesis (in English), Università di Pavia
(Italy) and Université de Paris XI (France).
Merlo, X., 1988. Techniques probabilistes d’intégration et
de contrôle de la perception en vue de son exploitation
par le système de décision d’un robot, PhD thesis (in
French), Université de Paris Sud (Paris 11), Paris,
France.
Rabiner, L.R., 1989. A tutorial on hidden Markov models.
In Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 77, pp. 257-286.
Rimey, R.D., 1993. Control of Selective Perception using
Bayes Nets and Decision Theory. Available at http://
citeseer.nj.nec.com/rimey93control.html.
Roli, F., G. Giacinto, S.B. Serpico, 2001. Classifier Fusion
for Multisensor Image Recognition. In Image and
Signal Processing for Remote Sensing VI, Sebastiano
B. Serpico, Editor, Proceedings of SPIE, v. 4170,
pp.103-110.
Rosenfeld, A., R.A. Hummel, S.W. Zucker, 1976. Scene
labeling by relaxation operations. In IEEE Trans. Syst.
Man Cybern., v. 6, pp. 420-433.
Shekhar, C., S. Kuttikkad, R. Chellappa, 1996.
KnowledgeBased Integration of IU Algorithms. In
Proc. Image Understanding Workshop, ARPA, v. 2,
pp. 1525-1532, 1996.
Stauffer, C., W.E.L. Grimson, 1999. Adaptive Background
Mixture Models for Real-Time Tracking. In Proc.
IEEE Conf. Comp. Vis. Patt. Rec. CVPR99, pp. 246-
252.
Strat, T.M., 1993. Employing Contextual Information in
Computer Vision. In Proc. DARPA93, pp. 217-229.
Tissainayagam, P., D. Suter, 2003. Contour tracking with
automatic motion model switching. In Pattern
Recognition.
Torralba, A., K.P. Murphy, W.T. Freeman, M.A. Rubin,
2003. Context-based vision system for place and
object recognition. In Proc. ICCV’03, available at
http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/torralba03contextbased.html.
Toyama, K., E.Horvitz, 2000. Bayesian Modality Fusion:
Probabilistic Integration of Multiple Vision
Algorithms for Head Tracking. In Proc. ACCV’00, 4
th
Asian Conf. Comp. Vision, Tapei, Taiwan, 2000.
ICINCO 2004 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
142
