
USING A DISCRETE-EVENT SYSTEM FORMALISM FOR THE
MULTI-AGENT CONTROL OF MANUFACTURI
NG SYSTEMS
Guido Maione
DIASS, Politecnico di Bari, Viale del Turismo, 8, 74100, Taranto, Italy
David Naso
DEE, Politecnico di Bari, Via Re David, 200, 70125, Bari, Italy
Keywords: Multi-Agent Systems, Discrete Event Dynamic Systems, Distributed Manufacturing Control, Heterarchical
Manufacturing Systems
Abstract: In the area of Heterarchical Manufacturing Systems
modelling and control, a relatively new paradigm is that
of Multi-Agent Systems. Many efforts have been made to define the autonomous agents concurrently
operating in the system and the relations between them. But few results in the current literature define a
formal and unambiguous way to model a Multi-Agent System, which can be used for the real-time
simulation and control of flexible manufacturing environments. To this aim, this paper extends and develops
some results previously obtained by the same authors, to define a discrete event system model of the main
distributed agents controlling a manufacturing system. The main mechanism of interaction between three
classes of agents is presented.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, the study of appropriate tools for
modelling and designing Multi-Agent Systems
(MAS) technologies is a key-issue involving all their
application areas, including telecommunication and
computer networks, communities of intelligent
robots, web-based agents for information retrieval,
to mention a few. Moreover, considerable research
efforts have been devoted to the definition of
standards and to the development of platforms for
unambiguous agent specification, especially in the
context of software engineering.
Focusing on the specific con
text of industrial
manufacturing, this paper proposes an approach
based on the Discrete EVent System (DEVS)
specification (Zeigler et al., 2000) to obtain a
complete and unambiguous characterization of a
multi-agent control system. By using the DEVS
formalism, we describe agents as atomic dynamic
systems, subject to external inputs from (and
generating outputs to) other agents. Furthermore, we
directly obtain the model of the entire network of
agents by specifying the relationships between the
atomic agents. The DEVS technique is fully
compatible with the heterarchical design principles,
and leads to MAS where all information and control
functions are distributed across autonomous entities.
In particular, the DEVS formalism is an interesting
alternative to other recently proposed tools for MAS
specification, e.g. the UML (Huhns and Stephens,
2001), Petri Nets (Lin and Norrie, 2001). The
success of this formalism is due to its suitability for
developing useful models both for discrete event
simulation, and for implementation of the software
controllers on plant’s operating system. Namely, the
DEVS formalism can effectively model many recent
MAS architectures, such as part-driven heterarchical
manufacturing systems (Duffie and Prabhu, 1996,
Prabhu and Duffie, 1999) and schemes inspired by
the Contract Net protocol (Smith, 1980, Parunak,
1994, Sousa and Ramos, 1999).
As in most MAS for manufacturing control
(
Heragu, 2002, Shen and Norrie, 1999), in our
model all the agents use decision algorithms
emulating micro-economic environments. Each
agent uses a fictitious currency to buy services from
other seller agents which, on their turn, use pricing
strategies. Sellers and buyers have to reach an
equilibrium between conflicting objectives, i.e. to
maximize profit and to minimize costs, respectively.
84
Maione G. and Naso D. (2004).
USING A DISCRETE-EVENT SYSTEM FORMALISM FOR THE MULTI-AGENT CONTROL OF MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 84-91
DOI: 10.5220/0001145400840091
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Recently, there have been efforts to develop
analytical models of negotiation processes using, for
instance, Petri nets (Hsieh, 2004), underlining the
need of a systematical analysis and validation
method for distributed networks of autonomous
control entities. Many other researches have focused
on the experimental validation of MAS on
distributed simulation platforms (Shattenberg and
Uhrmacher, 2001, Logan and Theodoropoulos,
2001), which allow to perform detailed
investigations on the interaction schemes. Sharing
the same motivations with the mentioned researches,
our work focuses on the development of DEVS
models of MAS, which combines the rigor of a tool
suitable for performing the theoretical analysis of
structural properties of the MAS, with its efficiency
in directly translating the model in a detailed
simulation environment, and its flexibility in testing
both the individual and collective dynamics of the
autonomous entities. Namely, our main goal is to
find a multi-agent design platform that allows users
to assess the relative effectiveness of agents’
decision and interaction strategies, with special
interest to adaptive learning mechanisms that allow
agents to improve their performance during their
operation (Maione and Naso, 2003a).
In this paper, we develop a detailed model of the
interactions between the main agents in a
manufacturing system. This contribution extends
previous researches by the authors, in which, for
sake of simplicity, the interactions with transport
units were not considered in detail, and illustrates
the basic mechanisms of the modelling procedure.
The paper also outlines other main directions of the
research in progress. Section 2 introduces the basic
components of the proposed MAS, and specifies
their roles and relations. Section 3 specifies how to
model agents as atomic DEVS. Section 4 focuses on
the main interactions between agents, describing the
negotiation for a manufacturing process on a part.
Sections 5 and 6 give some experimental results,
overview the advantages of the approach, and
enlighten the issues open for further research.
2 THE MULTI-AGENT SYSTEMS
CONTROL APPROACH
We consider each Part Agent (PA) as a control unit
connected to the corresponding physical part (piece)
flowing through the system. In accordance with the
related literature (Duffie and Prabhu, 1996, Heragu,
2002, Prabhu and Duffie, 1999), we associate each
part into a batch of identical items in process with a
PA that identifies in real-time (i.e. shortly before a
part is ready for a new process) the most suitable
workstation for the imminent operation on that part
and, consequently, the most suitable vehicle to
transfer it to the station. The selection is based on
real-time updated information directly received from
the alternative stations and transport vehicles,
through an exchange of messages with other agents.
Namely, a Workstation Agent (WA) is a software
entity controlling a workstation or a cell of machines
performing the same operations, and a Transport
Agent (TA) is associated with the transport system
or with a single or group of transport units.
At each operation step, by interacting with WAs
and TAs, a PA chooses the machine servicing the
associated part and the transport device moving the
piece from its current position (the output buffer of
the occupied machine) to the chosen workstation.
In this framework, one can consider also specific
agents designed to execute other tasks necessary for
the global operation of the manufacturing plant
(Maione and Naso, 2003b). In particular, one can
associate an Order Agent (OA) with each different
order issued by the management level. The OA
retains information on quantity and type of products
to be processed. Similarly, one can define a Loading
Agent (LA) to manage the loading/unloading station
where the raw/completed parts enter/exit the system.
The global control of the manufacturing floor
emerges from the concurrent actions of the various
agents in the system. The careful analysis of their
interactions is fundamental to understand how to
obtain the desired global behaviour. For instance, the
OA interacts with PAs to control the release of the
quantity and type of raw parts necessary to realize
that order. The PAs interact with the LA to negotiate
the loading/unloading of raw/completed parts. Here,
we concentrate on the interactions between a PA and
WAs and TAs when a part is ready for a new
process and its PA has to decide the resources
(workstation and transport device) necessary to fulfil
the operations, among a set of available alternatives.
The high-level agents’ decisions are executed by
low-level plant controllers that are not modelled
here. One can also view the network of interacting
agents as a distributed controller supervising and
synchronizing the underlying physical hardware.
3 THE DISCRETE-EVENT
MODELLING FRAMEWORK
The agents operating in our MAS model interact one
with another by exchanging event messages. Outputs
from an agent become inputs for other agents. The
agent state is updated by external input events
(inputs) and internal events. Each event in the life of
an agent is considered an instantaneous or “atomic”
USING A DISCRETE-EVENT SYSTEM FORMALISM FOR THE MULTI-AGENT CONTROL OF
MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS
85

action without duration. Time-consuming actions are
represented by a pair of events, the first denoting its
start and the second denoting its finish.
So, unambiguous models for the agents in the
system are identified by all the classified events
which affect the dynamics of each type of agent. The
internal events are generated by the internal
dynamics of the agent, and the exogenous events are
inputs which are not determined by the agent.
Finally, the external output events (or outputs)
represent the reaction of the agents. Then, it is
important to define the sequential state of each
agent. Namely, events change the state. An agent
stays in a state until either it receives an input, or an
amount of time determined by a time advance
function elapses. In the latter case, an internal event
occurs to change state according to a specified
internal transition function. Otherwise, if an agent
receives an input, an external transition function
specifies the state transition according to the current
total state of the agent, defined by the sequential
state, the time elapsed since the last transition and
some additional information. Finally, agents
generate outputs according to an output function.
Delays and faults in the communication process are
also considered in our model. Although the effects
of these phenomena are often neglected in technical
literature, we evaluate their effects both on overall
production performance and on the efficiency of the
MAS, expressed by ad-hoc performance measures.
This allows us to track, monitor and optimize the
interaction among agents.
To conclude, each agent may be modeled as an
atomic DEVS as follows:
A = < X, Y, S,
δ
int
,
δ
ext
,
λ
, ta > (1)
where X is the set of inputs, Y is the set of outputs, S
is the set of sequential states,
δ
int
: S→S is the
internal transition function,
δ
ext
: Q×X→S is the
external transition function,
λ
: S→Y is the output
function, ta: S→ℜ
0
+
is the time advance function
(ℜ
0
+
set of positive real numbers with 0 included),
Q = {(s,e,DL) | s∈S,0≤e≤ta(s)} is the total state set.
The sequential state s contains the main
information on the status, specifying the condition
of an agent between two successive events. Other
data strictly depend on the type of the agent. E.g.,
for a PA, one can consider the current residual
sequence of operation steps necessary to complete
the procedure, the set of available machines for the
negotiated operation, and prospected time in current
state before the next internal event. For a WA, s
includes the queues of the requests received from
PAs for availability, information and confirmation of
negotiated operations (see below), and the time
before the next internal event. For a TA, s may
contain similar queues of requests received from
PAs, and the time before the next internal event.
The total state q depends on s, the time e elapsed
since the last transition and the decision law DL
used by the agent to select and rank the offers
received from other agents and to decide its action.
Usually, to build the models, one observes that
each agent may require or offer a service to other
agents. A precise mechanism usually defines the
negotiation protocols working according to a cycle
“announce-offer-reward-confirm”: an agent starts a
bid by requiring availability for a service to one or
more agents, requests the available agents
information representing an offer for the negotiated
service, collects the replies from the queried agents,
selects the best offer, sends a rewarding message,
waits for a confirmation and finally acquires the
service from the rewarded agent.
In this paper, we focus on the interactions of a
PA with WAs and TAs when contracting for an
operation in the procedure to be accomplished for a
part in process. We describe the main part of the PA
DEVS model, by concentrating on the mechanism
ruling the status-transitions of a PA, which are
triggered by inputs or internal events, and the
outputs generated for each status. We don’t go into
the details of the DL used by each agent. To this
aim, we exploit the models already defined and
developed in precedent papers (Maione and Naso,
2003a,b) for PAs, WAs and TAs, but we expand and
better clarify them to put them together.
4 THE INTERACTIONS OF A PA
WITH WAS AND TAS
To accomplish the manufacturing tasks, each PA
interacts with WAs to choose the workstation for the
next operation and with TAs to select the vehicle
moving the part from the station currently occupied
to the next one. We assume that the PA firstly
communicates exclusively with WAs, then with TAs
only.
For t<t
P0
let the PA associated with a generic
part, say P, be in a quiescent status (QUIESC) and
let it begin its activity at t
P0
(event X
P0
). Then P
spends the interval [t
P0
, t
P1
] to send outputs Y
P01
,
Y
P02
,…, Y
P0w
at instants t
01
>t
P0
, t
02
,…, t
0w
=t
P1
. These
messages request the availability to all the WAs of
the alternative stations (w in number) that can serve
the part. The sequence of requests cannot be
interrupted by any internal or external occurrence.
For sake of simplicity, instead of modelling a
sequence of w status-values, we refer to REQWAV
for the whole duration of the activity and assume
that P makes transition at t
P1
(event I
P1
).
In [t
P1
, t
P2
] P waits for answers (WAIWAV).
Namely, the request P transmits to each WA may
ICINCO 2004 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
86

queue up with similar ones sent by other PAs. Next
transition occurs at t
P2
when either P receives all the
answers from the queried WAs (X
P1
), or a specified
time-out of WAIWAV expires before P receives all
the answers. In case it receives no reply within the
timeout (I
P2
), P returns to REQWAV and repeats the
request procedure. In case of time-out expiration and
some replies received (I
P3
), P considers only the
received answers to proceed. The repeated lack of
valid replies may occur for system congestion, for
machine failures or communication faults, or for
other unpredictable circumstances. In all cases
permanent waits or deadlocks may occur. To avoid
further congestion and improve system fault-
tolerance, we use time-outs and let P repeat the
cycle REQWAV-WAIWAV only a finite number of
times, after which P is unloaded from the system.
If all or some replies are received before the
time-out expiration, P starts requesting service to the
m≤w available WAs at t
P2
. In [t
P2
, t
P3
] P requests
information to these WAs by sending them Y
P11
,
Y
P12
, …, Y
P1m
at instants t
11
>t
P2
, t
12
,…, t
1m
=t
P3
. If the
sequence of requests cannot be interrupted, we refer
to REQWSE for the whole activity. We assume that
at t
P3
P makes transition (I
P4
).
Then, P spends [t
P3
, t
P4
] waiting for offers from
the available WAs (WAIWOF), as the request P
transmits to each WA may queue up with those sent
by other PAs. Next transition occurs at t
P4
when
either P receives all the answers from the queried
WAs (X
P2
) or a time-out of WAIWOF expires. In
case it receives no reply within the timeout (I
P5
), P
returns to REQWSE and repeats the procedure. In
case of time-out expiration and some replies are
received (I
P6
), P considers only the received offers to
select the next server. Again, to avoid congestion, P
repeats the cycle REQWSE-WAIWOF a finite
number of times, then it is discharged.
Once received the offers from WAs, P utilizes
[t
P4
, t
P5
] to take a decision for selecting the
workstation (TAKWDE). At t
P5
the decision
algorithm ends (I
P7
), after selecting a WA and
building a queue to rank all the offers of other WAs.
Subsequently, P reserves the chosen machine by
transmitting a booking message (Y
P2
) to the
corresponding WA. So P takes [t
P5
, t
P6
] for
communicating the choice to the WA (COMCHW).
At t
P6
the communication ends (I
P8
). Now, the WA
has to send a rejection if there is a conflict with
another PA or a booking confirmation (X
P5
). Hence,
P uses [t
P6
, t
P7
] to wait for a confirmation from the
selected WA (WAIWCO). The confirmation is
necessary because during the decision interval the
condition of the plant can be modified by actions of
other PAs, and the selected server can be no longer
available. If P receives a rejection (X
P3
), or does not
receive any reply within a time-out (I
P9
), it returns to
COMCHW, sends a new request of confirmation to
the second WA in the decision rank. If P has no
other alternative destinations and the rejection (X
P4
)
or the time-out (I
P10
) occurs, it returns to REQWAV
and repeats the negotiation. Also WAIWCO,
WAIWAV and WAIWOF cannot lead to deadlocks,
thanks to the time-out.
At t
P7
, after receiving a confirmation from the
selected WA, P starts the negotiation with TAs for a
device to carry the part from the current position to
the input buffer of the selected workstation, where
the last negotiated operation is to be made. Then P
opens the bid and spends [t
P7
, t
P8
] to send Y
P31
, Y
P32
,
…, Y
P3v
at instants t
31
>t
P7
, t
32
,…, t
3v
=t
P8
to all the v
possible TAs to request their availability
(REQTAV). In [t
P8
, t
P9
] after the end of transmission
(I
P11
), P waits for availability-answers (WAITAV)
until a time-out expires: if no reply is received, P
gets back to REQTAV (I
P12
) to repeat the request.
Otherwise, if all replies are received before the time-
out expiration (X
P6
) or u≤v replies are received and
the time-out expires (I
P13
), at t
P9
P starts requesting
service to the u available TAs (REQTSE).
Then P uses [t
P9
, t
P10
] to send outputs Y
P41
, Y
P42
,
…, Y
P4u
at instants t
41
>t
P9
, t
42
,…, t
4u
=t
P10
to all the
available TAs and, after the transmission is
completed (I
P14
), P waits for offers from TAs
(WAITOF) in [t
P10
, t
P11
] until a time-out expires. If
no offer is received (I
P15
), the PA repeats the request.
If only some offers arrive and the time-out expires
(I
P16
) or all offers arrive before the time-out (X
P7
), P
can take a transport-decision (TAKTDE) for
selecting the best offering TA in [t
P11
, t
P12
]. After
selection (I
P17
), in [t
P12
, t
P13
] P communicates its
choice by sending Y
P5
to this TA (COMCHT). After
this communication (I
P18
), P waits for a rejection or
a confirmation from the selected TA (WAITCO)
until a time-out expires. If no reply is received in the
waiting period [t
P13
, t
P14
] and a time-out expires (I
P19
)
or a rejection is received (X
P8
), in case other offers
from TAs are available P gets back to COMCHT
and selects a new TA; in case no other TA is
available and there is a time-out expiration (I
P20
) or a
rejection (X
P9
), the availability request is repeated
and P gets back to REQTAV.
If a confirmation is received (X
P10
), P makes a
transition to issue a transport command (TRANSP).
It takes the interval [t
P14
, t
P15
] to issue the command
Y
P6
to load the part on the vehicle associated with
the selected TA and to start the transport process.
When, at time t
P15
, the command is complete (I
P21
),
P gets back to QUIESC. In case of the last
operation, Y
P6
also signals the completion of the
working procedure to a controller, which influences
and adapts the DL the PA uses for ranking the offers
(Maione and Naso, 2003a). In this case, P leaves the
system.
USING A DISCRETE-EVENT SYSTEM FORMALISM FOR THE MULTI-AGENT CONTROL OF
MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS
87
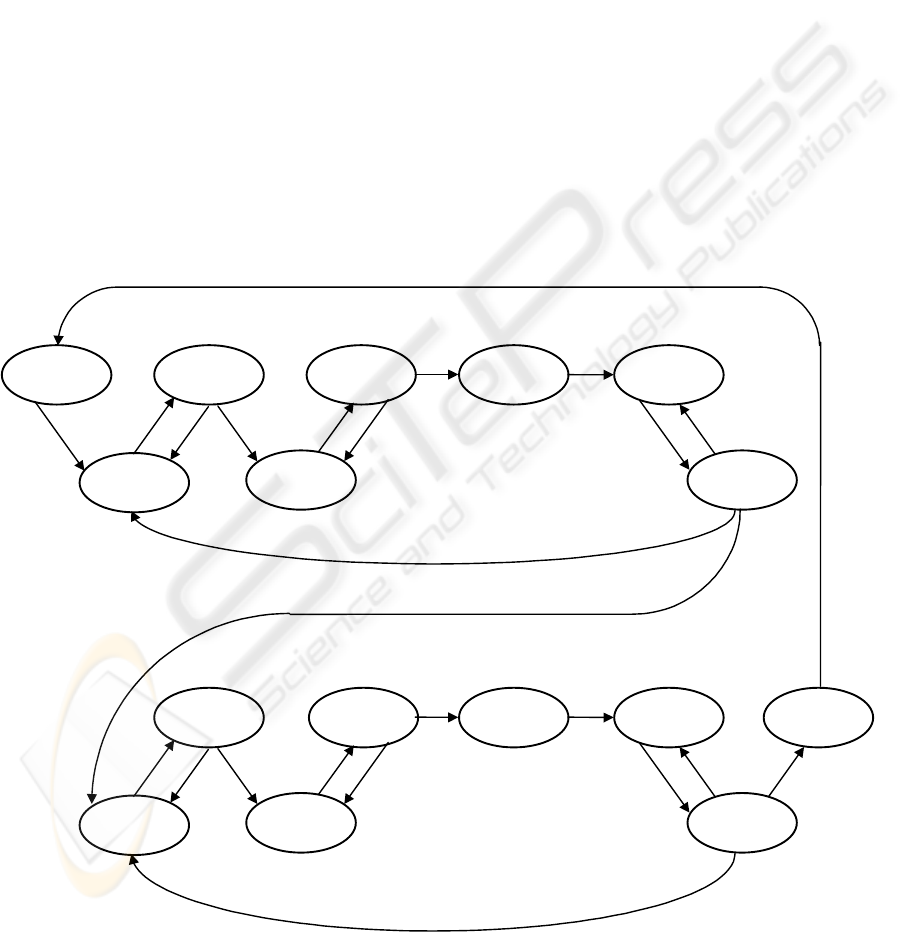
In general, from t
P15
to the beginning of the next
operation (if any), P stops making decisions,
receiving and sending messages and remains
quiescent. The associated part is loaded on the
transport vehicle and transferred to the next
workstation where it is downloaded in the input
buffer. Here, it waits in queue until receiving
service, after a proper set-up. After the operation, the
part reaches the output buffer and is ready for the
next destination. All the above processes are driven
by low-level controllers and do not involve agent
activities. So, only when the processes are over, P is
again ready to start a new negotiation phase. If for
t>t
P15
faults occur to the selected machine or vehicle,
P remains in QUIESC and there is no need to restart
negotiations with WAs or TAs. In fact, the plant
controllers manage the repair process: when the
normal operating conditions are restored, the part is
transported to the selected machine.
Note that, after the negotiation cycle is complete,
when the chosen and confirmed WA (or TA) signals
to the PA the end of the operation (or transport)
process, the PA can take into account its new
availability. If, at this time, the PA is requesting or
waiting for availability or information from other
WAs (or TAs), or is taking a decision for operation
(transport) on other parts, the received messages
from the past-selected WA (or TA) wait in a queue
until the PA gets to REQWSE (or REQTSE). In this
case, the PA will send an output Y
P1m+1
(or Y
P4u+1
)
also to this new available WA (TA).
Figure 1 depicts all this complex interaction
dynamics. Circles represent the PA status-values,
arrows represent the events, and the outputs, directly
associated with status-values, are encapsulated into
the circles. As the figure shows, the PA may receive
confirmation from a WA (or a TA) after several
successive couples COMCHW-WAIWCO (or
COMCHT-WAITCO). Also, time-outs can bring the
PA back to REQWAV (from WAIWAV when no
answer is received from WAs or from WAIWCO
after a WA-rejection) or to REQTAV (from
WAITAV when no answer is received from TAs or
from WAITCO after a TA-rejection).
X
P0
(t
P0
)
QUIESC
I
P21
(t
P15
)
I
P18
(t
P13
)
X
P9
/ I
P20
(t
P14
)
[t
P14
, t
P15
]
X
P5
(t
P7
)
X
P4
/ I
P10
(t
P7
)
I
P5
(t
P4
)
X
P1
/ I
P3
(t
P2
)
[t
P5
, t
P6
] [t
P4
, t
P5
]
[t
P3
, t
P4
]
[t
P1
, t
P2
]
[t
P8
, t
P9
] [t
P10
, t
P11
] [t
P11
, t
P12
] [t
P12
, t
P13
]
[t
P13
, t
P14
]
COMCHT
Y
P5
X
P10
(t
P14
)
X
P8
/ I
P19
(t
P14
)
WAITCO
TRANSP
Y
P6
WAITAV
[t
P9
, t
P10
]
X
P6
/ I
P13
(t
P9
)
REQTSE
Y
P41
…Y
P4
u
I
P14
(t
P10
)
I
P15
(t
P11
)
I
P17
(t
P12
)
X
P7
/ I
P16
(t
P11
)
TAKTDEWAITOF
I
P12
(t
P9
)
I
P11
(t
P8
)
[t
P7
, t
P8
]
REQTAV
Y
P31
…Y
P3v
[t
P2
, t
P3
]
REQWSE
Y
P11
…Y
P1
m
I
P2
(t
P2
)
I
P1
(t
P1
)
[t
P0
, t
P1
]
REQWAV
Y
P01
…Y
P0w
X
P3
/ I
P9
(t
P7
)
I
P8
(t
P6
)
[t
P6
, t
P7
]
WAIWCO
COMCHW
Y
P2
I
P4
(t
P3
)
I
P7
(t
P5
)
X
P2
/ I
P6
(t
P4
)
TAKWDEWAIWOFWAIWAV
Figure 1: dynamics of a PA when negotiating with WAs and TAs.
ICINCO 2004 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
88
On one hand, one could simplify the model by
merging REQWAV, WAIWAV, REQWSE and
WAIWOF, i.e. by considering the PA sending
requests for availability and information all together.
So, each WA would offer availability and the
information necessary to the PA decision at the same
time. Only two status-values would be necessary,
the first for the request, the second for the wait. The
same reduction is possible for REQTAV, WAITAV,
REQTSE and WAITOF.
On the other hand, the more detailed model of
the PA activities, which considers two different
time-outs for the two different waiting conditions
previously defined, can be more effective in
reducing the PA waiting times and in avoiding
deadlocks. In fact, the effect of delays and losses of
messages due to workstation or transport
unavailability (faults, malfunctions, overloaded
workstations, etc.) and to communication faults are
reduced. Also, the cyclic repetition of requests and
waits and the consequent delays in the decision
processes are limited. As a consequence, the risk of
discharging PAs from the system is reduced.
To better enlighten the negotiation mechanism,
we summarize in Tables I-III the status-values,
inputs, internal events and outputs.
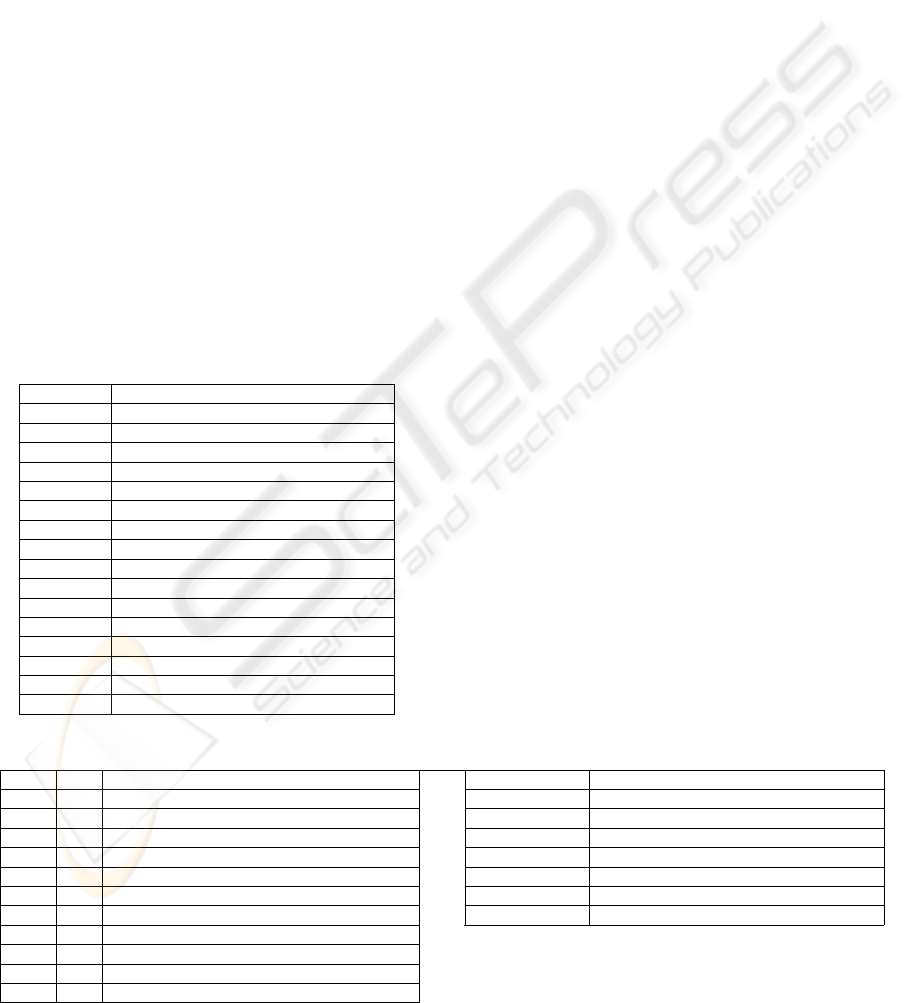
Table I: status-values for a Part Agent
Status Agent’s Activity Description
QUIESC Agent inactive
REQWAV Request availability to all possible WAs
WAIWAV Wait for availability signal from WAs
REQWSE Request service to available WAs
WAIWOF Wait for offers from available WAs
TAKWDE Take decision for the best WA offer
COMCHW Communicate choice to selected WA
WAIWCO Wait confirm./reject. from selected WA
REQTAV Request availability to all possible TAs
WAITAV Wait for availability signal from TAs
REQTSE Request service to available TAs
WAITOF Wait for offers from available TAs
TAKTDE Take decision for the best TA offer
COMCHT Communicate choice to selected TA
WAITCO Wait confirm./reject. from selected TA
TRANSP Command selected TA to move the part
Figure 1 shows that the negotiation mechanism
maintains a well defined structure with other agents
participating to a negotiation process.
In a similar way, a DEVS model can be defined
for other interactions between classes of agents
(Maione and Naso, 2003b). The common structure
of the negotiation mechanism is advantageous for
building up complex models in a modular way.
The DEVS model of the agents’ interactions is
particularly suitable for developing a complete
simulation platform for the analysis of the dynamics
of the complex MAS controlling a manufacturing
plant. In particular, our model allows the simulation
of both the plant processes and their macroscopic
hardware components (machines, AGVs, parts, etc.),
and the details of the control activities performed by
agents (inputs, outputs, states, time-outs). So, we can
evaluate the classical indices of a manufacturing
system performance (throughput, number of
completed items, lateness, etc.), but also the effects
of agents and their decision policies and the MAS
efficiency (number of negotiation cycles, number of
requests). Also, we can measure the agents’ behavior
in steady-state operating conditions and their
adaptation to abrupt disturbances (shortages of
materials, workload changes, hardware faults, etc.).
In this sense, we made all these measures when
agents were using different decision policies, to see
how they dynamically react to disturbances (Maione
and Naso, 2003a,c). We compared other MAS that
use conventional decision heuristics (based on the
delivery time of parts to machines, the distance to
the next workstation, the required set-up time) with
our MAS, both with and without adaptation. We let
agents use a set of decision rules for a limited
amount of time (the agent life-cycle) and then we
replace the rules by using the most successful ones.
The replacement at the end of life-cycle was guided
by a mechanism emulating the ‘survival of the
fittest’ natural selection process and propagating the
fittest rules to the next population of agents. The
fitness of each decision rule was the average lateness
of the parts controlled (Maione and Naso, 2003a).
Table II: inputs received and outputs sent by a PA when negotiating with WAs and TAs
Inputs Time Description
Outputs Description
X
P0
t
P0
Start negotiation for a new operation
Y
P01
Y
P02
… Y
P0w
Requests of availability
X
P1
t
P2
Last reply for WA availability received
Y
P11
Y
P12
… Y
P1m
Requests of service to available WAs
X
P2
t
P4
Last reply for WA offer received
Y
P2
Choice communication to the selected WA
X
P3
t
P7
Rejection & alternative WAs in the PA rank
Y
P31
Y
P32
… Y
P3v
Requests of availability TAs
X
P4
t
P7
Rejection & no alternative WA in the PA rank
Y
P41
Y
P42
… Y
P4u
Requests of service to available TAs
X
P5
t
P7
Confirmation from a WA
Y
P5
Choice communication to the selected TA
X
P6
t
P9
Last reply for TA availability
Y
P6
Transport command
X
P7
t
P11
Last reply for TA offer
X
P8
t
P14
Rejection & alternative TAs in the PA rank
X
P9
t
P14
Rejection & no alternative TA in the PA rank
X
P10
t
P14
Confirmation from a TA
USING A DISCRETE-EVENT SYSTEM FORMALISM FOR THE MULTI-AGENT CONTROL OF
MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS
89

Table III: internal events of a PA when negotiating with WAs and TAs
Internal Event Time Description
I
P1
t
P1
End of WA availability request process
I
P2
t
P2
Time-out and no availability signal received from WAs
I
P3
t
P2
Time-out and some (m) availability signals received from WAs
I
P4
t
P3
End of WA service request process
I
P5
t
P4
Time-out and no offer received from the m available WAs
I
P6
t
P4
Time-out and some offers (o<m) received from the available WAs
I
P7
t
P5
End of workstation-decision process
I
P8
t
P6
End of choice communication to the selected WA
I
P9
t
P7
Time-out and no confirmation received from the selected WA when other ranked WA offers are available
I
P10
t
P7
Time-out and no confirmation received from the selected WA when no other ranked WA offers are available
I
P11
t
P8
End of TA availability request process
I
P12
t
P9
Time-out and no availability signal received from TAs
I
P13
t
P9
Time-out and some (u) availability signals received from TAs
I
P14
t
P10
End of TA service request process
I
P15
t
P11
Time-out and no offer received from the u available TAs
I
P16
t
P11
Time-out and some offers (o<u) received from the available TAs
I
P17
t
P12
End of transport-decision process
I
P18
t
P13
End of choice communication to the selected TA
I
P19
t
P14
Time-out and no confirmation received from the selected TA when other ranked TA offers are available
I
P20
t
P14
Time-out and no confirmation received from the selected TA when no other ranked TA offers are available
I
P21
t
P15
End of transport command
5 SOME EXPERIMENTAL
RESULTS AND FUTURE PLANS
The DEVS model is particularly suitable for
developing a simulation platform for the analysis of
the complex dynamics of distributed multi-agent
control systems. Differently from traditional discrete
event models of manufacturing plants, mainly
devoted to simulate the macroscopic components,
our model considers also the detailed dynamics of
the software agents (exchanged event messages,
internal events and outputs). In this way, we may
study also the effects of hardware faults, congestion
of the communication network, message losses or
similar circumstances.
For instance, it is possible to compare various
decision policies used by the various agents to
negotiate operations in a detailed simulation model,
as done in (Maione and Naso, 2003a).
The simulation model also allows us to perform
comparative analysis in dynamic conditions, and
define reactive policies that minimize the effects of
disturbances, e.g. a workstation fault. For example
Figure 2 compares four different agents’ decision
policies by throughput: minimizing the distance
between consecutive workstations (A), minimizing
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
x 10
5
2
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.7
2.8
2.9
3
Com parison by Average Throughput
tim e [s ]
Throughput [parts/min]
D [8]
C
B
A
Figure 2: comparison of performance in dynamic conditions (workstation fault at t = 1 0^5 s).
ICINCO 2004 - INTELLIGENT CONTROL SYSTEMS AND OPTIMIZATION
90

the wait for set-up of the workstation (B),
minimizing the wait in queue at the workstation (C),
and using a learning strategy (D). It can be noted
how the reactive policy (D), designed with the aid of
the DEVS model, outperforms the common (static)
decision rules using MAS.
Future research aims at applying the proposed
approach to other complex distributed control and
optimization problems, such as those involved in
large-scale logistic or supply chains.
6 CONCLUDING REMARKS
In this paper, we used the DEVS formalism to
specify the model of the main agents operating in a
MAS controlling part-driven heterarchical
manufacturing systems. In this context, we detailed
the interactions guiding the negotiations related to a
generic step in a working procedure associated with
a part process. The model respects heterarchical
principles and can be used in a simulation platform
which allows us to analyze both the classical
performance indices of a manufacturing system and
the effectiveness of the MAS, using decision
policies which implement adaptation strategies.
The proposed method leaves many interesting
issues open for further research. The next step
toward the experimentation of the multi-agent
control system on an automated manufacturing
plant, is to test the DEVS model on a distributed
network of computers, each hosting one or more of
the agents in the heterarchical network. This aims at
investigating and properly addressing the critical
issues related to distributed autonomous controllers
that cannot be examined when simulating the whole
set of agents on a centralized platform.
REFERENCES
Duffie, N.A., Prabhu, V.V., 1996. Heterarchical control of
highly distributed manufacturing systems.
International Journal of Computer Integrated
Manufacturing, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 270-281.
Han, W., Jafari, M.A., 2003. Component and Agent-Based
FMS Modeling and Controller Synthesis. IEEE Trans.
Sys., Man, and Cybernetics – Part C, Vol. 33, No. 2,
pp. 193-206.
Heragu, S.S., Graves, R.J., Kim, B.-I., Onge, A.St., 2002.
Intelligent Agent Based Framework for Manufacturing
Systems Control. IEEE Trans. Sys., Man, and Cyber. -
Part A, Vol. 32, No. 5.
Hsieh, F.-S., 2004. Model and control holonic
manufacturing systems based on fusion of contract
nets and Petri nets. Automatica, 40, pp. 51-57.
Huhns, M.N., Stephens, L.M., 2001. Automating supply
chains. IEEE Int. Comput., Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 90-93.
Kotak, D., Wu, S., Fleetwood, M., Tamoto, H., 2003.
Agent-based holonic design and operations
environment for distributed manufacturing. Computers
in Industry, 52, pp. 95-108.
Lee, J.S., Hsu, P.L., 2004. Design and Implementation of
the SNMP Agents for Remote Monitoring and Control
via UML and Petri Nets. IEEE Trans. Control Sys.
Techn., Vol. 12, No. 2, pp.293-302.
Lin, F., Norrie, D.H., 2001. Schema-based conversation
modeling for agent-oriented manufacturing systems.
Computers in Industry, Vol. 46, pp. 259-274.
Logan, B., Theodoropoulos, G., 2001. The distributed
Simulation of Multiagent systems. Proceedings of the
IEEE, Vol. 89, No.2, pp. 174-185.
Maione, G., Naso, D., 2003a. A Genetic Approach for
Adaptive Multi-Agent Control in Heterachical
Manufacturing Systems. IEEE Trans. Sys., Man, and
Cyb. – Part A: Spec. Issue Collective Intelligence in
Multi-Agent Systems, Vol. 33, No. 5, pp. 573-588.
Maione, G., Naso, D., 2003b. A Discrete-Event System
Model for Multi-Agent Control of Automated
Manufacturing Systems. In IEEE SMC’03, Int. Conf.
on Sys., Man and Cyb., Washington D.C., USA.
Maione, G., Naso, D., 2003c. A Soft Computing Approach
for Task Contracting in Multi-Agent Manufacturing
Control. Comp. Ind., Vol. 52, No. 3, pp. 199-219.
Parunak, H.V.D., 1994. Applications of Distributed
Artificial Intelligence in Industry. In O’Hare,
Jennings, (Eds.), Foundations of Distributed Artificial
Intelligence, Wiley-Inter-Science.
Prabhu, V., Duffie, N., 1999. Nonlinear dynamics in
distributed arrival time control of heterarchical
manufacturing systems, IEEE Trans. Control Systems
Technology, Vol. 7, No. 6, pp. 724-730.
Shattenberg, B., Uhrmacher, A.M., 2001. Planning Agents
in James. Proc. of the IEEE, Vol. 89, No. 2, pp. 158-
173.
Shen, W., Norrie, D.H., 1999. Agent-Based Systems for
Intelligent Manufacturing: A State-of-the-Art Survey,
Knowledge and Information Systems, an International
Journal, Vol. 1, No. 2, pp. 129-156.
Smith, R.G., 1980. The Contract Net Protocol: High Level
Communication and Control in a Distributed Problem
Solver. IEEE Trans. Computers, Vol. 29, No. 12, pp.
1104-1113.
Sousa, P., Ramos, C., 1999. A distributed architecture and
negotiation protocol for scheduling in manufacturing
systems. Computers in Industry, Vol. 38, pp. 103-113.
Zeigler, B.P., Praehofer, H., Kim, T.G., 2000. Theory of
Modelling and Simulation, Academic Press, 2nd edit..
USING A DISCRETE-EVENT SYSTEM FORMALISM FOR THE MULTI-AGENT CONTROL OF
MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS
91
