
A DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM FOR THE INTEGRATED
MANAGEMENT OF HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS
NETWORKS
Nikolaos Koutsouris, George Koundourakis, Louisa Papadopoulou, Dimitris Kouis, Vera
Stavroulaki, Nikolas Mitrou
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National Technical University of Athens, 9 Heroon Polytechneiou Street,
Zographou 15773, Greece
Panagiotis Demestichas
Department of Technology Education & Digital Systems, University of Piraeus, Piraeus, Greece
Keywords: Composite Radio, GPRS, WLAN, DVB-T.
Abstract: In a composite radio environment, different wireless access techn
ologies can be co-operating components of
a combined heterogeneous infrastructure. The exploitation of a wireless system, operating in a composite
radio context, requires upgraded service and network management capabilities. This paper presents an
integrated management system and gives evidence of its capability of optimising service delivery and traffic
distribution in a prototype composite radio environment comprised of three different wireless network
technologies, i.e., GPRS, 802.11b WLAN, and DVB-T.
1 INTRODUCTION
Wireless/mobile communications continue to attract
immense research and development effort
(Varshney, 2000). Major technical evolutions
include the migration towards 2.5G and 3G mobile
communications, the introduction of Broadband
Radio Access Networks (BRAN) (Varshney, Vetter,
2000), and the advent of Digital Video Broadcasting
(DVB). Moreover, the composite radio (CR) or
“wireless beyond 3G”, concept has emerged, in an
attempt to exploit further the potential of these
individual wireless technologies. It assumes that
mobile, BRAN and DVB networks can be co-
operating systems in a CR infrastructure. Users,
equipped with multi-mode or reconfigurable
terminals, access their services through the most
appropriate, in terms of cost and Quality of Service
(QoS), radio network.
This paper presents an integrated management
syste
m that allows the provision of enhanced
applications in composite radio environments
(CREs) (work conducted within the IST Project
CREDO). The paper gives measurement results of
the system’s operation that prove its efficiency and
its ability to optimize the use of the composite radio
infrastructure. The rest of this paper is organized as
follows. Section 2 describes the network architecture
of the CR infrastructure. Section 3 presents the
management platform that is essential for the
operation of different wireless segments as parts of
the CRE, while section 4 introduces the terminal
functionality for enabling the exploitation of the
potential of a CRE architecture. Section 5 presents
results from various test case scenarios. Finally,
concluding remarks are given in section 6.
2 NETWORK ARCHITECTURE
The composite radio environment examined by the
project consists of three different radio access
technologies, GSM/GPRS, IEEE 802.11b WLAN
and DVB-T. This section demonstrates the general
network architecture for the exploitation of all these
wireless systems operating in a CR context. As
depicted in Figure 1, the private networks of all the
32
Koutsouris N., Papadopoulou L., Koundourakis G., Kouis D., Stavroulaki V., Demestichas P. and Mitrou N. (2004).
A DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM FOR THE INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS NETWORKS.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on E-Business and Telecommunication Networks, pages 32-39
DOI: 10.5220/0001396400320039
Copyright
c
SciTePress
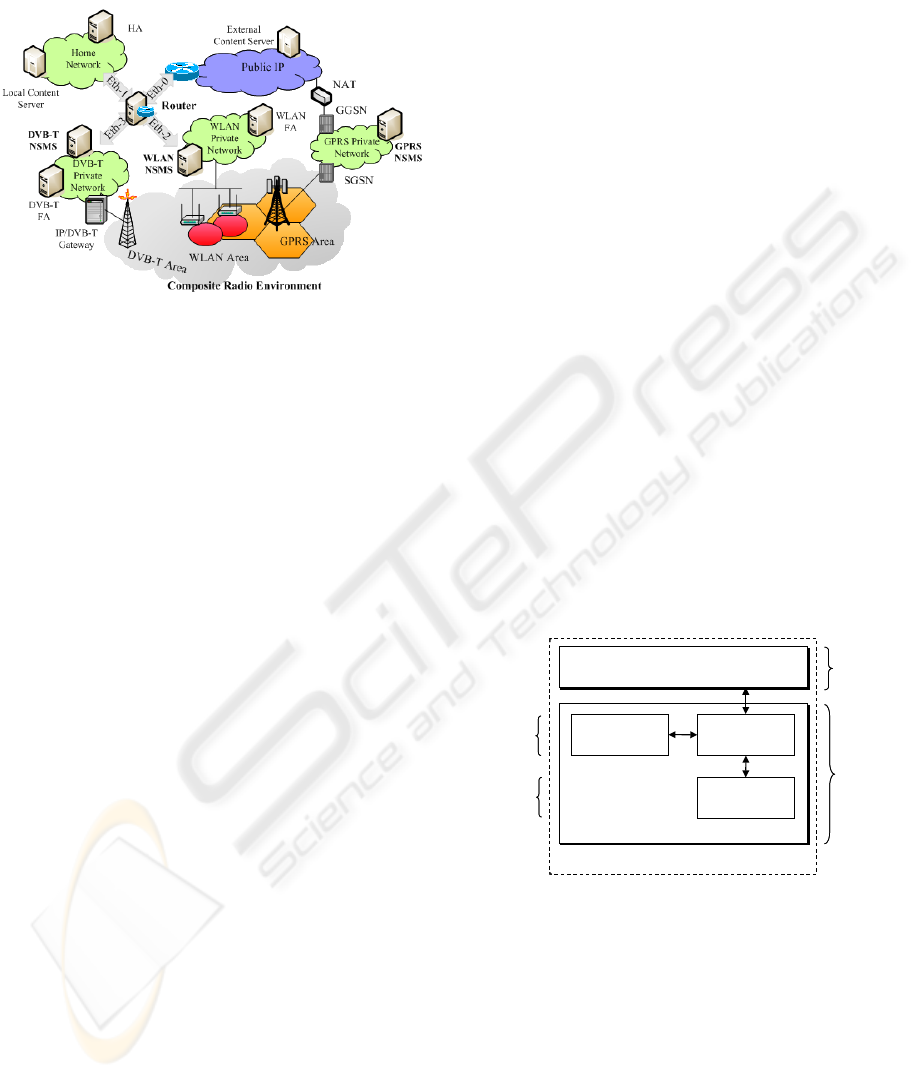
involved radio access technologies are
interconnected either through a specific router or by
means of the public IP network (GSM/GPRS case).
Figure 1: Composite Radio Environment Architecture
The functionality of the platform includes the
following features:
Management systems for each radio access
technology. These systems, called Network
and Service Management Systems (NSMSs)
are located in the relative subnets, but they
can inter-communicate and cooperate.
Appropriate terminals, capable of
communicating over different wireless
technologies. These multimode terminals are
equipped with the required intelligence for
taking decisions, performing measurements
and interacting with the local NSMS. The
management system of the terminals used in
the specific project, called Terminal Station
Management System (TSMS), as well as the
protocol implemented for the interaction
with the NSMS are presented in section 4.
Content servers for retrieving information
relative to the applications and services
provided.
IPv4 backbone solution, selected for reasons
explained below. Consequently, a Mobile
IPv4 infrastructure is employed for the
mobility management, especially during
inter-system handovers. The home network
(Figure 1), hosts the Home Agent (HA),
while the Foreign Agents (FAs) are located
in the corresponding subnets (WLAN and
DVB-T). Moreover, the HA has been
properly modified (with advanced tunneling
functionality), thus enabling it to cooperate
with the GPRS Network Address
Translation (NAT) gateway. Also, proper
modifications to the software of the DVB-T
FA for enabling the establishment of the
return channel were realized. The return
channel is required due to the unidirectional
nature of the DVB-T functionality. In the
specific case, the wireless medium that acts
as the missing uplink is the GPRS or the
WLAN network.
It is obvious that IPv4 is selected everywhere,
although IPv6 would be more convenient for the
whole architecture because there is no need for
including foreign agents and the NAT gateway is not
necessary. The reasons for choosing IPv4 are the
following (as studied at the time of the
implementation of the project):
IPv4 is much more widely deployed and
multiple commercial products and networks
are based on Mobile IPv4. On the other
hand, IPv6 networks are still in development
and Mobile IPv6 is not standard yet.
The commercial GPRS segment and the
commercial DVB-T products used do not
support IPv6.
The applications’ clients and servers used
are also IPv4 based.
3 MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
FUNCTIONALITY
This section intends to provide useful information
related to the Network and Service Management
System (NSMS) introduced previously. As
presented in Figure 2, NSMS consists of two main
modules, namely Session Manager and Network
Manager.
Network and Service Management System (NSMS)
Network Manager
Monitoring and
Configuration
Monitoring and
Configuration
Resource
Brokerage
Resource
Brokerage
Service
Management
Service
Management
Session Manager
radio access
technology
independent
radio access
technology
dependent
Mid-term
functionality
Short-term
functionality
Network and Service Management System (NSMS)
Network Manager
Monitoring and
Configuration
Monitoring and
Configuration
Resource
Brokerage
Resource
Brokerage
Service
Management
Service
Management
Session Manager
radio access
technology
independent
radio access
technology
dependent
Mid-term
functionality
Short-term
functionality
Figure 2: Management system architecture
Session Manager is the module responsible for
the interface with the terminal, that is, the interface
between NSMS and TSMS. Additionally, Session
Manager issues recommendations to the terminal on
the best network and the provided QoS level. These
recommendations are based on lookup operations
and/or “light” optimization problems.
On the other hand, Network Manager is
responsible for the monitoring of the managed
network infrastructure. It also assesses the relevant
network and service-level performance, and
dynamically finds and imposes the appropriate
A DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM FOR THE INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS
NETWORKS
33

traffic distribution, through which the service
management requests or new service area conditions
are handled in the most cost-efficient manner. As
depicted in Figure 2, Network Manager includes the
following entities: Monitoring and Configuration,
Resource Brokerage, and Service Management.
3.1 Session Manager
As already mentioned, Session Manager is the
NSMS component responsible for performing all
operations concerning the communication between
the NSMS and the terminal. It also holds
information about the active terminals that are
served by each network, and also about the quality
level assigned to them. Based on that information,
and on consequent calculations, Session Manager
issues recommendations to the terminals on
choosing the best available network for the provision
of a particular service. Thus, Session Manager
addresses a short-term optimization problem,
targeted to the assignment of the user terminal to a
specific network. The solution of this optimization
problem enables the sophisticated selection of the
appropriate radio technology, for a specific user,
through which services can be obtained efficiently in
terms of cost and QoS, in near real time.
The optimization problem addressed by the
Session Manager relies on the following input data:
(a) the set of services the user is requesting and the
corresponding set of quality levels at which these
services are requested; (b) the profile of the user
requesting the set of services (this includes
parameters such as the maximum price that the user
is willing to pay for the requested services); (c) the
network policies, which mainly involves the cost
deriving from the assignment of user demand to
several quality levels and possible inabilities of a
network to handle a specific service.
The optimization process carried out by the
Session Manager should result in an allocation of the
requested services to specific quality levels, and to
specific networks. The calculation of these two
allocations should optimize an objective function,
which is associated with the quality levels at which
each service will be provided, and the utility
deriving from the assignment of the user demand to
high quality levels. These allocations are bound to
certain constraints, such as the capabilities of the
user terminal, or the limit to the overall price that the
user is willing to pay during usage of the composite
radio system.
3.2 Network Manager
This section presents in more detail the three entities
comprising the Network Manager. The Resource
Brokerage entity has the general functionality of
coordinating all the other entities of the NSMS so as
to handle various conditions, such as congestion in a
certain service area. Apart from this, Resource
Brokerage has also an important role as regards to
the efficient communication and co-operation of
affiliated network providers in a composite radio
environment, since it enables and assists the latter in
exchanging, and negotiating on, sets of offers.
The Service Management entity provides
optimization functionality for determining the
appropriate service configuration (allocation of
services to QoS levels) and aggregate traffic
distribution (allocation of traffic to networks). In
contrast with Session Manager short-term
optimization, this is a mid-term optimization
procedure, as it is explained in the sequence.
The functionality of the Service Management
entity is similar to the functionality of the Session
Manager, as related to the network selection of the
TSMS. The difference between the algorithms of
each entity is that Service Management provides a
decision for a redistribution of the users of a service
area, due to congestion, and not a recommendation
to a single TSMS about the best network choice. As
for the input and output data and the constraints,
Service Management uses the same information
described in the Session Manager’s section, but for
all the involved TSMSs.
The operation of Resource Brokerage and
Service Management entities is independent from
the underlying radio access technology, while the
Monitoring and Configuration entity operation
depends on the radio access technology.
Monitoring and Configuration entity provides
auxiliary functionality for handling new service area
conditions or management requests. The aim of this
entity is to provide insight on the status (offered load
and performance) of the underlying network, ensure
that the latter operates properly, and perform the
necessary configuration actions to the managed
network segments. These actions are achieved by
using the Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP). Apart from communicating monitoring
related information to the Resource Brokerage
entity, the Monitoring and Configuration entity also
processes the rough network parameters and
compares them with corresponding thresholds. In
case some thresholds are exceeded for a number of
sequential updates, the entity is responsible for
triggering a redistribution request to Resource
Brokerage.
ICETE 2004 - WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
34

3.3 Operation Sample
WLAN network status acquisition phase
takes place (step 3). The status of the
network (e.g., traffic carried by cells) in the
affected service area regions is obtained. It
is noted that this information may already be
available through monitoring.
The sample operation of the network and service
management system, provided in this sub-section
(depicted in Figure 3), presents the interactions
between the various components of NSMS and the
terminals. It should be mentioned that the scenario is
initiated from the WLAN network, but could be
similar if it was initiated from the GPRS or the
DVB-T network. The following steps are identified:
Offer exchange phase takes place (step 4).
The WLAN Network Manager requests for
offers from the co-operating (GPRS and
DVB-T) networks. These offers should
contain cost and capacity information.
The Monitoring and Configuration entity of
the WLAN NSMS identifies a new
environment condition (e.g., degradation of
service quality or increased traffic load),
which may require redistribution of the
traffic load to the radio systems (step 1). It
triggers (Alarm Request) the Resource
Brokerage entity functionality (of the same
NSMS). The latter forwards this request to
the Session Manager, in order to obtain the
current status of the users (per service and
user class) in the affected service area.
Based on the WLAN network status, and the
offers provided by the GPRS and DVB-T
networks, the Service Management entity of
the WLAN NSMS decides on the
assignment of services to quality levels, and
of traffic to networks (step 5).
Acceptance phase takes place (step 6).
During this phase, the three co-operating
Network Managers are accepting the
solution proposed by the WLAN Service
Management entity, in Step 5.
The Session Manager and the terminals are
notified about the decision of the WLAN
Network Manager (step 7).
The Session Manager collects the
aforementioned information (step 2) and
triggers the WLAN Network Manager
functionality (Distribution Request).
Redistribution phase takes place (step 8).
GPRS Network
Manager
GPRS Network
Manager
DVB Network
Manager
DVB Network
Manager
Session
Manager
(W)
Session
Manager
(W)
Resource
Brokerage
(W)
Resource
Brokerage
(W)
Service
Management
(W)
Service
Management
(W)
Monitoring &
Configuration
(W)
Monitoring &
Configuration
(W)
WLAN Network Manager
Distribution Request
TSMS
TSMS
Alarm Request
Alarm Request
4.Offer exchange phase
3.Network status acquisition phase (monitoring) and
load evaluation
2.User related
information collection
1.Identification of new
environment condition
5.Assignment of services
to quality levels and of
traffic to networks
6.Acceptance phase
7.Session Manager Notification phase
8.Distribution phase
GPRS Network
Manager
GPRS Network
Manager
DVB Network
Manager
DVB Network
Manager
Session
Manager
(W)
Session
Manager
(W)
Resource
Brokerage
(W)
Resource
Brokerage
(W)
Service
Management
(W)
Service
Management
(W)
Monitoring &
Configuration
(W)
Monitoring &
Configuration
(W)
WLAN Network Manager
Distribution Request
TSMS
TSMS
Alarm Request
Alarm Request
4.Offer exchange phase
3.Network status acquisition phase (monitoring) and
load evaluation
2.User related
information collection
1.Identification of new
environment condition
5.Assignment of services
to quality levels and of
traffic to networks
6.Acceptance phase
7.Session Manager Notification phase
8.Distribution phase
Figure 3: Management system sample operation
A DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM FOR THE INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS
NETWORKS
35

4 TERMINAL FUNCTIONALITY
The Terminal Station Management System (TSMS)
resides in the user terminal and controls its operation
within the CREDO system (Catalina, 2003). It is
necessary for the exploitation of the benefits offered
by the composite radio environment. TSMS is
responsible for the following tasks:
It receives service start and stop requests
from the CREDO applications. In this way it
can keep track of all the currently running
applications. The communication with the
applications is based on message exchange
between the TSMS and the server through a
specific interface.
It monitors the terminal status: TCP/IP
status, network interface status, application
status, etc. Concerning the status of the
network interface, the TSMS monitors IP
and link layer parameters, related to each
radio technology.
It reports all the gathered information to the
Session Manager on the NSMS.
Together with NSMS it selects the best
access network to use at each moment.
It manages the terminal network
configuration. It configures the network
drivers and the TCP/IP stack according to
the decisions it takes.
Additionally it has a user interface, which allows
the configuration of the TSMS. The user can select
his/her preferences and see the current status of the
terminal and the network, as reported by the terminal
monitoring system and the TSMS.
Finally, there is a module responsible for the
communication between the terminal and the NSMS,
through a specific protocol, implemented for this
purpose. The TSMS – NSMS interactions, governed
by this protocol, include the following messages:
Service Contract Information Request and
Reply. These messages are used once, at
start-up, in order to specify the set of
services to which a user is registered.
Service Request and Reply. Through these
messages, the terminal reports to the NSMS
its current status (serving network, available
networks, services used, request for a new
service, etc) and the NSMS indicates by its
response the list of the preferred networks,
towards guiding the terminal in network
selection. The messages are sent
periodically (acting also as keep – alive
probes), but also whenever a change in the
current terminal status occurs (either in the
network availability or in the services used).
Quality Report Request and Reply. The
terminal uses the request message in order to
report to the NSMS quality degradation
observed at the utilized services (e.g. a
major traffic load alteration sensed). The
NSMS after processing all the relative data,
instructs the terminal which is the best
action suggested in this case, by sending the
reply message.
Handover Required Notification. This
message is sent by the NSMS and forces the
terminal to switch to another network. A
handover indication could also be included
in the service reply message, but this is sent
only after the service request from the
terminal. The handover required notification
does not require any trigger from the
terminal and covers cases where the
handover is necessary, without waiting for
the next service request.
5 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
In order to evaluate the benefits gained by the
composite radio concept, several experiments and
performance measurements took place under the
framework of the project.
5.1 Test Environment Description
The overall platform used, consists of the relative
infrastructure components, described in section 2.
More specifically, the access networks comprise
one GPRS Base Transceiver Station (BTS)
connected directly to a commercial GSM/GPRS
provider, two IEEE 802.11b access points (APs)
jointly forming a single ESS (Extended Service Set)
and one IP/DVB-T multiplexer feeding a DVB-T
modulator. Concerning the GPRS network, the CS-2
coding scheme is used and up to four non-dedicated
time slots are used for packet switched traffic (the
rest is only voice traffic). As for the IP traffic over
DVB-T, a separate PID (Packet Identifier) has been
allocated. The local NSMS entities are Windows
PCs located at the corresponding subnets, while the
application server (also a Windows PC) is at the
home agent’s subnet, in order to avoid additional
delays. The multimode terminal used for the
experiments is a desktop Linux PC, equipped with
an IEEE 802.11b access card, a DVB-T receiver
card and interconnected to a GSM/GPRS phone
through the serial interface. The terminal possesses
the full TSMS functionality described in section 4.
Moreover, software applications have been
developed for simulation of the terminal behaviour;
ICETE 2004 - WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
36

these applications have been used as virtual
terminals in order to evaluate the NSMS
functionality, because of the lack of equipment for
more real terminals. Finally, a traffic generator tool
has been used for simulating congestion situations. It
is a software engine that runs over Linux systems
and produces UDP packets creating background
traffic in a specific radio segment (Loukatos, 2002).
During the experiments, three types of
applications have been tested and provided in two
different quality levels (high – low):
Video Streaming Service, for retrieving
streamed MPEG-4 encoded content from the
application server. This service is accessible
only through DVB-T and WLAN due to
high bandwidth requirements (nominal bit
rate 512 Kbps for the high quality level and
128 Kbps for the low one).
Sports Event browsing, for acquiring
information for the Olympic games from the
application server. The bandwidth needed is
64 Kbps for the high quality level (not
through GPRS) and 32 Kbps for the low one
(served also by GPRS).
Generic Internet Service Provision (GISP),
for web browsing. This service is not
decisive for the experiments due to its low
demand in bandwidth (32 Kbps and 8 Kbps
for each quality level). It is supported by all
the examined radio access technologies.
Two typical scenarios are selected from the
experiments and presented in the following
subsections. Both scenarios are related to handling
of congestion situations. Their difference lies on the
results view aspect. Scenario 1 presents results of a
more user-centric approach, while scenario 2 of a
network-centric one.
5.2 Scenario 1
This scenario demonstrates the benefits deriving
from the diverse radio networks interworking during
high traffic situations (inside hot-spots regions).
More specifically, when a stand-alone radio network
cannot confront aggregate IP-based services requests
from users inside a specific area, it is more
preferable to divert the exceeding traffic to an
affiliated segment rather than to reject it or
downgrade the QoS levels provided. During the
experiments and validation of the composite radio
framework, many scenarios of this type where
tested. The most representative scenario refers to the
case where the terminal accessing the video
streaming service through the WLAN network faces
a congestion situation (simulated by a 4.4 Mbps
UDP stream injected to the WLAN by the traffic
generator tool). Consequently, the quality of the
videos begins to downgrade as the aggregate traffic
exceeds the alarm threshold (4.8 Mbps). At the same
time, the NSMS located in the WLAN segment
triggers the optimization process for solving the
problem. After the completion of this process, the
terminal is forced to handover to the DVB-T
network with return path GPRS. During the
handover procedure, the video continues without any
interruption and after its completion it regains the
best quality.
Figure 4 depicts, for the whole observation time,
the traffic monitored in the WLAN and DVB-T
segments as well as the traffic generator output and
the alarm threshold. It must be noticed that the total
response time of the platform against the congestion
situation is app. 30 seconds from the point that
traffic excesses the threshold value. The initiation of
the optimization algorithm is deliberately delayed
for 15 seconds, avoiding this way false alarm events
triggered by short peak values of the aggregate
traffic. The time interval and the alarm threshold are
both configurable parameters.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0 50 100 150 200
Time (sec)
Traffic (Mbps)
WLAN AP
monitored Traffic
DVB-T Traffic
Traffic Generator
Output (UDP)
Alarm Threshold
Handover to DVB-T/GPRS
Start of Optimization Process
Figure 4: Traffic streams over time
Figure 5 displays the video’s frame rate during
the previous procedure.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
0 50 100 150 200
Time (sec)
Frame Rate (fps)
Handover to DVB-T/GPRS
Start of Congestion Situation
Figure 5: Frame Rate of the video stream during the
congestion situation
A DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM FOR THE INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS
NETWORKS
37
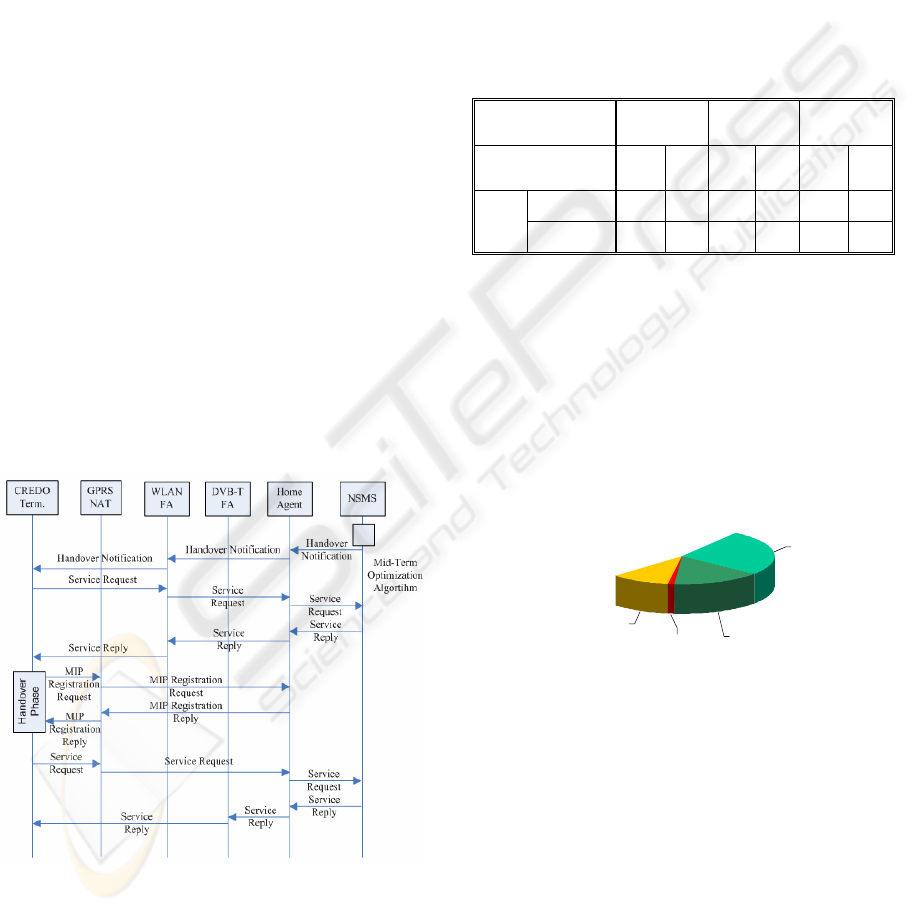
Figure 6 demonstrates the interactions between
the various components as the terminal switches
from the WLAN to the DVB-T network. As depicted
in the figure, the following steps are visible:
After the completion of the mid term
optimization algorithm, the NSMS sends the
handover notification message to the
terminal through the Home Agent (HA) and
the WLAN Foreign Agent (FA), because
WLAN is at this moment the serving
network.
The terminal sends a service request through
the WLAN network. The WLAN FA
delivers this message to the Home Agent
(HA) that forwards it to the NSMS.
The NSMS-response, suggesting of
handover to the DVB-T network with return
channel GPRS, follows the reverse way and
reaches the terminal.
The terminal sends a MIP registration
request to the HA (for switching to the
DVB-T network) through the GRPS NAT
(return channel) and receives the reply
through the same entity. After receiving the
reply, the terminal has finished all the
required actions in order to change the
serving network from WLAN to DVB-T.
The terminal sends a new service request
through the GPRS network, which is
delivered from the GRPS NAT to the HA
and then to the NSMS. The NSMS response
is sent through the HA and the DVB-T FA.
Figure 6: WLAN to DVB-T/GPRS handover procedure
5.3 Scenario 2
For the purposes of this scenario more than one
terminal were essential, so a set of virtual terminals
has been used. Furthermore, two user classes have
been assumed: the Gold and the Economy user class.
A user can choose to subscribe to different user
classes for different services. Users of the Gold class
are provided the service at the corresponding high
quality level, whereas users of the Economy class
can be provided the service at either of the two
reference quality levels.
Table 1 depicts the distribution of concurrent
users in the considered service area in the WLAN
network. Background traffic was simulated in the
WLAN network so as to create, over a period of
time, a hot spot.
Table 1: Demand volume in the WLAN network
Service
Generic
Internet
Sports
Event
Streaming
Video
QoS Levels
Description
High Low High Low High Low
Gold 2 0 4 0 1 0
User
Class
Economy 0 0 10 0 2 0
The normal condition of the service area is
configured to allow a cell load of 45% to 55% for
the cell (cells) covering the particular service area. A
snap shot of the WLAN cell under normal
conditions, serving the demand volume presented in
the previous, is depicted (Figure 7). The cell load
has reached 52% of its overall capacity. The
simulated traffic gradually increases.
Video Streaming
26%
Sports Event
15%
Simulated Traffic
10%
Generic Internet
1%
Figure 7: Traffic distribution: normal condition
Under loaded service area conditions the
simulated traffic has reached 30% of the cells
capacity. In other words, the cell is now
approximately 72% loaded (Figure 8).
There are two typical solutions that can be
proposed. (i) To maintain all the users at the WLAN
network. Actually, this will result to the degradation
of the quality offered (Figure 9). In fact this is the
solution that would be imposed without the
composite radio concept and the exploitation of the
NSMS functionality. (ii) To maintain all users, of
both user classes, at the high quality level by
exploiting the GPRS and DVB-T networks. In this
ICETE 2004 - WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
38

respect, a subset of the users (specified by the mid-
term optimisation algorithm) will obtain the
corresponding service through the WLAN network,
and the remaining users will be instructed to obtain
the service either through GPRS or DVB-T.
Simulated traffic
30%
Generic Internet
1%
Sports Event
15%
Video Streaming
26%
Load has increased
due to simulated
traffic (20% increase)
Figure 8: Traffic distribution: loaded condition
Generic
Internet
1%
S
p
orts Event
Degradation
6%
Video
Streaming
Degradation
4%
Video
Streaming
9%
Simulated
Traffic
30%
Sports Event
4%
Figure 9: Degradation of Economy user class
As depicted in Figure 10, exploitation of the
networks of GPRS and DVB-T results in part of the
terminals being instructed to switch to these
networks. The Session Manager functionality and
the overall NSMS operation assist in avoiding
congestion while continuing to provide all users with
the highest possible quality level.
Video
Streaming
9%
Sports Event
6%
Sports Event
9%
Simulated
traffic
30%
Generic
Internet
1%
Video
Streaming
17%
Part of the load
transferred to GPRS
Part of the load
transferred to DVB-T
Part of the load
transferred to DVB-T
Figure 10: Exploitation of GPRS and DVB-T networks
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper tries to validate the benefits of the
composite radio concept by demonstrating results
from the prototype architecture of the IST project
CREDO. It addresses the profits gained for the
network operator (resolution of congestion
situations) and also for the user (usage of demanding
services with the best quality level). Simulations
could estimate the efficiency of this architecture in a
more realistic environment (larger areas to cover,
many real terminals to serve) (Kontovasilis, 2003).
The structure of the architecture is flexible enough
to be adapted for handling of larger scale situations
and encompass other radio network types with
minimum effort, because of its distributed form and
technology independent optimization algorithm. The
study of such extensions and the feasibility of
producing more practical terminals are issues for
future research.
REFERENCES
Varshney, U., “Recent advances in wireless networking”,
IEEE Computer, Vol. 33, No. 6, June 2000.
3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Web Site,
www.3gpp.org, Jan. 2002.
Varshney, U., Vetter, R., “Emerging mobile and
broadband wireless networks”, Commun. of the ACM,
Vol. 43, No. 6, June 2000.
Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) Web site,
www.dvb.org, Jan. 2002.
IST project CREDO (Composite radio for enhanced
service delivery during the Olympics) Web site,
www.ist-credo.org, Feb. 2001.
Catalina, M., Stathopoulos, P., 2003. Terminal
Management System for Optimized Service Delivery
in Composite Radio Environments. In IST Mobile
&Wireless Telecommunications Summit.
Loukatos, D., 2002. Traffic Generation and Analysis,
Emphasizing on ATM and IP Network Technologies.
Ph.D. Thesis. National Technical University of
Athens, Athens.
Kontovasilis, K., Skianis, C., Kormentzas, G., 2003.
Estimating Signalling Efficiency in a Composite
Radio Environment. In 1st International Working
Conference on Performance Modelling and
Evaluation of Heterogeneous Networks (HET-
NETs’03).
A DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM FOR THE INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS
NETWORKS
39
