
FORMAL SPECIFICATION AND VERIFICATION OF XML-
BASED BUSINESS DOMAIN MODELS
Wolfgang Schuetzelhofer
IBM Austria, Tullnertalgasse 74/1, A-1230 Vienna, Austria
Karl M. Goeschka
Vienna University of Technology, Gusshausstrasse 27-29/384, A-1040 Vienna, Austria
Key
words: Semantic meta model, Business domain model, Graph theory, Constraint modeling, XML language
Abstract: The rapidly growing use of XML in the development of business to business (B2B) applications requires
new approaches in building enterprise application infrastructures. In this field the modeling of business
domain semantics, thus focusing on the user’s perception of data, in contrast to physical data representation,
is gathering more and more importance. It is increasingly important to provide a sound mathematical
foundation on modeling business domains, together with a well defined way to map business domain
semantics to XML-structures. In our recent work we propose a semantic meta model, built on set- and
algebra-theory, considered to serve for the formal definition of operations and transformations and to prove
the correctness and completeness of design methods. Based on the mathematical model we propose an XML
language to construct domain models and to formally express business domain semantics. The language not
only allows to express structural schemas and static constraints but also provides to formulate dynamic
business rules, which is considered critical for the quality of a business domain model and which is
therefore centrally focused in our work. In addition we provide an XML syntax to encode domain instances
and we apply standardized XML technologies to formally verify the validity of domain instances with
respect to their specifying domain models. With our paper we contribute to the field of formal software
engineering by proposing a business domain modeling language based on XML and founded on a sound
mathematical model. The expression of dynamic business rules and the application of XML technologies to
formally verify validity of domain instances and of entire domain models are the strength of our approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
The field of research on semantic data models has
grown rapidly over the last years (Schmidt 1975,
Peckham 1988, Gogolla 1991, Schnase 1993, Chen
1999, Trastour 2002) with a continuous change of
focus towards modeling complex business domains.
We contribute to this development with our recent
work by introducing a semantic meta model based
on set- and algebra-theory. It provides a framework
for the specification of complex business domains,
and it serves as a basis for the formal definition of
operations, mappings and transformations and to
prove the correctness and completeness of new and
extended design methods. Algebraic specifications,
by means of algebraic equations (called Σ-
equations), serve to formally define validity of
business domain models as well as of domain
instances. Our special focus is on the seamless
integration of business knowledge in form of static
and dynamic business rules, which highly influences
the expressiveness and quality of a business domain
model.
On the other hand XML, as a standardized data
description language, is gathering more and more
importance in the field of data interchange in B2B
applications. XML-based data exchange between
different systems requires transformations of XML-
structures. These transformations in turn have to be
proved for equivalence and soundness.
In our work we propose a formal method to map
business domain semantics to XML-structures based
on our theoretical model, and we additionally
provide an XML-encoding for domain instances.
This allows to formally verify validity of XML-
based business domain models and of XML-encoded
209
Schuetzelhofer W. and M. Goeschka K. (2004).
FORMAL SPECIFICATION AND VERIFICATION OF XML-BASED BUSINESS DOMAIN MODELS.
In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 209-216
DOI: 10.5220/0002605302090216
Copyright
c
SciTePress

domain instances and it provides for the formal
proof of equivalence and soundness of
transformations on XML-structures.
The contribution of our recent work to the field
of formal software engineering is
• to provide a sound mathematical foundation in
form of a semantic meta model, which builds a
framework for the specification of complex
business domains,
• to provide a mathematical method which allows
to verify validity of business domain models
and of domain instances,
• to propose a formal method how to apply
domain semantics to XML-structures,
• to outline an approach, which allows to leverage
standardized XML-technologies to verify
validity of XML-based business domain models
as well as of XML-encoded domain instances.
2 A SEMANTIC META MODEL
FOR SPECIFYING BUSINESS
DOMAINS
As core of our work we introduce a semantic meta
model, which allows to formally specify business
domains. Business domains are commonly
expressed by means of their concepts (e.g. person,
car, address, ...) and by means of relationships
between these concepts (e.g. ownership, residence,
...). Directed graphs are considered to serve as the
basis to describe business domain models. Research
in the field of semantic nets (Rada 1990) has
successfully proven that directed graphs are well
suited to express business domain concepts and
relationships between business domain concepts. We
call such graphs domain graphs. We furthermore
introduce types on nodes and links of directed
graphs, so that business domain concepts are
mapped to node-types and so that relationships
between these business domain concepts are mapped
to link-types. Recursive link composition and type
hierarchies are proposed as powerful means of
abstraction. Structural constraints on types, together
with a formalism to describe complex dependencies
between model elements, are used to express
business knowledge in form of business rules. The
consequent separation of structure and content in
combination with the proposed method to define
business rules, enforces the introduction of a three-
layer meta model. We also introduce algebraic
specifications to formally define validity of domain
graphs as well as of domain instances. A number of
simplified examples and graphical views are used to
provide an intuitive approach to the underlying
mathematical theory.
2.1 Typed Directed Graphs –
Foundation of the Meta Model
An extended version of directed graphs serves as the
fundamental basis for our approach. In contrast to a
common definition, where a directed graph (DG)
consists of a set of vertices (nodes) and of a set of
edges, we propose an extended definition by
introducing the concept of links. Links allow to
recursively specify connections between nodes of a
directed graph. Every edge of a DG is represented as
a link and every connected sequence of links forms a
link in turn. This recursive approach serves as a
powerful means of abstraction, which especially
proves profitable when the goal is to model business
domains with the necessity to view and describe
those business domains at different levels of
abstraction.
By additionally defining mappings of nodes to
node-types and of links to link-types, the concept of
typed directed graphs (simply called typed graphs) is
introduced. Two layers, called type-level and
instance-level, provide a clear separation of type and
instance. The graph type GT populates the type-
level:
GT = (NT, LT)
NT... a set of node-types,
LT ... a set of link-types.
The typed graph TG populates the instance-level:
TG = (N, L)
N... a set of typed nodes,
L ... a set of typed links.
Type mappings are defined:
type: N → NT and type: L → LT
Additionally nodes are mapped to node-values, so
that a node of a typed graph can be written as a pair
consisting of a node-value and of a node-type:
n = 〈v
node
, t
node
〉; t
node
∈ NT
Typed links are defined recursively:
1.
l
0
= 〈(〈n
s
, n
t
〉), t
link
〉; l
0
∈ L, n
s
, n
t
∈ N,
t
link
∈ LT
... every edge of the graph is represented
(encapsulated) by a link. Such a link is called
direct link (l
0
).
2.
l = 〈( l
1
, l
2
, ..., l
k
), t
link
〉; l, l
1
, l
2
, ..., l
k
∈ L;
k ≥ 1 ∧∀ i, 1 ≤ i < k : t(l
i
) = s(l
i+1
), t
link
∈ LT
... a connected sequence of links is a link in turn
and it is called indirect link (l). s(l) maps a link to its
source node and t(l) maps a link to its target node.
ICEIS 2004 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
210
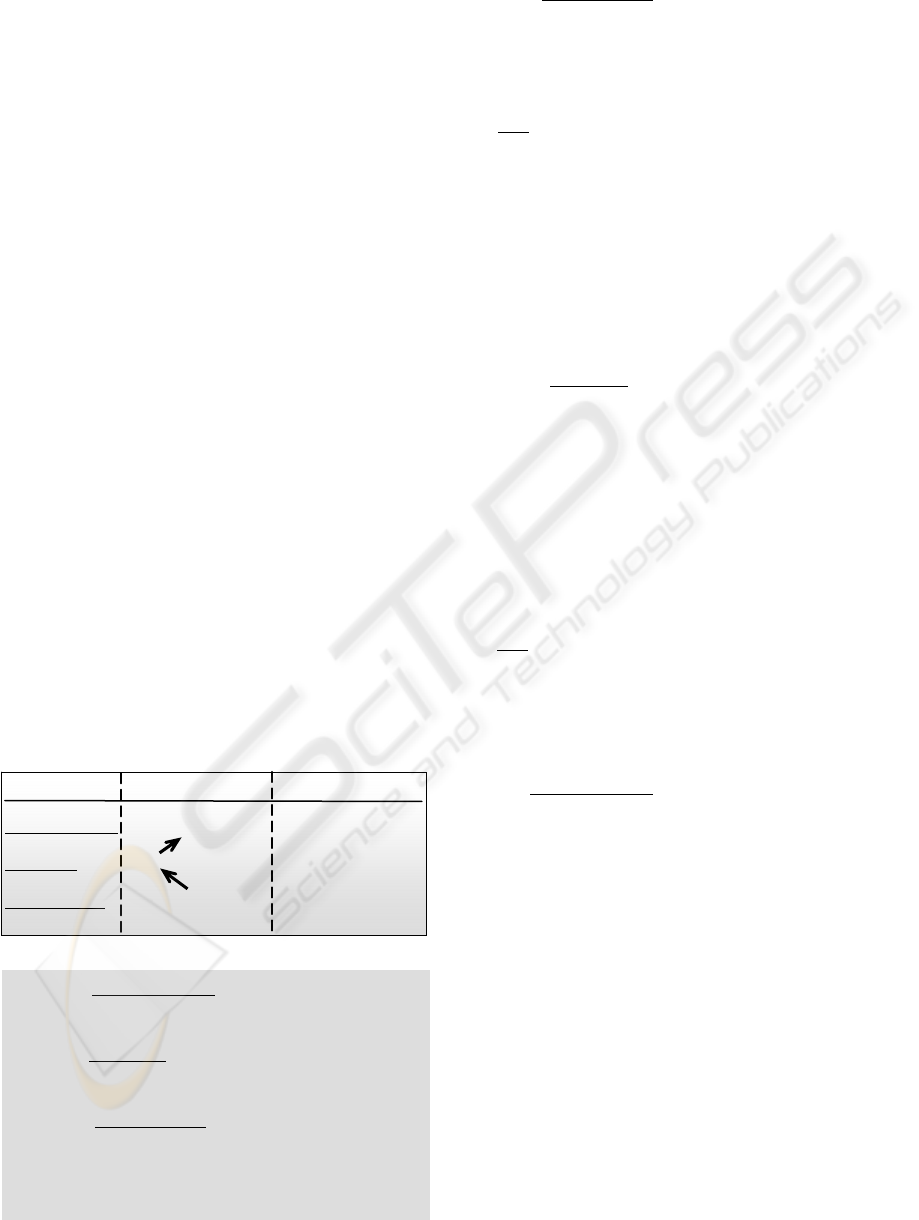
2.2 Three Layer Meta Model
So far the graph type (GT) simply consists of a set
of node-types and of a set of link-types. Business
domain concepts are mapped to node-types and
relationships between business domain concepts are
mapped to link-types. Hence a graph type models a
business domain and specifies the domain’s
structure. Business rules express structural
constraints on domain instances. Consequently they
are specified as part of the graph type. In particular,
the structural constraints are expressed on link-types
and on node-types. Whereas one possibility is to
specify constraints in form of structured values of
the appropriate node- and link-types, the proposed
approach is to express the structural constraints in
form of distinct nodes and links as part of a directed
graph, moreover, as part of a typed directed graph
which is modeled at the type-level. This means, the
graph type (GT) itself is extended to form a typed
directed graph. The semantic of a specific constraint
is then covered by a link of GT, whereas a value for
a constraint whenever needed (e.g. a range for a
cardinality constraint) is defined by means of a node
of GT.
This approach enforces the introduction of a
third layer which we call meta-type-level. The layer
is introduced, so that nodes and links at the type-
level are instances of meta-types. These meta-types
are defined at the meta-type-level.
More generally stated, nodes and links at the
instance-level are instances of nodes at the type-
level, which in turn are instances of meta-node-
types. The three layers of the resulting meta model
are depicted in Figure 1.
At the meta-type-level
, a set of meta-node-types
and a set of meta-link-types define the model
semantic.
At the type-level
, typed graphs are constructed to
model specific business domains (e.g. the sales
domain).
At the instance-level
, typed graphs are used to
present business domain instances (e.g. a specific
sales transaction).
The entire three-layer model is called Domain
Graph Model (DGM).
At the instance-level
a node of the typed graph
represents either
• an
OBJECT i.e. an instance of a business domain
concept (e.g. a specific person) or
• a
PRIMITIVE-VALUE ( instance of a primitive
data type) (e.g. the integer value 20).
A link
at the instance-level represents a RELATION
between an
OBJECT and/or a PRIMITIVE-VALUE (e.g.
a link of type residence may relate a specific person
to a certain address, or a link of type birthDate may
relate a person to a primitive D
ATE value).
A simple analogy with E-R modeling concepts
can be constructed, so that an
OBJECT corresponds to
an entity-instance, so that a
PRIMITIVE-VALUE
corresponds to an attribute-value and so that a
RELATION corresponds to either a relationship-
instance or to an attribute-name respectively.
At the type-level
a node of the typed graph
represents either
• a business domain
CONCEPT (e.g. Person),
which specifies a type of
OBJECTs or
• a primitive
DATA TYPE (e.g. Integer, Date, ...),
which specifies a type of
PRIMITIVE-VALUEs or
• a
CONCEPT-RELATIONSHIP, a relationship
between business domain concepts (e.g.
residence), which is a link-(
RELATION-) type
or
• a
CONSTRAINT-VALUE (e.g. a specific range for
a cardinality constraint).
A link
at the type-level covers constraint semantics
(e.g. a distinct super-type relation, a source-node-
type constraint, a cardinality constraint, ...), hence it
is called a
SEMANTIC-RELATION. The graph at the
type-level is called Domain Graph (DoG) because it
is the means to model business domains.
At the meta-type-level
the model semantic is covered
by a set of meta-node-types which represent the
types of possible nodes for the type-level, and by a
set of meta-link-types representing all possible sorts
of
SEMANTIC-RELATIONs.
2.3 Model Semantic
Figure 2 lists the set of meta-node-types and the set
of meta-link-types. Possible links between nodes at
the type-level with respect to the nodes’ and links’
meta-types are also shown.
Figure 1: Three-layer meta model
meta-type-level
type-level
instance-level
meta-types
types
instances
instance-of
instance-of
Level
Elements
Covers / Expresses
Model Semantic
Business Domain
Model
Domain Instance
FORMAL SPECIFICATION AND VERIFICATION OF XML-BASED BUSINESS DOMAIN MODELS
211

Meta-Node-Types
bd_concept ... Instances represent business
domain
CONCEPTs (e.g. Person, Address, ...).
p-type ... Instances represent primitive
DATA TYPEs
(e.g. Integer, String, Date, ...).
bd-relat ... Instances describe relationships between
business domain concepts (e.g. residence,
ownership, ...).
range ... Instances serve to specify valid ranges
for cardinality constraints.
condition ... Instances are used to formulate
dynamic business rules.
lt-sequ ... Instances constrain the sequence of
intermediate links of composed
RELATIONs
(indirect links at the instance-level).
Meta-Link-Types
Meta-link-types cover the semantic of structural
constraints. Instances of meta-link-types are
SEMANTIC-RELATIONs at the type-level.
super ... Instances of super relate types to their
super-type.
s-type ... Instances constrain the source-node-type
of
RELATIONs.
t-type ... Instances constrain the target-node-type
for
RELATIONs.
s-card, t-card ... Instances are used to model
cardinality constraints.
composition ... Instances of composition connect
CONCEPT-RELATIONSHIPs to lt-sequ instances,
thus constraining intermediate link sequences of
composed
RELATIONs.
abstract ... Instances of abstract connect
CONCEPTs
or
CONCEPT-RELATIONSHIPs to condition nodes
in order to specify abstract types.
if ... Instances represent if-branches of condition
trees.
else ... Instances represent else-branches of
condition trees.
2.4 Static and Dynamic Business
Rules
A major concern of our work is the seamless
integration of business rules. In the proposed
approach such business rules are defined in form of
cardinality constraints which are specified on
CONCEPT-RELATIONSHIPs. We distinguish between
static and dynamic business rules. Dynamic business
rules, in contrast to static ones, depend on the state
of distinct domain instances. As an example one can
think of a sales transaction which, depending on the
age of the customer, allows only certain products to
be added as line-items. In DGM such dynamic
business rules are expressed in form of conditional
cardinality constraints. Figures 3 and 4 provide a
simplified example. Whereas Figure 3 shows a UML
representation, Figure 4 outlines a graphical view of
the appropriate domain graph.
Fi
g
ure 3: D
y
namic business rule ex
p
ressed as annotation.
Person
birthDate
Sales-
Transaction
customer
line-item
Item
Product
minAg
e
spec
[1..1]
[0..n]
[0..n]
[1..1]
An Item of
certain product
can be purchased
by a customer
only if the
customer’s age is
≥ the product’s
minAge
[0..n]
[1..1]
Figure 2 : The model semantic is defined by meta-node-
types and by meta-link-types
b
d-conce
pt
p-type
bd-relat
range
condition
lt-sequ
Meta-
Node-
Types
Meta-
Link-
Types
BC
PT
BR
Instance-Level
O
V
R
super
s-type
t-type
if
compo-
sition
s-card
t
-card
else
abstract
O – OBJECTs
V –
PRIMITIVE-VALUEs
R –
RELATIONs
B
R
– CONCEPT-RELATIONSHIPs
CV –
CONSTRAINT-VALUEs
BC – CONCEPTs
PT – primitive
DATA TYPEs
Meta-T
yp
e-Level
Type-Level
CV
ICEIS 2004 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
212
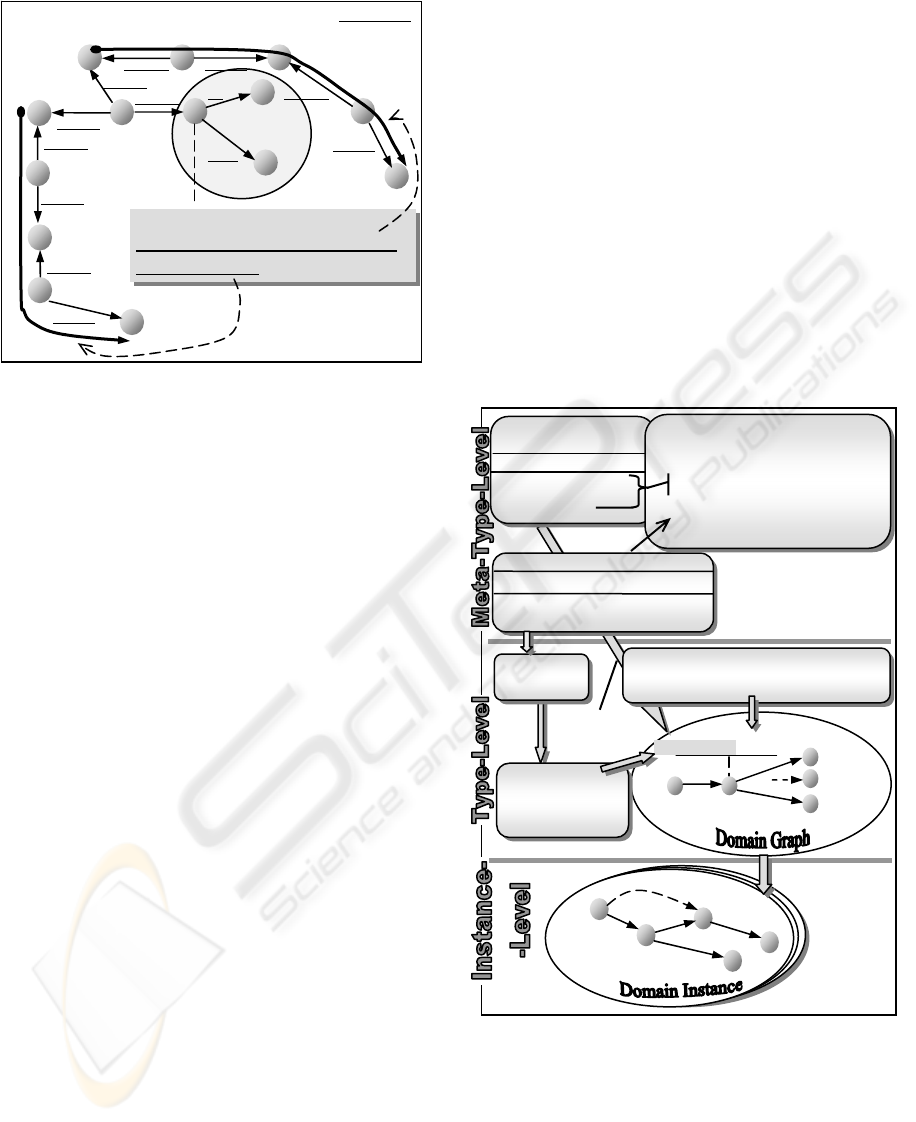
Figure 4 provides a graphical representation of
the set theory based formalism. It is more suitable
and easier to read, especially as the presented model
is based on graph theory. Note, that the
representation in Figure 4 can be unambiguously
transformed into the set theory based formalism.
However, the used notation is not intended to serve
as a graphical modeling language (although
possible). Other graphical notations, such as used
with UML (UML, 2001), are specifically designed
to accomplish this task. Figure 4 demonstrates how a
boolean expression is used to formulate a dynamic
business rule. Path expressions are the means to
select values out of distinct domain instances. These
values serve as arguments for the boolean
expression. Based on the result of evaluating the
boolean expression, the condition tree (encircled in
Figure 4) is traversed (if, else branches). The
traversal results in a specific range node which
specifies the cardinality constraint to be applied.
OCL (OCL, 2002), a constraint language, has been
adapted to the DGM in order to formulate dynamic
business rules.
2.5 Domain Graph Model - Summary
DGM provides a semantic meta-model to formally
specify and verify business domains. The meta-
model consists of three layers, which are called
levels. The topmost layer is named meta-type-level
and defines the model semantic. The medium layer
is called type-level and hosts typed-directed-graphs,
called domain graphs (DoGs), which model distinct
business domains. The bottom layer is named
instance-level, and it is the layer where instances of
specific business domains, again in form of typed-
directed-graphs, are constructed.
At the type-level,
CONCEPTs and CONCEPT-
RELATIONSHIPs describe the basic domain structure,
and constraints in combination with boolean OCL-
expressions are used to formulate static- and
dynamic business rules. At the instance-level,
OBJECTs, (PRIMITIVE-)VALUEs and RELATIONs
compose domain instances, and they are constructed,
so that they satisfy the structural constraints and
business rules defined by their domain graph.
The theory of algebraic specifications is applied
to formally define validity. Algebraic specifications
are based on algebraic signatures, so that a
specification extends a signature with the formal
construction of
Σ
-equations. A set of such
Σ
-
equation provides the formal specification of valid
domain graphs and of valid domain instances. Figure
5 outlines the basic building blocks of the DGM.
3 XML-ENCODING OF THE
DOMAIN GRAPH MODEL
Based on the semantic meta model we propose an
XML-language to specify domain graphs (DoGs),
thus modeling business domains. We call this
language XDoG. We also provide an XML-
Fi
g
ure 5: Domain
g
ra
p
h Model
(
DGM
)
(bool. xprsn)
:condition
Algebraic Spec of
Domain Graphs
Spec
DoG
:
sorts: bd-concept, ..
s-type, t-type, ...
opns: vars: eqns:
Terms define Path-Expessions
T
Σ-Path
:
n
s
:bd-concept . l:bd-relat =
n
t
:bd-concept
Model Semantic (Meta-Types)
MS = {MNT, MLT}
MNT = {bd-concept, p-type, bd-relat,
range, condition, lt-sequ}
MLT = {super, s-type, t-type,
s-card, t-card, composition,
abstract, if, else
}
Meta-types are sorts in
Spec
DoG
and T
Σ-Path
instances(bd-concept) ... CONCEPTs
instances(bd-relat) ...
CONCEPT-
RELATI
ONS
HIP
s
path-
expressions
l:bd-relat
:
:if
:else
:s-card
[0..0]:
range
[1..1]:
range
[3..n]:range
are
part-
of
specifies valid
domain-
instances
specifies valid
domain graphs
OBJECTs,
(
PRIMITIVE-)VALUEs,
RELATIONs
boolean-
OCL-expressions
(specify
business rules)
Figure 4 : Business rules expressed as conditional
cardinality constraints
(Date.today –
Sales-Transaction.customer.birthDate
≥
Item.spec.minAge
) :condition
birthDate
:bd-relat
Person
:bd-concept
type-level
:s-card
:if
:else
[1.. 1]:range
:s-type
Sales-Transaction
:bd-concept
Item
:bd-concept
int:p-type
Product
:bd-concept
line-item
:bd-relat
minAge :
b
d-rela
t
spec:
b
d-rela
t
customer
:
b
d-rela
t
Date
:p-type
:s-type
:s-type
:s-type
:s-type
:t-type
:t-type
:t-type
:t-type
:t-type
[0.. 0]:range
FORMAL SPECIFICATION AND VERIFICATION OF XML-BASED BUSINESS DOMAIN MODELS
213

encoding for domain instances, so that instances of a
business domain (e.g. specific sales-transactions)
can be encoded in form of XML-structures.
The decision to develop a business domain
modeling language based on XML is motivated by
several reasons. Beside its already leading role in
data interchange in business to business (B2B)
applications, XML is also gathering more and more
importance in the field of semantic data modeling.
Based on the foundation of the XML Information
Set (W3C, 2004) and on a clear and simple syntax,
the extensibility of XML is targeted towards the
development of domain specific languages. Grouped
around a set of stable and consistent standards, a
rapidly growing number of tools and applications are
established. This allows new developments to build
on mature and well tested technologies and to
benefit from a high amount of re-use. This, together
with the widespread use of XML, leads to an ever
growing number of XML-languages arising in the
field of formal software engineering. Recent
developments on Web-Ontologies (W3C, 2001)
specify XML-languages which aim to define the
terms used to describe and represent specific areas
of knowledge. DAML+OIL (DAML + OIL, 2001) is
an example of such languages.
For our work, interoperability, standards
compliance and the possibility to re-use software
tools for practical implementations are the major
motivations to develop an XML-language for
modeling business domains as well as to provide an
XML-encoding for business domain instances.
Rather than providing the complete specification
of the domain modeling language XDoG and of the
XML-encoding for domain instances as part of this
paper, we will focus on how we utilize XML
technologies to model XML-based, valid business
domains and how we apply standardized XML
technologies to verify validity of XML-encoded
domain instances.
Figure 6 depicts how formal modeling languages
in general and the XDoG language in particular are
aligned with the domain graph model (DGM).
Expressions of the XDoG language are used to
encode a domain graph in XML thus modeling a
business domain. The XDoG language itself is
specified by means of an XML-Schema, which is
derived from Spec
DoG
and which restricts the XDoG
language to describe valid domain graphs (Figure 6
(1)). A domain graph is encoded in XDoG and
serves to specify valid domain instances (Figure 6
(2)). Domain instances are XML-encoded in turn.
The encoding follows an instance-encoding-
specification, which basically defines how
OBJECTs,
PRIMITIVE VALUEs and RELATIONs of a domain
instance are represented as XML elements and
attributes respectively (Figure 6 (3)).
Just like an XML-schema provides the structural
constraints for XML-documents which are instances
of that schema, a domain graph or the domain
graph’s XML encoding respectively, constrains
domain instances. With that relationship in mind, it
seems straight forward to derive an XML-schema
from a domain graph, or, even better, to directly
encode a domain graph in form of an XML-schema.
However, the XML-schema-language proves not to
be powerful enough to express all constraints
specified by a domain graph. Especially dynamic
business rules, which play a central role in the DGM
theory, but also the composition property of
composed
RELATIONs cannot be formulated by
means of the XML-schema-language. On one hand
this is the reason why the XDoG language was
developed to provide an appropriate domain graph
encoding. On the other hand it is the reason why an
XML-schema alone is not sufficient to completely
specify domain instances. Nevertheless, the XML-
schema-language is not entirely omitted in the
specification of the domain instance encoding.
Instead, constructs of the XML-schema-language are
provided to specify the static constraints on XML-
encoded domain instances. This ‘static schema’ is
derived from the XML-encoded domain graph. This
is done by providing a set of transformation rules in
form of an XSL-stylesheet, so that a standard XSL-
processor can generate the ‘static schema’ out of the
XML-encoded domain graph (Figure 6 (4)).
In order to perform validation of XML-encoded
domain instances with respect to dynamic business
rules and composed
RELATIONs, a different approach
Figure 6: DGM and XML-encoding
Modeling Language
Specification
XML Modeling Language
Specification
(XDoG Schema
)
Meta-Types
Spec
DoG
derived
DoG
specifies
specifies
specifies
type-level
instance-level
XDoG - instance
XML
domain instance
XSL
static schema
construction rules
transformation
XSL
(validation
stylesheet)
XSL
validation stylesheet
construction rules
XSD
(static schema)
validity-
statement
encodes
encodes
(1)
(2)
instance
encoding
spec
follows
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
schema
validation
transformation
Domain Instance
validity-
statement
meta-type-level
transformation
ICEIS 2004 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
214

is required. A set of rules in form of another XSL-
stylesheet serves to generate the ‘XSL-validation-
stylesheet’ (Figure 6 (5)) out of the XML-encoded
domain graph. The ‘XSL-validation-stylesheet’ is
constructed, so that it contains XPath (W3C, 1999)
expressions which properly encode path-expressions
(they are part of boolean OCL expressions) which in
turn specify dynamic business rules. The XPath
expressions serve to select values or value sets out of
domain instances. The ‘XSL-validation-stylesheet’
itself is an XSL-stylesheet. Applied to an XML-
encoded domain instance it generates a statement
about the domain instance’s validity (with respect to
dynamic business rules and composed
RELATIONs).
By performing schema-validation based on the
‘static schema’ and by applying the ‘XSL-
validation-stylesheet’ (Figure 6 (6)), we provide
validation of XML-encoded domain instances,
utilizing standard XML technologies.
4 RELATED WORK
In the field of semantic data modeling a number of
publications can be found, which apply set- and
graph-theory to map domain semantics to structured
hypertext systems and hyperlinked data sets. Our
work, providing a semantic meta model together
with a proposed XML-encoding, is highly related to
this field of research, as the origin of XML can be
found in hypertext systems. Moreover, hypertext
systems may profitably be viewed as semantic nets
(Wang, 1998), which actually provide the basis of
our approach on business domain modeling.
Beside publications on formal models for
hypertext (Lange, 1990) and on constraining
hypertext structures (Chidlovskii, 2000), a lot of
related approaches stresses the need for our work:
Bench-Capon and Dunne (Bench, 1889), in an early
approach use a DAG (directed graph) structure and a
set of constraints to model electronic documents.
Contrasting our approach links are not typed and
only represent the containment relationship,
providing limited possibilities to express domain
semantics. The formal hypertext model described in
Tochtermann and Dittrich (Dittrich, 1995) provides
some formally defined structural concepts, lacking
mechanisms to define more powerful structural and
relational constraints. Wang and Rada (Wang, 1998)
have developed a semantic data model based on the
concept of a semantic net, introducing organizational
and relational link types on a DAG. In contrast to
our work they do not provide an extensible type
system and they also do not provide a mechanism to
formulate dynamic constraints. Abiteboul and Hull
(Abiteboul, 1987) in their well known approach on
formalizing a semantic model recognize the
importance of types which are used to model object
structures (IFO model), but they do not provide link
type hierarchies. E-R modeling, which is very much
influenced by the work of P.P.Chen (Chen, 1976,
Chen, 1999) provides another field of related work.
In contrast to E-R approaches our work is highly
built on graph theory and we centrally focus on the
possibility to formulate dynamic business rules.
H.V.Jagadish et.al. (Jagadish, 2001) provide an
algebraic approach for query and transformation of
XML tree structures. Whereas they propose a sound
mathematical theory, their approach in contrast to
our work applies to tree graphs rather than to
directed graphs. The OMG with its MOF (Meta-
Object-Facility) specification (OMG, 2000),
introduces a four layer meta-data architecture in
contrast to the three layer model we are proposing in
our paper. The Unified Modeling Language (UML)
specifies semantics on the level of Meta-Models
(UML, 2001, Schleicher, 2001), but does not
provide expressing complex business rules as
integral part (although the recent integration of OCL
as part of UML is targeted in that direction). Recent
developments in the field of (Web-) Ontologies
(W3C, 2001), such as DAML+OIL, aim to define
the terms used to describe and represent specific
areas of knowledge. They provide expressing object
constraints, but are limited in specifying dynamic
constraints which express complex element
dependencies (Trastour, 2002).
Our work is mainly build on a theoretical
approach which is inherently complex, especially
concerning the integration of dynamic business
rules. Whereas most of the related work, discussed
in this section, has already successfully proven its
applicability and usefulness in many practical
implementations, applications, providing a proof of
concept for our approach, are currently still under
construction.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we have presented the theory of a
three-layered semantic meta model for specifying
business domains, which we call domain graph
model (DGM). We have introduced a Domain Graph
(DoG) as a directed graph with typed nodes and
typed links which models business domains at the
type-level of the DGM. We have outlined, how
domain semantics are applied to a DoG and how
static and dynamic business rules, playing a central
role, are seamlessly integrated by specifying types,
structural constraints, and conditions. We have
FORMAL SPECIFICATION AND VERIFICATION OF XML-BASED BUSINESS DOMAIN MODELS
215

discussed how construction rules for DoGs are
specified at the meta-type-level, how business
domains are modeled at the type-level and how valid
domain instances are provided at the instance-level.
This leads to a clear separation of structure and
content and is proposed as a flexible way to deliver
semantic data. The concept of type hierarchies as
well as the approach of recursive link composition
were introduced as powerful means of abstraction.
We have based the domain graph model (DGM)
on set- and algebra- theories, providing a sound
mathematical foundation for the formal definition of
operations and transformations and to prove the
correctness and completeness of design methods.
The formal verification of valid domain graphs and
of valid domain instances, by use of algebraic
specifications, satisfies the requirement for
robustness of semantic data. It was outlined, that by
proposing an XML-encoding for domain graphs and
for domain instances we provide an approach to
apply domain semantics to XML-structures. This
allows to utilize DGM theories for interchange of
semantic data in XML-based B2B applications.
We have discussed structural constraints, the
specification of static and dynamic business rules
and different abstraction mechanisms. The definition
of operations, built on the mathematical basis of the
DGM, is considered to specify additional dynamic
aspects as part of future work. Manipulating a
domain instance by inserting, deleting or updating
nodes and links, thereby maintaining consistency
and validity of the domain instance are such
dynamic aspects to be specified. New and extended
design methods, which can be formally specified
and verified, are seen to be another profitable output
of future work based on this paper.
REFERENCES
Wang W., Rada R., 1998. “Structured Hypertext with
Domain Semantics”; ACM TIS, 16,4, pp.372-412
Schnase J.L., Leggett J.J., Hicks D.L., Szabo R.L., Jan.
1993. “Semantic data modeling of hypermedia
associations”, ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 11, 1, pp. 27-50
Tochtermann K., Dittrich G., 1995. “Towards a family of
formal models for hypermerdia”, HIM’95
Proceedings, pp. 77–91
Bench-Capon T., Dunne P., 1989. “Some computational
properties of a model for electronic documents”,
Electr. Pub.Orig.Dissem. Des.2, 4, pp. 231–256.
Peckham J., Mariansky F., 1988. “Semantic data models”,
ACM Comput. Surv. 20,3, pp. 153-189
Abitoul S., Hull R., 1987. “IFO: a formal semantic
database model”, ACM Trans. Database Syst. 12, 4
Chidlovskii B., 2000. “Using Regular Tree Automata as
XML Schemas”, Proceedings of the IEEE Advances
in Digital Libraries 2000
Schleicher A., Westfechtel B., 2001. “Beyond
Stereotyping: Metamodeling Approaches for the
UML”, Proceedings of the 34th Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences 2001 ( HICSS-34)
Schmidt H.A., Swenson J.R., 1975. “On the semantics of
the relational data models”, Proceedings of the
SIGMOD San Jose, Calif.
Lange D., 1990. “A formal model for hypertext”,
Proceedings of the NIST Hypertext Standardisation
Workshop. NIST, Gaithersburg, Md., pp. 145-166
Gogolla M., U. Hohenstein, 1991. “Towards a semantic
view of an extended entity-relationship model”, ACM
Trans. Database Syst. 16, 3, pp.369-416
Chen, P.P., 1976. “The Entity-Relationship Model -
Toward a Unified View of Data” ACM Transactions
on Database Systems, 1976. 1(1): p. 9-36.
Chen P.P., Akoka J., Kangassalo H., Thalheim B (Eds.),
1999. “Conceptual Modeling, Current Issues and
Future Directions”, Selected Papers from Symposium
on Conceptual Modeling, held before ER'97. Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, Vol.1565, Springer 1999.
Chen P.P., 1999. “ER Model, XML and the Web” in J.
Akoka, M. Bouzeghoub, I. Comyn-Wattiau, E. Métais
(Eds.): Conceptual Modeling - ER '99, 18
th
International Conference on Conceptual Modeling,
Paris, France, Nov. 15-18, 1999, Proceedings.
Jagadish H. V., Lakshmanan L. V. S., Srivastava D., and
Thompson K., 2001. “TAX: A Tree Algebra for
XML” In Proceedings of DBPL'01.
Trastour D., Bartolini C., Preist C., 2002. “Semantic Web
Support for the Business-to-Business E-Commerce
Lifecycle”, Proc. of WWW2002
Rada R., 1990. “Hypertext Writing and Document Reuse:
The Role of a Semantic Net". Electr. Pub. Orig.
Dissem. and Design, 3(3):125-140, August 1990.
W3C, XML Information Set http://www.w3.org/TR/xml-
infoset/
W3C, Web-Ontology
http://www.w3.org/2001/sw/WebOnt/
UML, Meta-Model Specification ( v1.4)
http://www.rational.com/uml
OMG-MOF, Meta Object Facility Specification (v1.3),
http://www.omg.org, march 2000
W3C, DAML + OIL
http://www.w3.org/TR/daml+oil-reference
OMG, Specification of the Object Constraint Language
http://www.omg.org/
W3C XPath, XML Path Language Recommendation,
http://www.w3c.org/TR/xpath, Nov. 1999
ICEIS 2004 - INFORMATION SYSTEMS ANALYSIS AND SPECIFICATION
216
